概率DP训练
http://www.codeforces.com/problemset/problem/148/D
题意:
一个袋子里面装有n个小白鼠,m个小黑鼠,A,B两人轮流从中取老鼠,A先取,规定谁先取到白色小鼠谁就赢。B比较特殊,每当他取完一只老鼠时,总是会惊动其他的老鼠,所以取完之后剩下的老鼠会从袋子中溜掉一只。 而对于A取完后不会存在这种情况。问A取胜的概率。
思路:
首先我想了一个4维的dp[i][j][k][2] i表示到了第几步(这里可以用滚动数组优化,然后就可以存了) j表示还剩下白鼠j只,k表示还剩下黑鼠k只,最后一维: 0 表示取白鼠,1表示取黑鼠,
状态转移就很好想了,就是分取白鼠还是取黑鼠的情况讨论,我想这应该是最笨的方法了吧。不过时间复杂度是不会允许的(O(10^9)),不过我还是试着写了一下,结果到1000 1000 肯定挂了。
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <set> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <sstream> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <queue> #define CL(arr, val) memset(arr, val, sizeof(arr)) #define lc l,m,rt<<1 #define rc m + 1,r,rt<<1|1 #define ll __int64 #define L(x) (x) << 1 #define R(x) (x) << 1 | 1 #define MID(l, r) (l + r) >> 1 #define Min(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (x) : (y) #define Max(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (y) : (x) #define E(x) (1 << (x)) #define iabs(x) (x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x) #define OUT(x) printf("%I64d\n", x) #define lowbit(x) (x)&(-x) #define Read() freopen("din.txt", "r", stdin) #define Write() freopen("dout.txt", "w", stdout); #define M 26 #define N 1007 using namespace std; const int inf = 0x1F1F1F1F; const int mod = 1000000007; const int X = 1000000005; double dp[2][N][N][2]; int main() { int n,m; int i,j,k; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); if (n == 0) { printf("0\n"); return 0; } if (m == 0) { printf("1\n"); return 0; } int u = 0,v = 1; for (j = n; j >= 0; --j) { for (k = m; k >= 0; --k) { dp[u][j][k][0] = dp[u][j][k][1] = 0; } } dp[u][n][m][1] = 1.0; double ans = 0; for (i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (j = n; j >= 0; --j) { for (k = m; k >= 0; --k) { dp[v][j][k][0] = dp[v][j][k][1] = 0; } } for (j = n; j >= 0; --j) { for (k = m; k >= 0; --k) { if (dp[u][j][k][1] != 0) { if (i % 2 == 0) { if (j - 2 >= 0) { double tmp = 1.0*(j - 1)/(1.0*(j - 1 + k)); dp[v][j - 2][k][0] += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*j)/(1.0*(j + k)))*tmp; } if (j - 1 >= 0 && k - 1 >= 0) { double tmp = 1.0*k/(1.0*(k + j - 1)); dp[v][j - 1][k - 1][0] += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*j)/(1.0*(j + k)))*tmp; } } else if (i % 2 == 1 && j - 1 >= 0) { dp[v][j - 1][k][0] += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*j)/(1.0*(j + k))); ans += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*j)/(1.0*(j + k))); } if (i % 2 == 0) { if (k - 2 >= 0) { double tmp = 1.0*(k - 1)/(1.0*(k - 1 + j)); dp[v][j][k - 2][1] += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*k)/(1.0*(j + k)))*tmp; } if (j - 1 >= 0 && k - 1 >= 0) { double tmp = 1.0*j/(1.0*(k - 1 + j)); dp[v][j - 1][k - 1][1] += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*k)/(1.0*(j + k)))*tmp; } } else if (i % 2 == 1 && k - 1 >= 0) dp[v][j][k - 1][1] += dp[u][j][k][1]*((1.0*k)/(1.0*(j + k))); // cout<<"Ans = "<<ans<<endl; } } } // for (j = 0; j <= n; ++j) // { // for (k = 0; k <= m; ++k) // { // printf("%.3lf ",dp[v][j][k][0]); // } // printf("\n"); // } // printf("\n******************\n"); // for (j = 0; j <= n; ++j) // { // for (k = 0; k <= m; ++k) // { // printf("%.3lf ",dp[v][j][k][1]); // } // printf("\n"); // } swap(u,v); } printf("%.9lf\n",ans); return 0; }
再想如何维数优化呢? n m <= 1000所以我们可以试着压缩一维然后就是(O(2*10^6))了,我们注意到只要记录到这一步时,选择多少,和剩下的白色小鼠的个数即可。
dp[i][j][2] i表示到了第几步, j表示还剩下j只小鼠还没有取出,最后一维表达的意思还是一样。 tot记录小鼠的总数,sub记录一共选择了多少。
然后黑鼠的个数就是 tot - sub - j了。
 View Code
View Code
//#pragma comment(linker,"/STACK:327680000,327680000") #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <set> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <sstream> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <queue> #define CL(arr, val) memset(arr, val, sizeof(arr)) #define lc l,m,rt<<1 #define rc m + 1,r,rt<<1|1 #define ll __int64 #define L(x) (x) << 1 #define R(x) (x) << 1 | 1 #define MID(l, r) (l + r) >> 1 #define Min(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (x) : (y) #define Max(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (y) : (x) #define E(x) (1 << (x)) #define iabs(x) (x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x) #define OUT(x) printf("%I64d\n", x) #define lowbit(x) (x)&(-x) #define Read() freopen("din.txt", "r", stdin) #define Write() freopen("dout.txt", "w", stdout); #define M 26 #define N 1007 using namespace std; const int inf = 0x1F1F1F1F; const int mod = 1000000007; const int X = 1000000005; double dp[2][N][2]; int main() { int n,m; int i,j; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); double tot = n + m; if (n == 0) { printf("0\n"); return 0; } if (m == 0) { printf("1\n"); return 0; } int u = 0,v = 1; for (j = n; j >= 0; --j) { dp[u][j][1] = dp[u][j][0] = 0; } dp[u][n][1] = 1.0; double ans = 0; double tmp = 0; double sub = 0; for (i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (j = n; j >= 0; --j) { dp[v][j][0] = dp[v][j][1] = 0; } for (j = n; j >= 0; --j) { if (dp[u][j][1] != 0) { //B取 if (i%2 == 0) { //取白鼠,溜走的也是白鼠 if (j - 2 >= 0 && (tot - sub - 1) > 0) { tmp = (1.0*(j - 1))/(tot - sub - 1); dp[v][j - 2][0] += dp[u][j][1]*((1.0*j)/(tot - sub))*tmp; } //取白鼠,溜走的也是黑鼠 if (j - 1 >= 0 && (tot - sub - 1) > 0) { tmp = (1.0*(tot - sub - j))/(tot - sub - 1); dp[v][j - 1][0] += dp[u][j][1]*((1.0*j)/(tot - sub))*tmp; } //取黑鼠,溜走的也是白鼠 if (j - 1 >= 0 && tot - sub - 1 > 0) { tmp = 1.0*(j)/(tot - sub - 1); dp[v][j - 1][1] += dp[u][j][1]*(1.0*(tot - sub - j)/(tot - sub))*tmp; } //取黑鼠,溜走的也是黑鼠 if (tot - sub - 1 > 0) { tmp = 1.0*(tot - sub - j - 1)/(tot - sub - 1); dp[v][j][1] += dp[u][j][1]*(1.0*(tot - sub - j)/(tot - sub))*tmp; } }//A取 else { //取白鼠 if (j - 1 >= 0) { dp[v][j - 1][0] += dp[u][j][1]*((1.0*j)/(tot - sub)); ans += dp[u][j][1]*((1.0*j)/(tot - sub)); } //取黑鼠 dp[v][j][1] += dp[u][j][1]*(1.0*(tot - sub - j)/(tot - sub)); } } } if (i % 2 == 0) sub += 2; else sub += 1; swap(u,v); } printf("%.9lf\n",ans); return 0; }
后来看了一下牛人的代码,惭愧啊。直接一个二维DP,然后记忆化搜索搞定,我搞的有一百多行,人家就几十行。膜拜啊。
dp[i][j]表示剩下i个白鼠,j个黑鼠
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <set> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <sstream> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <queue> #define CL(arr, val) memset(arr, val, sizeof(arr)) #define lc l,m,rt<<1 #define rc m + 1,r,rt<<1|1 #define ll __int64 #define L(x) (x) << 1 #define R(x) (x) << 1 | 1 #define MID(l, r) (l + r) >> 1 #define Min(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (x) : (y) #define Max(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (y) : (x) #define E(x) (1 << (x)) #define iabs(x) (x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x) #define OUT(x) printf("%I64d\n", x) #define lowbit(x) (x)&(-x) #define Read() freopen("din.txt", "r", stdin) #define Write() freopen("dout.txt", "w", stdout); #define M 26 #define N 1007 using namespace std; const int inf = 0x1F1F1F1F; const int mod = 1000000007; const int X = 1000000005; double dp[N][N]; double eps = 1e-10; int dblcmp(double x) { if (x > eps) return 1; else if (x < -eps) return -1; else return 0; } double DP(int n,int m) { if (n <= 0 || m < 0) return 0.0; if (m == 0) return 1.0; if (dp[n][m] > 0) return dp[n][m]; double dn = n,dm = m; dp[n][m] = dn/(dn + dm); if (n + m - 2 > 0) { dp[n][m] += (dm/(dn + dm)*(dm - 1.0)/(dn + dm - 1.0)) * ((dm - 2.0)/(dn + dm - 2.0)*DP(n,m - 3) + dn/(dn + dm - 2.0)*DP(n - 1,m - 2)); } return dp[n][m]; } int main() { int n,m; int i,j; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for (i = 0; i <= n; ++i) { for (j = 0; j <= m; ++j) { dp[i][j] = 0; } } printf("%.9lf\n",DP(n,m)); return 0; }
sgu http://acm.sgu.ru/problem.php?contest=0&problem=495
|
/*************************************************************************
题意:
m个人,n个奖品放在n个盒子里面,m个人轮流取盒子拿奖品,每个人取每个盒子的概率是一样的。当人i取盒子的时候可能取到已经被取过的,所以他不会得到奖品,问m个人取盒子,求所有人取到奖品的数学期望。
思路:
才开始理解错题意以为是求取到的奖品个数的数学期望,这里是求的取的盒子的数学期望。每个人要么取到奖品,要么取不到只有两中情况,dp[i]表示第i个人取到奖品的概率,dp[i] = (1 - dp[i - 1])*dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 1]*(dp[i - 1] - 1/n); 表示当第 i - 1个人取不到时的,我取道奖品的概率就是dp[i - 1].如果上一个人取道了奖品,那么我取到的概率为dp[i - 1] - 1/n ; 因为减少了可取的奖品。
这里还可以逆向来向每个精品不被取到的概率为p = ((n - 1)/n)^m 然后算出不被取到的数学期望 n*p 最后 n - n*p 就是被选到的数学期望了。
************************************************************************/
|
 View Code
View Code
#include<iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> using namespace std; #define N 100007 double dp[N]; int main() { int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); double ans = 1; dp[1] = 1; dp[0] = 0; for (int i = 2; i <= m; ++i) { dp[i] = (1 - dp[i - 1])*dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 1]*(dp[i - 1] - 1.0*1/n); ans += dp[i]; } printf("%.9lf\n",ans); return 0; }
zoj 3380 Patchouli's Spell Cards
题意:
有m种不同的元素,每种元素都有n种不同的相位,现在假设有每种元素各一个,其相位是等概率随机的。如果几个元素的相位相同,那么帕琪就可以把它们组合发动一个符卡(Spell Card)。现在问帕琪能够发动等级不低于l,即包含大于等于l个相同相位的不同元素的附卡的概率。
思路:
才开始我是推出了组合数的公式,用java的大数写的。不知道为什么不对。后来看了一下解题报告,发现只有l < m/2时用组合公式算是对的。否则要用dp来算,不清楚为什么,好像解题报告也没说可能是中间计算数据溢出吧。这里我们吧把问题转为求m个位置,每个位置是1到n的一个数,问没有l个位置数相同的方案数
dp[i][j]表示前i个相位占据了j个位置, dp[i][j]+= dp[i - 1][j - k]*C[m - (j - k)][k] 等于前i - 1个占据j - k 个位置的情况诚意在从剩下的空位中占据k个位置
 View Code
View Code
import java.math.BigInteger; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { // public static BigInteger gcd(BigInteger a,BigInteger b) // { // if (b.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) == 0) return a; // else return gcd(b,a.mod(b)); // } public static void main(String args[]) { BigInteger c[][] = new BigInteger[107][107]; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i) c[i][i] = c[i][0] = BigInteger.ONE; for (int i = 2; i <= 100; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) { c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1].add(c[i - 1][j]); } } Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in); int n, m, l; while (cin.hasNext()) { m = cin.nextInt(); n = cin.nextInt(); l = cin.nextInt(); if (l > m) { System.out.println("mukyu~"); continue; } BigInteger fm = BigInteger.valueOf(n); fm = fm.pow(m); BigInteger fz = BigInteger.ZERO; if (l > m / 2) { for (int i = l; i <= m; ++i){ BigInteger tmp = c[m][i]; BigInteger tp = BigInteger.valueOf(n - 1); tp = tp.pow(m - i); fz = fz.add(tp.multiply(tmp)); } fz = fz.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n)); BigInteger t = fz.gcd(fm); System.out.println(fz.divide(t) + "/" + fm.divide(t)); } else{ BigInteger dp[][] = new BigInteger[107][107]; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i){ for (int j = 0; j <= 100; ++j){ dp[i][j] = BigInteger.ZERO; } } dp[0][0] = BigInteger.ONE; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){ for (int j = 0; j <= m; ++j){ for (int k = 0; k < l && k <= j; ++k){ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j].add(dp[i - 1][j - k].multiply(c[m - (j - k)][k])); } } } // if (n > m) n = m; fz = fm.subtract(dp[n][m]); BigInteger t = fz.gcd(fm); System.out.println(fz.divide(t) + "/" + fm.divide(t)); } } } }
上边的时间复杂度为O(n*m*l),我们可以优化到O(min(n,m)*m*l) 的,dp[i][j]表示的是用i个相位占据j个位置的情况数,dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - k]*C(m - (i - 1),k)*(n - (i - 1)). 这里算的是排列数,所以在最后相加时想除以i的阶乘,转化成组合数即可。
 View Code
View Code
import java.math.BigInteger; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { // public static BigInteger gcd(BigInteger a,BigInteger b) // { // if (b.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) == 0) return a; // else return gcd(b,a.mod(b)); // } public static void main(String args[]) { BigInteger c[][] = new BigInteger[107][107]; BigInteger f[] = new BigInteger[107]; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i) { c[i][i] = c[i][0] = BigInteger.ONE; f[i] = i == 0 ? BigInteger.ONE : f[i - 1].multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i)); } for (int i = 2; i <= 100; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) { c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1].add(c[i - 1][j]); } } Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in); int n, m, l; while (cin.hasNext()) { m = cin.nextInt(); n = cin.nextInt(); l = cin.nextInt(); if (l > m) { System.out.println("mukyu~"); continue; } BigInteger fm = BigInteger.valueOf(n).pow(m); if (l > m / 2) { BigInteger fz = BigInteger.ZERO; for (int i = l; i <= m; ++i){ BigInteger tmp = c[m][i]; BigInteger tp = BigInteger.valueOf(n - 1); tp = tp.pow(m - i); fz = fz.add(tp.multiply(tmp)); } fz = fz.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n)); BigInteger t = fz.gcd(fm); System.out.println(fz.divide(t) + "/" + fm.divide(t)); } else{ BigInteger dp[][] = new BigInteger[107][107]; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i){ for (int j = 0; j <= 100; ++j){ dp[i][j] = BigInteger.ZERO; } } BigInteger fz = BigInteger.ZERO; dp[0][0] = BigInteger.ONE; for (int i = 0; i < n && i < m; ++i){ for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j){ if (dp[i][j].signum() == 0) continue; for (int k = 1; k < l && j + k <= m; ++k){ dp[i + 1][j + k] = dp[i + 1][j + k].add(dp[i][j].multiply(c[m - j][k].multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n - i)))); // dp[i + 1][j + k] = dp[i + 1][j + k].add(dp[i][j].multiply(c[m - j - 1][k - 1].multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n - i)))); } } } for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){ fz = fz.add(dp[i][m].divide(f[i])); } fz = fm.subtract(fz); BigInteger t = fz.gcd(fm); System.out.println(fz.divide(t) + "/" + fm.divide(t)); } } } }
zoj 3640 Help Me Escape
题意:
一个吸血鬼,每次可以随机的选择n个洞中的任意一个,如果该吸血鬼的攻击值大于 该洞c[i]那么直接可以花费t[i]的时间就可以出去,不然要奋斗一天该吸血鬼攻击值增加c[i],然后再]随机选择n个洞口,问该吸血鬼掏出该洞所需要的天数的数学期望。
思路:
dp[i]表示当吸血鬼拥有攻击值为i为逃出迷宫所需天数的数学期望 if(i > k) dp[i] += t[i] else dp[i] += DP(i + c[i]) + 1;
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <set> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <sstream> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <queue> #define CL(arr, val) memset(arr, val, sizeof(arr)) #define lc l,m,rt<<1 #define rc m + 1,r,rt<<1|1 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ll __int64 #define L(x) (x) << 1 #define R(x) (x) << 1 | 1 #define MID(l, r) (l + r) >> 1 #define Min(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (x) : (y) #define Max(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (y) : (x) #define E(x) (1 << (x)) #define iabs(x) (x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x) #define OUT(x) printf("%I64d\n", x) #define lowbit(x) (x)&(-x) #define Read() freopen("din.txt", "r", stdin) #define Write() freopen("dout.txt", "w", stdout); #define M 107 #define N 2000007 using namespace std; const int inf = 100000007; const int mod = 1000000007; double dp[N]; bool vt[N]; int c[M]; int t[M]; int n,m; double DP(int f) { if (vt[f]) return dp[f]; vt[f] = true; dp[f] = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (f > c[i]) dp[f] += t[i]; else dp[f] += DP(f + c[i]) + 1; } return dp[f]/=n; } int main() { while (~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { scanf("%d",&c[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { t[i] = (1 + sqrt(5))/2*c[i]*c[i]; } CL(vt,false); printf("%.3lf\n",DP(m)); } return 0; }
hdu 4405 Aeroplane chess
题意:
玩飞行棋,起点为0,通过投掷骰子(数字为1,2,3,4,5,6)来决定做的 步数,假设当前位置为i,掷得j, 则走到i + j。 同时还有一些特别的点,可以直接传送i->j;当我走到>=n的时候就结束,问结束时我投掷骰子次数的数学期望。
思路:
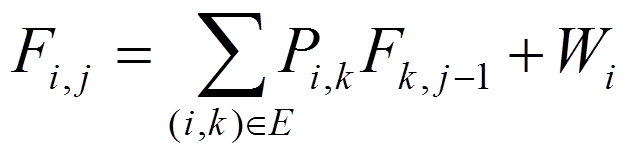
这里权值在边上所以是这个方程:
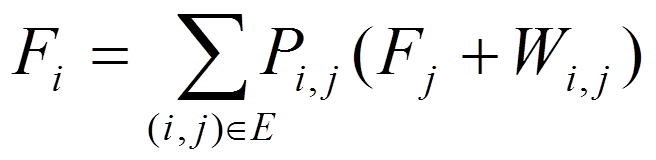
就是利用这个模型计算。
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <set> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <sstream> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <queue> #define CL(arr, val) memset(arr, val, sizeof(arr)) #define lc l,m,rt<<1 #define rc m + 1,r,rt<<1|1 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ll __int64 #define L(x) (x) << 1 #define R(x) (x) << 1 | 1 #define MID(l, r) (l + r) >> 1 #define Min(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (x) : (y) #define Max(x, y) (x) < (y) ? (y) : (x) #define E(x) (1 << (x)) #define iabs(x) (x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x) #define OUT(x) printf("%I64d\n", x) #define lowbit(x) (x)&(-x) #define Read() freopen("din.txt", "r", stdin) #define Write() freopen("dout.txt", "w", stdout); #define M 107 #define N 100007 using namespace std; const int inf = 100000007; const int mod = 1000000007; double dp[N]; map<int,int> mp; bool vt[N]; int main() { Read(); int n,m; int i,j; while (~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) { if (!n && !m) break; mp.clear(); CL(vt,false); int x,y; for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); mp[x] = y; vt[x] = true; } for (i = 0; i < n + 6; ++i) dp[i] = 0; for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) { for (j = 1; j <= 6; ++j) { int pos = (i + j) > n ? n : i+j; dp[i] += (dp[pos] + 1)/6.0; } if (vt[i]) dp[i] = dp[mp[i]]; } printf("%.4lf\n",dp[0]); } return 0; }
