TensorFlow Lite(实战系列三):YOLOV3嵌入Android版APP实现对象检测案例
摘要
本次实战案例,少奶奶给大家带来了使用Tensorflow Lite方式把YOLOV3嵌入Android版APP中,该APP通过调用手机摄像头,实现实时检测并返回具体结果,从而实现自定义网络模型移植边缘设备的可能。通过阅读本篇博客,大家也可以获得以下提升:
1)自定义训练的网络模型都可以通过TensorFlow Lite移植到Android版的APP中,实现实时监测。
2)讲解Android项目中的核心源码,让大家理解TensorFlow Lite工作的整个流程,使得大家在开发不同APP时,从被动变成主动。
备注:不熟悉Android开发的朋友不必紧张,少奶奶也不懂Android开发,但我们使用的是Google官网提供的目标检测模型demo,大家只需要把它下载下来,然后跟着少奶奶一起修改源码就可以了(主要是Java代码)。
感谢前辈1的贡献
开发环境
window 10、Python 3.6、pycharm、anaconda、TensorFlow-GPU 1.13.0、Android studio
YOLO-V3模型转tflite
少奶奶使用的是原始的YOLO-V3模型权重,既官方通过训练coco数据集得到的权重,大家可以从 GitHub中下载到所需的YOLO-V3配置文件和模型转换文件convert.py,而YOLO-V3的weights文件网上可以搜到。
感谢前辈2的贡献
模型转换思路:weights转h5,h5转tflite
具体代码如下:
weights转h5:
python convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights yolov3.h5
h5转tflite
import tensorflow as tf
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model_file('yolov3.h5')
tflite_model = converter.convert()
open("yolov3.tflite", "wb").write(tflite_model)
自定义模型嵌入与源码修改
在本小节中,少奶奶会带领大家修改TensorFlow Lite给出的官方示例的源码,让大家能够根据自定义模型来修改官方示例。
步骤一:下载官方示例代码
Google为了让开发者能更好的接入TensorFlow Lite,其提供了很多示例demo,少奶奶使用的是Android版本的对象检测示例。大家直接下载到本地,再使用android studio打开即可运行代码,使用真机调试功能,就能快速体验一把TensorFlow Lite的魅力。
 成功导入Android Studio后,我们可以看到如下项目结构。
成功导入Android Studio后,我们可以看到如下项目结构。
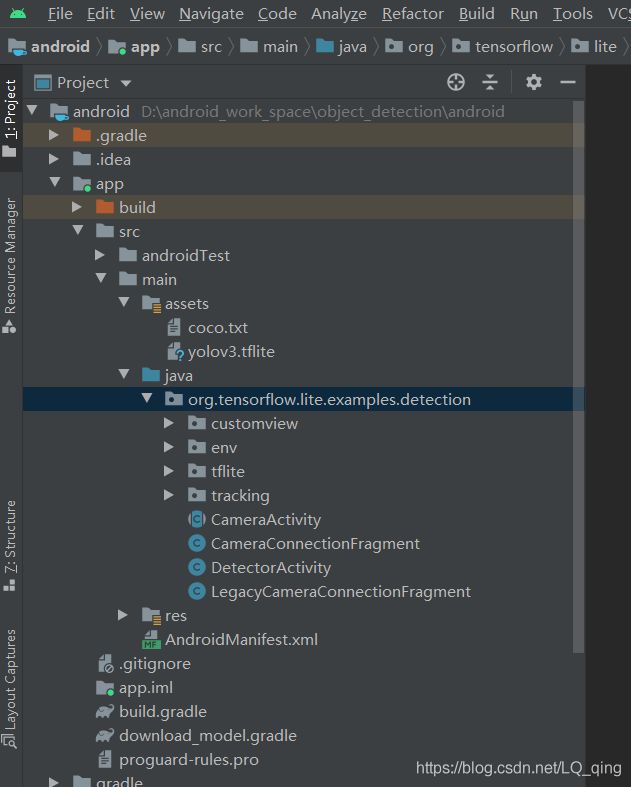
我们需要修改的地方如图所示:
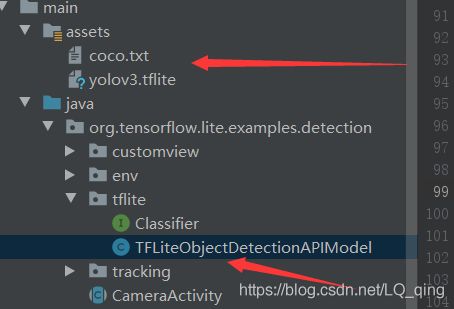
assets:存放前一小节中,转换好的tflite模型和标签。
TFLiteObjectDetectionAPIModel.java:主要修改的源码文件。
步骤二:修改Google示例代码,使得示例兼容YOLOV3模型
Google示例代码使用的模型是SSD模型,在该模型的基础上进行重训练很繁琐,而且,该模型是直接输出检测目标的坐标值和置信度,所以在绘制检测框时可以直接使用模型的输出信息。而我们使用的YOLOV3模型直接输出的是三张不同尺寸的特征图,既:[1,13,13,255]、[1,26,26,255]、[1,52,52,255],修改后的YOLOV3模型会也可以直接输出[1,13,13,3,85]、[1,26,26,3,85]、[1,52,52,3,85],这些特征图都是一个意思,只是使用了不同的维度进行表示而已。在本次实战中,我们需要做的就是把这三张特征图转换成物体检测的坐标和置信度,进而绘制矩形框。这里少奶奶建议大家先看看其他博主对于YOLOV3的详细解释。
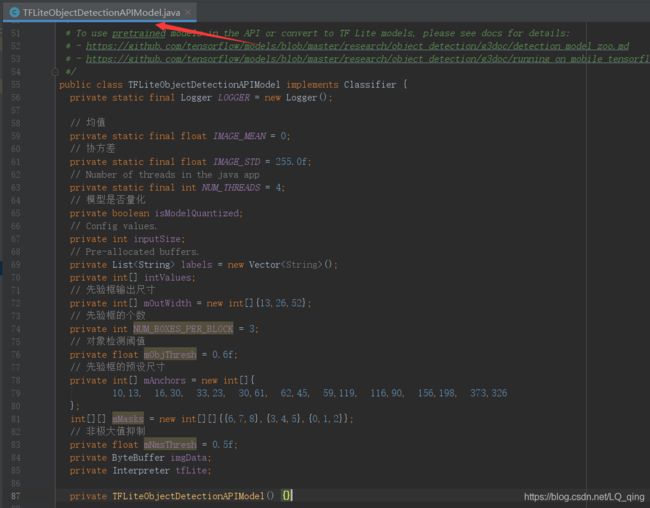
1)打开TFLiteObjectDetectionAPIModel.java,把前面部分的参数修改成如下形式,然后把该文件中的所有报错都删掉。
 2)添加YOLOV3位置信息转换的相关函数
2)添加YOLOV3位置信息转换的相关函数
private float expit(final float x) {
return (float) (1. / (1. + Math.exp(-x)));
}
protected void softmax(final float[] vals) {
float max = Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
for (final float val : vals) {
max = Math.max(max, val);
}
float sum = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < vals.length; ++i) {
vals[i] = (float) Math.exp(vals[i] - max);
sum += vals[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < vals.length; ++i) {
vals[i] = vals[i] / sum;
}
}
//non maximum suppression
protected ArrayList<Recognition> nms(ArrayList<Recognition> list) {
ArrayList<Recognition> nmsList = new ArrayList<Recognition>();
for (int k = 0; k < labels.size(); k++) {
//1.find max confidence per class
PriorityQueue<Recognition> pq =
new PriorityQueue<Recognition>(
10,
new Comparator<Recognition>() {
@Override
public int compare(final Recognition lhs, final Recognition rhs) {
// Intentionally reversed to put high confidence at the head of the queue.
return Float.compare(rhs.getConfidence(), lhs.getConfidence());
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i) {
if (list.get(i).detectedClass == k) {
pq.add(list.get(i));
}
}
Log.d("wangmin", "class[" + k + "] pq size: " + pq.size());
//2.do non maximum suppression
while(pq.size() > 0) {
//insert detection with max confidence
Recognition[] a = new Recognition[pq.size()];
Recognition[] detections = pq.toArray(a);
Recognition max = detections[0];
nmsList.add(max);
Log.d("wangmin", "before nms pq size: " + pq.size());
//clear pq to do next nms
pq.clear();
for (int j = 1; j < detections.length; j++) {
Recognition detection = detections[j];
RectF b = detection.getLocation();
if (box_iou(max.getLocation(), b) < mNmsThresh){
pq.add(detection);
}
}
Log.d("wangmin", "after nms pq size: " + pq.size());
}
}
return nmsList;
}
protected float box_iou(RectF a, RectF b)
{
return box_intersection(a, b)/box_union(a, b);
}
protected float box_intersection(RectF a, RectF b)
{
float w = overlap((a.left + a.right) / 2, a.right - a.left,
(b.left + b.right) / 2, b.right - b.left);
float h = overlap((a.top + a.bottom) / 2, a.bottom - a.top,
(b.top + b.bottom) / 2, b.bottom - b.top);
if(w < 0 || h < 0) return 0;
float area = w*h;
return area;
}
protected float box_union(RectF a, RectF b)
{
float i = box_intersection(a, b);
float u = (a.right - a.left)*(a.bottom - a.top) + (b.right - b.left)*(b.bottom - b.top) - i;
return u;
}
protected float overlap(float x1, float w1, float x2, float w2)
{
float l1 = x1 - w1/2;
float l2 = x2 - w2/2;
float left = l1 > l2 ? l1 : l2;
float r1 = x1 + w1/2;
float r2 = x2 + w2/2;
float right = r1 < r2 ? r1 : r2;
return right - left;
}
3)修改recognizeImage函数
public List<Recognition> recognizeImage(final Bitmap bitmap) {
// Log this method so that it can be analyzed with systrace.
Trace.beginSection("recognizeImage");
Trace.beginSection("preprocessBitmap");
// Preprocess the image data from 0-255 int to normalized float based
// on the provided parameters.
bitmap.getPixels(intValues, 0, bitmap.getWidth(), 0, 0, bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight());
imgData.rewind();
for (int i = 0; i < inputSize; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < inputSize; ++j) {
int pixelValue = intValues[i * inputSize + j];
if (isModelQuantized) {
// Quantized model
imgData.put((byte) ((pixelValue >> 16) & 0xFF));
imgData.put((byte) ((pixelValue >> 8) & 0xFF));
imgData.put((byte) (pixelValue & 0xFF));
} else { // Float model
imgData.putFloat((((pixelValue >> 16) & 0xFF) - IMAGE_MEAN) / IMAGE_STD);
imgData.putFloat((((pixelValue >> 8) & 0xFF) - IMAGE_MEAN) / IMAGE_STD);
imgData.putFloat(((pixelValue & 0xFF) - IMAGE_MEAN) / IMAGE_STD);
}
}
}
Trace.endSection(); // preprocessBitmap
// Copy the input data into TensorFlow.
Trace.beginSection("feed");
Object[] inputArray = {imgData};
Map<Integer, Object> outputMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < mOutWidth.length; i++) {
float[][][][] out = new float[1][mOutWidth[i]][mOutWidth[i]][ mOutWidth.length * (5 +labels.size())];
outputMap.put(i, out);
}
// Run the inference call.
Trace.beginSection("run");
tfLite.runForMultipleInputsOutputs(inputArray, outputMap);
// 经过yolov3模型后的imgData 会返回3个特征图 [1,13,13,255],[1,26,26,255],[1,52,52,255]
// 经过yolov3-tiny模型后的imgData 会返回2个特征图[1,13,13,255],[1,26,26,255]
Trace.endSection();
ArrayList<Recognition> detections = new ArrayList<Recognition>();
/**
* 重新编写一个转换方法用于提取yolo-v3中检测到的对象信息
* **/
int labels_size = labels.size();
for (int i = 0; i < mOutWidth.length; i++) {
int gridWidth = mOutWidth[i];
float[][][][] out = (float[][][][])outputMap.get(i);
for (int y = 0; y < gridWidth; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < gridWidth; ++x) {
for (int b = 0; b < NUM_BOXES_PER_BLOCK; ++b) {
final int offset =
(gridWidth * (NUM_BOXES_PER_BLOCK * (labels_size + 5))) * y
+ (NUM_BOXES_PER_BLOCK * (labels_size + 5)) * x
+ (labels_size + 5) * b;
final float confidence = expit(out[0][y][x][(labels_size + 5) * b + 4]);
int detectedClass = -1;
float maxClass = 0;
final float[] classes = new float[labels_size];
for (int _c = 0; _c < labels_size; ++_c) {
classes[_c] = out[0][y][x][(labels_size + 5) * b + 5 +_c];
}
softmax(classes);
// 得到最大各个类别中概率最大的类
for (int _c = 0; _c < labels_size; ++_c) {
if (classes[_c] > maxClass) {
detectedClass = _c;
maxClass = classes[_c];
}
}
final float confidenceInClass = maxClass * confidence;
if (confidenceInClass > mObjThresh) {
final float xPos = (x + expit(out[0][y][x][(labels_size + 5) * b])) * (inputSize / gridWidth);
final float yPos = (y + expit(out[0][y][x][(labels_size + 5) * b + 1])) * (inputSize / gridWidth);
final float w = (float) (Math.exp(out[0][y][x][(labels_size + 5) * b + 2]) * mAnchors[2 * mMasks[i][b] + 0]);
final float h = (float) (Math.exp(out[0][y][x][(labels_size + 5) * b + 3]) * mAnchors[2 * mMasks[i][b] + 1]);
Log.d("wangmin","box x:" + xPos + ", y:" + yPos + ", w:" + w + ", h:" + h);
final RectF rect =
new RectF(
Math.max(0, xPos - w / 2),
Math.max(0, yPos - h / 2),
Math.min(bitmap.getWidth() - 1, xPos + w / 2),
Math.min(bitmap.getHeight() - 1, yPos + h / 2));
Log.d("wangmin", "detect " + labels.get(detectedClass)
+ ", confidence: " + confidenceInClass
+ ", box: " + rect.toString());
detections.add(new Recognition("" + offset, labels.get(detectedClass),
confidenceInClass, rect, detectedClass));
}
}
}
}
Log.d("wangmin", "out[" + i + "] detect end");
}
final ArrayList<Recognition> recognitions = nms(detections);
return recognitions;
}
4)打开DetectorActivity.java 修改模型输入的尺寸,使用模型的名称和标签。
 5)真机调试(在检测过程中,有3秒左右的延迟,这是由于YOLOV3网络模型给出的是三张特征图,而手机的cpu并没有电脑的计算力,导致特征图在转换过程中消耗了时间)
5)真机调试(在检测过程中,有3秒左右的延迟,这是由于YOLOV3网络模型给出的是三张特征图,而手机的cpu并没有电脑的计算力,导致特征图在转换过程中消耗了时间)

总结
本次教程主要讲解了如何修改Google官网提供的对象检测示例源码,实现YOLOV3网络模型的嵌入。通过上述操作,我们能使用YOLOV3自训练其他数据集,然后嵌入到边缘设备中。若想使用Yolo-tiny的话,需要修改recognizeImage函数中特征图转换的三个循环,因为tiny只输出了两个特征图。此外,少奶奶还注解了TFLiteObjectDetectionAPIModel.java中所有函数的功能(为了减少篇幅,本文没有贴出来),大家可以在下载中找到。