深度学习之路=====11=====>>ShuffleNet(tensorflow2)
简介
来源:CVPR2017 作者:张祥雨,西安交通大学本硕博,原微软亚洲研究院研究员
特点
- 逐点分组卷积(pointwise group conv):使用了kernel_size=1的分组卷积,大大降低模型参数量和计算量
- 深度卷积也称逐通道卷积(Depthwise Convolution):区别于深度可分离卷积(depthwise separable convolution==depthwise convoluton+pointwise convolution),进一步降低模型参数
创新点
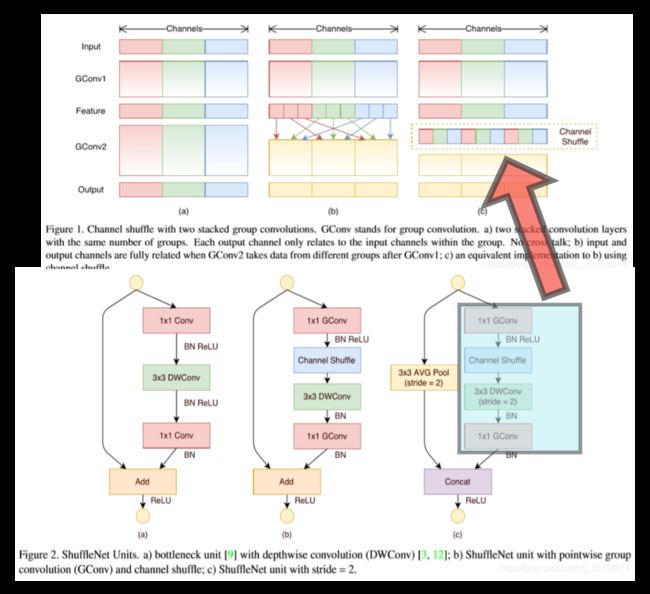
- 通道重组(channel shuffle):分组卷积后的特征图的某个通道仅仅来自输入通道的一部分(边界效应),channel shuffle能将这种边界效应消除,使得第二次分组卷积前的每个组的输入都能包含所有组的特征图。
分组卷积
通过下图可明显看到分组卷积带来的参数量和计算量降低,下面通过公式定量分析分组卷积带来的降参优势
设输入特征shape为 M × H × W M\times H\times W M×H×W,卷积核shape为 N × h × w N\times h\times w N×h×w
对于普通卷积,参数量为: M × h × w × N M\times h\times w\times N M×h×w×N,计算量为: M × h × w × N × H × W M\times h\times w\times N\times H\times W M×h×w×N×H×W
对于分组卷积,设组数为G,每组输入通道数为 M G \frac{M}{G} GM,每组卷积核数为 N G \frac{N}{G} GN,每组卷积后再CONCAT,
则参数量为: M G × h × w × N G × G \frac{M}{G}\times h\times w\times \frac{N}{G}\times G GM×h×w×GN×G,计算量为: M G × h × w × N G × G × H × W \frac{M}{G}\times h\times w\times \frac{N}{G}\times G\times H\times W GM×h×w×GN×G×H×W
所以分组卷积的参数量和计算量为普通卷积参数量和计算量的 1 G \frac{1}{G} G1。
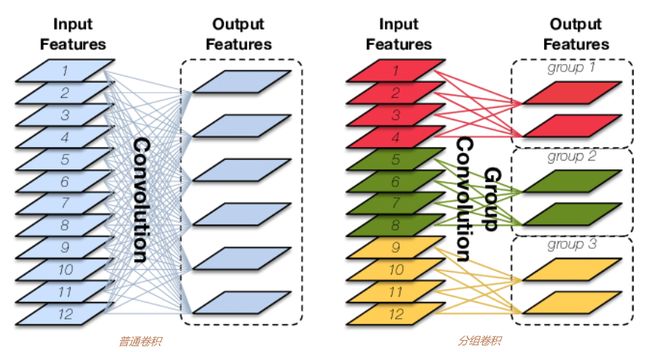
分组卷积过程为:先将输入split为groups组,每组分组卷积,最后再concat
具体代码为:见下文
深度卷积(depthwise conv)
在深度学习之路=====8=====>>Xception(tensorflow2)中对深度卷积进行了介绍,这里不再介绍,简而言之,深度卷积就是分组数等于输入通道数的分组卷积,且每个组卷积核数为1,即卷积核数于输入通道数相等。
通道重组(channel shuffle)
下图为通道重排示意图,首先将特征图的通道维度reshape为 ( g r o u p s , c h a n n e l s / g r o u p s ) \left(groups,channels/groups\right) (groups,channels/groups),再将其在这两个维度上进行转置,最后再reshape为原shape:
具体代码为:
def channel_shuffle(self,input,groups):
n, h, w, c = input.shape
x= tf.reshape(input, [-1, h, w, groups, c // groups])
x = tf.transpose(x, [0, 1, 2, 4, 3])
output = tf.reshape(x, [-1, h, w, c])
return output

下图为shuffleNet基本模块,由1X1->3x3->1x1的bottleneck结构变化而来,主要为了降低参数量,Bottleneck 三步走是先 pointwise conv 对数据进行降维(降低通道数),再进行常规卷积核的卷积,最后 pointwise conv 对数据进行升维(将通道数恢复为输入时的Channels)。
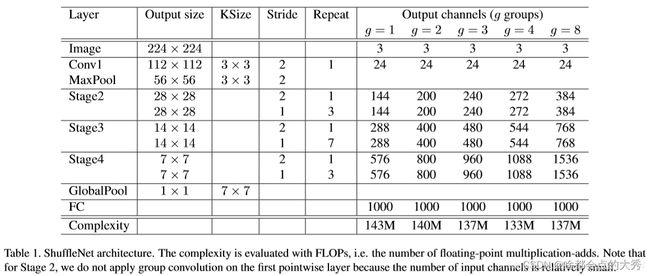
ShuffleNet 网络结构
在Stage2, Stage3,Stage4)中,先使用步长为 2 的 ShuffleNet Unit(上图中的(c)),又堆叠若干个个步长为 1 的 ShuffleNet Unit(上图中的(b))。另外,某一个 stage 的输出通道数是上一个 stage 的输出通道数的两倍,且在每个 Unit 里,设置 Bottleneck 的通道数是输出通道数的四分之一
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
from tensorflow.keras import Model
class Conv(Model):
def __init__(self,filters,kernel_size,strides):
super().__init__()
self.layers_list=[]
self.layers_list.append(Conv2D(filters=filters,kernel_size=kernel_size,strides=strides,padding='same'))
self.layers_list.append(BatchNormalization())
self.layers_list.append(Activation('relu'))
def call(self,x):
for layer in self.layers_list:
x=layer(x)
return x
class ShuffleNet_unit(Model):
def __init__(self,filters,in_channels,groups,mode=0):
super().__init__()
self.mode=mode
self.groups=groups
if self.mode==0:
self.filters=filters
else:
self.filters=filters-in_channels
self.bottleneck_filters=self.filters//4
self.gc_list1=[]
for i in range(groups):
self.gc_list1.append(Conv2D(self.bottleneck_filters//groups,kernel_size=1,strides=1,padding='same'))
self.b1=BatchNormalization()
self.a1=Activation('relu')
if self.mode==0:
self.dwc=DepthwiseConv2D(kernel_size=3,strides=1,padding='same')
else:
self.dwc=DepthwiseConv2D(kernel_size=3,strides=2,padding='same')
self.gc_list2=[]
for i in range(groups):
self.gc_list2.append(Conv2D(self.filters//groups,kernel_size=1,strides=1,padding='same'))
if self.mode==1:
self.residual=AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3,3),strides=2,padding='same')
self.a_last=Activation('relu')
def call(self,x):
#print(x.shape)
if self.mode==0:
residual=x
else:
residual=self.residual(x)
x_list1=tf.split(x,self.groups)
##第一个逐点分组卷积
for i in range(len(self.gc_list1)):
x_list1[i]=self.gc_list1[i](x_list1[i])
x=tf.concat(x_list1,-1)
#print(x.shape)
##通道重组
x=self.channel_shuffle(x,self.groups)
x=self.dwc(x)
x_list2=tf.split(x,self.groups)
##第二个逐点分组卷积
for i in range(len(self.gc_list2)):
x_list2[i]=self.gc_list2[i](x_list2[i])
x=tf.concat(x_list2,-1)
#print(x.shape)
#print('------next unit-----')
if self.mode==0:
y=x+residual
else:
y=tf.concat([x,residual],-1)
return y
def channel_shuffle(self,input,groups):
n, h, w, c = input.shape
x= tf.reshape(input, [-1, h, w, groups, c // groups])
x = tf.transpose(x, [0, 1, 2, 4, 3])
output = tf.reshape(x, [-1, h, w, c])
return output
class stage(Model):
def __init__(self,out_channels,in_channels,repeat,groups):
super().__init__()
self.unit_s2=ShuffleNet_unit(out_channels,in_channels,groups,1)
self.unit_s1=[]
for i in range(repeat):
self.unit_s1.append(ShuffleNet_unit(out_channels,in_channels,groups,0))
def call(self,x):
x=self.unit_s2(x)
for unit in self.unit_s1:
x=unit(x)
print(x.shape)
return x
class Shuffle_Net(Model):
def __init__(self,num_filters,in_channels,repeat_list):
super().__init__()
self.layers_list=[]
self.layers_list.append(Conv(24,3,2))
self.layers_list.append(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(3,3),strides=2,padding='same'))
self.out_channels=num_filters
self.in_channels=in_channels
for i,repeat in enumerate(repeat_list):
channels_in_stage=self.in_channels[i]
#print("this stage: in channels is %d,out channel is %d,repeats is %d >>>>>>>>>>>>"%(self.in_channels[i],self.out_channels,repeat))
self.layers_list.append(stage(self.out_channels,channels_in_stage,repeat,1))
self.out_channels *=2
self.layers_list.append(GlobalAveragePooling2D())
self.layers_list.append(Dense(1000))
def call(self,x):
for layer in self.layers_list:
x=layer(x)
return x
##最后,还是验证模型正确性
model=Shuffle_Net(144,[24,144,288,576],[3,7,3])
inputs = np.zeros((1, 224, 224, 3), np.float32)
print(inputs.shape)
model(inputs)
model.summary()
##输出:
#####与表格中网格结构一致
(1, 224, 224, 3)
(1, 28, 28, 144)
(1, 28, 28, 144)
(1, 28, 28, 144)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 14, 14, 288)
(1, 7, 7, 576)
(1, 7, 7, 576)
(1, 7, 7, 576)
##下面是sumarry
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv_10 (Conv) multiple 768
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_10 (MaxPooling multiple 0
_________________________________________________________________
stage_30 (stage) multiple 37494
_________________________________________________________________
stage_31 (stage) multiple 308772
_________________________________________________________________
stage_32 (stage) multiple 546696
_________________________________________________________________
global_average_pooling2d_10 multiple 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_10 (Dense) multiple 577000
=================================================================
Total params: 1,470,730
Trainable params: 1,470,682
Non-trainable params: 48
________________________________________________
bottlenet介绍
ShuffleNet算法详解
轻量级神经网络——shuffleNet
Tensorflow笔记——channel shuffle的实现
keras实现分组卷积
ShuffleNet V1 网络结构的原理与 Tensorflow2.0 实现