nn.Conv2d——二维卷积运算解读
PyTorch学习笔记:nn.Conv2d——二维卷积运算解读
- nn.Conv2d——二维卷积运算
- 代码案例
-
- 一般用法
- 输出卷积运算的参数
- 填充方式
-
- 零填充
- 镜像填充
- 复制填充
- 循环填充
- 官方文档
nn.Conv2d——二维卷积运算
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)
功能:对多个输入平面组成的输入信号应用2D卷积运算,常用于图像处理。
输入:
in_channels:输入图像中的通道数out_channels:经过卷积运算产生的通道数kernel_size:卷积核大小,整数或者元组类型stride:卷积运算的步幅,整数或者元组类型,默认1padding:边界处的填充大小,整数或者元组类型,默认0padding_mode:填充方式,zeros、reflect、replicate、circular,默认是zeros
zeros:零填充,在张量边界全部填充0
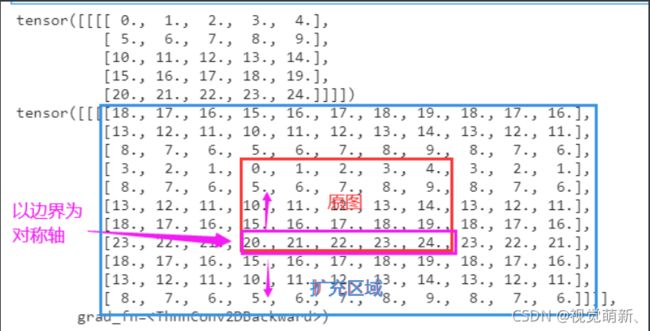
reflect:镜像填充,以矩阵边缘为对称轴,将反方向的对称元素填充到最外围。
replicate:复制填充,使用输入边界的复制值填充张量
circular:循环填充,重复矩阵边界另一侧的元素
具体区别请见代码案例dilation:控制点之间的距离,默认是1,如果大于1,则该运算又称为扩张卷积运算。
一图看懂扩张卷积运算
图片来源:https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic
groups:控制输入和输出之间的连接,默认是1。- 在
groups=1时,所有输入都被卷积为输出 - 在
groups=2时,该操作相当于先把输入通道对半分,分别经过相同的conv运算(因此卷积参数会减半),产生对应的输出,然后再将两者的输出连接起来。groups>2的情况类似,最大不能超过输入的通道数。 groups必须可以整除in_channels和out_channels
- 在
bias:是否有偏置项,默认True,即默认存在偏置项。- 输入的数组数据类型必须是
TensorFloat32类型
注意:
in_channels、out_channels和kernel_size是必须指定的参数,其他参数都有默认值,可以不指定。kernel_size、stride、padding和dilation既可以指定为整数类型,也可以指定为元组类型。- 如果被指定为整数时,则高度和宽度尺寸使用相同的值(正方形)
- 如果被指定为元组类型时,元组中第一个值用于高,第二个维度用于宽(长方形)
补充:
- 输出图像的高、宽计算公式(公式转自官方文档):
假 设 : 输 入 i n p u t : ( N , C i n , H i n , W i n ) , 输 出 o u t p u t : ( N , C o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) 其 中 N 是 b a t c h _ s i z e 、 C i 是 通 道 , H i 是 图 像 的 高 、 W i 是 图 像 的 宽 假设: 输入input:(N,C_{in},H_{in},W_{in}),输出output:(N,C_{out},H_{out},W_{out})\\ 其中N是batch\_size、C_i是通道,H_i是图像的高、W_i是图像的宽 假设:输入input:(N,Cin,Hin,Win),输出output:(N,Cout,Hout,Wout)其中N是batch_size、Ci是通道,Hi是图像的高、Wi是图像的宽
H o u t = H i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 0 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 0 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 0 ] + 1 W o u t = W i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 1 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 1 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 1 ] + 1 H_{out}=\frac{H_{in}+2\times padding[0]-dilation[0]\times(kernel\_size[0]-1)-1}{stride[0]}+1\\ W_{out}=\frac{W_{in}+2\times padding[1]-dilation[1]\times(kernel\_size[1]-1)-1}{stride[1]}+1\\ Hout=stride[0]Hin+2×padding[0]−dilation[0]×(kernel_size[0]−1)−1+1Wout=stride[1]Win+2×padding[1]−dilation[1]×(kernel_size[1]−1)−1+1
- 卷积层的权重可通过方法
Conv2d.weight提取,输出的权重数组尺寸为:
( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ) (out\_channels,\frac{in\_channels}{groups},kernel\_size[0],kernel\_size[0]) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size[0],kernel_size[0])
并且初始化权重分部服从均匀分布:
u ( − k , k ) , 其 中 k = g r o u p s C i n × ∏ i = 0 1 k e r n e l _ s i z e [ i ] u(-\sqrt{k},\sqrt{k}),其中k=\frac{groups}{C_{in}\times \prod\limits_{i=0}^1 kernel\_size[i]} u(−k,k),其中k=Cin×i=0∏1kernel_size[i]groups
- 卷积层的偏置参数可以通过方法
Conv2d.bias提取(前提bias=True),输出的数组尺寸与out_channels大小一样,初始化分部与weight权重分部一样。 - 卷积层参数也可以通过
.parameters()方法获取
代码案例
一般用法
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
img=torch.arange(49,dtype=torch.float32).view(1,1,7,7)
conv=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=1,kernel_size=3)
img_2=conv(img)
print(img)
print(img_2)
输出
# 经过卷积运算前
tensor([[[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.],
[14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.],
[21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.],
[35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41.],
[42., 43., 44., 45., 46., 47., 48.]]]])
# 卷积运算后
tensor([[[[4.7303, 4.8851, 5.0398, 5.1945, 5.3492],
[5.8134, 5.9681, 6.1228, 6.2775, 6.4323],
[6.8964, 7.0512, 7.2059, 7.3606, 7.5153],
[7.9795, 8.1342, 8.2889, 8.4436, 8.5984],
[9.0625, 9.2172, 9.3720, 9.5267, 9.6814]]]],
grad_fn=<ThnnConv2DBackward>)
图像尺寸的变化
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
img=torch.arange(4*64*28*28,dtype=torch.float32).view(4,64,28,28)
conv=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64,out_channels=128,kernel_size=3,padding=1)
img_2=conv(img)
print(img.shape)
print(img_2.shape)
输出
# 卷积前
torch.Size([4, 64, 28, 28])
# 卷积后
torch.Size([4, 128, 28, 28])
通道数变为了原来的两倍,由于填充了一格,所以卷积后尺寸不变
输出卷积运算的参数
卷积层数值
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
conv=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=1,kernel_size=3)
print(conv.weight)
print(conv.bias)
print(type(conv.weight))
# 利用.parameters()方法调用参数
for i in conv.parameters():
print(i)
print(type(i))
输出
# 卷积层权重参数
Parameter containing:
tensor([[[[-0.1891, -0.2296, 0.0362],
[-0.1552, -0.0747, 0.2922],
[-0.1434, 0.0802, -0.0778]]]], requires_grad=True)
# 卷积层偏置参数
Parameter containing:
tensor([0.1998], requires_grad=True)
# 参数的类型,均为Parameter类
<class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>
# 下面是通过.parameters()方法调用参数,与前面的方法结果一样
Parameter containing:
tensor([[[[-0.1891, -0.2296, 0.0362],
[-0.1552, -0.0747, 0.2922],
[-0.1434, 0.0802, -0.0778]]]], requires_grad=True)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0.1998], requires_grad=True)
# 返回的数据类型也一样
<class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>
卷积层参数尺寸
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
conv=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64,out_channels=128,kernel_size=[5,3],padding=2)
print(conv.weight.shape)
print(conv.bias.shape)
输出
# 权重参数,从第一维到第四维依次代表:
# 输出通道数、输入通道数、卷积核的高、卷积核的宽
torch.Size([128, 64, 5, 3])
# 偏置项参数,大小和输入通道数一样
torch.Size([128])
填充方式
为了消除卷积运算对原图的影响,我们首先将卷积核大小设为1,并且参数也设为1,不设置偏置项,并且为了凸显扩充后的效果,我们将padding调整为3。
初始化过程
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
conv_1=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=1,kernel_size=1,bias=False,padding=3,mode='zeros')
conv_1.weight=nn.parameter(torch.ones((1,1,1,1)))
conv_2=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=1,kernel_size=1,bias=False,padding=3,mode='reflect')
conv_2.weight=nn.parameter(torch.ones((1,1,1,1)))
conv_3=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=1,kernel_size=1,bias=False,padding=3,mode='replicate')
conv_3.weight=nn.parameter(torch.ones((1,1,1,1)))
conv_4=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=1,kernel_size=1,bias=False,padding=3,mode='circular')
conv_4.weight=nn.parameter(torch.ones((1,1,1,1)))
img=torch.arange(25,dtype=torch.float32).reshape(1,1,5,5)
零填充
img_1=conv_1(img)
print(img)
print(img_1)
镜像填充
img_2=conv_2(img)
print(img)
print(img_2)
输出
复制填充
img_3=conv_3(img)
print(img)
print(img_3)
输出
循环填充
img_4=conv_4(img)
print(img)
print(img_4)
输出
官方文档
nn.Conv2d():https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv2d.html?highlight=conv2d#torch.nn.Conv2d
点个赞支持一下吧