学渣笔记:opencv-python识别图像
import cv2
import numpy as np
引入cv2和numpy包
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
图像堆叠,将多个图像放入一个窗口
参数1:窗口大小
参数2:图像列表
# 根据轮廓获取曲线, 根据曲线获取折线,根据折线获取拐点,根据拐点获取角数
def getContours(img):
# 找轮廓
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 遍历每一个轮廓
for cnt in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt) # 计算图像轮廓面积
print(area)
if area > 500:
cv2.drawContours(imgContour, cnt, -1, (255, 0, 0), 3) # 画出轮廓
peri = cv2.arcLength(cnt, True) # 轮廓长度
# print(peri)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, 0.02 * peri, True) # 拟合轮廓, 返回(一组拐点)角数 (对指定的点集进行多边形拟合)
print(len(approx))
objCor = len(approx) # 得到轮廓角数(拐点数)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(approx) # 计算轮廓的垂直边界最小矩形 x,y:左上点宽高, w,h:宽高
if objCor == 3:
objectType = "Tri"
elif objCor == 4: # 区分正方形和矩形
aspRatio = w / float(h)
if aspRatio > 0.98 and aspRatio < 1.03:
objectType = "Square"
else:
objectType = "Rectangle"
elif objCor > 4:
objectType = "Circles"
else:
objectType = "None"
cv2.rectangle(imgContour, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(imgContour, objectType,
(x + (w // 2) - 10, y + (h // 2) - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.7,
(0, 0, 0), 2)
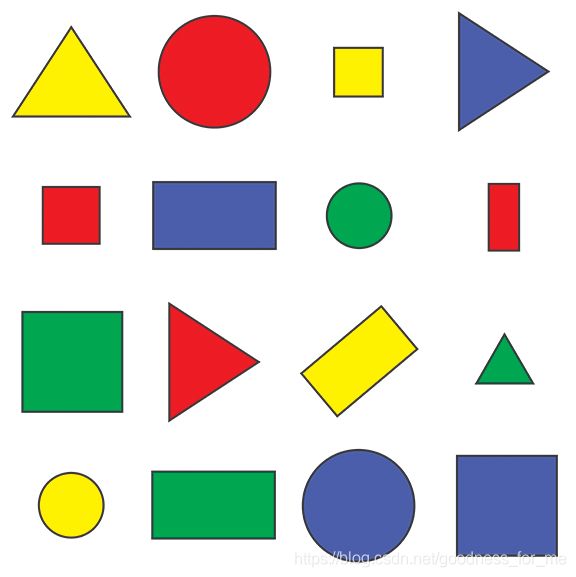
path = 'C:/Users/PC/Desktop/zd3.png' #'Resources/shapes.png'
img = cv2.imread(path)
imgContour = img.copy()
imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgBlur = cv2.GaussianBlur(imgGray, (7, 7), 1)
imgCanny = cv2.Canny(imgBlur, 50, 50)
getContours(imgCanny)
imgBlank = np.zeros_like(img)
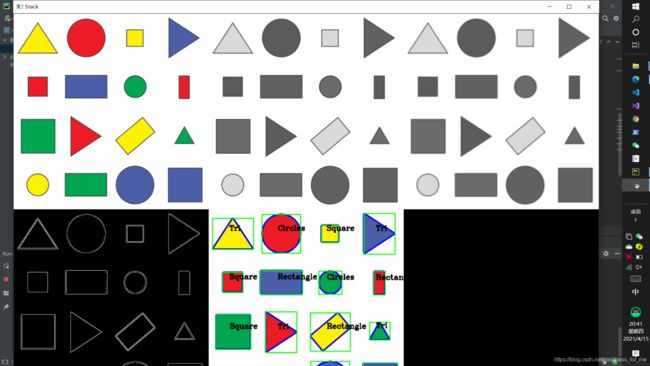
imgStack = stackImages(0.8, ([img, imgGray, imgBlur],
[imgCanny, imgContour, imgBlank]))
cv2.imshow("Stack", imgStack)
cv2.waitKey(0)
- 以上代码可以复制到你的编辑器看
函数getcontours:传入一张图片,获取轮廓,进行识别
核心思想:据轮廓获取曲线, 根据曲线获取折线,根据折线获取拐点,根据拐点获取角数
核心函数:
- cv2.findContours()
参数1:需要寻找轮廓的图像
参数2:
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL 表示只检测外轮廓
cv2.RETR_LIST 检测的轮廓不建立等级关系
cv2.RETR_CCOMP 建立两个等级的轮廓,上面的一层为外边界,里面的一层为内孔的边界信息。如果内孔内还有一个连通物体,这个物体的边界也在顶层。
cv2.RETR_TREE 建立一个等级树结构的轮廓。
参数3: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE 存储所有的轮廓点,相邻的两个点的像素位置差不超过1
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE 压缩水平方向,垂直方向,对角线方向的元素,只保留该方向的终点坐标,例如一个矩形轮廓只需4个点来保存轮廓信息
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS 使用teh-Chinl chain 近似
返回值1:图像中的轮廓,用numpy中ndarray表示
返回值2:ndarray,每个轮廓contours[i]对应4个hierarchy元素hierarchy[i][0] ~hierarchy[i][3],分别表示后一个轮廓、前一个轮廓、父轮廓、内嵌轮廓的索引编号,如果没有对应项,则该值为负数
其他函数的作用已经做了批注,有兴趣的伙伴可以仔细研究.