深入理解和使用nginx
深入理解和使用nginx
-
- 1. nginx简介
- 2. nginx安装和命令介绍
-
- 2.1 centos7下使用yum安装
- 2.2 源码编译安装
-
- 2.2.1 环境准备
- 2.2.2 下载源码并且解压
- 2.2.3 为nginx设置安装目录和启用的模块
- 2.2.4 编译和安装
- 2.2.5 启动和停止nginx服务
- 2.2.6 访问测试
- 2.3 nginx命令介绍
- 3. nginx安装目录、常用模块、内置变量
-
- 3.1 nginx安装目录
- 3.2 nginx常用模块
- 3.3 nginx内置变量
- 4. nginx配置文件介绍
-
- 4.1 全局块中的配置
- 4.2 events事件块配置
- 4.3 http块配置
- 4.4 server块配置
- 4.5 location块配置
- 5. Rewrite指令
-
- 5.1 Rewrite基本概述
- 5.2 Rewrite基本语法
- 5.3 正则表达式
- 5.4 flag案例演示
-
- 5.4.1 break和last
- 5.4.2 redirect和permanent
- 5.5 需求和实现
-
- 5.5.1 需求1:基于域名跳转
- 5.5.2 需求2:基于域名跳转并且加目录
- 5.5.3 需求3:基于客户端IP访问跳转
- 5.5.4 需求4:http强制跳转到https
- 5.6 Rewrite匹配优先级
- 6. nginx日志配置和切割
-
- 6.1 日志配置
-
- 6.1.1 access.log配置
- 6.1.2 error_log配置
- 6.1.3 log_format日志格式配置
- 6.1.4 open_log_file_cache配置
- 6.2 日志切割
-
- 6.2.1 使用set指令
- 6.2.2 使用logrotate工具切割nginx日志
- 7. nginx状态监控和nginx站点下载
-
- 7.1 nginx状态监控
- 7.2 nginx实现站点下载
- 7.3 root和alias的区别
- 8. nginx静态资源服务
-
- 8.1 静态资源类型
- 8.2 静态资源配置语句
- 8.3 静态资源⽂件压缩
- 8.4 静态资源浏览器缓存
- 8.5 静态资源防盗链
- 9. nginx访问限制和nginx访问控制
-
- 9.1 nginx访问限制
- 9.2 nginx访问控制
-
- 9.2.1 基于ip访问控制
- 9.2.2 基于用户登录认证
- 10. http层反向代理
-
- 10.1 代理概述
- 10.2 http反向代理配置
- 10.3 反向代理案例演示
- 11. 四层反向代理(TCP代理)
-
- 11.1 TCP反向代理概述
- 11.2 配置语句
- 11.3 TCP反向代理案例演示
- 12. http负载均衡和健康检查
-
- 12.1 简介
- 12.2 配置语法
- 12.2 负载均衡算法
-
- 12.2.1 轮询
- 12.2.2 最小连接数
- 12.2.3 ip-hash
- 12.3 基于max_fails和fail_timeout的健康检查
- 12.4 基于Tengine的ngx_http_upstream_check_module模块的健康检查
-
- 12.4.1 yum安装的nginx添加第三方模块: ngx_http_upstream_check_module
- 12.4.2 配置语法
- 12.4.3 案例演示
- 13 nginx配置https
-
- 13.1 HTTPS基本概述
- 13.2 HTTPS常用配置
- 13.3 配置https
- 13.4 http强制跳转到https
- 14. nginx中的return指令、set指令、map指令、if指令
-
- 14.1 return指令
- 14.2 set指令
- 14.3 if指令
- 14.4 map指令
- 15. nginx跨域配置
-
- 15.1 跨域基本配置
- 15.2 跨域请求时Cookie丢失问题
- 15.3 map指令优化允许跨域的域名
- 16. nginx实现灰度发布
-
- 16.1 基于header进行转发
- 16.2 基于cookie进行转发
- 16.3 基于arg进行转发
- 16.4 基于weight
- 17. WebSocket代理
-
- 17.1 WebSocket基本概述
- 17.2 配置语法
- 17.3 nginx服务器配置、Springboot后台服务器代码
- 17.4 案例演示
-
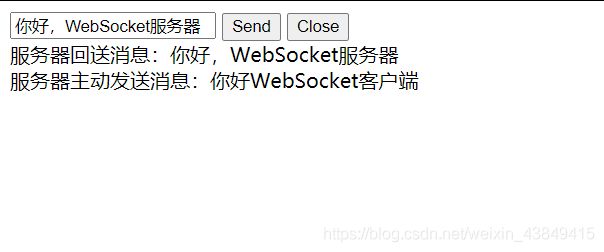
- 17.4.1 浏览器和服务器建立连接
- 17.4.2 浏览器发送消息给服务器
- 17.4.3 服务器主动发消息给浏览器
nginx官方文档
1. nginx简介
nginx [engine x]是HTTP和反向代理服务器,邮件代理服务器和通用TCP/UDP代理服务器,最初由Igor Sysoev编写。nginx具有高性能、占用资源小等特点,广泛应用于各大互联网公司。对于java程序员来说,掌握nginx的基本配置和使用是必须的。
nginx的主要使用场景:
- 静态处理(动静分离、站点文件下载)
- 反向代理(提供4层和7层代理)
- 负载均衡(提供丰富的调度算法轮询、hash、权重等)
- 资源缓存(对于静态资源进行缓存、压缩,以及防盗链等)
- 访问限制和控制(基于连接限制、ip限制控制等)
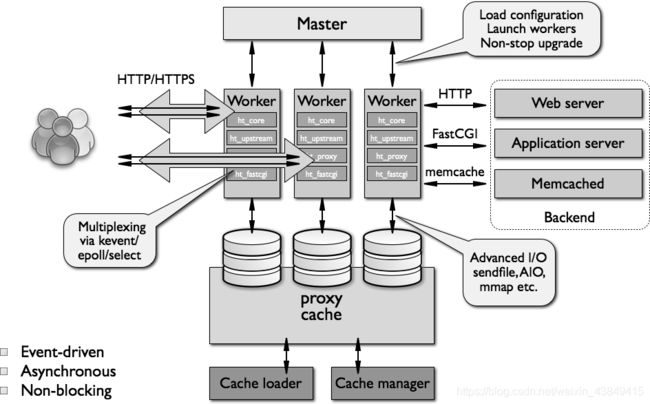
nginx有四种进程:
-
master进程。master进程是父进程,其他进程都是子进程,master进程对worker进程进行管理。
-
worker进程。worker进程有多个,是负责处理具体的请求的。nginx为什么采用多进程而不是多线程的进程结构呢?是因为nginx要保证高可用性,多线程之间会共享地址空间,当某一个第三方模块引发了一个错误时,就会导致整个nginx进程挂掉。而采用多进程模型不会出现这个问题。
-
cache manager和cache loader进程。缓存除了要被多个worker进程使用,也要被cache进程使用,cache loader做缓存的载入,cache manager做缓存的管理,实际上每一个请求所使用的缓存还是由worker进程来进行的。这些进程间的通信都是通过共享内存来进行的。
一个master有多个worker,每个worker可响应n个请求,每个worker有核心模块core和外围的诸多模块modules组成,为了实现http功能有http协议的http_core模块,为了功能完善还有很多其它模块,如实现负载均衡的http_upstream模块,http_proxy反代模块,Fastcgi模块ht_fastcgi模块等。
2. nginx安装和命令介绍
2.1 centos7下使用yum安装
安装前置工具
[root@localhost ~]# yum install yum-utils -y
创建一个nginx.repo配置文件,该文件配置nginx官方的yum源仓库
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo << EOF
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
[nginx-mainline]
name=nginx mainline repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/7/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
EOF
安装nginx,这里一般默认安装最新版本的nginx。
[root@localhost ~]# yum install nginx -y
查看安装的nginx的版本
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -v
启动nginx,并且设置开机自启
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nginx && systemctl enable nginx
访问测试
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://localhost
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
2.2 源码编译安装
2.2.1 环境准备
使用yum提前安装nginx需要的软件
[root@localhost ~]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ automake pcre pcre-devel zlip zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel -y
- gcc为GNU Compiler Collection的缩写,可以编译C和C++源代码等,它是GNU开发的C和C++以及其他很多种语言 的编译器(最早的时候只能编译C,后来很快进化成一个编译多种语言的集合,如Fortran、Pascal、Objective-C、Java、Ada、 Go等。)
gcc 在编译C++源代码的阶段,只能编译 C++ 源文件,而不能自动和 C++ 程序使用的库链接(编译过程分为编译、链接两个阶段,注意不要和可执行文件这个概念搞混,相对可执行文件来说有三个重要的概念:编译(compile)、链接(link)、加载(load)。源程序文件被编译成目标文件,多个目标文件连同库被链接成一个最终的可执行文件,可执行文件被加载到内存中运行)。因此,通常使用 g++ 命令来完成 C++ 程序的编译和连接,该程序会自动调用 gcc 实现编译。 - gcc-c++也能编译C源代码,只不过把会把它当成C++源代码,后缀为.c的,gcc把它当作是C程序,而g++当作是c++程序;后缀为.cpp的,两者都会认为是c++程序,注意,虽然c++是c的超集,但是两者对语法的要求是有区别的。
- automake是一个从Makefile.am文件自动生成Makefile.in的工具。为了生成Makefile.in,automake还需用到perl,由于automake创建的发布完全遵循GNU标准,所以在创建中不需要perl。
- libtool是一款方便生成各种程序库的工具。
- pcre pcre-devel:在Nginx编译需要 PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expression),因为Nginx 的Rewrite模块和HTTP 核心模块会使用到PCRE正则表达式语法。
- zlip zlib-devel:nginx启用压缩功能的时候,需要此模块的支持。
- openssl openssl-devel:开启SSL的时候需要此模块的支持。
2.2.2 下载源码并且解压
目前nginx最新版本1.16.1,去nginx官方下载地址下载源码
这里使用wget命令下载nginx源码,如果下载较慢可以使用迅雷下载,然后进行上传
#下载nginx源码
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
#解压压缩包
[root@localhost ~]# tar -zxvf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
#进入nginx源码目录
[root@localhost ~]# cd nginx-1.16.1
#查看目录
[root@localhost ~]# ll
总用量 752
drwxr-xr-x. 6 1001 1001 4096 11月 25 23:14 auto
-rw-r--r--. 1 1001 1001 296463 8月 13 2019 CHANGES
-rw-r--r--. 1 1001 1001 452171 8月 13 2019 CHANGES.ru
drwxr-xr-x. 2 1001 1001 168 11月 25 23:14 conf
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 1001 1001 2502 8月 13 2019 configure
drwxr-xr-x. 4 1001 1001 72 11月 25 23:14 contrib
drwxr-xr-x. 2 1001 1001 40 11月 25 23:14 html
-rw-r--r--. 1 1001 1001 1397 8月 13 2019 LICENSE
drwxr-xr-x. 2 1001 1001 21 11月 25 23:14 man
-rw-r--r--. 1 1001 1001 49 8月 13 2019 README
drwxr-xr-x. 9 1001 1001 91 11月 25 23:14 src
2.2.3 为nginx设置安装目录和启用的模块
进入到nginx的解压文件夹并且执行configure命令
[root@localhost ~]# ./configure \
--prefix=/etc/nginx \
--sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \
--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid \
--lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock \
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp \
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp \
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp \
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp \
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-file-aio \
--with-threads \
--with-http_addition_module \
--with-http_auth_request_module \
--with-http_dav_module \
--with-http_flv_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_mp4_module \
--with-http_random_index_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_secure_link_module \
--with-http_slice_module \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_sub_module \
--with-http_v2_module \
--with-mail \
--with-mail_ssl_module \
--with-stream \
--with-stream_realip_module \
--with-stream_ssl_module \
--with-stream_ssl_preread_module
参数说明:
- –prefix 用于指定nginx编译后的安装目录。
- –add-module 为添加的第三方模块,此次添加了fdfs的nginx模块。
- –with…_module 表示启用的nginx模块,如此处启用了http_ssl_module模块。
可能出现的错误:
- 出现:./configure: error: the HTTP rewrite module requires the PCRE library.
解决方法:yum -y install pcre-devel - 出现:SSL modules require the OpenSSL library
解决方法:yum install openssl-devel
如果安装好nginx后,查看nginx编译参数
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
下表展示了nginx编译参数选项以及作⽤
| 编译选项 | 作⽤ |
|---|---|
| –prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock |
程序安装⽬录和路径 |
| –http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_tem --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp |
临时缓存⽂件 |
| –user=nginx --group=nginx |
设定nginx进程启动⽤户和组(安全) |
| –with-cc-opt | 设置额外的参数将被添加到CFLAGS变量 |
| –with-ld-opt | 设置附加的参数, 链接系统库 |
2.2.4 编译和安装
[root@localhost ~]# make && make install
查看prefix中定义的安装路径
[root@localhost ~]# ll /etc/nginx
总用量 40
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 11月 10 22:34 conf.d
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1007 10月 29 23:25 fastcgi_params
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2837 10月 29 23:25 koi-utf
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2223 10月 29 23:25 koi-win
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5231 10月 29 23:25 mime.types
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 29 11月 9 22:16 modules -> ../../usr/lib64/nginx/modules
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 805 11月 10 23:05 nginx.conf
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 670 11月 9 22:10 nginx.conf.rpmsave
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 636 10月 29 23:25 scgi_params
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 82 11月 9 23:35 ssl
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 664 10月 29 23:25 uwsgi_params
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3610 10月 29 23:25 win-utf
2.2.5 启动和停止nginx服务
添加nginx用户和nginx用户组
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# groupadd nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# useradd -g nginx nginx
查看nginx的版本
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.16.1
查看nginx的编译参数
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.16.1
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module
启动nginx
[root@localhost /]# nginx
nginx: [emerg] mkdir() "/var/cache/nginx/client_temp" failed (2: No such file or directory)
#报错,提示没有/var/cache/nginx文件夹
#创建/var/cache/nginx文件夹 -p 参数如果中间文件夹不存在,就创建
[root@localhost /]# mkdir -p /var/cache/nginx/
[root@localhost /]# nginx
查看80端口是否监听
[root@localhost /]# netstat -ntlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1428/master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 11076/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1191/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1428/master
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1191/sshd
可以看到80端口被nginx监听
2.2.6 访问测试
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://localhost
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
2.3 nginx命令介绍
nginx官方文档命令解释
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -h
- ? | -h — 显示命令行参数的帮助。
- -c file — 使用指定路径的配置文件而不是默认文件。
- -g directives — 设置全局配置指令,例如,
nginx -g "pid /var/run/nginx.pid; worker_processes sysctl -n hw.ncpu;" - -p prefix — 设置nginx路径前缀,即将保留服务器文件的目录(默认值为
/usr/local/nginx)。 - -q — 在配置测试期间抑制非错误消息。
- -s signal — 向主进程发送信号。参数信号可以是以下之一:
stop — 快速关闭
quit — 正常关闭
reload — 重新加载配置,使用新配置启动新工作进程,并正常关闭旧工作进程。 - -reopen — 重新打开日志文件
- -t — 测试配置文件:nginx检查配置的语法是否正确,然后尝试打开配置中引用的文件。
- -T— 与-t相同,但另外将配置文件转储到标准输出(1.9.2)。
- -v — 打印nginx版本。
- -V — 打印nginx版本,编译器版本和配置参数。
比较常用的命令:
nginx -s reload重新加载配置文件nginx -s stop停止nginx服务nginx -t检测配置语句是否正确nginx reopen重新打开日志文件
3. nginx安装目录、常用模块、内置变量
3.1 nginx安装目录
为了让⼤家更清晰的了解 nginx 软件的全貌,有必要介绍下nginx安装后整体的⽬录结构及⽂件功能。
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ql nginx
如下表格对 nginx 安装⽬录做详细概述
| 路径 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf |
配置⽂件 | nginx主配置⽂件 |
| /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params /etc/nginx/scgi_params /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params |
配置⽂件 | Cgi、Fastcgi、Uwcgi配置⽂件 |
| /etc/nginx/win-utf /etc/nginx/koi-utf /etc/nginx/koi-win |
配置⽂件 | nginx编码转换映射⽂件 |
| /etc/nginx/mime.types | 配置⽂件 | http协议的Content-Type与扩展名 |
| /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service | 配置⽂件 | 配置系统守护进程管理器 |
| /etc/logrotate.d/nginx | 配置⽂件 | nginx⽇志轮询、⽇志切割 |
| /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/sbin/nginx-debug |
命令 | nginx终端管理命令 |
| /etc/nginx/modules /usr/lib64/nginx /usr/lib64/nginx/modules |
⽬录 | nginx模块⽬录 |
| /usr/share/nginx /usr/share/nginx/html /usr/share/nginx/html/50x.html /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html |
⽬录 | nginx默认站点⽬录 |
| /usr/share/doc/nginx-1.12.2 /usr/share/man/man8/nginx.8.gz |
⽬录 | nginx的帮助⼿册 |
| /var/cache/nginx | ⽬录 | nginx的缓存⽬录 |
| /var/log/nginx | ⽬录 | nginx的⽇志⽬录 |
3.2 nginx常用模块
nginx模块分为 nginx官⽅模块以及nginx第三⽅模块
| nginx模块名称 | 模块作⽤ |
|---|---|
| ngx_http_core_module | 包含⼀些核⼼的http参数配置,对应nginx的配置区块部分 |
| ngx_http_access_module | 访问控制模块,⽤来控制⽹站⽤户对nginx的访问 |
| ngx_http_gzip_module | 压缩模块,对nginx返回的数据压缩,属于性能优化模块 |
| ngx_http_fastcgi_module | fastci模块,和动态应⽤相关的模块,例如PHP |
| ngx_http_proxy_module | proxy代理模块 |
| ngx_http_upstream_module | 负载均衡模块,可以实现⽹站的负载均衡功能及节点的健康检查 |
| ngx_http_rewrite_module | URL地址重写模块 |
| ngx_http_limit_conn_module | 限制⽤户并发连接数及请求数模块 |
| ngx_http_limit_req_module | 限制nginx request processing rate根据定义的key |
| ngx_http_log_module | 访问⽇志模块,以指定的格式记录nginx客户访问⽇志等信息 |
| ngx_http_auth_basic_module | Web认证模块,设置Web⽤户通过账号密码访问nginx |
| nginx_http_ssl_module | ssl模块,⽤于加密的http连接,如https |
3.3 nginx内置变量
nginx官方文档内置变量说明
| 变量 | 解释说明 |
|---|---|
| $uri | 当前请求的uri,不带参数 |
| $request_uri | 请求的uri,带完整参数 |
| $host | http请求报⽂中host⾸部,如果没有则以处理此请求的虚拟主机的主机名代替 |
| $hostname | nginx服务运⾏在主机的主机名 |
| $remote_addr | 客户端IP |
| $remote_port | 客户端端⼝ |
| $remote_user | 使⽤⽤户认证时客户端⽤户输⼊的⽤户名 |
| $request_filename | ⽤户请求中的URI经过本地root或alias转换后映射的本地⽂件路径 |
| $request_method | 请求⽅法, GET POST PUT |
| $server_addr | 服务器地址 |
| $server_name | 服务器名称 |
| $server_port | 服务器端⼝ |
| $server_protocol | 服务器向客户端发送响应时的协议, 如http/1.1 http/1.0 |
| $scheme | 在请求中使⽤scheme, 如http://xxx.com中的http |
| $http_header | 匹配请求报⽂中指定的HEADER |
| $http_host | 匹配请求报⽂中的host⾸部 |
| $document_root | 当前请求映射到的root配置 |
| $arg_name | 获取url路径中参数对应的value |
| $cookie_name | 获取对应cookie中的name的值,如果不存在,就是空串 |
4. nginx配置文件介绍
这里主要以yum安装的nginx进行演示。
nginx主要配置文件是/etc/nginx/nginx.conf以及默认/etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf,nginx的配置文件是一个纯文本的配置文件,整个配置文件是以区块的形式组织的。
每个区块用一对 {} 来表示开始和结束,每个区块内使用 key value的形式进行配置,每个配置的末尾必须使用分号结尾。
如果有注释使用"#"进行标识。
nginx配置文件组织形式如下:
- main位于nginx.conf配置⽂件的最⾼层
- main层下可以有event、http层
- http层下⾯有允许有多个server层,⽤于对不同的⽹站做不同的配置
- Server层也允许有多个location,⽤于对不同的路径进⾏不同模块的配置
- location块主要定义具体的路由规则、代理规则、转发规则
下面是对nginx.conf配置文件的简单解释
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
#nginx全局块
#设置nginx服务的系统使⽤⽤户,使用默认即可
user nginx;
#⼯作进程, 配置和CPU个数保持⼀致
worker_processes 1;
#定义全局的错误⽇志路径, 后⾯接⼊的是路径和级别 日志级别[debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit]
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
#Nginx服务启动时的pid存在文件的路径
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
#events事件模块
events {
#每个worker进程⽀持的最⼤连接数
worker_connections 1024;
#内核模型,select,poll,epoll
use epoll;
}
#⾮虚拟主机的配置或公共配置定义在http{}段内,server{}段外。因此
http {
#导入一些文件类型
include mime.types;
#默认返回的数据格式
default_type application/octet-stream;
#定义日志格式
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#定义访问的日志路径和使用的格式
access_log logs/access.log main;
#开启零拷贝,默认on,表示开启
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#是否开启gzip压缩
gzip on;
#引入其他配置文件,这里需要注意的是这行配置的位置,在http内server块外。
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
#必须使⽤虚拟机配置站点,每个虚拟机使⽤⼀个server{}段
server {
#监听端⼝,默认80,在server内可以监听多个端口
listen 80;
#提供服务的域名或主机名
server_name localhost;
#控制⽹站访问路径
location / {
#存放⽹站路径
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#默认访问⾸⻚⽂件
index index.html index.htm;
}
#指定错误代码, 统⼀定义错误⻚⾯, 错误代码重定向到新的Locaiton
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
...
#第⼆个虚拟主机配置
server {
...
}
}
4.1 全局块中的配置
全局块中的配置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组、nginx进程pid存放路径、日志存放路径、配置文件引入、允许生成worker process数等。
| 配置 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| user nginx; | 设置nginx服务的系统使⽤⽤户,一般而言使用默认即可 |
| worker_processes auto; | 启动worker进程的个数, 配置和CPU个数保持⼀致。 使用auto,nginx自动会根据cpu的核心数进行调整 |
| worker_cpu_affinity auto; | cpu亲和性,使用auto即可 |
| error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log error; | 配置错误日志的路径和日志级别,使用默认即可 |
| pid /run/nginx.pid; | 使用默认即可 |
| worker_rlimit_nofile 65535; | worker进程可打开最大的文件描述符 |
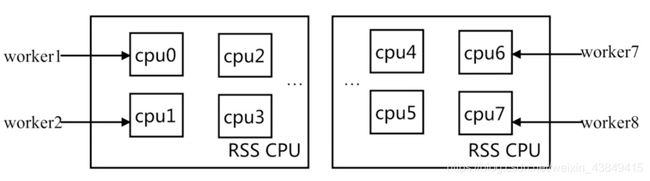
需要注意的是关于worker_processes和worker_cpu_affinity这两个配置
建议将worker进程的个数设置成与CPU核心数一致,减少进程之间不断频繁迁移,减少线程的上下文切换, 减少性能损耗。
下面进行案例演示,设置worker进程数与CPU亲和性的效果。
- 查看当前CPU物理状态
[root@localhost ~]# lscpu |grep "CPU(s)"
CPU(s): 8
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
- 将worker进程绑到不同的核⼼上
#启动多少worker进程, 官⽅建议和cpu核⼼⼀致, 第⼀种绑定组合⽅式
#worker_processes 24;
#worker_cpu_affinity 000000000001 000000000010 000000000100 000000001000 0000000100
00 000000100000 000001000000 000010000000 000100000000 001000000000 010000000000 10
000000000;
#第⼆种⽅式
#worker_processes 2;
#worker_cpu_affinity 101010101010 010101010101;
#最佳⽅式绑定⽅式
worker_processes auto;
worker_cpu_affinity auto;
检查nginx配置文件,重新启动nginx
[root@localhost nginx]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost nginx]# nginx -s reload
- 查看worker进程绑定⾄对应cpu
[root@localhost nginx]# ps -eo pid,args,psr | grep [n]ginx
1193 nginx: master process /usr/ 1
1973 nginx: worker process 0
1974 nginx: worker process 1
1975 nginx: worker process 2
1976 nginx: worker process 3
1977 nginx: worker process 4
1978 nginx: worker process 5
1979 nginx: worker process 6
1980 nginx: worker process 7
4.2 events事件块配置
events事件块中的配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数、选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求、是否允许同时接受多个网路连接、开启多个网络连接序列化等。
| 配置 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| use [epoll、select、poll]; | 使用epoll,多路复用I/O中的一种方式,仅用于linux2.6以上内核,大大提升nginx性能 |
| accept_mutex {on、off}; | master调度用户请求至各worker进程时使用的负载均衡锁,“on”表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地去响应新请求 |
| lock_file file; | accept_nutex用到的互斥锁锁文件路径 |
| worker_connections 1024; | 每个进程能够接受的最大连接数 |
| multi_accept on; | 尽可能多的接受请求 |
关于select、poll、epoll可以查看相关的博客:select、poll、epoll之间的区别(搜狗面试)
4.3 http块配置
nginx官方文档httpcore模块
http块中的配置可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入、mime-type定义、日志自定义、是否使用sendfile传输文件、连接超时时间、单连接请求数等。
| 配置 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| include mime.types; | 引入外部的配置文件,例如引入外部的数据类型 |
| log_format name string …; | 定义日志格式,后面详细解释说明 |
| access_log logs/access.log main; | 定义访问的日志路径和使用的格式 |
| send file on; | 是否开启零拷贝,默认开启 |
4.4 server块配置
server块中的配置主要定义虚拟主机的相关参数,例如监听的端口、域名、日志、路由规则等,一个http中可以有多个server。
| 配置 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| listen 80; | 监听80端口,可以同时监听多个端口 |
| server_name localhost; | 虚拟机主机的域名,可以定义多个,也可以是正则 |
| keepalive_timeout 120s; | 配置连接超时的时间 |
| root /user/local/nginx/html; | 配置站点目录 |
| access_log /var/log/nginx/$host/access.log combine ; | 配置日志的路径和使用的格式 |
4.5 location块配置
location块中配置具体的路由和转发规则
Syntax: location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { … }
location @name { … }
Default: —
Context: server, location
location [ = | ~ | ~* | … ] uri 解释说明:
- = 开头表示精确匹配
- ^ ~ 开头表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码
- ~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
- ~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
- !~ 和 !~* 分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配 的正则
- / 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到
- @name 用于定义一个 location 块,且该块不能被外部 Client 所访问,只能被nginx内部配置指令所访问,比如try_files or error_page
配置示例
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
location = / {
# 精确匹配 / ,主机名后面不能带任何字符串
return 200 '等于匹配';
}
location / {
return 200 '根路径匹配';
}
location /documents/ {
return 200 'documents匹配';
}
location ^~ /images/ {
return 200 '正则匹配,以images开头';
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
return 200 '正则匹配,以gif、jpg、jpeg结尾';
}
}
location匹配逻辑,按照优先级进行查找,一旦查找到就不再往下执行。location指令中匹配优先级
(location =) > (location 完整路径) > (location ^~ 路径) > (location ,* 正则顺序) > (location 部分起始路径) > (/)
最佳实践,配置"/"根路径、配置静态资源、配置后台业务反向代理,负载均衡
- 直接匹配网站根,通过域名访问网站首页比较频繁。
location = / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
- 处理静态文件请求,这是nginx作为http服务器的强项。有两种配置模式,目录匹配或后缀匹配,任选其一或搭配使用
#匹配静态目录
location ^~ /static/ {
rewrite ^/static(.*)$ /usr/share/nginx$1 break;
#或者是配置alias站点路径,alias不会带上static,root会带上static
alias /usr/share/nginx;
}
#匹配静态资源的后缀
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
root /user/local/nginx/static/;
}
- 后台业务系统,配置反向代理和负载均衡
upstream business {
server localhost:8080;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#注意这里的api后面加上了/,而且business后面也加上了/,这样反向代理会截取api路径。
#例如访问http://localhost/api/user/update => 反向代理的路径 http://localhost:8080/user/update
location ^~ /api/ {
proxy_pass http://business/;
}
}
5. Rewrite指令
nginx官方文档rewrite指令
5.1 Rewrite基本概述
nginx的rewrite功能是基于ngx_http_rewrite_moudle模块实现的。rewrite使用nginx全局变量或者是自定义变量,结合正则表达式和标志位实现URL重写和重定向

5.2 Rewrite基本语法
Syntax: rewrite regex replacement [flag];
Default: –
Context: server, location, if
//所有请求转发⾄/pages/maintain.html
rewrite ^(.*)$ /pages/maintain.html break;
flag解释说明
| flag | 解释说明 |
|---|---|
| last | 停止处理后续rewrite指令集,然后对当前重写的新URI,重新进行匹配 |
| break | 停止处理后续rewrite指令集,并不在重新查找 |
| redirect | 返回302临时重定向, 地址栏会显示跳转后的地址 |
| permanent | 返回301永久重定向, 地址栏会显示跳转后的地址。该单词的英文含义就是永久的 |
语法解释:
- rewrite可以出现在server、location、if语句中。
- 如果一个URI匹配指定的正则表达式regex,URI就按照
replacement重写,可以同时配置多个rewrite。 - rewrite按配置文件中出现的顺序执行。flags标志可以停止/继续处理。
- 如果
replacement以http://、https://开始,将不再继续处理,这个重定向将返回给客户端。
5.3 正则表达式
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| . | 匹配除”\n”,即换行符之外的任何单个字符 |
| ? | 重复0次或1次 |
| + | 重复1次或更多次 |
| * | 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。要匹配 * 字符,请使用 \ * |
| \d | 匹配数字 |
| ^ | 匹配字符串的开始 |
| $ | 匹配字符串的结尾 |
| {n} | 重复n次 |
| {n,} | 重复n此或更多次 |
| [c] | 匹配单个字符c |
| [a-z] | 匹配a-z⼩写字⺟的任意⼀个 |
正则表达式中特殊字符
- 转义字符:例如
rewrite index\.php$ /pages/maintain.html break;这里在正则中想要匹配".",需要使用"\ ."进行转义。 - 使用匹配括号中的内容:原始为 http://www.baidu.com/abc/def/index.html,想要匹配得到路径
abc和def,可以这样写rewrite ^/(.*)/(.*)/(.*)$ /chrome/$1/$2 break;
5.4 flag案例演示
5.4.1 break和last
下面的案例演示break和last之间的区别
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location ~ ^/break {
charset utf-8,gbk;
#这里匹配将路径重写到test下。
#如果url为http://localhost/break/a.html => 会去寻找 /root路径/test/a.html 文件,如果找不到,就会报404
rewrite ^/break/(.*)$ /test/$1 break;
}
location /last {
rewrite ^/last$ /test last;
}
location /test {
default_type application/json;
return 200 'It is Ok';
}
}
测试 break
访问http://localhost/break/a.html 结果为404
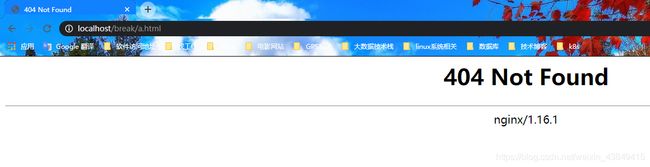
查看nginx的错误日志
2020/10/29 19:31:06 [error] 19244#16044: *25 CreateFile() "E:\nginx-1.16.1/html/test/a.html" failed (2: The system cannot find the file specified), client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET /break/a.html HTTP/1.1", host: "localhost"
会去寻找/root路径下/test/a.html文件,发现并没有去访问/test的location
在指定路径下创建a.html,重新进行访问

last 与 break 对⽐总结:
last与break都停止处理后续rewrite指令集,最大的不同是,last会重新发起一个新请求,并重新匹配location。
5.4.2 redirect和permanent
redirect 与 permanent案例演示
配置文件
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /baidu {
rewrite ^/baidu$ https://www.baidu.com redirect;
rewrite ^/baidu$ https://www.baidu.com permanent;
}
}
测试redirect,现将permanent那一行的配置注释掉

发现返回的状态码为302,且跳转到了百度。
这时候停止nginx服务,发现已经无法访问了。
测试permanent,将redirect那一行注释掉,先检测语法nginx -t,然后重新启动nginx -s reload
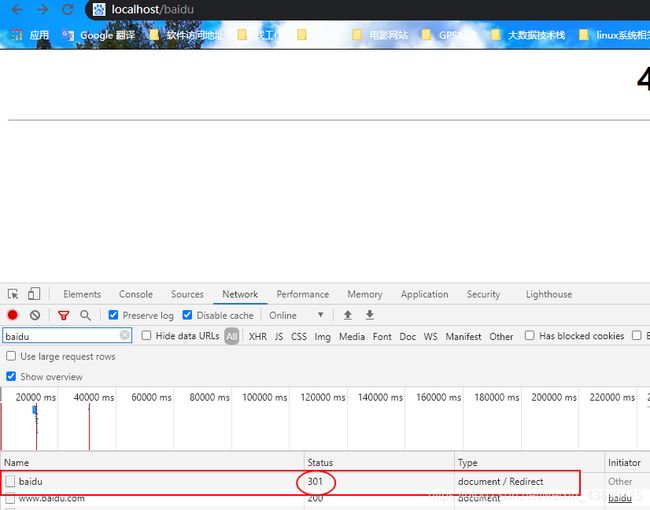
返回的状态码为301,且成功跳转到了百度
这时候停止nginx服务器nginx -s stop,重新访问nginx
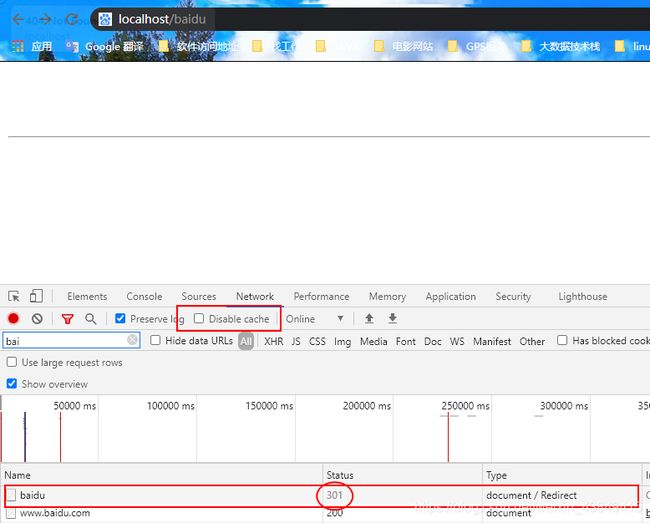
发现仍然可以访问nginx,需要特别注意的是不能禁用缓存。
5.5 需求和实现
下面我们使用rewrite指令来完成几个常见的业务需求
- 基于域名跳转
- 基于客户端IP访问跳转
- 基于旧、新域名跳转并加目录
- http强制跳转到https
5.5.1 需求1:基于域名跳转
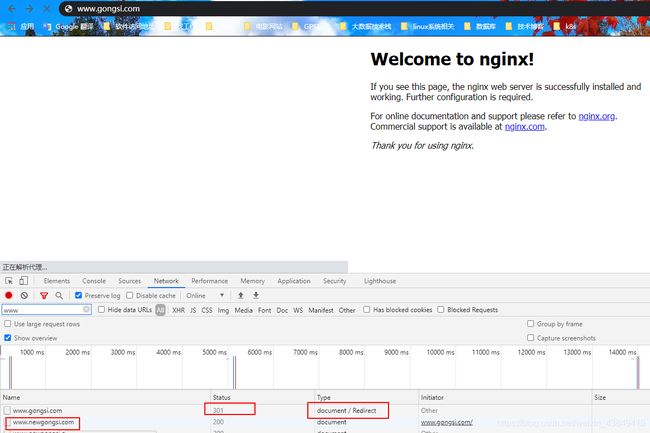
需求:公司旧域名,www.gongsi.com,因业务需求有变更,需要使用新域名www.newgongsi.com代替,不能废除旧域名,从旧域名跳转到新域名,且保持其参数不变
这里需要提前在hosts文件中进行相关域名的配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.gongsi.com;
#这里实现永久跳转,且使用的内置变量request_uri会将所有url路径以及参数都传递过去
rewrite ^ http://www/newgongsi.com$request_uri permanent;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.newgongsi.com;
}
5.5.2 需求2:基于域名跳转并且加目录
需求:将域名http://bbs.gongsi.com下面的发帖全部都跳转到http://www.gongsi.com/bbs,且域名跳转后保持参数不变
server {
listen 80;
server_name bbs.gongsi.com;
rewrite ^ http://www.gongsi.com/bbs$request_uri? permanent;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.gongsi.com;
}
打开浏览器访问bbs.gongsi.com/index.html
需要在root路径下,创建bbs文件夹和index.html文件
5.5.3 需求3:基于客户端IP访问跳转
需求描述:今天公司业务版本上线,所有IP访问任何内容都显示一个固定维护页面,只有公司IP访问正常
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.gongsi.com;
#定义一个变量,默认跳转到错误页面
set $rewrite true;
#如果是公司内网ip进行访问
if ($remote_addr = '127.0.0.1') {
set $rewrite false;
}
#如果不是公司内网ip,跳转到错误页面
if ($rewrite = true) {
rewrite (.*) /error.html last;
}
}
可以使用虚拟机中的curl进行访问,发现被定位到error.html页面
5.5.4 需求4:http强制跳转到https
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#返回301,永久跳转到https
rewrite ^ https://localhost$request_uri permanent;
}
server {
listen 443;
server_name localhost ssl;
#ca证书地址
ssl_certificate C:/Users/DELL/test.crt;
#ca证书的key的地址
ssl_certificate_key C:/Users/DELL/test.keystore;
}
访问测试,先访问http,看能否跳转到https
5.6 Rewrite匹配优先级
- 执⾏server块的rewrite指令
- 执⾏location匹配
- 执⾏选定的location中的rewrite
6. nginx日志配置和切割
nginx官方文档日志配置
日志对于统计排错来说非常有利的,同时对于统计UV、PV等也是非常有用的。本文总结了nginx日志相关的配置如access_log、error_log、log_format、open_log_file_cache、rewrite_log等。
nginx有一个非常灵活的日志记录模式。每个级别的配置可以有各自独立的访问日志。日志格式通过log_format命令来定义。
6.1 日志配置
6.1.1 access.log配置
Syntax: access_log path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] [flush=time] [if=condition]];
#关闭日志输出
access_log off;
Default: access_log logs/access.log combined;
Context: http, server, location, if in location, limit_except
配置解释:
- path 指定日志的存放位置。
- format 指定日志的格式。默认使用预定义的combined。
- buffer 用来指定日志写入时的缓存大小。默认是64k。
- gzip 日志写入前先进行压缩。压缩率可以指定,从1到9数值越大压缩比越高,同时压缩的速度也越慢。默认是1。
- flush 设置缓存的有效时间。如果超过flush指定的时间,缓存中的内容将被清空。
- if 条件判断。如果指定的条件计算为0或空字符串,那么该请求不会写入日志。
配置示例
map $status $loggable {
default 1;
~^[23] 0;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
access_log /var/log/nignx/access.log combined buffer=128k gzip=1l if=$loggable;
}
上面的配置日志路径为/var/log/nginx/access.log,日志格式为默认的combined,启用缓存,开启gzip压缩,使用if判断。
当返回的状态码不是2XX或者是3XX时进行日志记录。
6.1.2 error_log配置
Syntax: error_log file [level];
Default:
error_log logs/error.log error;
Context: main, http, mail, stream, server, location
配置解释
配置错误日志的路径和级别,可以配置在main、http、stream、server、location配置块中
日志级别:debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit、alert、emerg。
6.1.3 log_format日志格式配置
#Nginx默认日志格式配置
Syntax: log_format name [escape=default|json|none] string …;
Default: log_format combined “…”;
Context: http
nginx中默认的日志格式
log_format combined ‘$remote_addr - r e m o t e u s e r [ remote_user [ remoteuser[time_local]’
‘"$request" $status KaTeX parse error: Double superscript at position 42: … '̲"http_referer" “$http_user_agent”’;
日志格式中常用变量
| 变量名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| $remote_addr | 表示客户端地址 |
| $remote_user | http客户端请求nginx认证⽤户名 |
| $time_local | nginx的时间 |
| $request | request请求⾏,GET等⽅法、http协议版本 |
| $status | respoence返回状态码 |
| $body_bytes_sent | 从服务端响应给客户端body信息⼤⼩ |
| $http_referer | http上⼀级⻚⾯, 防盗链、⽤户⾏为分析 |
| $http_user_agent | http头部信息、客户端访问设备 |
| $http_x_forwarded_for | http请求携带的http信息 |
6.1.4 open_log_file_cache配置
Syntax: open_log_file_cache max=N [inactive=time] [min_uses=N] [valid=time];
open_log_file_cache off;
Default:
open_log_file_cache off;
Context: http, server, location
定义一个缓存,该缓存存储名称中包含变量的常用日志的文件描述符。
该指令具有以下参数:
- max 设置缓存中描述符的最大数量; 如果缓存已满,则关闭最近最少使用(LRU)描述符。
- inactive 设置在此期间如果没有访问权限则关闭缓存的描述符的时间; 默认情况下为10秒。
- min_uses 设置非活动参数定义的时间内文件使用的最小数量,以使描述符在缓存中保持打开状态; 默认值为1。
- valid 设置时间,在该时间之后应检查文件是否仍然具有相同名称; 默认情况下为60秒。
配置示例:
open_log_file_cache max=1000 inactive=20s valid=1m min_uses=2;
6.2 日志切割
6.2.1 使用set指令
配置示例
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#获取对应的年-月-日 时:分:秒
if ($time_iso8601 ~ "^(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})T(\d{2}):(\d{2}):(\d{2})") {
set $year $1;
set $month $2;
set $day $3;
set $hour $4;
set $minutes $5;
set $seconds $6;
}
#这里需要注意的是如果前面的文件夹不存在,nginx不会去创建对应的文件夹,而是直接报错
#运行nginx进程的用户需要有写入文件和进入文件夹的权限
access_log logs/$host/access-$year-$month-$day.log;
}
localhost文件夹需要提前创建,nginx不会去创建文件夹,而是直接报错
2020/11/04 16:12:53 [crit] 18868#13180: *4 CreateFile() “E:\nginx-1.16.1/logs/localhost/access-2020-11-04.log” failed (3: The system cannot find the path specified) while logging request, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: “GET / HTTP/1.1”, host: “localhost”
6.2.2 使用logrotate工具切割nginx日志
logrotate是一个linux系统日志的管理工具。可以对单个日志文件或者某个目录下的文件按时间/大小进行切割,压缩操作
具体的使用和配置可以参照linux环境下使用logrotate工具实现nginx日志切割
7. nginx状态监控和nginx站点下载
7.1 nginx状态监控
--with-http_stub_status_module 记录 nginx 客户端基本访问状态信息
Syntax: stub_status;
Default: —
Context: server, location
具体配置如下:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /status {
#这个配置打开就可以访问
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
}
nginx_status概述
//Nginx当前活跃连接数
Active connections:2
server accepts handled requests
16 16 19
server表示Nginx处理接收握⼿总次数。
accepts表示Nginx处理接收总连接数。
请求丢失数=(握⼿数-连接数)可以看出,本次状态显示没有丢失请求。
handled requests,表示总共处理了19次请求。
Reading Nginx读取数据
Writing Nginx写的情况
Waiting Nginx开启keep-alive⻓连接情况下, 既没有读也没有写, 建⽴连接情况
7.2 nginx实现站点下载
nginx官方文档autoindex指令
我们经常可以看见一些镜像网站实现文件下载,哪么这是如何实现的呢?用nginx实现站点下载的功能非常简单,一起来学习一下。
nginx默认是不允许列出整个⽬录浏览下载。
Syntax: autoindex on | off;
Default:
autoindex off;
Context: http, server, location
//autoindex常⽤参数
autoindex_exact_size off;
默认为on, 显示出⽂件的确切⼤⼩,单位是bytes。
修改为off,显示出⽂件的⼤概⼤⼩,单位是kB或者MB或者GB。
autoindex_localtime on;
默认为off,显示的⽂件时间为GMT时间。
修改为on, 显示的⽂件时间为⽂件的服务器时间。
charset utf-8,gbk;默认中⽂⽬录乱码,添加上解决乱码。
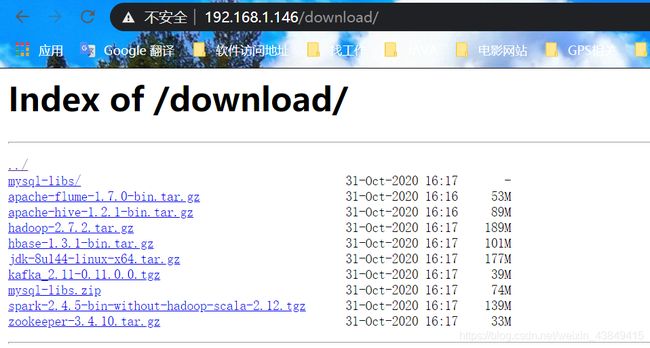
这里创建/opt/software文件夹mkdir /opt/software,且在/opt/software路径下上传一些压缩包
[root@localhost conf.d]# ll /opt/software/
总用量 915708
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 55711670 10月 31 16:16 apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 92834839 10月 31 16:16 apache-hive-1.2.1-bin.tar.gz
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 197657687 10月 31 16:17 hadoop-2.7.2.tar.gz
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 105718722 10月 31 16:17 hbase-1.3.1-bin.tar.gz
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 185515842 10月 31 16:17 jdk-8u144-linux-x64.tar.gz
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 41414555 10月 31 16:17 kafka_2.11-0.11.0.0.tgz
drwxrwxr-x. 3 root root 171 10月 31 16:17 mysql-libs
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 77807942 10月 31 16:17 mysql-libs.zip
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 145961599 10月 31 16:17 spark-2.4.5-bin-without-hadoop-scala-2.12.tgz
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 35042811 10月 31 16:17 zookeeper-3.4.10.tar.gz
配置站点下载功能
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#开启⽬录浏览
location /download {
#需要注意的是,这里使用alisa,而非root
alias /opt/software;
autoindex on;
autoindex_localtime on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}
}
7.3 root和alias的区别
nginx官方文档-alias
这里需要特别注意的是root和alias的区别。
root
语法:root path
默认值:root html
配置段:http、server、location、if
alias
语法:alias path
配置段:location
alias也支持$i的方式进行取值
location ~ ^/users/(.*\.(gif|jpeg|png))$ {
alias /data/w3/images/$1;
}
root的配置为root /opt/software; 访问/download,nginx会去/opt/software/dowload路径下寻找文件
alias的配置为alias /opt/software; 访问/download,nginx会去/opt/sofware路径下寻找文件
也就说root的配置会带上uri路径,而alias则不会。
最佳实践:在根“/”location下配置root,在其他子location下配置alias。
8. nginx静态资源服务
8.1 静态资源类型
nginx作为静态资源 Web 服务器部署配置,传输⾮常的⾼效,常常⽤于静态资源处理、请求、动静分离等

⾮服务器动态运⾏⽣成的⽂件属于静态资源。例如html、js、image、MP4等
| 类型 | 种类 |
|---|---|
| 浏览器端渲染 | HTML、CSS、JS |
| 图⽚ | JPEG、GIF、PNG |
| 视频 | FLV、Mp4 |
| ⽂件 | TXT、任意下载⽂件 |
8.2 静态资源配置语句
- ⽂件读取⾼效 sendfile
Syntax: sendfile on | off;
Default: sendfile off;
Context: http, server, location, if in location
- 提⾼⽹络传输效率nopush
Syntax: tcp_nopush on | off;
Default: tcp_nopush off;
Context: http, server, location
作⽤: sendfile开启情况下, 提⾼⽹络包的传输效率
- 与tcp_nopush之对应的配置tcp_nodelay
Syntax: tcp_nodelay on | off;
Default: tcp_nodelay on;
Context: http, server, location
作⽤: 在keepalive连接下,提⾼⽹络的传输’实时性’
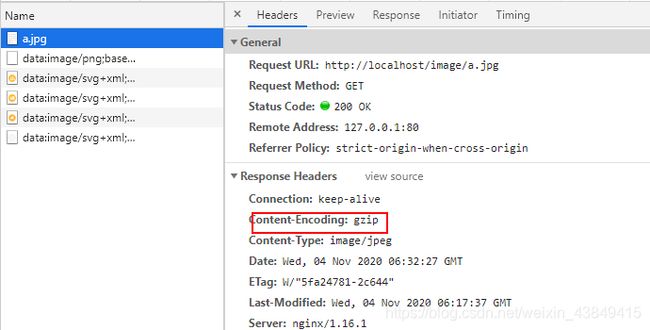
8.3 静态资源⽂件压缩
nginx官方文档gzip压缩
一般而言静态资源较大,经过压缩之后,可以节约带宽。压缩本身是需要消耗服务器的CPU资源的,这里需要做一个权衡。

- gzip 压缩配置语法
Syntax: gzip on | off;
Default: gzip off;
Context: http, server, location, if in location
作⽤: 是否启用gzip压缩
- gzip 压缩⽐率配置语法
Syntax: gzip_comp_level level;
Default: gzip_comp_level 1;
Context: http, server, location
作⽤: 压缩本身⽐较耗费服务端性能,压缩比例不能设置得太高
- gzip 压缩协议版本
Syntax: gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1;
Default: gzip_http_version 1.1;
Context: http, server, location
作⽤: 压缩使⽤在http哪个协议, 主流版本1.1,使用默认即可
- 设置启用gzip压缩最小的内容大小
Syntax: gzip_min_length length;
Default: gzip_min_length 20;
Context: http, server, location
作用: 通过“Content-Length”响应头中的数值大小,决定是否压缩
- 配置哪些数据类型进行gzip压缩
Syntax: gzip_types mime-type …;
Default:
gzip_types text/html;
Context: http, server, location
作用: 除了“text/html”之外,还对指定的MIME类型启用gzipping响应。 特殊值“*”与任何MIME类型(0.8.29)匹配。始终会压缩“text/html”类型的响应。
案例演示:图⽚压缩
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
sendfile on;
location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ {
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_min_length 100;
gzip_types text/plain application/json application/x-javascript application/css application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/gif image/png;
}
}
8.4 静态资源浏览器缓存
HTTP协议定义的缓存机制(如:Expires;Cache-control等)
-
浏览器⽆缓存
浏览器请求->⽆缓存->请求WEB服务器->请求响应->呈现 -
浏览器有缓存
浏览器请求->有缓存->校验过期->是否有更新->呈现
校验是否过期 Expires HTTP1.0, Cache-Control(max-age) HTTP1.1
协议中Etag头信息校验 Etag ()
Last-Modified头信息校验 Last-Modified (具体时间)
缓存配置语法 expires
Syntax: expires [modified] time;
expires epoch | max | off;
Default: expires off;
Context: http, server, location, if in location
作⽤: 添加Cache-Control Expires头
配置示例
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#对于js、css、html等缓存时间不要太长
location ~ .*\.(js|css|html)$ {
expires 1h;
}
#对于图片等缓存的时间可以长一点
location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ {
expires 7d;
}
}
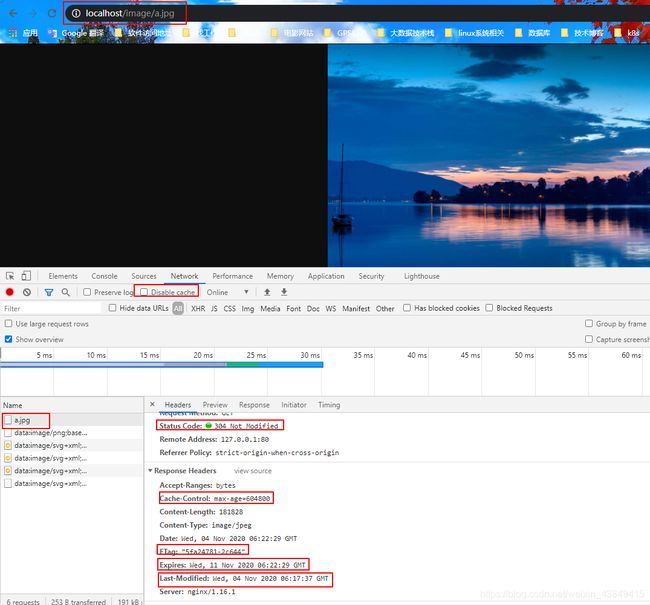
这时候点击刷新按钮,在图片过期时间内,浏览器不会再去访问服务器了
有时候在开发代码没有正式上线时,希望静态⽂件不被缓存,添加对应不要缓存的响应头信息即可
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
//取消js css html等静态⽂件缓存
location ~ .*\.(css|js|swf|json|mp4|htm|html)$ {
add_header Cache-Control no-store;
add_header Pragma no-cache;
}
}
8.5 静态资源防盗链
nginx官方文档防盗链和什么是防盗链
盗链指的是在自己的界面展示不在自己服务器上的内容,通过技术手段获取他人服务器的资源地址,绕过别人资源展示页面,在自己页面向用户提供此内容,从而减轻自己服务器的负担,因为真实的空间和流量来源于别人的服务器。
防盗链的基本思路:基于请求头中的Refer的值进行判断。
基于http_refer配置防盗链模块
Syntax: valid_referers none | blocked | server_names | string …;
Default: -
Context: server, location
配置解释:
指定“Referer”请求头字段值,该值将导致将嵌入的$invalid_Referer变量设置为空字符串。否则,变量将设置为“1”。搜索匹配项不区分大小写。
- none:允许缺失的头部访问。
- blocked:允许referer没有对应值的请求。
- server_names:若referer站点域名与server_name中本机配的域名一样允许访问。
- arbitrary string:定义服务器名称和可选的URI前缀。服务器名的开头或结尾可以有一个“*”。检查时,忽略“Referer”字段中的服务器端口。
- regular expression:第一个符号应该是“~”。需要注意的是,表达式将与“http://”或“https://”后面的文本匹配。
配置示例:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.你公司的域名.com;
valid_referers *.你公司的域名.com ~.*\.你公司的域名\.com;
location ~* .*\.(jpg|git|png)$ {
#if指令中,变量为0或者是空字符串表示false,如果没有匹配成功,$invalid_referer的值会被设置成1,也会返回403,表示未授权
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}
root /usr/share/nginx;
}
}
9. nginx访问限制和nginx访问控制
9.1 nginx访问限制
nginx官方文档连接限制和nginx官方文档请求限制
nginx的访问限制分为连接限制和请求限制,对应的模块分别为ngx_http_limit_conn_module和ngx_http_limit_req_module
limit_conn 配置语法
Syntax: limit_conn zone number;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
解释说明:
设置共享内存区域和给定键值的最大允许连接数。当超过此限制时,服务器将返回错误信息。
配置示例
http {
#http连接配置,同一时刻只允许一个客户端ip连接
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=conn_zone:10m;
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.1.120;
location / {
#同一时刻只允许一个客户单ip连接
limit_conn conn_zone 1;
}
}
}
设置共享内存区域的参数,该参数将保留各种键的状态。特别是,状态包括当前的连接数。该key可以包含文本,变量,他们的组合。具有空键值的请求不予考虑。
limit_conn_zone 配置语法
Syntax: limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size;
Default: —
Context: http
配置示例
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone = addr:10m;
在此,客户端IP地址用作密钥,同时指定共享内存区域的名称为addr,大小为10m。注意,代替$remote_addr,该 $binary_remote_addr变量在这里使用。如果区域存储已用尽,服务器将把错误返回 给所有其他请求。
访问测试
9.2 nginx访问控制
9.2.1 基于ip访问控制
nginx官方文档基于ip访问控制
基于ip访问控制由ngx_http_access_module提供
allow 配置语法
Syntax: allow address | CIDR | unix: | all;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
deny 配置语法
Syntax: deny address | CIDR | unix: | all;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
例如对于查看nginx的状态,这是nginx非常核心的信息,限制只有nginx所在主机才能访问
配置示例
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /status {
#这个配置打开就可以访问
allow 127.0.0.1;
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
}
使用虚拟机的curl命令去访问,发现返回403,没有权限
如果同时配置了allow、deny,那么nginx会如何处理呢?allow语句和deny指令只要有一条匹配了,则不再执行其他的allow和deny指令。 如果没有匹配才继续往下执行其他的allow或者deny指令继续进行匹配。
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#测试allow和deny同时配置的情况
location /testAll {
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny 127.0.0.1;
add_header 'context-type' 'application/json';
return 200 'testAll';
}
}
这里同时配置了allow和deny,匹配到了allow 127.0.0.1;命令那么就不再继续执行后面的配置,也就说允许ip为127.0.0.1的客户端进行访问。
基于ip的访问控制存在一定的局限性。如果客户端使用的是代理ip,使用remote_addr无法获取客户端的真实ip,那么基于ip的访问控制就是无意义的。
9.2.2 基于用户登录认证
配置语法
这里配置的是输入账号和密码的提示信息
Syntax: auth_basic string | off;
Default: auth_basic off;
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
这里配置的是账号和密码的文件路径
Syntax: auth_basic_user_file file;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
配置示例
我们可以对前面的查看nginx服务器状态,添加一个访问认证
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
status /status {
stub_status on;
auth_basic '请输入账号和密码';
auth_basic_user_file path;
}
}
基于账号和密码的认证存在很大的局限性:
- 用户信息管理依赖于文件方式,不够直观的方便。
- 用户管理文件过多,无法联动。
- 操作管理机械,效率低下。
解决办法:
- nginx结合lua实现高效认证。
- nginx结合ldap利用nginx-auth-ldap模块。
10. http层反向代理
nginx官方文档http反向代理。nginx的http反向代理功能由ngx_http_proxy_module提供。
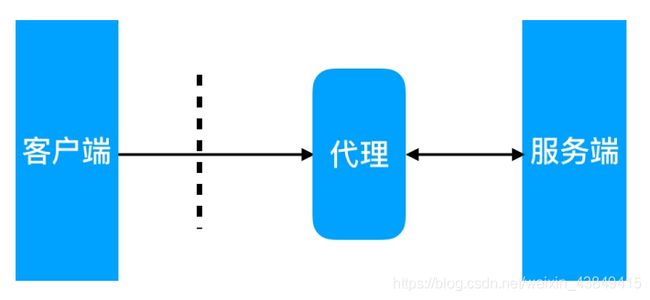
10.1 代理概述
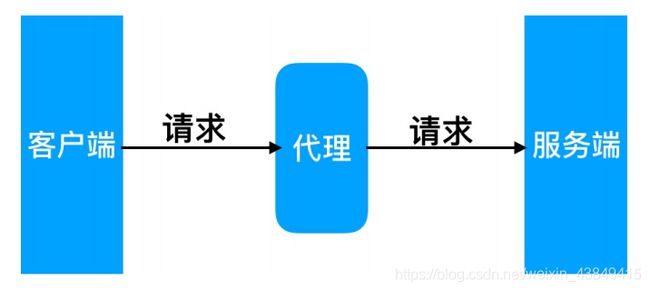
在互联⽹请求⾥⾯, 客户端⽆法直接向服务端发起请求, 那么就需要⽤到代理服务, 来实现客户端和服务通信。
nginx可以代理多种协议http、IMAP\POP、https等
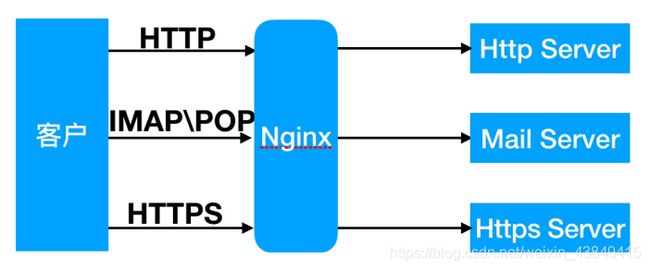
代理有正向代理和反向代理,区别在于代理的对象不⼀样。正向代理代理的对象是客户端,反向代理代理的对象是服务端
正向代理,代理客户端
正向代理(内部上⽹) 客户端<–>代理->服务端
反向代理,代理服务器
反向代理 客户端->代理<–>服务端
这里主要讲解http七层的反向代理。
10.2 http反向代理配置
配置示例
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '8080服务器返回OK信息';
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
}
- proxy_pass配置示例
Syntax: proxy_pass URL;
Default: —
Context: location, if in location, limit_except
设置代理服务器的协议和地址以及位置应映射到的可选URI。作为协议,可以指定“http”或“https”。该地址可以指定为域名或IP地址,以及可选端口。
配置示例
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000/uri/;
nginx反向代理配置时location与proxy_pass 加与不加 “/” 区别
当在proxy_pass中设置了"/"
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /name {
proxy_pass http://localhost:81/;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '81端口服务器,根路径';
}
}
访问http://localhost/name/ => nginx反向代理访问的路径 http://localhost:81/
也就是说代理的后端服务器不会带上/name
当没有在proxy_pass设置"/"
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /name {
proxy_pass http://localhost:81;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name localhost;
location /name {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '81服务器 /name路径';
}
}
访问http://localhost/name/ => nginx反向代理访问的路径 http://localhost:81/name
也就是说代理的后端服务器会带上/name
另外一种常见的写法就是使用rewrite指令进行路径重写
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /name/ {
#获取name后面的除/以外的字符串,并且使用$1获取内容。break标记,不再执行后面的rewrite指令,进行访问路径重写
rewrite /name/([^/]+) /users?name=$1 break;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
}
location /users {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
#使用$arg_参数名的方式获取url中的对应参数名的参数值
return 200 $arg_name;
}
}
- 设置代理请求的头信息proxy_set_header
Syntax: proxy_set_header field value;
Default: proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header Connection close;
Context: http, server, location
常见的设置反向代理的头信息
- proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
- proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
- proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
- 代理到后端TCP的超时时间
Syntax: proxy_connect_timeout time;
Default: proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
这里可以将proxy反向代理的常用参数抽取出来,然后使用include进行引入即可。这里需要注意proxy_params文件的路径。
proxy_params常见的配置,可以在反向代理中的配置include参数,引入proxy_params参数文件。
proxy_redirect default;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_buffer_size 32k;
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffers 4 128k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 256k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 256k;
proxy_params和nginx.conf位于同级目录下。
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:81$request_uri;
include proxy_params;
}
}
10.3 反向代理案例演示
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
include proxy_params;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '8080端口的服务器';
}
}
这里访问nginx的80端口,然后nginx反向代理去访问nginx的8080端口。
11. 四层反向代理(TCP代理)
11.1 TCP反向代理概述
nginx官方文档四层反向代理、nginx官方文档nginx如何代理TCP/UDP、ngx_stream_proxy_module模块
nginx除了可以进行7层的http反向代理,还可以4层的TCP反向代理,也就是基于端口的数据包转发。TCP反向代理由ngx_stream_core_module 模块提供。
这里列举一个实际的业务场景。例如GPS设备定时或者是定距上传GPS轨迹数据(部标jt808协议的16进制数据包)到服务器,在GPS设备中配置stream中server的ip和端口,经过nginx的负载均衡之后,转发到后台对应的业务服务器。这里GPS设备上传的一般都是16进制的TCP数据包,使用nginx进行TCP数据包的转发,同时nginx作为负载均衡器和进行健康检查。后台业务服务器如果使用java语言编写可以使用netty解析jt808数据包。
nginx四层代理仅能配置在main代码块内
nginx如果要绑定TCP端口,需要关闭centos的selinux
#如下图,将SELINUX的值设置为disabled。下次开机SELinux就不会启动了
[root@local ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
#重启虚拟机
[root@localhost ~]# reboot
提前关闭和禁止开机自启防火墙
11.2 配置语句
配置示例
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
stream {
upstream ssh_proxy {
server 192.168.1.121:22;
}
upstream mysql_proxy {
server 192.168.1.121:3306;
}
server {
listen 6666;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
proxy_timeout 300s;
proxy_pass ssh_proxy;
}
server {
listen 5555;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
proxy_timeout 300s;
proxy_pass mysql_proxy;
}
}
配置解释
在nginx中配置TCP/UDP的四层反向代理需要定义在在主配置文件中,因为TCP/UDP反向代理属于第四层的代理,不属于HTTP的7层代理,因此不能定义在http代码块内。
使用stream代码块包裹起来,在stream代码块内定义server、upstream。也就是定义nginx监听的端口和反向代理的配置,当然了在upstream中也可以进行负载均衡的配置。
上面的配置定义了nginx监听两个端口6666和5555,分别反向代理到192.168.1.121:22和192.168.1.121:3306
stream配置解释
Syntax: stream { … }
Default: —
Context: main
server配置解释
Syntax: server { … }
Default: —
Context: stream
listen配置解释
Syntax: listen address:port [ssl] [udp] [proxy_protocol] [backlog=number] [rcvbuf=size] [sndbuf=size] [bind] [ipv6only=on|off] [reuseport] [so_keepalive=on|off|[keepidle]:[keepintvl]:[keepcnt]];
Default: —
Context: server
主要配置监听的端口
在代理配置中主要配置proxy_connect_timeout、proxy_timeout、proxy_pass
proxy_connect_timeout配置解释
Syntax: proxy_connect_timeout time;
Default:
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
Context: stream, server
proxy_timeout配置解释
Syntax: proxy_timeout timeout;
Default:
proxy_timeout 10m;
Context: stream, server
设置客户端或代理服务器连接上两个连续读或写操作之间的超时。如果在这段时间内没有数据传输,则连接关闭。
关于nginx中各种超时时间的配置请参照nginx.conf配置文件中timeout超时时间设置
proxy_pass配置解释
Syntax: proxy_pass address;
Default: —
Context: server
proxy_pass可以定义为域名或者是ip和端口,当然也可以定义upstream服务器组进行负载均衡。
在stream中定义的upstream服务器组,upstream功能由ngx_stream_upstream_module模块提供
配置示例
upstream backend {
hash $remote_addr consistent;
server backend1.example.com:12345 weight=5;
server backend2.example.com:12345;
server unix:/tmp/backend3;
server backup1.example.com:12345 backup;
server backup2.example.com:12345 backup;
}
server {
listen 12346;
proxy_pass backend;
}
这里就不详细解释了,可以参照nginx官方文档ngx_stream_upstream_module模块
11.3 TCP反向代理案例演示
检测nginx配置语法和重启nginx
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
查看监听的端口
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -nltp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1379/master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1160/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1160/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5555 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1160/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1156/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1379/master
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1156/sshd
发现5555和6666端口都已经被nginx的master进程监听。
访问逻辑示意图
一般而言,数据库都是独立部署,为了安全起见,没有独立公网ip。现在我想要ssh方式连接服务器和访问数据库如何处理呢?
假设192.168.1.121这个机器没有公网ip,上面部署了核心的数据库服务,而192.168.1.120这台机器有公网ip。我们想要ssh连接192.168.1.121和访问192.168.1.121上的mysql怎么办呢?可以通过nginx的TCP反向代理进行配置,我们只要访问192.168.1.120这个主机的6666和5555端口就可以访问了对应的ssh和mysql服务了。
ssh登录演示
[root@localhost ~]# ssh 192.168.1.120 -p 6666
[email protected]'s password:
Last login: Mon Nov 9 22:08:44 2020 from 192.168.1.1
#显示ip地址
[root@localhost ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:3e:0a:fb brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.121/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::8b70:7a8c:4371:9f7f/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 02:42:1e:04:dd:c0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#退出登录之后重新查看服务器的ip地址
[root@localhost ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.1.120 closed.
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:3c:e4:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.120/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::f300:317f:ec3a:57b8/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 02:42:8a:e0:00:54 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
可以发现成功登录到了192.168.1.121这台服务器上,退出登录之后,重新查看ip,ip地址为192.168.1.120。
mysql连接演示
在192.168.1.121这台服务器上安装mysql服务器,这里使用docker安装mysql,需要提前安装docker
[root@localhost ~]# docker pull mysql
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -p 3306:3306 --name mymysq -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mysql
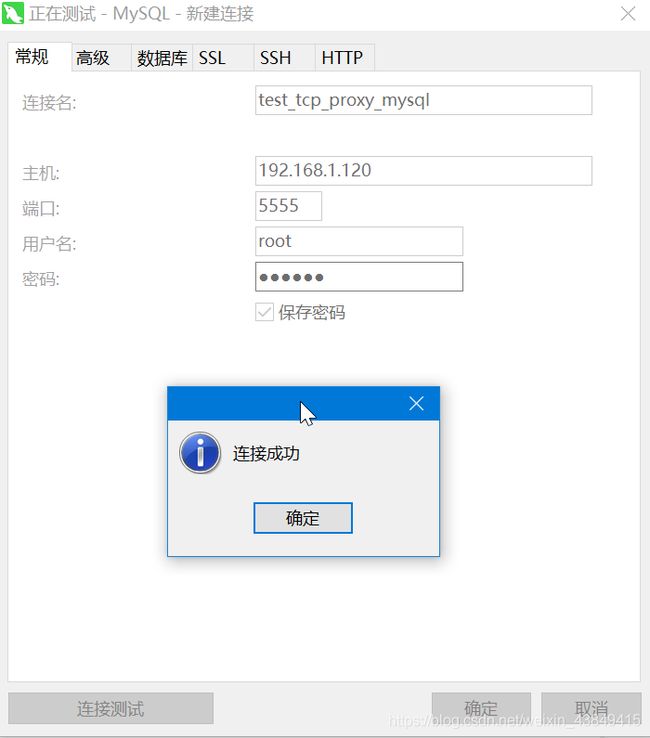
使用Navicat去连接192.168.1.120的5555端口
12. http负载均衡和健康检查
12.1 简介
跨多个应用程序实例的负载平衡是一种用于优化资源利用率,最大化吞吐量,减少延迟和确保容错配置的常用技术。
可以将nginx用作非常有效的HTTP负载平衡器,以将流量分配到多个应用程序服务器,并使用nginx改善Web应用程序的性能,可伸缩性和可靠性。
负载均衡一般和反向代理配合使用。后端java开发人员使用最多的也是这两个功能,反向代理和负载均衡。
多个后台业务服务器同时对外提供服务,需要对后台服务器进行健康检查。
nginx负载均衡模块主要由ngx_http_upstream_module模块。
12.2 配置语法
简单案例演示和配置示例
upstream backend {
server localhost:8080;
server localhost:8081;
server localhost:8082;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
include proxy_params;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
server {
listen 8081;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
server {
listen 8082;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
这里访问http://localhost,返回访问服务器的端口是8080,默认的负载均衡策略是轮询。即8080、8081、8082、8080…。
- upstream语法
Syntax: upstream name { … }
Default: —
Context: http
upstream定义http代码块内,server代码块外,定义为一个服务器组,在upstream代码块中定义server,然后在proxy_pass中进行引用服务器组。
配置示例
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server 127.0.0.1:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
server unix:/tmp/backend3;
server backup1.example.com backup;
}
默认情况下,使用加权循环轮询的方式在服务器之间分发请求。在上面的示例中,每个7个请求将按如下方式分配:5个请求发送到后端1。example.com网站向第二台和第三台服务器各发送一个请求。如果在与服务器通信期间发生错误,请求将被传递到下一个服务器,依此类推,直到所有正常运行的服务器都将被尝试。如果无法从任何服务器获得成功响应,则客户端将收到与最后一个服务器通信的结果。
- server配置
Syntax: server address [parameters];
Default: —
Context: upstream
server定义在upstream代码块内,可以定义多个server,多个server共同组成一个server group也就是负载均衡服务器组
配置示例
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server 127.0.0.1:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
server unix:/tmp/backend3;
server backup1.example.com backup;
}
server定义的格式为 address [parameters],也就是定义服务器地址和一些参数
parameters可以使用如下参数
- weight=number
设置服务器的权重,默认是1。 - max_conns=number
设置限制到代理服务器的最大同时活动连接数。默认为0。 - max_fails=number
设置在fail_timeout参数设置的持续时间内与服务器通信的失败尝试次数,以考虑服务器在fail_timeout参数设置的持续时间内不可用。默认情况下,不成功的尝试次数设置为1。零值禁止计算尝试次数。 - fail_timeout=time
在指定次数的尝试与服务器通信失败时,认为服务器不可用的时间;服务器不可用的时间段。默认情况下,该参数设置为10秒。 - backup
将服务器标记为备份服务器。当主服务器不可用时,备份服务器接收请求。backup参数不能与hash、ip-hash、random一起使用。 - down
将服务器标记为永久不可用。
12.2 负载均衡算法
nginx支持以下负载平衡机制(或方法):
- round-robin - 轮询访问后端服务。
- least-connected - 将下一个请求分配给活动连接最少的服务器.
- ip-hash - 哈希函数用于确定应为下一个请求选择哪个服务器(基于客户端的IP地址)。
nginx默认的负载均衡策略是轮询。
12.2.1 轮询
下面的配置是简单的实例:
http {
upstream myapp {
server localhost:8080;
server localhost:8081;
server localhost:8082;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myapp;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
server {
listen 8081;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
server {
listen 8082;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
在上面的示例中,同一应用程序的3个实例分别是3个Springboot项目,除了端口的配置不一样,其他全都是一样的。如果未特别配置负载平衡方法,则默认为轮询。所有请求都被代理到服务器组myapp,nginx应用HTTP负载平衡来分发请求。这里为分别打印出对应的端口。
12.2.2 最小连接数
另一个负载平衡原则是连接最少的。最少连接允许在某些请求需要较长时间才能完成的情况下更公平地控制应用程序实例上的负载。
使用最少连接的负载平衡,nginx将尝试不使繁忙的应用程序服务器因过多的请求而过载,而是将新的请求分配给不太繁忙的服务器。
当 least_conn指令用作服务器组配置的一部分时,将激活nginx中的最低连接负载平衡 :
upstream myapp {
least_conn;
server localhost:8080;
server localhost:8081;
server localhost:8082;
}
12.2.3 ip-hash
使用ip-hash进行负载均衡可以达到会话亲和的目的,也就是说同一个ip会一直访问同一个后台服务器。
指定服务器组应使用负载平衡方法,其中请求根据客户端IP地址在服务器之间分布。客户端IPv4地址的前三个八位字节或整个IPv6地址用作哈希键。该方法确保来自同一客户机的请求将始终传递到同一服务器,除非此服务器不可用。在后一种情况下,客户端请求将被传递到另一个服务器。最有可能的是,它也永远是同一个服务器。
如果需要临时删除其中一个服务器,则应使用down参数标记该服务器,以便保留当前对客户端IP地址的哈希处理。
配置示例
upstream backend {
ip_hash;
server backend1.example.com;
server backend2.example.com;
server backend3.example.com down;
server backend4.example.com;
}
12.3 基于max_fails和fail_timeout的健康检查
nginx社区版在upstream的server中的两个参数max_fails以及fail_timeout这两个参数可以对后端server进行健康检查。
max_fails的默认值是1,fail_timeout的默认值是10s。
nginx基于连接探测,如果发现后端异常,在单位周期为fail_timeout设置的时间,中达到max_fails次数,这个周期次数内,如果后端同一个节点不可用,那么接将把节点标记为不可用,并等待下一个周期(同样时常为fail_timeout)再一次去请求,判断是否连接是否成功。如果成功,将恢复之前的轮询方式或者是其他方式,如果不可用将在下一个周期(fail_timeout)再试一次。
在两个节点都可用的情况下,突然有一个节点挂掉,客户端请求过来后哪怕请求到了不可用的节点,此次请求也不会失败,因为nginx会把此次请求转发到另外一个可用节点,再把结果返回给客户端。
当一个节点挂掉,nginx不知道节点是否恢复的时候,会把客户端的请求同时转发到两个节点,判断节点健康情况。
配置示例
upstream backend {
server 127.0.0.1:8080 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=5;
server 127.0.0.1:8081 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=5;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
include proxy_params;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
server {
listen 8081;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UFT-8';
return 200 '访问的服务器端口是$server_port';
}
}
12.4 基于Tengine的ngx_http_upstream_check_module模块的健康检查
淘宝Tengine官方文档健康检查
nginx是高度模块化的项目,如果需要添加新模块,重新编译替换即可。
12.4.1 yum安装的nginx添加第三方模块: ngx_http_upstream_check_module
首先查看yum安装的nginx的版本
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
将nginx源码和ngx_http_upstream_check_module模块的源码都下载到/usr/local/src路径下。
进入到/usr/local/src路径。
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/src
然后去nginx官方网站下载对应的源码包,并进行解压
[root@localhost src]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# tar -zxvf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# ll
总用量 1016
drwxr-xr-x 8 1001 1001 158 4月 21 2020 nginx-1.18.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1039530 4月 21 2020 nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
然后下载ngx_http_upstream_check_module模块的源码,并进行解压
[root@localhost src]# wget https://codeload.github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_upstream_check_module/zip/master
[root@localhost src]# unzip master
[root@localhost src]# ll
drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 11月 3 2019 nginx_upstream_check_module-master
使用yum下载一些必要的软件
[root@localhost src]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ automake pcre pcre-devel zlip zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel -y
查看当前系统中nginx的编译参数
[root@localhost src]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf......
进入到nginx-1.18.0文件夹中,进行参数配置,复制之前nginx -V命令得到的编译参数
[root@localhost src]# cd nginx-1.18.0
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# ./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx ... --add-module=/usr/local/src/nginx_upstream_check_module-master
最后加上--add-module=/usr/local/src/nginx_upstream_check_module-master编译参数。
进行编译
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# make -j2
不可使用make install
编译好以后会在nginx的解压目录objs目录下生成一个nginx文件,先测试一下这个文件,输入 objs/nginx -t,然后看结果
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# objs/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
替换老nginx二进制文件
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# cp objs/nginx /usr/sbin/nginx
校验
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx......
重新启动nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# systemctl restart nginx
12.4.2 配置语法
配置示例
http {
upstream cluster1 {
# simple round-robin
server localhost:7000;
server localhost:7001;
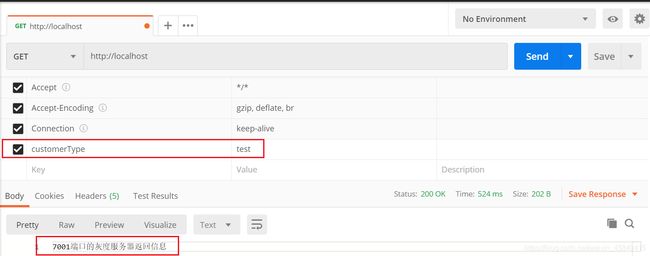
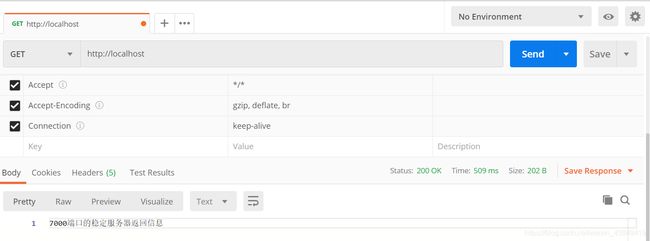
check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=1000 type=http;
check_http_send "HEAD / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n";
check_http_expect_alive http_2xx http_3xx;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://cluster1;
}
}
}
上面的两个localhost:7000和localhost:7001返回服务器端口。
- check指令
Syntax: check interval=milliseconds [fall=count] [rise=count] [timeout=milliseconds] [default_down=true|false [type=tcp|http|ssl_hello|mysql|ajp] [port=check_port]
Default: 如果没有配置参数,默认值是:interval=30000 fall=5 rise=2 timeout=1000 default_down=true type=tcp
Context: upstream
该指令可以打开后端服务器的健康检查功能。
指令后面的参数意义是:
- interval:向后端发送的健康检查包的间隔。单位是毫秒
- fall(fall_count): 如果连续失败次数达到fall_count,服务器就被认为是down。
- rise(rise_count): 如果连续成功次数达到rise_count,服务器就被认为是up。
- timeout: 后端健康请求的超时时间。
- default_down: 设定初始时服务器的状态,如果是true,就说明默认是down的,如果是false,就是up的。默认值是true,也就是一开始服务器认为是不可用,要等健康检查包达到一定成功次数以后才会被认为是健康的。
- type:健康检查包的类型,现在支持以下多种类型
- tcp:简单的tcp连接,如果连接成功,就说明后端正常。
- ssl_hello:发送一个初始的SSL hello包并接受服务器的SSL hello包。
- http:发送HTTP请求,通过后端的回复包的状态来判断后端是否存活。
- mysql: 向mysql服务器连接,通过接收服务器的greeting包来判断后端是否存活。
- ajp:向后端发送AJP协议的Cping包,通过接收Cpong包来判断后端是否存活。
- port: 指定后端服务器的检查端口。你可以指定不同于真实服务的后端服务器的端口,比如后端提供的是443端口的应用,你可以去检查80端口的状态来判断后端健康状况。默认是0,表示跟后端server提供真实服务的端口一样。该选项出现于Tengine-1.4.0。
- check_keepalive_requests指令
Syntax: check_keepalive_requests request_num
Default: 1
Context: upstream
该指令可以配置一个连接发送的请求数,其默认值为1,表示Tengine完成1次请求后即关闭连接。一般使用默认即可
- check_http_send指令
Syntax: check_http_send http_packet
Default: “GET / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n”
Context: upstream
该指令可以配置http健康检查包发送的请求内容。为了减少传输数据量,推荐采用"HEAD"方法。
当采用长连接进行健康检查时,需在该指令中添加keep-alive请求头,如:“HEAD / HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\n\r\n”。
同时,在采用"GET"方法的情况下,请求uri的size不宜过大,确保可以在1个interval内传输完成,否则会被健康检查模块视为后端服务器或网络异常。
- check_http_expect_alive指令
Syntax: check_http_expect_alive [ http_2xx | http_3xx | http_4xx | http_5xx ]
Default: http_2xx | http_3xx
Context: upstream
该指令指定HTTP回复的成功状态,默认认为2XX和3XX的状态是健康的。
12.4.3 案例演示
nginx的配置文件
http {
upstream cluster1 {
# simple round-robin
server localhost:7000;
server localhost:7001;
check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=1000 type=http;
check_http_send "HEAD / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n";
check_http_expect_alive http_2xx http_3xx;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://cluster1;
}
}
}
localhost:7000和localhost:7001两个后台服务由SpringBoot进行编写,请求"/"根路径,返回服务器端口号。
系统中需要提前安装jdk,且将JAVA_HOME添加到PATH环境变量中。这里就不演示下载jdk和添加PATH环境变量了。
localhost:7000和localhost:7001两个后台项目也可以由其他编写,只需要返回对应的端口号即可。
java项目启动命令
[root@localhost src]# nohup java -jar springboot-demo-1.0.0.jar > /dev/null 2>&1 &
[root@localhost src]# nohup java -jar springboot-demo-1.0.0.jar --server.port=7001 > /dev/null 2>&1 &
打开一个窗口,使用curl命令循环访问nginx,观察数据的返回情况
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# while true; do curl localhost; echo; sleep 1; done
7000
7000
7000
7001
7001
7000
7000
7001
7001
7000
由于默认的负载均衡策略是轮询,返回端口号的数量大致相同。
这时候打开另外一个shell窗口。使用jps -ml命令查看java进程的进程号
[root@localhost src]# jps -ml
11298 springboot-demo-1.0.0.jar --server.port=7001
9230 springboot-demo-1.0.0.jar
11326 sun.tools.jps.Jps -ml
这时候使用kill -9 pid命令,杀死端口号为7001的进程
[root@localhost src]# kill -9 11298
查看之前的shell窗口,发现只打印7000端口,且在一直访问,说明健康检测成功。
[root@localhost nginx-1.18.0]# while true; do curl localhost; echo; sleep 1; done
7000
7000
7000
7000
7000
到此健康检查的案例演示就结束了。
13 nginx配置https
nginx官方网站配置https
13.1 HTTPS基本概述
为什么需要使⽤HTTPS, 因为HTTP不安全
- 传输数据被中间⼈盗⽤, 信息泄露
- 数据内容劫持, 篡改
13.2 HTTPS常用配置
nginx关于ssl的参数详细解释
| 参数名 | 含义 | 语法 | 默认值 | 位置 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ssl | 开启或者关闭ssl | ssl on或者off; | off | http、server |
| ssl_certificate | 设置ca证书的路径 | ssl_certificate file_path; | 无 | http、server |
| ssl_certificate_key | 设置私钥的路径 | ssl_certificate_key private_key_path; | 无 | http、server |
| ssl_session_timeout | 安全会话的超时时间 | ssl_session_timeout 10m; | 5m | http、server |
| ssl_prefer_server_ciphers | 是否由服务器决定采用哪种加密算法 | ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; | off | http、server |
| ssl_ciphers | ssl加密算法 | ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; | HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5 | http、server |
| ssl_protocols | 支持的安全协议 | ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; | TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 | http、server |
13.3 配置https
检查nginx环境
生成密钥和ca证书
编写nginx配置文件
server {
listen 443;
server_name localhost;
ssl on;
index index.html index.htm;
#ssl_session_cache share:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_certificate ssl_key/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key ssl_key/server.key;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
}
生成自签名的ca证书
[root@localhost ssl]# cd /etc/nginx
[root@localhost nginx]# mkdir ssl
#创建ssl文件夹
[root@localhost nginx]# cd ssl
#生成key
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 1024
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
..................................++++++
.......++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
#输入密码
Enter pass phrase for server.key:
#再次输入密码
Verifying - Enter pass phrase for server.key:
#生成证书签署请求
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
Enter pass phrase for server.key:
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:
State or Province Name (full name) []:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
#设置域名
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:yanggu.com
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
#备份一下server.key
[root@localhost ssl]# cp server.key server.key.org
#去除server.key中的密码
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl rsa -in server.key.org -out server.key
Enter pass phrase for server.key.org:
writing RSA key
[root@localhost ssl]#
#根据server.key和server.csr生成自签名的ca证书
[root@localhost ssl]# openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt
Signature ok
subject=/C=XX/L=Default City/O=Default Company Ltd/CN=yanggu.com
Getting Private key
[root@localhost ssl]# ll
总用量 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 806 11月 9 23:35 server.crt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 627 11月 9 23:34 server.csr
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 887 11月 9 23:34 server.key
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 951 11月 9 23:34 server.key.org
访问测试
需要提前host文件中配置ip和域名
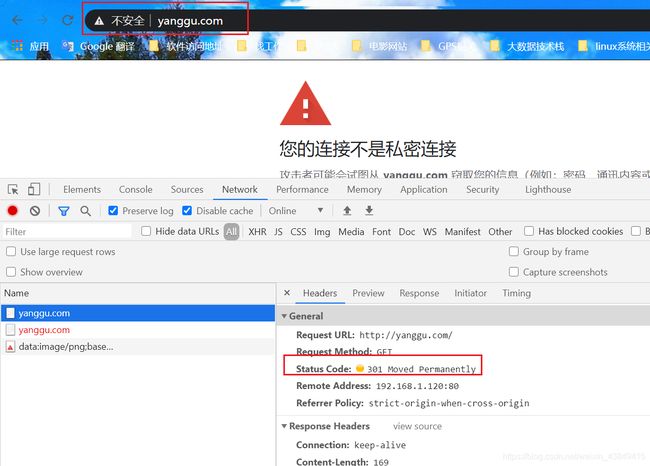
在浏览器的地址栏输入https://yanggu.com

这里显示证书不安全,因为我们的ca证书是自签名的,可以在云厂商购买认证的ca证书,也可以使用免费ca证书
13.4 http强制跳转到https
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name yanggu.com;
#ssl_session_cache share:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
if ($scheme = http) {
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
}
然后返回301,永久重定向到https://yanggu.com
14. nginx中的return指令、set指令、map指令、if指令
14.1 return指令
nginx官方文档return指令
return配置语法
Syntax: return code [text]; return code URL; return URL;
Default: —
Context: server、location、if
案例演示
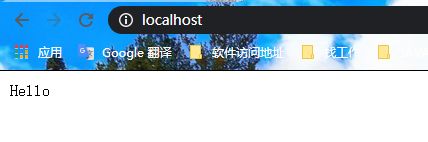
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 'Hello';
}
14.2 set指令
nginx官方文档set指令
set配置语法
Syntax: set $variable value;
Default: —
Context: server, location, if
定义变量,同时设置值。可以在server、location、if语句块中定义和使用。如果要使用值,使用$变量名即可。
在一处进行了定义,则可以在处处使用。
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
set $method $request_method;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/paln charset=UTF-8';
return 200 $method;
}
14.3 if指令
nginx官方文档if指令
if配置语法
Syntax: if (condition) { … }
Default: —
Context: server, location
语法:if (condition) {…},可以在server、location块内执行。顾名思义如果condition为真,执行花括号中的内容。
变量可以是nginx内置的变量,也可以是自定义的变量
condition可以是一下中的任意一项:
- 变量名,如果变量的值是空字符串或者0表示false
- 变量使用“=”和“!=”来跟字符串比较
- ~:与指定正则表达式模式匹配时返回“真”,判断匹配与否时区分字符大小写
- ~*:与指定正则表达式模式匹配时返回“真”,判断匹配与否时不区分字符大小写
- !~:与指定正则表达式模式不匹配时返回“真”,判断匹配与否时区分字符大小写
- !~*:与指定正则表达式模式不匹配时返回“真”,判断匹配与否时不区分字符大小写
- 检查文件是否存在使用“-f” 和 “!-f”
- 检查目录是否存在使用 “-d” 和 “!-d”
- 检查文件、目录、符号链接是否存在使用 “-e” 和 “!-e”
- 检查是否是可执行文件使用“-x” 和 “!-x”
案例演示
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
if ($http_user_agent ~* Chrome) {
return 200 '客户端类型为:谷歌浏览器';
}
if ($http_user_agent ~* Firefox) {
return 200 '客户端类型为:火狐浏览器';
}
if ($http_user_agent ~* Opera) {
return 200 '客户端类型为:欧朋浏览器';
}
if ($http_user_agent ~* IE) {
return 200 '客户端类型为:ie浏览器';
}
return 200 '未知的浏览器类型';
}
}
访问测试,使用不同类型的浏览器访问nginx服务器,返回不同的数据
14.4 map指令
nginx官方文档map指令
map指令使用ngx_http_map_module模块提供的。默认情况下,nginx有加载这个模块。
map指令的主要作用是根据nginx内置变量的值,匹配一些特定规则,去设置自定义变量,然后这个自定义变量可以在其他地方进行使用。map指令可以看成是if指令和set指令的结合,但是功能更加强大。
map指令语法
Syntax: map $var1 $var2 { … }
Default: —
Context: http
map指令的三个参数
- default : 指定源变量匹配不到任何表达式时将使用的默认值。当没有设置 default,将会用一个空的字符串作为默认的结果。
- hostnames : 允许用前缀或者后缀掩码指定域名作为源变量值。这个参数必须写在值映射列表的最前面。
- include : 包含一个或多个含有映射值的文件。
解释说明:
- map指令不能写在
server{}段,只能写在http{}段。 - map 的
$var1为源变量,通常可以是nginx的内置变量,$var2是自定义变量。 {}代码块中的内容为匹配规则,$var2的值取决于$var1在对应表达式的匹配情况。 如果一个都匹配不到则$var2就是default对应的值。 - 一个正则表达式如果以
“~”开头,表示这个正则表达式对大小写敏感。以“~*”开头,表示这个正则表达式对大小写不敏感。 - 这里需要特别注意的是和if语句中正则的区别,在if语句中正则表达式和匹配内容是分开的,而map指令是在一起的。
下面的配置示例匹配客户端访问,然后返回对应的客户端类型
map $http_user_agent $agent {
default 未知的浏览器;
~ curl curl;
~*apachebench ab;
~*Chrome "谷歌浏览器";
~*Firefox "火狐浏览器";
~*IE "IE浏览器";
~*Opera $http_user_agent;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
add_header 'content-type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
return 200 你访问你的客户端类型为:$agent;
}
注意事项:
- 不能在map块里面引用命名捕获或位置捕获变量。如
~^/qupeicom/(.*) /peiyin/$1;这样会报错nginx: [emerg] unknown variable。 - 如果源变量值包含特殊字符如‘~’,则要以‘\’来转义。
- 源变量匹配表达式对应的结果值可以是一个字符串也可以是另外一个变量。
15. nginx跨域配置
关于跨域的详细内容可以参照什么是跨域?怎么解决跨域
这里主要使用nginx解决跨域问题
add_header配置语法
Syntax: add_header name value [always];
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, if in location
nginx在响应中添加关于跨域的响应头
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' '*';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' '*';
如果是预检请求即OPTIONS请求,使用if指令和return指令返回204即可。
location / {
#当请求为非简单请求,发送了预检OPTIONS时返回204,同时控制预检请求的过期时间
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS'){
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' '*';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' '*';
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' '3600';
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 204;
}
}
15.1 跨域基本配置
主要实现的目的是www.cros.com去访问api.cros.com,这肯定是跨域的,因为二级子域名不同。同时测试跨域请求时,cookie是否丢失。
跨域配置示例
server {
listen 80;
server_name api.cros.com;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' '*';
#允许客户端传递cookie
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' '*';
location / {
#当请求为非简单请求,发送了预检OPTIONS时返回204,同时控制预检请求的过期时间
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS'){
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' '3600';
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 204;
}
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cros.com;
charset utf-8,gbk;
#添加了一个cookie,但是不知道如何设置cookie的value
userid on;
userid_name 'test-cookie=666';
userid_domain cros.com;
userid_path /;
userid_expires 365d;
}
打开浏览器访问www.cros.com
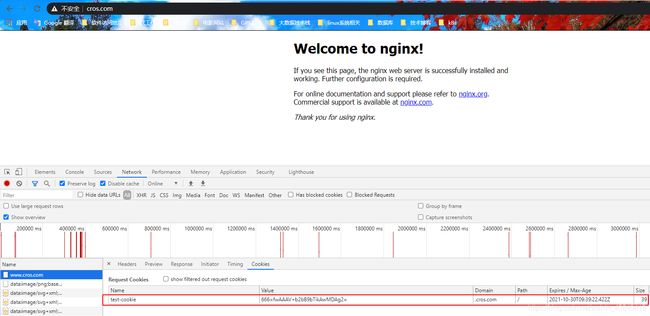
发现正常访问,且cookie成功返回
在root站点下,创建bbs文件夹,在bbs文件夹内创建index.html文件。
<h1>cros testh1>
<a href="http://api.cros.com">跳转到api.cros.coma>
然后访问www.cros.com/bbs/index.html

结果cookie没有丢失,且成功跨域访问。
15.2 跨域请求时Cookie丢失问题
服务器需要在响应头中添加add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';,设置允许传递cookie。同时Access-Control-Allow-Origin响应头不能返回'*'。
前端需要设置withCredentials为true
- 原生ajax
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); // IE8/9需用window.XDomainRequest兼容
// 前端设置是否带cookie
xhr.withCredentials = true;
xhr.open('post', 'http://www.domain2.com:8080/login', true);
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xhr.send('user=admin');
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200) {
alert(xhr.responseText);
}
};
- jQuery ajax
$.ajax({
url: 'http://www.test.com:8080/login',
type: 'get',
data: {},
xhrFields: {
withCredentials: true // 前端设置是否带cookie
},
crossDomain: true, // 会让请求头中包含跨域的额外信息,但不会含cookie
});
- vue-resource
Vue.http.options.credentials = true
- axios
axios.defaults.withCredentials = true
cookie属性项
| 属性项 | 属性项介绍 |
|---|---|
| NAME=VALUE | 键值对,可以设置要保存的 Key/Value,注意这里的 NAME 不能和其他属性项的名字一样 |
| Expires | 过期时间,在设置的某个时间点后该 Cookie 就会失效 |
| Domain | 生成该 Cookie 的域名,如 domain=“www.baidu.com” |
| Path | 该 Cookie 是在当前的哪个路径下生成的,如 path=/wp-admin/ |
| Secure | 如果设置了这个属性,那么只会在 SSH 连接时才会回传该 Cookie |
Cookie是不可以跨域名的,隐私安全机制禁止网站非法获取其他网站的Cookie。path属性决定允许访问Cookie的路径。比如,设置为"/"表示允许所有路径都可以使用Cookie。
如果仍然Cookie丢失,可以检查返回Cookie的域名和路径是否符合。
15.3 map指令优化允许跨域的域名
这里添加允许跨域的域名时写$http_origin或者是*都不太合适,写$http_origin会允许所有的域名都允许跨域,那就失去了跨域请求限制的意义。写*同样允许所有的域名都允许跨域,且不允许前端传递Cookie
这里可以使用map指令进行优化,允许跨域的域名
配置示例
map $http_origin $allow_origin_host {
default "";
*.gongsi.com $http_origin;
}
server {
listen 80;
#后台业务域名
server_name api.gongsi.com;
location / {
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' '3600';
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $allow_origin_host;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' '*';
#允许客户端传递cookie
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' '*';
return 204;
}
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $allow_origin_host;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' '*';
#允许客户端传递cookie
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' '*';
return 200 域名:$allow_origin_host成功跨域;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
#前台域名
server_name www.gongsi.com;
charset utf-8,gbk;
#添加了一个cookie,但是不知道如何设置cookie的value
userid on;
userid_name 'test-cookie=666';
userid_domain gongsi.com;
userid_path /;
userid_expires 365d;
}
在root站点下,创建testCookie.html文件。
<h1>cros cookie testh1>
<a href="http://api.gongsi.com">跳转到api.gongsi.coma>
打开浏览器,输入http://www.gongsi.com/testCookie.html,访问nginx服务器
16. nginx实现灰度发布
灰度发布(又名金丝雀发布)是指在黑与白之间,能够平滑过渡的一种发布方式。在其上可以进行A/B testing,即让一部分用户继续用产品特性A,一部分用户开始用产品特性B,如果用户对B没有什么反对意见,那么逐步扩大范围,把所有用户都迁移到B上面来。灰度发布可以保证整体系统的稳定,在初始灰度的时候就可以发现、调整问题,以保证其影响度。
http请求传输过程中,会自动带上User-Agent、Host、Referer、Cookie等头信息。我们只需要判断ip地址段,用户代理,Cookie中的信息等。同时在nginx中我们也可以通过$变量名的方式获取到这些值。
需求实现:在nginx中基于用户的某种标识进行转发到不同的后台业务服务。后台业务服务可以是不同的版本,这种标识可以是header、cookie、arg、用户的ip等。
需要注意的是proxy_pass配置反向代理服务器组时,不能使用map指令的$var2。只能使用set指令设置的$var。
例如下面的配置,使用map指令动态设置upstream的值
#获取customerType的请求头中的值,如果没有传递就是default
map $http_customerType $group {
default 'default';
test 'test';
stable 'default';
}
upstream default {
server localhost:7000;
}
upstream test {
server localhost:7001;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$group;
}
}
上面的配置是错误的,在进行nginx -t命令检测nginx语法的时候,提示错误找不到group这个upstream。这里只能使用set指令的方式。
16.1 基于header进行转发
自定义请求头customerType用于标识用户类型。例如test表示灰度用户,stable表示稳定用户。
使用$http_headerName的方式获取对应请求头中的值,如果请求头不存在则返回空字符串。
upstream default {
server localhost:7000;
}
upstream test {
server localhost:7001;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
set $group 'default';
if ($http_customerType = 'test') {
set $group 'test';
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://$group;
}
}
server {
listen 7000;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的稳定服务器返回信息';
}
}
server {
listen 7001;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的灰度服务器返回信息';
}
}
访问测试,使用postman进行测试。根据是否添加customerType请求头返回不同的数据
添加请求头信息为stable也是走的default服务器组

这里就不演示请求头中的值为其他的情况了,如果为其他值默认走default服务器组。
16.2 基于cookie进行转发
可以使用$cookie_cookie名称的方式获取对应cookie的值。
upstream default {
server localhost:7000;
}
upstream test {
server localhost:7001;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
set $group 'default';
if ($cookie_customerType = 'test') {
set $group 'test';
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://$group;
}
}
server {
listen 7000;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的稳定服务器返回信息';
}
}
server {
listen 7001;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的测试服务器返回信息';
}
}
使用postman进行访问测试
16.3 基于arg进行转发
可以使用$arg_参数名的方式获取参数对应的值,需要注意的是这里获取的参数只是拼接在url后面的参数值。无法获取到请求体中的参数
upstream default {
server localhost:7000;
}
upstream test {
server localhost:7001;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
set $group 'default';
if ($arg_customerType = 'test') {
set $group 'test';
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://$group;
}
}
server {
listen 7000;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的稳定服务器返回信息';
}
}
server {
listen 7001;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的测试服务器返回信息';
}
}
使用postman进行访问测试
16.4 基于weight
后台业务服务器部署两个版本,一个稳定版,一个测试版。基于权重,稳定版配置大权重,测试版配置小权重。先让小部分用户使用测试版,大部分用户使用稳定版。当测试版没有什么问题之后,然后将用户整体迁移到测试版。
这里可以使用weight,定义后台业务的权重来进行,让大部分用户访问稳定服务器,小部分用户访问测试服务器。
upstream default {
#稳定的后台业务服务
server localhost:7000 weight=2;
#新功能、不稳定的后台业务服务
server localhost:7001 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://default;
}
}
server {
listen 7000;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的稳定服务器返回信息';
}
}
server {
listen 7001;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header Content-Type 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 200 '$server_port端口的测试服务器返回信息';
}
}
17. WebSocket代理
nginx官方文档websocket代理和springboot整合websocket
17.1 WebSocket基本概述
WebSocket 协议在2008年诞生,2011年成为国际标准。所有浏览器都已经支持了。
它的最大特点就是,服务器可以主动向客户端推送信息,客户端也可以主动向服务器发送信息,是真正的双向平等对话,属于服务器推送技术的一种。
要将客户端和服务器之间的连接从HTTP / 1.1转换为WebSocket,同时增加两个头信息Upgrade和Connection。
默认情况下,如果代理服务器在60秒内未传输任何数据,则连接将关闭。可以使用proxy_read_timeout指令来增加此超时时间。或者,可以将代理服务器配置为定期发送WebSocket ping帧以重置超时并检查连接是否仍然有效。
17.2 配置语法
在nginx中的主要配置有
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection “upgrade”;
#超时设置
proxy_read_timeout 36000s;
17.3 nginx服务器配置、Springboot后台服务器代码
接下来使用浏览器、nginx、springboot服务器进行案例演示

nginx中的配置
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;
}
upstream backend {
server localhost:8080;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /websocket {
proxy_pass http://backend;
#超时设置
proxy_read_timeout 36000s;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
}
}
index.html文件
删除nginx中html文件夹中的index.html,使用新生成的html文件进行替换。
<html>
<head>
<title>My WebSockettitle>
head>
<body>
<input id="text" type="text"/>
<button onclick="send()">Sendbutton>
<button onclick="closeWebSocket()">Closebutton>
<div id="message">div>
body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var websocket = null;
//判断当前浏览器是否支持WebSocket, 主要此处要更换为自己的地址
if ('WebSocket' in window) {
websocket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost/websocket");
} else {
alert('Not support websocket')
}
//连接发生错误的回调方法
websocket.onerror = function () {
setMessageInnerHTML("error");
};
//连接成功建立的回调方法
websocket.onopen = function (event) {
//setMessageInnerHTML("open");
}
//接收到消息的回调方法
websocket.onmessage = function (event) {
setMessageInnerHTML(event.data);
}
//连接关闭的回调方法
websocket.onclose = function () {
setMessageInnerHTML("close");
}
//监听窗口关闭事件,当窗口关闭时,主动去关闭websocket连接,防止连接还没断开就关闭窗口,server端会抛异常。
window.onbeforeunload = function () {
websocket.close();
}
//将消息显示在网页上
function setMessageInnerHTML(innerHTML) {
document.getElementById('message').innerHTML += innerHTML + '
';
}
//关闭连接
function closeWebSocket() {
websocket.close();
}
//发送消息
function send() {
var message = document.getElementById('text').value;
websocket.send(message);
}
script>
html>
springboot项目,这里使用Spring Initializr初始化Springboot项目
项目结构
pom.xml文件,引入了spring-boot-start-web、websocket、lombok等依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.3.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.yanggu.websocketgroupId>
<artifactId>websocket-demoartifactId>
<version>1.0.0version>
<name>websocket-demoname>
<description>Demo project for Spring Bootdescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocketartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
OneWebSocket.java类
package com.yanggu.websocket.endpoint;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 前后端交互的类实现消息的接收推送(自己发送给自己)
*/
@Slf4j
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket")
@Component
@Data
public class OneWebSocket {
/**
* 记录当前在线连接数
*/
public static AtomicInteger onlineCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
/** 存放所有在线的客户端 */
public static Map<String, Session> clients = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 连接建立成功调用的方法
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session) {
// 在线数加1
onlineCount.incrementAndGet();
clients.put(session.getId(), session);
log.info("有新连接加入:{},当前在线人数为:{}", session.getId(), onlineCount.get());
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session) {
onlineCount.decrementAndGet(); // 在线数减1
clients.remove(session.getId());
log.info("有一连接关闭:{},当前在线人数为:{}", session.getId(), onlineCount.get());
}
/**
* 收到客户端消息后调用的方法
*
* @param message 客户端发送过来的消息
*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) throws IOException {
log.info("服务端收到客户端[{}]的消息:{}", session.getId(), message);
sendMessage("服务器回送消息:" + message, session);
}
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) {
log.error("发生错误");
error.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 服务端发送消息给客户端
*/
public void sendMessage(String message, Session toSession) throws IOException {
toSession.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
}
}
主启动类 WebsocketDemoApplication.java
package com.yanggu.websocket;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
@SpringBootApplication
public class WebsocketDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(WebsocketDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
控制器类PushMessageController.java
package com.yanggu.websocket.controller;
import com.yanggu.websocket.endpoint.OneWebSocket;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.websocket.Session;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @version V1.0
* @author: YangGu
* @date: 2020/11/4 18:43
* @description:
*/
@RestController
public class PushMessageController {
@Autowired
private OneWebSocket oneWebSocket;
@GetMapping("pushMessage")
public void pushMessage(@RequestParam String message) throws IOException {
Map<String, Session> clients = OneWebSocket.clients;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(clients.values)) {
List<Session> list = new ArrayList<>(clients.values());
Session session = list.get(0);
if (session != null) {
oneWebSocket.sendMessage("服务器主动发送消息:" + message, session);
}
}
}
}
17.4 案例演示
依次启动后台Springboot服务器、nginx服务器
17.4.1 浏览器和服务器建立连接
在浏览器地址栏输入http://localhost/index.html进行访问
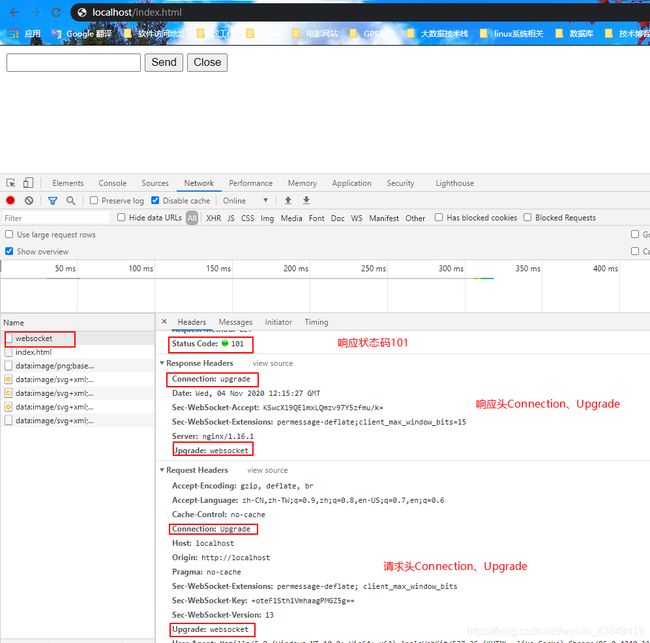
服务器日志输出
17.4.2 浏览器发送消息给服务器
17.4.3 服务器主动发消息给浏览器
postman发送消息 -> WebSocket服务器 -> 客户端浏览器