Flume实战案例(Flume接受telent数据,采集目录到HDFS、采集文件到HDFS、两个agent级联)
一、Flume接受telent数据
第一步:开发配置文件
vim /export/servers/flume/conf/netcat-logger.conf
# 定义这个agent中各组件的名字
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# 描述和配置source组件:r1
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = 192.168.119.131
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# 描述和配置sink组件:k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# 描述和配置channel组件,此处使用是内存缓存的方式
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# 描述和配置source channel sink之间的连接关系
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1Channel参数解释:
capacity:默认该通道中最大的可以存储的event数量
trasactionCapacity:每次最大可以从source中拿到或者送到sink中的event数量
第二步:启动配置文件
指定采集方案配置文件,在相应的节点上启动flume agent
先用一个最简单的例子来测试一下程序环境是否正常
启动agent去采集数据
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/netcat-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console-c conf 指定flume自身的配置文件所在目录
-f conf/netcat-logger.con 指定我们所描述的采集方案
-n a1 指定我们这个agent的名字
第三步:安装telent准备测试
在node02机器上面安装telnet客户端,用于模拟数据的发送
yum -y install telnet
telnet node01 44444 # 使用telnet模拟数据发送
二、采集目录到HDFS
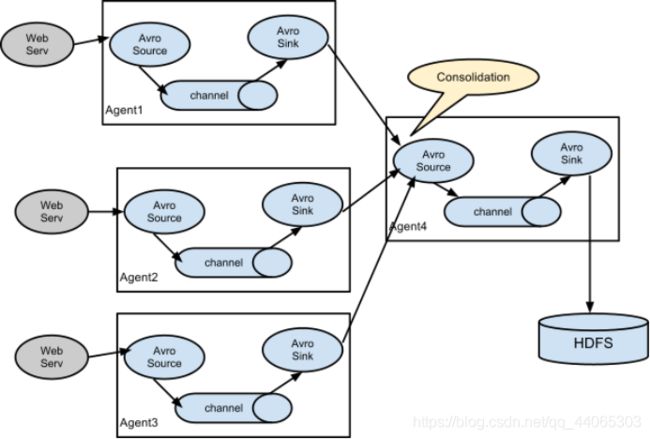
结构示意图:
采集需求:某服务器的某特定目录下,会不断产生新的文件,每当有新文件出现,就需要把文件采集到HDFS中去
根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素
- 数据源组件,即source ——监控文件目录 : spooldir
spooldir特性:
1、监视一个目录,只要目录中出现新文件,就会采集文件中的内容
2、采集完成的文件,会被agent自动添加一个后缀:COMPLETED
3、所监视的目录中不允许重复出现相同文件名的文件
- 下沉组件,即sink——HDFS文件系统 : hdfs sink
- 通道组件,即channel——可用file channel 也可以用内存channel
flume配置文件开发
配置文件编写:
cd /export/servers/flume/conf
mkdir -p /export/servers/dirfile
vim spooldir.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources=r1
a1.channels=c1
a1.sinks=k1
# Describe/configure the source
##注意:不能往监控目中重复丢同名文件
a1.sources.r1.type=spooldir
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir=/export/dir
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=hdfs://node01:8020/spooldir/
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1启动flume
bin/flume-ng agent -c ./conf -f ./conf/spooldir.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
上传文件到指定目录
将不同的文件上传到下面目录里面去,注意文件不能重名
cd /export/dir
三、采集文件到HDFS
采集需求:比如业务系统使用log4j生成的日志,日志内容不断增加,需要把追加到日志文件中的数据实时采集到hdfs
根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素
- 采集源,即source——监控文件内容更新 : exec ‘tail -F file’
- 下沉目标,即sink——HDFS文件系统 : hdfs sink
- Source和sink之间的传递通道——channel,可用file channel 也可以用 内存channel
定义flume的配置文件
node01开发配置文件
cd /export/servers/flume/conf
vim tail-file.conf
配置文件内容
a1.sources=r1
a1.channels=c1
a1.sinks=k1
# Describe/configure tail -F source1
a1.sources.r1.type=exec
a1.sources.r1.command =tail -F /export/servers/taillogs/access_log
# Describe sink1
a1.sinks.k1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=hdfs://node01:8020/spooldir/
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1启动flume
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/tail-file.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
开发shell脚本定时追加文件内容
mkdir -p /export/shells/
cd /export/shells/
vim tail-file.sh
创建文件夹
mkdir -p /export/servers/taillogs
启动脚本
sh /export/shells/tail-file.sh
#!/bin/bash
while true
do
date >> /export/servers/taillogs/access_log;
sleep 0.5;
done四、两个agent级联
第一个agent负责收集文件当中的数据,通过网络发送到第二个agent当中去,第二个agent负责接收第一个agent发送的数据,并将数据保存到hdfs上面去
第一步:node02安装flume
将node01机器上面解压后的flume文件夹拷贝到node02机器上面去
cd /export/servers
scp -r flume/ node02:$PWD
第二步:node02配置flume配置文件
在node02机器配置我们的flume
cd /export/servers/flume/conf
vim tail-avro-avro-logger.conf
##################
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /export/servers/taillogs/access_log
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
##sink端的avro是一个数据发送者
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.119.131
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1第三步:node02开发定脚本文件往写入数据
直接将node01下面的脚本和数据拷贝到node02即可,node01机器上执行以下命令
scp -r /export/shells /export/servers/taillogs/access_log node02:$PWD
第五步:node01开发flume配置文件
在node01机器上开发flume的配置文件
cd /export/servers/flume/conf
vim avro-hdfs.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
##source中的avro组件是一个接收者服务
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = 192.168.119.131
a1.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://node01:8020/avro
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1第六步:顺序启动
node01机器启动flume进程
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/avro-hdfs.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console node02机器启动flume进程
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/tail-avro-avro-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console node02机器启shell脚本生成文件
mkdir -p /export/servers/taillogs
cd /export/servers/shells
sh tail-file.sh
更多source和sink组件
Flume官方文档
http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/cdh/5/flume-ng-1.6.0-cdh5.14.0/FlumeUserGuide.html