第一模块:深度学习轻量级模型nanodet
第一模块:深度学习轻量级模型nanodet
- 第一部分:nanodet环境部署与数据集的准备
-
- nanodet简介
- 1.1 配置信息
- 1.2 环境配置
-
- 1.2.1 首先配置cuda11.0
- 1.2.2 创建nanodet工作环境
- 1.2.3 安装pytorch与所需依赖
- 1.3下载nanodet工作文件
- 1.4 准备数据集
-
- 1.4.1 收集数据
- 1.4.2 标注数据
- 1.4.3 整理数据
- 1.4.4 转换数据
第一部分:nanodet环境部署与数据集的准备

超快轻量级对象检测模型。能在移动设备上进行实时显示。
⚡超轻量级:标准型号文件只有 1.8 MB。
⚡超级快: 在ARM CPU运行速度可以达到97fps (10.23ms) 。
训练友好:GPU内存成本比其他型号低得多。
易于部署:根据 ncnn 推理框架提供C++实施和Android 演示。
nanodet简介
NanoDet是一种Fcos风格的一级无锚目标检测模型,使用ATSS进行目标采样,使用广义焦损失进行分类和盒回归。
详情请参阅这些论文:
Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection
ATSS:Bridging the Gap Between Anchor-based and Anchor-free Detection via Adaptive Training Sample Selection
Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection

1.1 配置信息
在本文中使用的服务器为联想服务器,单张显卡N卡2080Ti,cuda11.0,python3.8.0,pytorch1.7.1,cudatoolkit11.0,mkl-2020.2-256,torchvision-0.8.2-py38_cu110等等,这其中列举了一些在国内下载较慢的一些配置,这些资源我会专门进行搜集,然后建立一个服务站,以便大家更加快速方便的下载使用。当然我这边的配置包(linux下ubuntu18.04)会以百度云盘链接的形式给大家进行分享。
1.2 环境配置
1.2.1 首先配置cuda11.0
wget http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/11.0.2/local_installers/cuda_11.0.2_450.51.05_linux.run
apt-get update
apt-get install sudo
sudo sh cuda_11.0.2_450.51.05_linux.run
sudo apt-get install gedit
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
在打开的文件最后一行加入路径:
export PATH="/usr/local/cuda-11.0/bin:$PATH"export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/local/cuda-11.0/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"
然后save,退出
在命令行输入
source ~/.bashrc
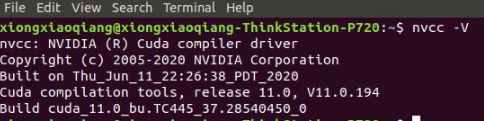
查询cuda版本进行检验
nvcc -V
1.2.2 创建nanodet工作环境
conda create -n nanodet python=3.8 -y
source activate
conda activate nanodet
1.2.3 安装pytorch与所需依赖
conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=11.0 -c pytorch
pip install Cython termcolor numpy tensorboard pycocotools matplotlib pyaml opencv-python tqdm
当然这里会下载非常慢,我这边提供百度云盘链接
cuda_11.0.2_450.51.05_linux 提取码:6xpu
pytorch-1.7.1-py3.8_cuda11.0.221_cudnn8.0.5_0.tar 提取码:4x63
cudatoolkit-11.0.221-h6bb024c_0.tar 提取码:h369
mkl-2020.2-256.tar 提取码:9y8g
torchvision-0.8.2-py38_cu110.tar 提取码:3rke
1.3下载nanodet工作文件
git clone https://github.com/RangiLyu/nanodet.git
cd nanodet
python setup.py develop
1.4 准备数据集
我在收集数据这方面一直是一个取巧者,但是一般来说都比较适用。但是无论是做深度学习的调研还是商业化功能,一个必不可少的部分就是数据。开源的框架和神经网络固然重要,开放的数据集也同样不能忽视。
我们一般做深度学习都是比较单一化,都是单个数据。这次就以“T”标为例来制作数据集。
1.4.1 收集数据
用无人机去拍摄几段不同角度的“T”子标的视频,然后对视频进行截取,取出其中有用的片段,去除没有拍到目标的片段。这样第一步的数据流就准备完毕了。
但是咱们制作的是一个基于图片识别的软件,那么需要的就是大量的图片数据,接下来的步骤就是讲视频流转换为图片数据集。
以下就是分割视频为图片的Python小程序
import cv2
def video2frame(videos_path,frames_save_path,time_interval):
'''
:param videos_path: 视频的存放路径
:param frames_save_path: 视频切分成帧之后图片的保存路径
:param time_interval: 保存间隔
:return:
'''
vidcap = cv2.VideoCapture(videos_path)
success, image = vidcap.read()
count = 0
while success:
success, image = vidcap.read()
count += 1
fenge=count/400
if count % (time_interval) == 0:
cv2.imencode('.jpg', image)[1].tofile(frames_save_path + "/%d.jpg" % count)
# if count == 20:
# break
print(count)
if __name__ == '__main__':
videos_path ='C:/Users/rexmatken/Desktop/xx/xx.mp4'#修改视频路径
frames_save_path = 'C:/Users/rexmatken/Desktop/xx'#修改图片保存路径
time_interval = 1#隔一帧保存一次
video2frame(videos_path, frames_save_path, time_interval)
这里涉及一个python-opencv模块的配置,我会专门写一篇来讲解这个步骤。
只需修改其中的路径信息即可使用。
接下来你会在你图片的保存路径看到这样一个场景。
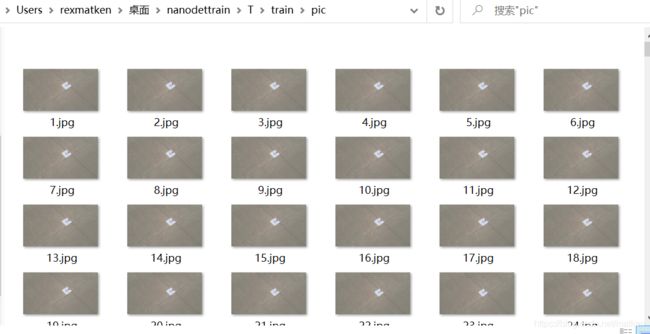
接下来要做的就是针对这些图片进行标注。
1.4.2 标注数据
labelImg这个软件,大家可以去网上自行寻找,标注主要用到这个软件。
接下来鼠标右击
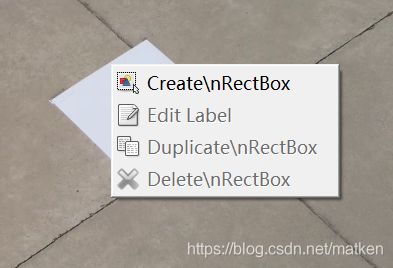
点击Create\nRectBox

鼠标左键一直拖着,即可选定标注区域

然后填入T即可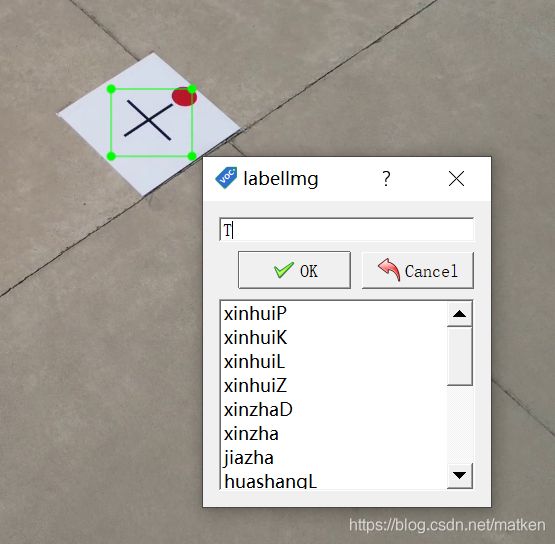
点击OK,再点击Save就算完成了一张的标注。
1.4.3 整理数据
将数据分为Train类和Val类两类,第一类是用于训练的数据集,第二类是用于检验的数据集,这两类数据集都会在训练中运用到,所以都是很关键的。大致分类可以参考下图。
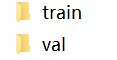
下图是train或者val文件夹下的文件
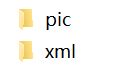
这样就是大致的文件分类。
1.4.4 转换数据
这些数据集的xml文件,也就是标注完生成的文件都需要进行一步转换,主要是将数据转换为coco格式,这样才可以在nanodet中用到(随着nanodet的更新也会逐渐支持其他格式)。
这里用到的也是一个python小程序。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import json
coco = dict()
coco['images'] = []
coco['type'] = 'instances'
coco['annotations'] = []
coco['categories'] = []
category_set = dict()
image_set = set()
category_item_id = -1
image_id = 20180000000
annotation_id = 0
def addCatItem(name):
global category_item_id
category_item = dict()
category_item['supercategory'] = 'none'
category_item_id += 1
category_item['id'] = category_item_id
category_item['name'] = name
coco['categories'].append(category_item)
category_set[name] = category_item_id
return category_item_id
def addImgItem(file_name, size):
global image_id
if file_name is None:
raise Exception('Could not find filename tag in xml file.')
if size['width'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find width tag in xml file.')
if size['height'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find height tag in xml file.')
image_id += 1
image_item = dict()
image_item['id'] = image_id
image_item['file_name'] = file_name
image_item['width'] = size['width']
image_item['height'] = size['height']
coco['images'].append(image_item)
image_set.add(file_name)
return image_id
def addAnnoItem(object_name, image_id, category_id, bbox):
global annotation_id
annotation_item = dict()
annotation_item['segmentation'] = []
seg = []
# bbox[] is x,y,w,h
# left_top
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1])
# left_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_top
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1])
annotation_item['segmentation'].append(seg)
annotation_item['area'] = bbox[2] * bbox[3]
annotation_item['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation_item['ignore'] = 0
annotation_item['image_id'] = image_id
annotation_item['bbox'] = bbox
annotation_item['category_id'] = category_id
annotation_id += 1
annotation_item['id'] = annotation_id
coco['annotations'].append(annotation_item)
def parseXmlFiles(xml_path):
for f in os.listdir(xml_path):
if not f.endswith('.xml'):
continue
bndbox = dict()
size = dict()
current_image_id = None
current_category_id = None
file_name = None
size['width'] = None
size['height'] = None
size['depth'] = None
xml_file = os.path.join(xml_path, f)
print(xml_file)
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
if root.tag != 'annotation':
raise Exception('pascal voc xml root element should be annotation, rather than {}'.format(root.tag))
# elem is , , ,
for elem in root:
current_parent = elem.tag
current_sub = None
object_name = None
if elem.tag == 'folder':
continue
if elem.tag == 'filename':
file_name = elem.text
if file_name in category_set:
raise Exception('file_name duplicated')
# add img item only after parse tag
elif current_image_id is None and file_name is not None and size['width'] is not None:
if file_name not in image_set:
current_image_id = addImgItem(file_name, size)
print('add image with {} and {}'.format(file_name, size))
else:
raise Exception('duplicated image: {}'.format(file_name))
# subelem is , , , ,
for subelem in elem:
bndbox['xmin'] = None
bndbox['xmax'] = None
bndbox['ymin'] = None
bndbox['ymax'] = None
current_sub = subelem.tag
if current_parent == 'object' and subelem.tag == 'name':
object_name = subelem.text
if object_name not in category_set:
current_category_id = addCatItem(object_name)
else:
current_category_id = category_set[object_name]
elif current_parent == 'size':
if size[subelem.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at size tag.')
size[subelem.tag] = int(subelem.text)
# option is , , , , when subelem is
for option in subelem:
if current_sub == 'bndbox':
if bndbox[option.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure corrupted at bndbox tag.')
bndbox[option.tag] = int(option.text)
# only after parse the
if bndbox['xmin'] is not None:
if object_name is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_image_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_category_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
bbox = []
# x
bbox.append(bndbox['xmin'])
# y
bbox.append(bndbox['ymin'])
# w
bbox.append(bndbox['xmax'] - bndbox['xmin'])
# h
bbox.append(bndbox['ymax'] - bndbox['ymin'])
print('add annotation with {},{},{},{}'.format(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id,
bbox))
addAnnoItem(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id, bbox)
if __name__ == '__main__':
xml_path = 'C:/Users/rexmatken/Desktop/nanodettrain/T/val/xml/' # 这是xml文件所在的地址
json_file = './val.json' # 这是你要生成的json文件
parseXmlFiles(xml_path) # 只需要改动这两个参数就行了
json.dump(coco, open(json_file, 'w'))
这里相信python程序大家都能看懂,其实也不用很会的,只要修改倒数第三四行的代码即可使用,倒数第四行主要是xml的文件夹,注意下路径斜杠的方向即可,倒数第三行就是这个xml的文件名,是val就写val,是train就写train。
这样一些步骤下来,也很费功夫了,但是总算的将数据集准备完了,接下来就可以在服务器上策马奔腾了。