0. 复习
0.1 虚继承
当我们使用多继承的时候,子类的多个父类有同名成员,访问的时候,会出现二义性
class CA
{
public:
int m_a;
};
class CB
{
public:
int m_a;
};
class CTest:public CA,public CB
{
};
int main()
{
CTest obj;
obj.m_a = 10;
return 0;
}
解决方式1:可以使用类的作用域访问具体某一个父类的成员
解决方式2:给CA和CB抽象出一个共同的父类,然后使用虚继承
class CBase
{
public:
int m_a;
};
class CA:virtual public CBase
{
public:
//int m_a;
};
class CB:virtual public CBase
{
public:
//int m_a;
};
class CTest :public CA, public CB
{
};
int main()
{
CTest obj;
obj.m_a = 20;
obj.CA::m_a = 10;
obj.CB::m_a = 20;
return 0;
}假如类B虚继承自类A,此时类A就是虚基类
0.2 虚函数与多态
当我们使用父类指针指向子类对象,调用虚函数,优先调用子类的虚函数。子类假如没有实现这个虚函数,就调用父类的。
虚函数是多态机制,属于动态联编。
virtual void fun() =0 ; 这个叫做纯虚函数。只是提供了接口,没有提供具体实现,实现由子类来完成。
抽象类:包含纯虚函数的类,也叫做抽象类。假如子类没有实现父类中的纯虚函数,子类也是抽象类。
抽象类的特点:不能定义对象
class Tuxing
{
public:
virtual int ClacArea() = 0;
};
class Sanjiaoxing:public Tuxing
{
public:
int ClacArea()
{
return m_nBottom * m_nHeight / 2;
}
private:
int m_nBottom;
int m_nHeight;
};
class CZhengfangxing :public Tuxing
{
int ClacArea()
{
//..
return m_nLenth * m_nLenth;
}
private:
int m_nLenth;
};
class CCircle:public Tuxing
{
};
int main()
{
CCircle obj;
CZhengfangxing obj2;
return 0;
}重载,重定义,虚函数定义
重载: 相同作用域 函数名相同 参数不同 调用的时候根据传参的不同,编译器自动调用相应的函数
重定义:继承关系中 函数名相同 参数可以相同也可以不相同 子类对象默认调用自己的
虚函数:继承关系中 函数名相同 参数相同 需要加上virtual 使用特点:父类指针指向子类对象,调用虚函数,优先调用子类的
0.3 模板
0.3.1函数模板
template
void Fun(M a, N b, L c, int nLenth)
{
}
int main()
{
Fun(1, 2.5, 'c', 100);
return 0;
} 模板的特化:
不能使用通用算法处理一些数据类型,可以为其单独实现算法。这个叫做特化
template <>
void Fun(int a, int b, double c, int nLenth)
{
}0.3.2 类模板
我们使用C语言的数组,它的长度只能是一个常量,不能动态扩展。使用起来不太方便。对于一些常规的数组操作,都需要自己去实现。没有面向对象的支持,我们实现一个动态数组,支持以下功能:
1.支持动态增长
2.支持任意数据类型
3.支持常规的数组操作
(增 删 改 查)
#pragma once
//先实现一个存储int类型的数组,元素假如最多100个
template
class CMyArr
{
public:
CMyArr(int nMax = 3);
//增加一个数据
bool Insert(T nData, int nLoc);
//删除一个数据
bool DeleteEle(int nLoc);
bool ModifyByLoc(T nData, int nLoc);
bool GetEleByLoc(int nLoc, T& Ele);
//获取当前元素个数
int GetLenth();
bool sort();
private:
T* m_buf;
int m_nLenth;
int m_nMax;
};
template
CMyArr::CMyArr(int nMax) :m_buf{ 0 }, m_nLenth(0), m_nMax(nMax)
{
m_buf = new T[nMax]{ 0 };
}
//增加一个数据
template
bool CMyArr::Insert(T nData, int nLoc)
{
//1. 检测传入的位置,是否正确
if (nLoc<0 || nLoc>m_nLenth)
{
return false;
}
//2. 是否缓冲区已经满了
if (m_nLenth == m_nMax)
{
//假如缓冲区满了,那么就可以申请更大的空间,然后去存储
T* pTemp = new T[m_nMax * 2]{ 0 };
//将老缓冲区中的数据拷贝到新申请的缓冲区
for (int i = 0; i < m_nMax; i++)
{
pTemp[i] = m_buf[i];
}
//释放原来的缓冲区
delete[]m_buf;
m_buf = pTemp;
m_nMax *= 2;
}
//3. 添加数据的位置,在结尾,直接添加
if (m_nLenth == nLoc)
{
m_buf[nLoc] = nData;
m_nLenth++;
return true;
}
//4. 添加数据的位置,在中间,需要移动数据,再添加
for (int i = m_nLenth - 1; i >= nLoc; i--)
{
m_buf[i + 1] = m_buf[i];
}
//已经移动完数据了,添加数据
m_buf[nLoc] = nData;
m_nLenth++;
return true;
}
//删除一个数据
template
bool CMyArr::DeleteEle(int nLoc)
{
//1. 检测位置是否正确
if (nLoc < 0 || nLoc >= m_nLenth)
{
return false;
}
//2. 删除的是结尾,不需要移动
if (nLoc == m_nLenth - 1)
{
m_nLenth--;
return true;
}
//3. 删除的是中间,就需要移动
for (int i = nLoc; i < m_nLenth - 1; i++)
{
m_buf[i] = m_buf[i + 1];
}
m_nLenth--;
return true;
}
template
bool CMyArr::ModifyByLoc(T nData, int nLoc)
{
//1. 检测位置是否正确
if (nLoc < 0 || nLoc >= m_nLenth)
{
return false;
}
//2. 位置没有问题,直接赋值
m_buf[nLoc] = nData;
return true;
}
template
bool CMyArr::GetEleByLoc(int nLoc, T& Ele)
{
//1. 检测位置是否正确
if (nLoc < 0 || nLoc >= m_nLenth)
{
return false;
}
//2. 位置没有问题,直接赋值
Ele = m_buf[nLoc];
return true;
}
//获取当前元素个数
template
int CMyArr::GetLenth()
{
return m_nLenth;
}
template
bool CMyArr::sort()
{
for (int j = 1; j < m_nLenth; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_nLenth - j; i++)
{
if (m_buf[i] > m_buf[i + 1])
{
T nTemp = m_buf[i];
m_buf[i] = m_buf[i + 1];
m_buf[i + 1] = nTemp;
}
}
}
return true;
} 具体的使用:
#include
#include "MyArr.h"
int main()
{
CMyArr obj;
obj.Insert(10, 0);
obj.Insert(20, 0);
obj.Insert(30, 0);
obj.Insert(100, 1);
obj.Insert(200, 2);
obj.DeleteEle(1);
obj.ModifyByLoc(500, 1);
obj.sort();
for (int i = 0; i < obj.GetLenth(); i++)
{
int nEle = 0;
obj.GetEleByLoc(i, nEle);
std::cout << nEle << " ";
}
CMyArr obj2;
obj2.Insert('a', 0);
obj2.Insert('b', 1);
obj2.Insert('c', 0);
obj2.Insert('d', 1);
obj2.Insert('e', 2);
obj2.Insert('f', 1);
for (int i = 0; i < obj2.GetLenth(); i++)
{
char nEle = 0;
obj2.GetEleByLoc(i, nEle);
std::cout << nEle << " ";
}
obj2.sort();
std::cout << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < obj2.GetLenth(); i++)
{
char nEle = 0;
obj2.GetEleByLoc(i, nEle);
std::cout << nEle << " ";
}
return 0;
} 1.STL -vector
1.1 vertor的基本使用
向量(Vector)是一个封装了动态大小数组的顺序容器(Sequence Container)。跟任意其它类型容器一样,它能够存放各种类型的对象。可以简单的认为,向量是一个能够存放任意类型的动态数组。
1.顺序序列
顺序容器中的元素按照严格的线性顺序排序。可以通过元素在序列中的位置访问对应的元素。
2.动态数组
支持对序列中的任意元素进行快速直接访问,甚至可以通过指针算述进行该操作。提供了在序列末尾相对快速地添加/删除元素的操作。
3.能够感知内存分配器的(Allocator-aware)
容器使用一个内存分配器对象来动态地处理它的存储需求
基本函数实现
1.构造函数
vector():创建一个空vector
vector(int nSize):创建一个vector,元素个数为nSize
vector(int nSize,const t& t):创建一个vector,元素个数为nSize,且值均为t
vector(const vector&):复制构造函数
vector(begin,end):复制[begin,end)区间内另一个数组的元素到vector中
2.增加函数
void push_back(const T& x):向量尾部增加一个元素X
iterator insert(iterator it,const T& x):向量中迭代器指向元素前增加一个元素x
iterator insert(iterator it,int n,const T& x):向量中迭代器指向元素前增加n个相同的元素x
iterator insert(iterator it,const_iterator first,const_iterator last):向量中迭代器指向元素前插入另一个相同类型向量的[first,last)间的数据
3.删除函数
iterator erase(iterator it):删除向量中迭代器指向元素
iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last):删除向量中[first,last)中元素
void pop_back():删除向量中最后一个元素
void clear():清空向量中所有元素
4.遍历函数
reference at(int pos):返回pos位置元素的引用
reference front():返回首元素的引用
reference back():返回尾元素的引用
iterator begin():返回向量头指针,指向第一个元素
iterator end():返回向量尾指针,指向向量最后一个元素的下一个位置
reverse_iterator rbegin():反向迭代器,指向最后一个元素
reverse_iterator rend():反向迭代器,指向第一个元素之前的位置
5.判断函数
bool empty() const:判断向量是否为空,若为空,则向量中无元素
6.大小函数
int size() const:返回向量中元素的个数
int capacity() const:返回当前向量所能容纳的最大元素值
int max_size() const:返回最大可允许的vector元素数量值
7.其他函数
void swap(vector&):交换两个同类型向量的数据
void assign(int n,const T& x):设置向量中前n个元素的值为x
void assign(const_iterator first,const_iterator last):向量中[first,last)中元素设置成当前向量元素
#include
#include
#include
using std::vector;
int main()
{
vector obj;
//1. 增加
//push_back 在结尾添加
//insert 在中间添加
obj.push_back(1);
obj.push_back(2);
obj.push_back(3);
obj.push_back(4);
obj.push_back(5);
obj.push_back(6);
//vector中使用迭代器来标识位置
//我们可以暂且认为迭代器是一个指针
//可以有 + - *的操作
//获取起始位置的迭代器
vector::iterator it1 = obj.begin();
obj.insert(it1+2, 100);
//2. 删除
//pop_back 删除结尾
//erase 删除中间
//clear 全部删掉
obj.pop_back();
vector::iterator it2 = obj.begin();
obj.erase(it2+3);
//3. 查询
//支持下标运算
//size 获取元素个数
std::cout << obj[2];
std::cout << obj.size();
//4. 修改
obj[2] = 10;
std::cout << std::endl;
//5. 遍历
//第一种遍历方式
for (int i = 0; i < obj.size(); i++)
{
std::cout << obj[i]<<" ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//第二种遍历方式
//obj.end()是结尾的迭代器,是最后一个元素的后面
vector::iterator it3 = obj.begin();
for (; it3 != obj.end(); it3++)
{
std::cout << *it3 << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//6. 排序
std::sort(obj.begin(), obj.end());
for (int i = 0; i < obj.size(); i++)
{
std::cout << obj[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
} 1.2 使用vector实现一个密码本
#include
#include
using std::vector;
class CPassWordInfo
{
public:
CPassWordInfo(const char* szWeb = nullptr,
const char* szUserName = nullptr,
const char* szPwd=nullptr)
{
strcpy_s(m_szWeb, 20, szWeb);
strcpy_s(m_szUserName, 20, szUserName);
strcpy_s(m_szPwd, 20, szPwd);
}
char* GetWeb()
{
return m_szWeb;
}
char* GetUserName()
{
return m_szUserName;
}
char* GetPwd()
{
return m_szPwd;
}
void SetWeb(const char* szWeb = nullptr)
{
strcpy_s(m_szWeb, 20, szWeb);
}
void SetUserName(const char* szUserName)
{
strcpy_s(m_szUserName, 20, szUserName);
}
void SetPwd(const char* szPwd = nullptr)
{
strcpy_s(m_szPwd, 20, szPwd);
}
bool Veryrify()
{
}
private:
char m_szWeb[20];
char m_szUserName[20];
char m_szPwd[20];
};
vector g_PwdBook;
int main()
{
//1. 用户输入要进行的操作
int nSelect = 0;
while (true)
{
system("cls");
std::cout << "增加" << std::endl;
std::cout << "删除" << std::endl;
std::cout << "查询所有" << std::endl;
std::cout << "修改" << std::endl;
std::cout << "输入你的选择(1~4):" << std::endl;
std::cin >> nSelect;
switch (nSelect)
{
case 1://增加
{
char szWebSite[20] = { 0 };
char szUserName[20] = { 0 };
char szPwd[20] = { 0 };
//1. 输入站点的信息
std::cout << "站点:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> szWebSite;
std::cout << "账号:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> szUserName;
std::cout << "密码:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> szPwd;
//2. 构建一个对象,存储到vector
CPassWordInfo obj(szWebSite, szUserName, szPwd);
g_PwdBook.push_back(obj);
break;
}
case 2://删除
{
int nDelete = 0;
std::cout << "请输入你要删除的序号:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> nDelete;
//删除的时候,需要传递迭代器
vector::iterator it = g_PwdBook.begin();
g_PwdBook.erase(it+nDelete);
break;
}
case 3://查询所有
{
vector::iterator it = g_PwdBook.begin();
for (; it != g_PwdBook.end(); it++)
{
std::cout << "站点:"<<(*it).GetWeb()<<" ";
std::cout << "用户名:" << (*it).GetUserName()<<" ";
std::cout << "密码:" << (*it).GetPwd()<> nModify;
//2. 输入具体数据
char szWebSite[20] = { 0 };
char szUserName[20] = { 0 };
char szPwd[20] = { 0 };
//3. 输入站点的信息
std::cout << "站点:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> szWebSite;
std::cout << "账号:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> szUserName;
std::cout << "密码:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> szPwd;
//4. 进行修改
g_PwdBook[nModify].SetWeb(szWebSite);
g_PwdBook[nModify].SetUserName(szUserName);
g_PwdBook[nModify].SetPwd(szPwd);
//5. 校验密码
g_PwdBook[nModify].Veryrify();
}
default:
break;
}
system("pause");
}
} 2. 控制台编程
2.1 会移动的A
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while (true)
{
system("cls");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
printf("A");
n++;
//停顿多少毫秒
Sleep(100);
}
return 0; 2.2 会移动的方块
上面的代码,不能方便进行上下移动,有多个移动物体的时候,会互相干扰
#include
#include
#include
void WriteChar(int x, int y, const char* pBuf)
{
HANDLE hHandle = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
COORD pos = { x*2,y };
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hHandle, pos);
printf(pBuf);
}
int main()
{
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
while (true)
{
WriteChar(x, y, " ");
y++;
WriteChar(x, y, "□");
}
return 0;
} 2.3实现贪吃蛇最基本功能
仅仅框架,很多功能缺乏
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define 上 1
#define 下 2
#define 左 3
#define 右 4
#define Map_X 30
#define Map_Y 30
#define 空地 0
#define 食物 1
#define 障碍物 2
#define 蛇 3
COORD g_Snake[100];
int g_Dir = 右;
int g_nLength = 4;
int g_Map[Map_X][Map_Y] = {};
int g_FoodExist = 0;
//实现一个能在屏幕任何位置输出字符串的函数
void WriteChar(int x, int y, char* szInfo, int color = 0)
{
COORD pos = { x*2, y }; //在x轴的偶数位置输出
//获得输出句柄
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
//设置光标位置
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut,pos);
//输出字符串
printf("%s", szInfo);
}
int keyWait() {
if (_kbhit()) //判断用户是否按键,有则函数返回1
return _getch(); //接收用户按键,并将按键码返回
return 0; //没有按键,则返回0
}
void InitGame()
{
//初始化贪吃蛇游戏
g_Snake[0].X = 10;
g_Snake[0].Y = 3;
g_Snake[1].X = 10;
g_Snake[1].Y = 4;
g_Snake[2].X = 10;
g_Snake[2].Y = 5;
g_Snake[3].X = 10;
g_Snake[3].Y = 6;
//判断蛇移动的前方是否有障碍物
for (int i = 0; i < Map_X; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Map_Y; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == Map_X - 1 || j == Map_Y - 1)
{
g_Map[i][j] = 障碍物;
}
else
{
g_Map[i][j] = 空地;
}
}
}
}
void DrawMap()
{
//绘制地图边界
for (int i = 0; i < Map_X; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Map_Y; j++)
{
if (g_Map[i][j] == 障碍物)
{
WriteChar(i, j, (char*)"*");
}
}
}
}
void CreateFood()
{
while (true)
{
//在空地随机生成食物
int FoodX = rand() % 28 + 1;
int FoodY = rand() % 28 + 1;
if (g_Map[FoodX][FoodY] == 空地)
{
g_Map[FoodX][FoodY] = 食物;
WriteChar(FoodX, FoodY, (char*)"●");
g_FoodExist = 1;
return;
}
}
}
void GetPlayerInput()
{
int Opera = 0;
//接收用户的输入,修改蛇的方向
Opera = keyWait();
switch (Opera)
{
case 'w':
case 'W':
g_Dir = 上;
break;
case 's':
case 'S':
g_Dir = 下;
break;
case 'a':
case 'A':
g_Dir = 左;
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
g_Dir = 右;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void ClearSnake()
{
//根据蛇的当前坐标,将其在屏幕上清除掉
for (int i = 0; i < g_nLength; i++)
{
WriteChar(g_Snake[i].X, g_Snake[i].Y, (char*)" ");
}
}
void DrawSnake()
{
//根据蛇的新坐标,将其在屏幕上画出来
for (int i = 0; i < g_nLength; i++)
{
WriteChar(g_Snake[i].X, g_Snake[i].Y, (char*)"■");
}
}
int MoveSnake()
{
//根据蛇的方向去移动蛇
int nTempX = g_Snake[0].X;
int nTempY = g_Snake[0].Y;
switch (g_Dir)
{
case 上:
nTempY--;
break;
case 下:
nTempY++;
break;
case 左:
nTempX--;
break;
case 右:
nTempX++;
break;
default:
break;
}
//判断蛇的前方是什么
if (g_Map[nTempX][nTempY] == 空地)
{
}
else if (g_Map[nTempX][nTempY] == 食物)
{
g_nLength++;
g_Map[nTempX][nTempY] = 空地;
g_FoodExist = 0;
}
else if (g_Map[nTempX][nTempY] == 障碍物)
{
return 0;
}
else if (g_Map[nTempX][nTempY] == 蛇)
{
for (int i = 0; i < g_nLength; i++)
{
if (g_Snake[0].X == g_Snake[i].X && g_Snake[0].Y == g_Snake[i].Y)
{
return 0;
}
}
}
//根据当前蛇的位置,后一位坐标往前一位赋值
for (int i = g_nLength - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
g_Snake[i + 1].X = g_Snake[i].X;
g_Snake[i + 1].Y = g_Snake[i].Y;
}
//获取蛇的新坐标
g_Snake[0].X = nTempX;
g_Snake[0].Y = nTempY;
return 1;
}
int main() {
//WriteChar(1, 2, (char*)"hello"); //按坐标位置打印字符串
//实现一个受控制的自由移动的小点
/*int i = 0;
while (true)
{
WriteChar(i, 20, (char*)"A");
WriteChar(i - 1, 20, (char*)" ");
i++;
Sleep(200);
}*/
//初始化游戏
InitGame();
DrawMap();
int nLive = 1;
while (nLive)
{
//获取用户输入
GetPlayerInput();
//清除蛇的当前位置
ClearSnake();
//蛇头吃到自己身体的任意位置,将其在地图上清除
//移动蛇的位置
nLive = MoveSnake();
//绘制蛇的新位置
DrawSnake();
//将其设置在地图中
//创建食物
if (g_FoodExist == 0)
{
CreateFood();
}
Sleep(200);
}
return 0;
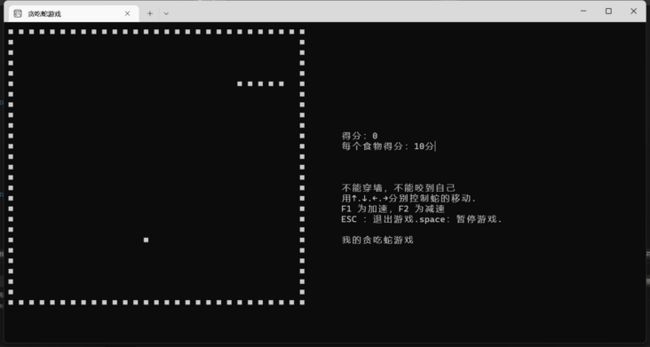
} 2.4 完整版的贪吃蛇
已经在vc,vs及多个编译环境下下测试运行,完全可运行通过,放心测试学习。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define U 1
#define D 2
#define L 3
#define R 4 //蛇的状态,U:上 ;D:下;L:左 R:右
typedef struct SNAKE //蛇身的一个节点
{
int x;
int y;
struct SNAKE *next;
}snake;
//全局变量//
int score=0,add=10;//总得分与每次吃食物得分。
int status,sleeptime=200;//每次运行的时间间隔
snake *head, *food;//蛇头指针,食物指针
snake *q;//遍历蛇的时候用到的指针
int endgamestatus=0; //游戏结束的情况,1:撞到墙;2:咬到自己;3:主动退出游戏。
//声明全部函数//
void Pos();
void creatMap();
void initsnake();
int biteself();
void createfood();
void cantcrosswall();
void snakemove();
void pause();
void gamecircle();
void welcometogame();
void endgame();
void gamestart();
void Pos(int x,int y)//设置光标位置
{
COORD pos;
HANDLE hOutput;
pos.X=x;
pos.Y=y;
hOutput=GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOutput,pos);
}
void creatMap()//创建地图
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<58;i+=2)//打印上下边框
{
Pos(i,0);
printf("■");
Pos(i,26);
printf("■");
}
for(i=1;i<26;i++)//打印左右边框
{
Pos(0,i);
printf("■");
Pos(56,i);
printf("■");
}
}
void initsnake()//初始化蛇身
{
snake *tail;
int i;
tail=(snake*)malloc(sizeof(snake));//从蛇尾开始,头插法,以x,y设定开始的位置//
tail->x=24;
tail->y=5;
tail->next=NULL;
for(i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
head=(snake*)malloc(sizeof(snake));
head->next=tail;
head->x=24+2*i;
head->y=5;
tail=head;
}
while(tail!=NULL)//从头到为,输出蛇身
{
Pos(tail->x,tail->y);
printf("■");
tail=tail->next;
}
}
int biteself()//判断是否咬到了自己
{
snake *self;
self=head->next;
while(self!=NULL)
{
if(self->x==head->x && self->y==head->y)
{
return 1;
}
self=self->next;
}
return 0;
}
void createfood()//随机出现食物
{
snake *food_1;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
food_1=(snake*)malloc(sizeof(snake));
while((food_1->x%2)!=0) //保证其为偶数,使得食物能与蛇头对其
{
food_1->x=rand()%52+2;
}
food_1->y=rand()%24+1;
q=head;
while(q->next==NULL)
{
if(q->x==food_1->x && q->y==food_1->y) //判断蛇身是否与食物重合
{
free(food_1);
createfood();
}
q=q->next;
}
Pos(food_1->x,food_1->y);
food=food_1;
printf("■");
}
void cantcrosswall()//不能穿墙
{
if(head->x==0 || head->x==56 ||head->y==0 || head->y==26)
{
endgamestatus=1;
endgame();
}
}
void snakemove()//蛇前进,上U,下D,左L,右R
{
snake * nexthead;
cantcrosswall();
nexthead=(snake*)malloc(sizeof(snake));
if(status==U)
{
nexthead->x=head->x;
nexthead->y=head->y-1;
if(nexthead->x==food->x && nexthead->y==food->y)//如果下一个有食物//
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
score=score+add;
createfood();
}
else //如果没有食物//
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q->next->next!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
Pos(q->next->x,q->next->y);
printf(" ");
free(q->next);
q->next=NULL;
}
}
if(status==D)
{
nexthead->x=head->x;
nexthead->y=head->y+1;
if(nexthead->x==food->x && nexthead->y==food->y) //有食物
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
score=score+add;
createfood();
}
else //没有食物
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q->next->next!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
Pos(q->next->x,q->next->y);
printf(" ");
free(q->next);
q->next=NULL;
}
}
if(status==L)
{
nexthead->x=head->x-2;
nexthead->y=head->y;
if(nexthead->x==food->x && nexthead->y==food->y)//有食物
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
score=score+add;
createfood();
}
else //没有食物
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q->next->next!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
Pos(q->next->x,q->next->y);
printf(" ");
free(q->next);
q->next=NULL;
}
}
if(status==R)
{
nexthead->x=head->x+2;
nexthead->y=head->y;
if(nexthead->x==food->x && nexthead->y==food->y)//有食物
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
score=score+add;
createfood();
}
else //没有食物
{
nexthead->next=head;
head=nexthead;
q=head;
while(q->next->next!=NULL)
{
Pos(q->x,q->y);
printf("■");
q=q->next;
}
Pos(q->next->x,q->next->y);
printf(" ");
free(q->next);
q->next=NULL;
}
}
if(biteself()==1) //判断是否会咬到自己
{
endgamestatus=2;
endgame();
}
}
void pause()//暂停
{
while(1)
{
Sleep(300);
if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_SPACE))
{
break;
}
}
}
void gamecircle()//控制游戏
{
Pos(64,15);
printf("不能穿墙,不能咬到自己\n");
Pos(64,16);
printf("用↑.↓.←.→分别控制蛇的移动.");
Pos(64,17);
printf("F1 为加速,F2 为减速\n");
Pos(64,18);
printf("ESC :退出游戏.space:暂停游戏.");
Pos(64,20);
printf("我的贪吃蛇游戏");
status=R;
while(1)
{
Pos(64,10);
printf("得分:%d ",score);
Pos(64,11);
printf("每个食物得分:%d分",add);
if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_UP) && status!=D)
{
status=U;
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_DOWN) && status!=U)
{
status=D;
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_LEFT)&& status!=R)
{
status=L;
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_RIGHT)&& status!=L)
{
status=R;
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_SPACE))
{
pause();
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_ESCAPE))
{
endgamestatus=3;
break;
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_F1))
{
if(sleeptime>=50)
{
sleeptime=sleeptime-30;
add=add+2;
if(sleeptime==320)
{
add=2;//防止减到1之后再加回来有错
}
}
}
else if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_F2))
{
if(sleeptime<350)
{
sleeptime=sleeptime+30;
add=add-2;
if(sleeptime==350)
{
add=1; //保证最低分为1
}
}
}
Sleep(sleeptime);
snakemove();
}
}
void welcometogame()//开始界面
{
Pos(40,12);
system("title 贪吃蛇游戏");
printf("欢迎来到贪食蛇游戏!");
Pos(40,25);
system("pause");
system("cls");
Pos(25,12);
printf("用↑.↓.←.→分别控制蛇的移动, F1 为加速,2 为减速\n");
Pos(25,13);
printf("加速将能得到更高的分数。\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void endgame()//结束游戏
{
system("cls");
Pos(24,12);
if(endgamestatus==1)
{
printf("对不起,您撞到墙了。游戏结束.");
}
else if(endgamestatus==2)
{
printf("对不起,您咬到自己了。游戏结束.");
}
else if(endgamestatus==3)
{
printf("您的已经结束了游戏。");
}
Pos(24,13);
printf("您的得分是%d\n",score);
exit(0);
}
void gamestart()//游戏初始化
{
system("mode con cols=100 lines=30");
welcometogame();
creatMap();
initsnake();
createfood();
}
int main()
{
gamestart();
gamecircle();
endgame();
return 0;
}