一文搞懂Spring Boot 事件监听机制
SpringBoot源码系列:
一文搞懂Spring Boot中java -jar启动jar包的原理
一文搞懂SpringBoot启动流程及自动配置
一文搞懂SpringBoot内嵌的Tomcat
一文搞懂SpringApplication对象的构建及spring.factories的加载时机
关于监听器模式、观察者模式请自行百度在此不再赘述。
1、Spring Boot 监听器模式要素
事件:SpringApplicationEvent,它是一个抽象类,继承了ApplicationEvent,是一个与SpringApplication相关的基类。
监听器:SpringApplicationRunListener,对SpringApplication的run方法进行监听。由SpringFactoriesLoader加载。
多播器:ApplicationEventMulticaster是一个接口,管理着多个ApplicationListener,并向其发布事件。他是一个应用程序事件发布者(ApplicationEventPublisher),通常一个ApplicationContext使用他来发布事件。
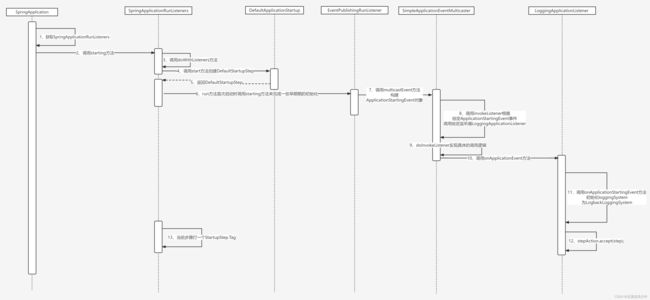
2、我们以Spring Boot中的应用启动事件来研究一下Spring Boot中的监听器机制。重点关注SpringApplication中的run()方法里面的下述内容。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
......
//获取SpringApplicationRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//触发应用启动事件ApplicationStartingEvent
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
......
}
3、进入SpringApplicationRunListeners。
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {
//创建一个新步骤他的名称是spring.boot.application.starting
//访问SpringApplicationRunListener类型的对象,并执行监听器动作starting,(listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext) 在run方法第一次启动时调用,完成早期的一些初始化。
//访问StartupStep类型的对象,并给当前步骤打一个StartupStep.Tag,标记key为mainApplicationClass,value为我们的主启动类com.example.springbootdemo.SpringbootdemoApplication
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),
//
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}
我们看一下上面的doWithListeners方法。看下面源码可知,这里使用了消费性接口java.util.function.Consumer,Consumer 表明我们想要访问SpringApplicationRunListener类型的对象,并对其执行某些操作如starting,Consumer stepAction表明我们想要访问StartupStep,并对其执行某些操作如打tag。
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction,
Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {
//创建一个stepName步骤并且标记他开始。通过DefaultApplicationStartup的start方法创建一个默认启动步骤(DefaultStartupStep)。
StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);
//执行给定的监听器动作starting
this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);
if (stepAction != null) {
//stepAction 不为空,执行启动步骤(StartupStep)
stepAction.accept(step);
}
//步骤结束。
step.end();
}
4、上面doWithListeners方法执行到this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction)时会执行给定的监听器动作starting,实际上执行的是SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类EventPublishingRunListener中的starting方法(run方法首次启动时调用starting方法,完成一些早期的初始),在该方法中通过SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象的multicastEvent方法多播应用启动事件ApplicationStartingEvent。
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster中的starting方法。
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
//多播事件
//这里构建的ApplicationStartingEvent继承自SpringApplicationEvent
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args));
}
5、我们进一步研究SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象的multicastEvent方法。
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//多播的event为org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication]
//默认的事件类型为org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
//此时eventType不为空所以type 此时为org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
//获取任务线程池,让监听器在不同的线程中执行。从而可以避免恶意监听器阻塞整个应用程序的危险。
//此时获取Executor的是null
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
//getApplicationListeners方法返回与给定类型匹配的ApplicationListener集合,不匹配的提前排除
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
//此时获取的listener是LoggingApplicationListener
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
//根据给定事件org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent调用给定监听器LoggingApplicationListener
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
6、继续看SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster中是如何调用监听器的。
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
//获取此多播器的错误处理程序,此时为null
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
//ErrorHandler 不为空需要处理error
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
//调用监听器具体逻辑
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
进入具体调用监听器的方法,重点关注listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
//LoggingApplicationListener 调用onApplicationEvent方法来处理应用启动事件(ApplicationStartingEvent)
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
......
}
}
7、接下来看一下LoggingApplicationListener 中的onApplicationEvent方法,此时我们的事件是ApplicationStartingEvent所以此时会进入onApplicationStartingEvent方法。
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent) {
onApplicationStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent
&& ((ContextClosedEvent) event).getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {
onContextClosedEvent();
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
onApplicationFailedEvent();
}
}
进入onApplicationStartingEvent方法。
private void onApplicationStartingEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
//获取从之前/META-INF/spring.factories加载出来的LoggingSystemFactory
//LoggingSystemFactory 该日志系统工厂支持生产提下三种日志系统
//LogbackLoggingSystem
//Log4J2LoggingSystem
//JavaLoggingSystem
//此处我们初始化loggingSystem 获取到的是LogbackLoggingSystem
this.loggingSystem = LoggingSystem.get(event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
//初始化LoggingInitializationContext之前调用beforeInitialize方法来减少不必要的日志输出,直至系统初始化完成。
this.loggingSystem.beforeInitialize();
}
8、到此doWithListeners方法中this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction)执行结束。接下来就执行doWithListeners方法中的stepAction.accept(step);
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction,
Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {
StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);
this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);
if (stepAction != null) {
stepAction.accept(step);
}
step.end();
}
执行stepAction.accept(step)相当于执行上述第三步中的starting方法的下面lambada表达式,因为我们使用了消费性接口java.util.function.Consumer。
//当前步骤打一个StartupStep.Tag,标记key为mainApplicationClass,value为 com.example.springbootdemo.SpringbootdemoApplication
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
}