Spirng 痛苦源码学习(一)——总起spring(一)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、总览Spring的bean
-
- 1)bean的过程【先了解具体的生命周期后面弄】
- 2)hello spring 简单bean操作
- 二、总览AOP
-
- - 1、test coding
- - 2、- debug
- - 3、- 总结debug
- 三、总览事务
-
- - 1、- test coding
- - 2、 debugging
- - 3、 事务失效
- - 4、事务总结
前言
对于spring来说最重要的两个特性就是老生常谈的IOC和AOP,这两个大哥先放一放。那我就先其中的一个重要小零件Bean来说,来看看spring是对Bean进行多牛逼的管理
一、总览Spring的bean
1)bean的过程【先了解具体的生命周期后面弄】
=》1、Spring底层会调用类的构造方法来完成对象创建
(这里先不管他是怎么拿到构造方法的,反正就是拿构造方法,默认是无参构造器。这里其实有一个推断构造方法的过程)
1 稍微解释一下构造方法推断
解决方法在你需要的构造器上加上@Autowired指定spring用;因为spring比较笨所以你要教他做事
2 Spring的设计思想是这样的:
- 如果一个类只有一个构造方法,那么没得选择,只能用这个构造方法
- 如果一个类存在多个构造方法,Spring不知道如何选择,就会看是否有无参的构
造方法,因为无参构造方法本身表示了一种默认的意义 - 不过如果某个构造方法上加了@Autowired注解,那就表示程序员告诉Spring就
用这个加了注解的方法,那Spring就会用这个加了@Autowired注解构造方法了
需要重视的是,如果Spring选择了一个有参的构造方法,Spring在调用这个有参构造方法
时,需要传入参数,那这个参数是怎么来的呢?
Spring会根据入参的类型和入参的名字去Spring中找Bean对象(以单例Bean为例,
Spring会从单例池那个Map中去找): - 先根据入参类型找,如果只找到一个,那就直接用来作为入参
- 如果根据类型找到多个,则再根据入参名字来确定唯一一个
- 最终如果没有找到,则会报错,无法创建当前Bean对象
确定用哪个构造方法,确定入参的Bean对象,这个过程就叫做推断构造方法。
=》 2、对象依赖注入(属性赋值)
=》 3、初始化前 ()
=》 4、初始化
=》 5、初始化后(AOP)
=》 5.1 代理对象【只有当有AOP织入的时候,才会产生代理对象】
=》 6、bean
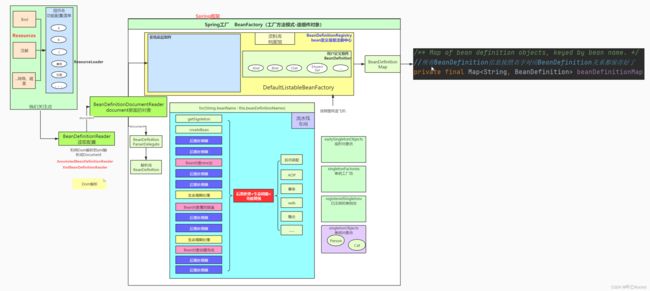
注:从源码的大的角度出发,就是先读取配置=》生成bean的定义信息(放到一个map里)=》按照bean的定义信息生成bean(也放到map里,要用的时候自取)
2)hello spring 简单bean操作
- 1、通过注解的方式
// 扫描该包下的所有组件
@ComponentScan("com.xusj")
public class AppConfig {
}
// 组件一、二如下
package com.xusj.future.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/26 22:59
*/
@Service
public class DogService {
}
// 这里有一个点值得我们在以后业务需求中可以使用,当项目一启动你要给对应的bean属性赋值,implements InitializingBean 重写afterPropertiesSet,在初始化bean的时候就直接赋值了
package com.xusj.future.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/26 22:58
*/
@Service
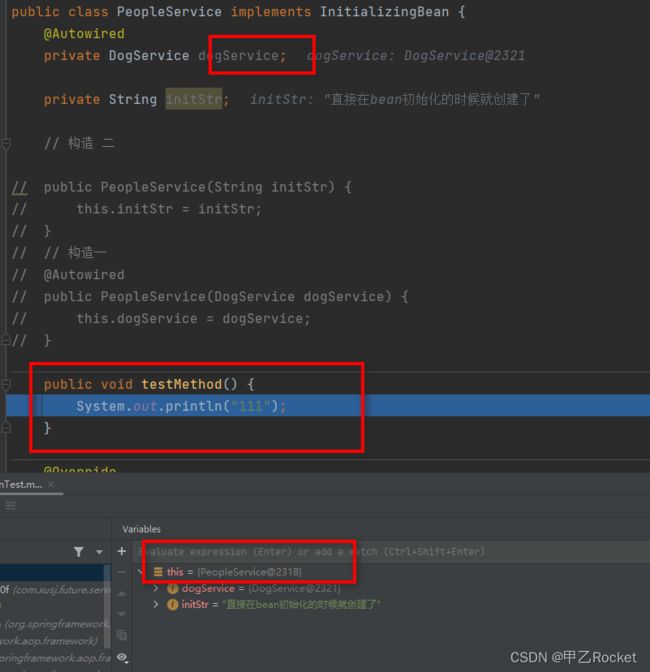
public class PeopleService implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private DogService dogService;
private String initStr;
public void testMethod() {
System.out.println("111");
}
// 这里就是你想在bean创建的时候给他赋值implements InitializingBean
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
initStr = "直接在bean初始化的时候就创建了";
System.out.println("在创建bean的时候自动和初始化一些值");
}
}
// main 函数直接getBean
package com.xusj.future;
import com.xusj.future.bean.Person;
import com.xusj.future.config.AppConfig;
import com.xusj.future.service.PeopleService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/5/9 22:15
*/
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// xml方式
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
// Person bean = classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
// System.out.println(bean);
// 注释方式
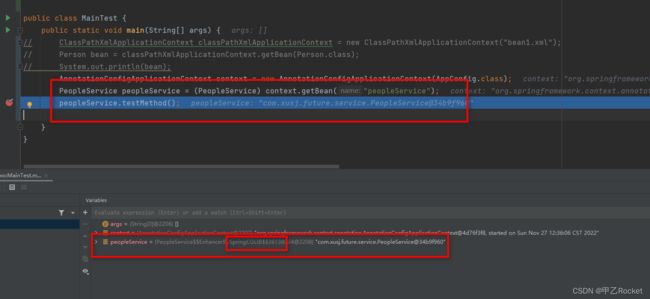
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
PeopleService peopleService = (PeopleService) context.getBean("peopleService");
peopleService.testMethod();
}
}
- 2、对于以上的一些代码我们放如下问题【希望学完,我自己能解决】
- 第一行代码,会构造一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象,
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext该如何理解,调用该构造方法除开会实例化得到
一个对象,还会做哪些事情? - 第二行代码,会调用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的getBean方法,会得到
一个UserService对象,getBean()是如何实现的?返回的UserService对象和我们自
己直接new的UserService对象有区别吗? - 第三行代码,就是简单的调用bean的test()方法,不难理解。
二、总览AOP
- 1、test coding
package com.xusj.future.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 切面bean 交给ioc管理
*
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/27 0:31
*/
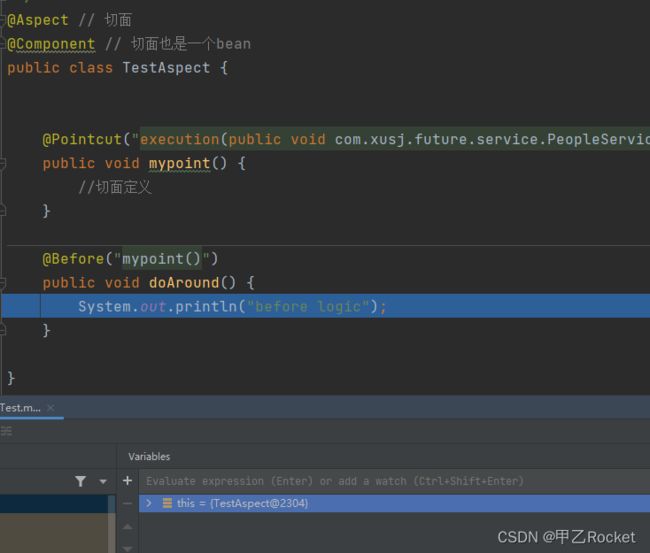
@Aspect // 切面
@Component // 切面也是一个bean
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public void com.xusj.future.service.PeopleService.testMethod())")
public void mypoint() {
//切面定义
}
@Before("mypoint()")
public void doAround() {
System.out.println("before logic");
}
}
package com.xusj.future.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/26 22:58
*/
@Service
public class PeopleService implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private DogService dogService;
private String initStr;
// 构造 二
// public PeopleService(String initStr) {
// this.initStr = initStr;
// }
// // 构造一
// @Autowired
// public PeopleService(DogService dogService) {
// this.dogService = dogService;
// }
public void testMethod() {
System.out.println("111");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
initStr = "直接在bean初始化的时候就创建了";
System.out.println("在创建bean的时候自动和初始化一些值");
}
}
// 这里很重要开启AOP代理
package com.xusj.future.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/26 22:58
*/
@ComponentScan("com.xusj")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 开启Aop代理
public class AppConfig {
// @Bean
// public PeopleService getPeople() {
// return new PeopleService();
// }
}
// 启动类
package com.xusj.future;
import com.xusj.future.config.AppConfig;
import com.xusj.future.service.PeopleService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/5/9 22:15
*/
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
// Person bean = classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
// System.out.println(bean);
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
PeopleService peopleService = (PeopleService) context.getBean("peopleService");
peopleService.testMethod();
}
}
- 2、- debug
- 3、- 总结debug
// 对于cglib代理来说,就是代理对象去继承被代理对象;为代码如下,这样代理对象就能使用bean中的方法和属性了【代理对象里面是没有值的】
public A extends B{
// spring 中
private B b;
// 这是继承父类的方法
public void test(){
// 怎么去调用父类的方法
// 1、直接去super.test
// 2、将B做为属性干到代理类中,spring是这么干的
b.test();
}
}

对于代理对象来说,以AOP为例子,我们只关注切到对应的方法上面,我们对被代理对象中的属性没有太大关注,所以代理对象是没有值得。
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();这个完全可以拿到被代理得对象
@Aspect // 切面
@Component // 切面也是一个bean
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public void com.xusj.future.service.PeopleService.testMethod())")
public void mypoint() {
//切面定义
}
@Before("mypoint()")
public void doAround(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 拿到得是普通对象(被代理对象得值,我们就可以通过这个去得到其中得属性)
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
System.out.println("before logic");
}
}
三、总览事务
- 1、- test coding
// 拿到数据库连接,然后给到事务管理器和jdbc进行操作
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/26 22:58
*/
@ComponentScan("com.xusj")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 开启Aop代理
@EnableTransactionManagement // 开启事务
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
// @Bean
// public PeopleService getPeople() {
// return new PeopleService();
// }
// 拿jdbc
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
// 将连接交给他
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
}
// 创建数据库连接
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useInformationSchema=true");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
// 交给事务管理
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource());
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}
// 添加注解
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/11/26 22:58
*/
@Service
public class PeopleService implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private DogService dogService;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Transactional// 事务注解
public void execute() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert student values (3,s,1)");
System.out.println("zhix ");
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
// 主方法调用
/**
* @author xusj
*
CreateDate 2022/5/9 22:15
*/
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
PeopleService peopleService = (PeopleService) context.getBean("peopleService");
peopleService.execute();
}
}
- 2、 debugging
这里也是用过代理对象完成事务的,流程如下,类似aop的代理,里面逻辑不一样
public A extends B{
// spring 中
private B b;
// 这是继承父类的方法
public void test(){
// 1先判断有没有@Transactional这个注解
// 2有的话,将conn置为false(默认是true自动提交,这里将他置为手动提交)
b.执行sql();
// 3没有异常直接commit
// 4有异常rollback
}
}
- 3、 事务失效
- 一个经典的事务失效(方法里面调用方法,事务失效)
- 由上面分析代理对象我们可以知道,只有当代理对象去调用方法的时候,事务ok
- 但是你在方法中调用方法的时候,一开始第一个方法你是代理对象调用过来的,但是后面第二个方法是普通对象搞来的,那么就失效了
@Transactional// 事务注解
public void execute() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert student values (3,s,1)");
System.out.println("zhix ");
a();
}
public void a() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert student values (3,s,1)");
System.out.println("zhix ");
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 解决方法,我们可以注入自己,然后调用方法,这样的话,我们在ioc拿出来的都是一个代理对象,所以就解决了
@Autowired
private PeopleService peopleService;
@Transactional// 事务注解
public void execute() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert student values (3,s,1)");
System.out.println("zhix ");
peopleService.execute();;
// a();
}
- 4、事务总结
Spring事务的代理对象执行某个方法时的步骤:
- 判断当前执行的方法是否存在@Transactional注解
- 如果存在,则利用事务管理器(TransactionMananger)新建一个数据库连接
- 修改数据库连接的autocommit为false
- 执行target.test(),执行程序员所写的业务逻辑代码,也就是执行sql
- 执行完了之后如果没有出现异常,则提交,否则回滚
Spring事务是否会失效的判断标准:某个加了@Transactional注解的方法被调用时,要判断到底是不是直接被代理对象调用的,如果是则事务会生效,如果不是则失效。