Jetson nano部署记录
文章目录
- 1、yolov5s模型转tensorrt
-
- 1、前期准备
- 2、运行yolov5
- 3、TensorRT加速推理
- 4、直接使用摄像头进行部署
- 2、deepstream检测
-
- 1、下载SDK
- 2、安装依赖
- 3、配置环境
- 4、测试效果
- 3、使用deepstream进行部署
- 4、yolov5目前比较新的版本训练和检测
-
- 1、前期准备
- 2、开始训练
- 3、进行检测
这篇文章不太成功,只能算是一个失败记录吧,先不管了,怕以后忘记了,主要是也快要交毕设了,虽然不想写论文,那也得花时间去弄啊对吧,更完这篇就休息!
这篇文章需要的基础
YOLOV5目标检测记录
jetson nano上手记录
还是延续之前的思路,需要部署一个方便进行训练和检测的平台,在电脑这边训练,然后部署就在jetson nano上来进行,尽量提高jetson nano的帧率。
1、yolov5s模型转tensorrt
1、前期准备
这里需要先安装一下torch&&torchvision,这个最好还是本地下载和安装吧,相关的文件我都放到我的网盘里面了,可以根据需要下载,口令如下:
「nano工具分享」https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/hEEe9UfsXv1
点击链接保存,或者复制本段内容,打开「阿里云盘」APP ,无需下载极速在线查看,视频原画倍速播放。
下面是分享内容

安装的话torch是直接安装,torchvision是需要编译安装的,这里下载到开发板之后进行解压
unzip xxx
之后就可以进入文件夹去安装了
pip3 install numpy torch-1.8.0-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl
等一段时间安装完成,安装有报错的话一般是缺了什么,缺啥安装啥就行了
之后是安装我们的torchvision
cd torchvision
export BUILD_VERSION=0.9.0
python3 setup.py install --user
2、运行yolov5
首先还是从github上下载代码
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
这里我的库基本都装过了,不需要继续安装了,可以直接运行

运行的话它会自动下载我们需要的模型文件,之后就会检测里面的两张图片,可以看到一张基本是0.1s,还是不太行啊
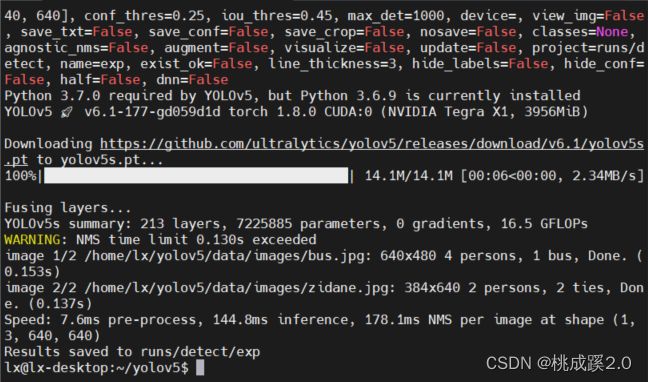
检测效果如下所示
运行过程下载我们需要的权重。
3、TensorRT加速推理
这里需要下载两个项目,这两个项目就是后面的基础了,首先是这个tensorrt的项目
git clone https://github.com/wang-xinyu/tensorrtx.git
之后是这个,如果下载失败可以多尝试几次,还是不行就直接电脑本地下载然后传过去
git clone -b v5.0 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
首先是进入tensorrts文件夹,把里面的一个pt转wts的代码复制到yolov5这个文件夹里面去,之后把我们下载好的yolov5的这个权重也复制进去,然后就可以生成wts文件了
cd tensorrtx
cp yolov5/gen_wts.py ~/yolov5
cd ~/yolov5
python3 gen_wts.py -m yolov5s.pt # 这里要事先把模型文件放到里面去
下面就是去生成模型文件然后进行推理了
cd ~/tensorrtx/yolov5
mkdir build && cd build
mv ~/yolov5/yolov5s.wts ./
cmake ..
make
这里看到下面结果就说明OK了

之后就是那我们的wts文件来生成engine文件了,并可以使用样例来进行一下测试
./yolov5 -s yolov5s.wts yolov5s.engine s #生成engine文件需要一段时间,请耐心等待
./yolov5 -d yolov5s.engine ../samples # 推理结果保存在samples文件夹下
检测输出,说实话也没什么提升,不知道视频咋样
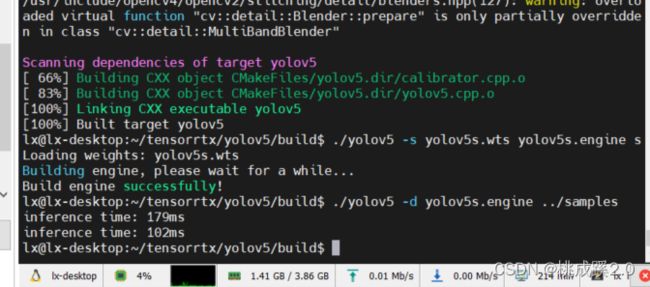
实际效果
这里有一个问题,就是之前那个官方权重必须是新版的,这里的新版是指当前时间的版本,目前是yolov5 6.1版本的,估计6.0版本的也是可以的,如果用5.0版本的肯定就不行的,会报错,报错信息如下。

这里也可以理解为一个版本对应的问题,就是他们的版本不对,不管是trt那边,还是yolo这边都需要用最新的版本,或者对应的版本才行,然后就是我们训练的pt文件都是基于一个官方的pt文件来的,所以神经网络的那些层其实就都和他一样的,所以就也没啥用的,就是源头的那个模型用不了,其他的也不能用。
4、直接使用摄像头进行部署
下面参考这位大佬的方案
https://blog.csdn.net/hahasl555/article/details/116500763
将下面的内容替换yolov5文件夹下的yolov5.cpp文件
vim yolov5.cpp
之后因为是vim编辑器,输入
#include (end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl;
int fps = 1000.0 / std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count();
std::vector<std::vector<Yolo::Detection>> batch_res(fcount);
for (int b = 0; b < fcount; b++) {
auto& res = batch_res[b];
nms(res, &prob[b * OUTPUT_SIZE], CONF_THRESH, NMS_THRESH);
}
for (int b = 0; b < fcount; b++) {
auto& res = batch_res[b];
//std::cout << res.size() << std::endl;
//cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_dir + "/" + file_names[f - fcount + 1 + b]);
for (size_t j = 0; j < res.size(); j++) {
cv::Rect r = get_rect(frame, res[j].bbox);
cv::rectangle(frame, r, cv::Scalar(0x27, 0xC1, 0x36), 2);
std::string label = my_classes[(int)res[j].class_id];
cv::putText(frame, label, cv::Point(r.x, r.y - 1), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.2, cv::Scalar(0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF), 2);
std::string jetson_fps = "Jetson Nano FPS: " + std::to_string(fps);
cv::putText(frame, jetson_fps, cv::Point(11, 80), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, cv::LINE_AA);
}
//cv::imwrite("_" + file_names[f - fcount + 1 + b], img);
}
cv::imshow("yolov5", frame);
key = cv::waitKey(1);
if (key == 'q') {
break;
}
fcount = 0;
}
capture.release();
// Release stream and buffers
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]));
CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]));
// Destroy the engine
context->destroy();
engine->destroy();
runtime->destroy();
return 0;
}
cd build
make
sudo ./yolov5 -v yolov5s.engine
就可以在看到摄像头检测的图像了
2、deepstream检测
1、下载SDK
关于DeepStream的介绍参考这篇文章
https://blog.csdn.net/Tosonw/article/details/104154090?msclkid=12bd0cf4cf6911ecb107816bf39a19e5
下面就是下载了,官方链接为
https://developer.nvidia.com/deepstream-sdk?msclkid=12bd94d8cf6911ecb9a72916005a0257
不过这个是针对jp4.6.1版本的,我这里用的不是对应的版本,所以不能下载这个
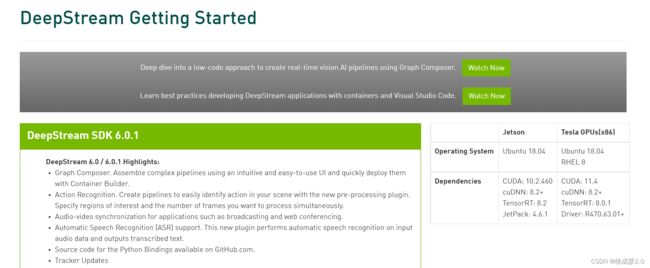
后面百度搜到了这个网站,去这里下载就可以了
https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/deepstream-on-jetson-downloads-archived
这里可以看到需要选择5.0.1版本,或者5.0版本的都可以的

这里有500多M的大小,因此决定就还是先本地下载吧
之后使用SSH远程传输到我们的jetson nano开发板上去

2、安装依赖
使用下面的命令安装所需的依赖
sudo apt-get install libssl1.0.0 libgstreamer1.0-0 gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-plugins-good gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav libgstrtspserver-1.0-0 libjansson4
sudo apt-get install libgstreamer1.0-0 gstreamer1.0-plugins-base gstreamer1.0-plugins-good gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-doc gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-x gstreamer1.0-alsa gstreamer1.0-gl gstreamer1.0-gtk3 gstreamer1.0-qt5 gstreamer1.0-pulseaudio libgstrtspserver-1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-rtsp
sudo apt-get install libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev
sudo apt-get install libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstrtspserver-1.0-dev libx11-dev libgstrtspserver-1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-rtsp ffmpeg
sudo apt-get install libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstrtspserver-1.0-dev libx11-dev libjson-glib-dev
下面对我们的安装包进行解压
sudo tar -jxvf deepstream_sdk_v5.0.1_jetson.tbz2 -C /
cd /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-5.0/
安装
sudo ./install.sh
sudo ldconfig
3、配置环境
下面需要配置下环境变量,编辑下面的文件
sudo vim /etc/ld.so.conf
在末尾加上这个,其实这个文件就一行
/opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-5.0/lib/
使我们的配置生效,退出后输入
sudo ldconfig
在将我们另一个位置配置下,就是之前配置cuda和cudnn的地方
sudo vim ~/.bashrc
在结尾处添加
unset DISPLAY
同样的使配置生效,退出后输入
source ~/.bashrc
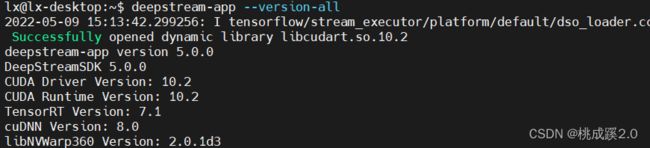
验证安装是否成功
deepstream-app --version-all
4、测试效果
下面运行下官方的demo
cd /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream
运行
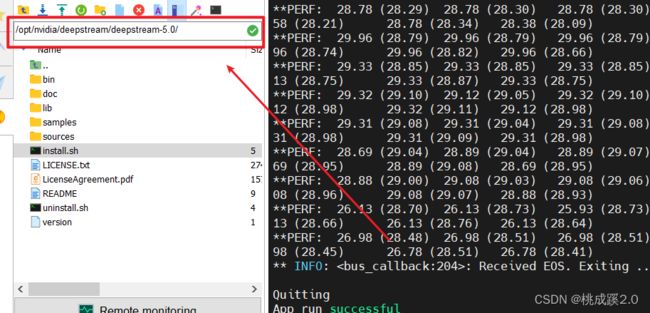
deepstream-app -c samples/configs/deepstream-app/source8_1080p_dec_infer-resnet_tracker_tiled_display_fp16_nano.txt
出现下面的输出,一个多路的视频检测

运行结束,可以看到测试成功!

3、使用deepstream进行部署
暂未尝试,试了再写
4、yolov5目前比较新的版本训练和检测
1、前期准备
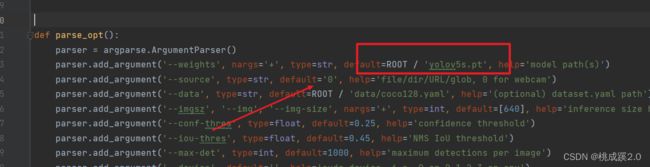
前面说到就是在部署的时候存在的新版和旧版的问题,这里干脆就看看新版怎么训练的,这样我们训练的模型就可以直接拿过去用了,首先还是修改配置文件,这里修改数量就行(复制yolovs的配置文件,因为用yolov5s来进行的训练)。
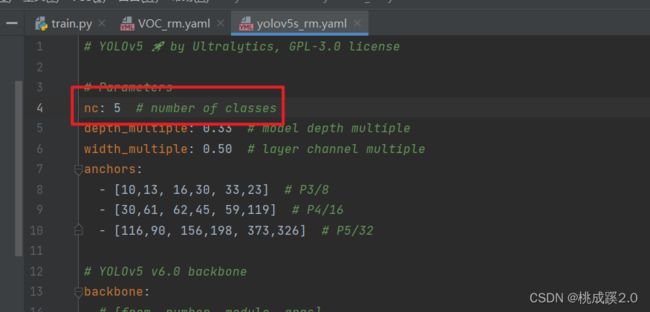
这里修改VOC文件,因为我们用的VOC的数据集,复制一份然后修改就行,加入训练集的目录还有标签。
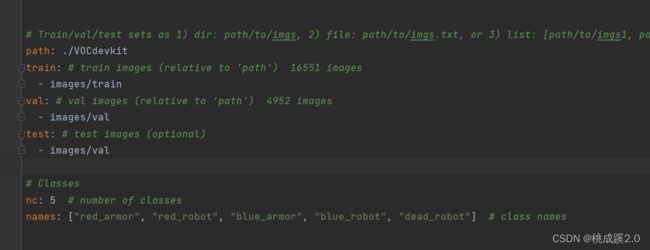
修改如下所示

准备好voc2007的数据集,如下所示

2、开始训练
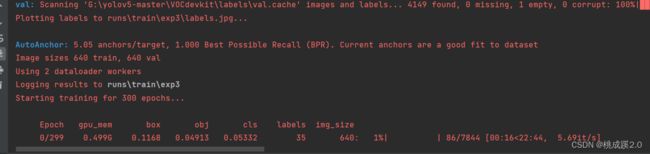
在train.py里面找到配置文件进行修改,加入我们之前的一些配置文件,这里有个一次训练的数目,不要选的太大了,选太大了容易出问题,就会提示你不够大什么的

最后就开始训练了,训练过程结果如下所示