Spring源码之启动过程(四)—— Bean的实例化详解
前面,我们把Bean的生命周期做了一个概述和梳理,为的是更深刻的理解容器启动及Bean的生命周期,最主要的是Bean的实例化过程,没有看过的,可以进去先看一下(文章链接:Spring源码之Bean的生命周期_奔跑的蜗牛_Kieasr-CSDN博客),也有助于理解本文内容,前面,我们分析了Spring容器初始化的核心方法是refresh(),方法执行原理,本章主要解析Bean的实例化过程,下面,我们进入主题:
目录
1. finishBeanFactoryInitialization()
2. preInstantiateSingletons()
3. getBean()
4. doGetBean()
5. 第一个getSingleton()
6. 第二个getSingleton()
6.1 beforeSingletonCreation()
6.2 afterSingletonCreation()
7. createBean()
9. createBeanInstance()
9.1 @Bean注解支持
9.2 有参构造方法
9.3 匹配构造方法
9.4 无参构造方法的实例化
10. applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors()
11. addSingletonFactory()
12. populateBean()
12.1 @Autowired注解的依赖注入
12.2 @Lazy注解的解析
12.3 @Resource注解的依赖注入
13. initializeBean()
13.1 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
13.2 invokeInitMethods()
13.3 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
1. finishBeanFactoryInitialization()
refresh()中其中最主要的方法就是finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory),这个方法很重要,没有之一,Bean的实例化过程就在这里:
/**
* 1、Bean实例化过程
* 2、IOC
* 3、注解支持
* 4、BeanPostProcesApplicationListenersor的执行
* 5、AOP的入口
*/
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);进入AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization () 方法:
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
* 完成这个上下文bean工厂的初始化,初始化所有剩余的单例bean。
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
// 设置类型转换器
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化所有剩余的非lazy单例。重点看这个方法,重要程度:5
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}2. preInstantiateSingletons()
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 实例化方法
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 前面的registerBeanDefinition()方法会把所有的beanName缓存到这里
List beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 在spring容器初始化时,遍历这个beanDefinitionNames,从这里拿beanDefinition的name
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 先合并BeanDefinition(如果存在parent,则合并父子BeanDefinition的属性,生成一个RootBeanDefinition)
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 如果是单例的、非抽象的、非懒加载的就实例化
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 判断bean是否实现FactoryBean接口
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 获取FactoryBean对象,创建完之后放到单例池
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction) ((SmartFactoryBean) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// SmartFactoryBean继承FactoryBean接口,有个isEagerInit()方法设置是否容器启动就创建getObject()的实例
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
// 创建真正的Bean对象(调用getObject()返回的对象)
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 再实例化(创建Bean对象)******
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// 所有的非懒加载单例Bean都创建完之后
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 从单例池中拿beanName对应的单例Bean
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction 3. getBean()
Bean实例化的条件
- 非抽象类的
- 单例的
- 非延迟加载的
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}4. doGetBean()
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory
protected T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
// 获取beanName,一种情况是FactoryBean(eg:'&xxx',那么beanName就是xxx);另一种情况:传进来的是别名,那么beanName就是id
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 去单例池拿对应的实例(第一次进来是空的)
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 如果缓存中能拿到实例,就不走else里面的代码,直接返回了
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
/**
* 该方法是FactoryBean接口的调用入口,
* 如果是普通Bean的话,直接返回sharedInstance(直接返回对象本身);
* 如果是FactoryBean的话,返回它创建的那个实例对象(返回指定方法返回的实例),
* 参数中这个name有可能加前缀&,但beanName一定没有
*/
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
// 单例池中拿不到实例进入这里
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
/**
* 处理原型模式下循环依赖,触发场景:
* 原型模式下,如果存在A中有B,B中有A,那么当依赖注入的时候,
* 就会产生创建A的时候需要实例化B,但是B的实例化又需要A,造成循环依赖。
* 如果是Scope是prototype的,校验是否出现循环依赖,是的话则直接报错
*/
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
// containsBeanDefinition()检查当前的beanName是否有对应的BeanDefinition
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
// 去父BeanFactory中拿
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
// 总结:到这里,要准备创建Bean了,对于singleton的Bean来说,容器中还没创建过此Bean;而对于prototype的Bean来说,是要创建一个新的Bean。
try {
// 父子BeanDefinition合并
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 检查BeanDefiniiton是不是Abstract的
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 获取依赖对象信息(依赖对象须先实例化)
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
// dep为依赖的对象名,判断beanName是不是被dep依赖了,如果是则出现了循环依赖
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 如果dep被beanName依赖,存入dependentBeanMap(dep为key,beanName为value)
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
// 创建所依赖的Bean*****
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
// 单例的情况
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 着重看getSingleton(),第二个参数是ObjectFactory(一个函数式接口,有个getObject()方法)
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// 当调用第二个参数的getObject()方法时,才会调用到该方法(创建实例)*****
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
// FactoryBean的调用入口,如果是,返回getObject()的实例
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 原型的情况
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
// 记录一下原型的Bean正在创建
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// 多例的情况每次都会createBean
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
// 创建完移除之前记录的标志
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
// 该方法是FactoryBean接口的调用入口,参数中这个name有可能加前缀&,但beanName一定没有&
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// Scope作用域的情况(如:request、session等情况)
else {
// registerScope()把scopeName和scope注册进去,这儿才能拿到
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean ?" + beanName + "'");
}
// Scope就是一个map
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
// 自定义Scope,就会调到自定义Scop的的get方法
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
// 把实例放到threadLocal中
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
// 如果request.getAttribute(beanName)为空,就会调用createBean()方法
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
// 检查所需类型是否与实际bean实例的类型匹配。
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
// 类型转换,转换失败,则为空,抛出异常
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
// 实例化过程结束,将bean返回
return (T) bean;
} 5. 第一个getSingleton()
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
// 获取单例Bean
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 根据beanName从缓存中拿实例,先从一级缓存拿
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果bean还正在创建,还没创建完成,其实是堆内存有了,属性还没有DI依赖注入
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 从二级缓存中拿
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果还拿不到,并且允许bean提前暴露
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 从三级缓存中拿(单例工厂)
ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 从工厂中拿到对象,第二次会调到getEarlyBeanReference()方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
// 放到二级缓存
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
// 删除三级缓存
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}在Spring的DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry类中,你会赫然发现类上方挂着这三个Map:
- singletonObjects它是我们最熟悉的朋友,俗称“单例池”、“容器”,缓存创建完成单例Bean的地方(一级缓存)。
- earlySingletonObjects映射Bean的早期引用,也就是说在这个Map里的Bean不是完整的,甚至还不能称之为“Bean”,只是一个Instance(二级缓存)。
- singletonFactories映射创建Bean的原始工厂(三级缓存)。
后两个Map其实是“垫脚石”级别的,只是创建Bean的时候,用来借助一下,创建完成就清掉了。
Spring容器中的三级缓存,是为了解决Spring 循环依赖的问题。保存在三级缓存中的Bean不是完整的Bean实例,因为Spring创建Bean的原则是:不等 Bean 创建完成就将创建Bean的 ObjectFactory 提早曝光,所以只有完整的Bean实例才会最终放到一级缓存中。
6. 第二个getSingleton()
看doGetBean()方法的第二个getSingleton():
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
// 获取单例bean,第二个参数ObjectFactory是函数式接口,它有个getObject()方法
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 如果缓存中有,则直接返回
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 记录单例Bean正在创建的标识(把beanName添加到singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中,这个容器存放的都是正在实例化的beanName)
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// 这个getObject()会调到前面的createBean()方法;如果有返回值,表示Bean创建成功(重点)
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
// 删除上面记录的标识(把beanName从singletonsCurrentlyInCreation容器中删除,表示实例化已经完成)
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
// 将创建成功的Bean放到单例池(一级缓存singletonObjects)
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}6.1 beforeSingletonCreation()
进入getSingleton()方法中的beforeSingletonCreation()方法,记录单例Bean正在创建。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
/**
* TODO 把beanName添加到singletonsCurrentlyInCreation (Set)容器中
*/
protected void beforeSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
// 在这个集合里面的bean都是正在实例化的bean,标识作用
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
}singletonsCurrentlyInCreation表示正在创建中的bean,可以理解为当前bean只是在JVM的堆内存中分配了地址,但是相关依赖属性并没有添加进来。
6.2 afterSingletonCreation()
进入getSingleton()方法中的afterSingletonCreation()方法,删除上面记录的标识,表示实例化已完成。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
protected void afterSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Singleton '" + beanName + "' isn't currently in creation");
}
}7. createBean()
回到doGetBean()方法中getSingleton()中的createBean()方法,如果是单例的情况,本来会进入getSingleton()方法,去调用singletonFactory.getObject()方法,而getObject()会调用外层Lambda表达式中实现getObject()的业务方法,即createBean()方法。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
// 马上就要实例化Bean了,确保beanClass已被加载
Class resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 实例化前
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 实例化(主要看这个)*****
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}8. doCreateBean()
这是 createBean() 的核心方法
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
// BeanWrapper是在实例化之后的对象上又做了包装
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 有可能在Bean创建之前,就是其他Bean把当前Bean创建出来了(比如依赖注入过程中)
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建实例,重点看****
// 1.实例化有@Bean注解对应的实例
// 2.实例化有@Autowired注解的有参构造函数
// 3.实例化没有@Autowired注解的有参构造函数
// 4.实例化无参构造函数
// 实例化之后堆内存中有了该实例,但是属性却是空的(一个不完整的对象)
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 从BeanWrapper中拿真正的实例对象
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
/**
* TODO CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor支持@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource注解
* AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor支持@Autowired、@Value注解
* 收集注解:对类中注解的装配过程
* 这个方法是BeanPostProcessor接口的典型运用, 重要程度5,必须看
* 收集类中有注解的属性和方法,包装成对象,并将对象加入到容器,并把容器包装成InjectionMetadata对象,并放到缓存中
* 缓存是beanName和InjectionMetadata的对应关系,然后通过这个对象可以知道哪个属性或方法上有注解,为下面的属性填充做准备
*/
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 为了解决循环依赖提前缓存单例创建工厂
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 循环依赖,添加三级缓存,即执行getEarlyBeanReference(),这里着重理解,助于理解循环依赖
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
/**
* (属性填充)IOC、DI,依赖注入的核心方法,重要程度:5,
* 主要是完成@Autowired、@Resource、xml配置方式的依赖注入,在此之前,堆内存已经有实例,只是属性为空
*/
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* (初始化)Bean实例化+IOC依赖注入完成之后执行,重要程度:5
* @PostConstruct注解方法-->InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法-->init-method属性,AOP代理对象的生成入口
*/
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
// 注册Bean销毁时的类DisposableBeanAdapter
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
} 9. createBeanInstance()
这是createBean的核心方法,分以下情况:
- 实例化factoryMethod方法对应的实例
- 实例化带有@Autowired注解的有参构造函数
- 实例化没有@Autowired注解的有参构造函数
- 实例化无参构造函数
createBeanInstance()只是将对象创建成功,在堆内存中开辟了一块空间,但对象的属性此时却为空。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
// args表示使用构造方法时传入的参数,如getBean()方法传入的参数
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 反射拿到Class对象
Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
// @Bean注解(或配置了factory-method属性)的支持
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
// 一个原型BeanDefinition会多次创建Bean,那么就可以把该BeanDefinition所要使用的构造方法缓存起来,避免每次都进行构造
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
// resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod表示BeanDefinition使用的是哪个构造方法
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
// autowireNecessary表示是否有必要进行注入,比如当前BeanDefinition用的是无参构造方法,constructorArgumentsResolved为false
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
// 如果确定了当前BeanDefinition的构造方法,则看是否需要对构造方法进行参数的依赖注入(构造方法注入)
if (autowireNecessary) {
// 该方法会拿到缓存好的构造方法入参
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
// 构造方法已找到但是没有参数,表示使用默认无参构造方法,直接进行实例化
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
// 找有@Autowired注解的有参构造函数,返回放到数组。BeanPostProcessor的应用,如果有多个构造函数,会找参数最多的
// 提供一个扩展点,可以利用SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor来控制使用beanClass中的哪个构造方法
Constructor[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
// 如果ctors有值,则需要进行构造方法注入,或AutowireMode是AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR,或BeanDefinition中添加了构造方法的参数和值,
// 或者调用getBean()方法时传入了args也会进入这里
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
// 反射实例化,返回带构造函数的实例BeanWrapper,进入autowireConstructor()方法
// 该方法就是找当前BeanDefinition用哪个构造方法,以及构造方法入参值
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
// ctors为空时进入这里,为无参构造函数的实例化,大部分是采用无参构造函数方式实例化****
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}9.1 @Bean注解支持
Spring启动时会把@Bean注解修饰的方法解析成BeanDefinition,会在ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions()方法:
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Set configurationModel) {
TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator = new TrackedConditionEvaluator();
for (ConfigurationClass configClass : configurationModel) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(configClass, trackedConditionEvaluator);
}
} 进入到本类的loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod():
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) {
ConfigurationClass configClass = beanMethod.getConfigurationClass();
MethodMetadata metadata = beanMethod.getMetadata();
String methodName = metadata.getMethodName();
// Do we need to mark the bean as skipped by its condition?
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
configClass.skippedBeanMethods.add(methodName);
return;
}
if (configClass.skippedBeanMethods.contains(methodName)) {
return;
}
AnnotationAttributes bean = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Bean.class);
Assert.state(bean != null, "No @Bean annotation attributes");
// Consider name and any aliases
List names = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(bean.getStringArray("name")));
String beanName = (!names.isEmpty() ? names.remove(0) : methodName);
// Register aliases even when overridden
for (String alias : names) {
this.registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
// Has this effectively been overridden before (e.g. via XML)?
// 存在的话就return,不会生成新的
if (isOverriddenByExistingDefinition(beanMethod, beanName)) {
if (beanName.equals(beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getBeanName())) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getResource().getDescription(),
beanName, "Bean name derived from @Bean method '" + beanMethod.getMetadata().getMethodName() +
"' clashes with bean name for containing configuration class; please make those names unique!");
}
return;
}
// 不存在则生成一个新的BeanDefinition
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition beanDef = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(configClass, metadata);
beanDef.setSource(this.sourceExtractor.extractSource(metadata, configClass.getResource()));
if (metadata.isStatic()) {
// static @Bean method
if (configClass.getMetadata() instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {
beanDef.setBeanClass(((StandardAnnotationMetadata) configClass.getMetadata()).getIntrospectedClass());
}
else {
beanDef.setBeanClassName(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);
}
else {
// instance @Bean method
beanDef.setFactoryBeanName(configClass.getBeanName());
beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);
}
if (metadata instanceof StandardMethodMetadata) {
beanDef.setResolvedFactoryMethod(((StandardMethodMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedMethod());
}
beanDef.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
beanDef.setAttribute(org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(beanDef, metadata);
Autowire autowire = bean.getEnum("autowire");
if (autowire.isAutowire()) {
beanDef.setAutowireMode(autowire.value());
}
----省略无关代码---- 这里会把加了@Bean注解的方法传进来,最终会在isOverriddenByExistingDefinition()中检查@Bean注解方法的唯一性:
protected boolean isOverriddenByExistingDefinition(BeanMethod beanMethod, String beanName) {
if (!this.registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
return false;
}
BeanDefinition existingBeanDef = this.registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 如果@Bean对应的beanName已经存在BeanDefinition,那么则把此BeanDefinition的isFactoryMethodUnique设置为false
// 后续根据此BeanDefinition取创建Bean时,就知道不止一个
if (existingBeanDef instanceof ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition) {
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition ccbd = (ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition) existingBeanDef;
if (ccbd.getMetadata().getClassName().equals(
beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata().getClassName())) {
if (ccbd.getFactoryMethodMetadata().getMethodName().equals(ccbd.getFactoryMethodName())) {
ccbd.setNonUniqueFactoryMethodName(ccbd.getFactoryMethodMetadata().getMethodName());
}
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
----省略无关代码---- 如果只有一个,则把RootBeanDefinition的isFactoryMethodUnique属性设置为true,否则为false。进入setUniqueFactoryMethodName():
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition
public void setUniqueFactoryMethodName(String name) {
Assert.hasText(name, "Factory method name must not be empty");
setFactoryMethodName(name);
this.isFactoryMethodUnique = true;
}然后,在实例化过程中在createBeanInstance()中首先会解析@Bean注解的方法:
// @Bean注解(或配置了factory-method属性)的支持
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}进入instantiateUsingFactoryMethod()方法:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
// 使用factoryBean实例化对象
return new ConstructorResolver(this).instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, explicitArgs);
}进入instantiateUsingFactoryMethod():
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver
public BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
Object factoryBean;
Class factoryClass;
boolean isStatic;
String factoryBeanName = mbd.getFactoryBeanName();
// 这里拿到的是factoryBeanName,而不是factoryMethodName,这里是非static修饰的方法
if (factoryBeanName != null) {
if (factoryBeanName.equals(beanName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"factory-bean reference points back to the same bean definition");
}
factoryBean = this.beanFactory.getBean(factoryBeanName);
if (mbd.isSingleton() && this.beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException();
}
factoryClass = factoryBean.getClass();
isStatic = false;
}
// 这里是static修饰的方法
else {
// It's a static factory method on the bean class.
if (!mbd.hasBeanClass()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"bean definition declares neither a bean class nor a factory-bean reference");
}
factoryBean = null;
factoryClass = mbd.getBeanClass();
isStatic = true;
}
Method factoryMethodToUse = null;
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
Object[] argsToUse = null;
if (explicitArgs != null) {
argsToUse = explicitArgs;
}
----后面代码和推断构造方法autowireConstructor()的逻辑基本一致---- 进入本类的instantiate()方法:
private Object instantiate(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
@Nullable Object factoryBean, Method factoryMethod, Object[] args) {
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
return AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction进入instantiate()方法:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.SimpleInstantiationStrategy
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner,
@Nullable Object factoryBean, final Method factoryMethod, Object... args) {
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction注意:如果有@Configuration注解的配置类里面存在@Bean注解的方法,在实例化执行invoke()方法时会通过代理对象执行方法,例如:
@Configuration
public class ConverterConfig {
@Bean
public UserService userService(){
kieasar();
return new UserService();
}
@Bean
public Kieasar kieasar() {
return new Kieasar();
}
}BeanMethodInterceptor是ConfigurationClassEnhancer的内部类,(代理对象)就会调用到BeanMethodInterceptor拦截器类的intercept()方法:
private static class BeanMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, ConditionalCallback {
/**
* Enhance a {@link Bean @Bean} method to check the supplied BeanFactory for the
* existence of this bean object.
* @throws Throwable as a catch-all for any exception that may be thrown when invoking the
* super implementation of the proxied method i.e., the actual {@code @Bean} method
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs,
MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable {
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(enhancedConfigInstance);
String beanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(beanMethod);
// Determine whether this bean is a scoped-proxy
if (BeanAnnotationHelper.isScopedProxy(beanMethod)) {
String scopedBeanName = ScopedProxyCreator.getTargetBeanName(beanName);
if (beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(scopedBeanName)) {
beanName = scopedBeanName;
}
}
// To handle the case of an inter-bean method reference, we must explicitly check the
// container for already cached instances.
// First, check to see if the requested bean is a FactoryBean. If so, create a subclass
// proxy that intercepts calls to getObject() and returns any cached bean instance.
// This ensures that the semantics of calling a FactoryBean from within @Bean methods
// is the same as that of referring to a FactoryBean within XML. See SPR-6602.
if (factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName) &&
factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, beanName)) {
Object factoryBean = beanFactory.getBean(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (factoryBean instanceof ScopedProxyFactoryBean) {
// Scoped proxy factory beans are a special case and should not be further proxied
}
else {
// It is a candidate FactoryBean - go ahead with enhancement
return enhanceFactoryBean(factoryBean, beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanFactory, beanName);
}
}
// 如果代理对象执行的方法是正在创建Bean的工厂方法,执行对应的方法得到对象作为Bean
if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) {
// The factory is calling the bean method in order to instantiate and register the bean
// (i.e. via a getBean() call) -> invoke the super implementation of the method to actually
// create the bean instance.
if (logger.isInfoEnabled() &&
BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) {
logger.info(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " +
"assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " +
"result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " +
"@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring " +
"@Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid " +
"these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.",
beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName()));
}
// 注意这里传入的是代理对象,相当于执行目标对象的方法
return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs);
}
// 如果代理对象正在执行的方法不是正在创建Bean的方法,那就直接根据方法的名字去Spring容器中获取(getBean()方法)
return resolveBeanReference(beanMethod, beanMethodArgs, beanFactory, beanName);
}上面的例子中,ConverterConfig的代理类在执行userService()方法会先进行判断,看是否为创建Bean的方法,如果是,则进行创建UserService的实例,相当于执行目标对象的方法,就会进入cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(),调用被代理对象的方法。
然后,代理对象接着执行userService()里面的kieasar()方法时,虽然该方法加了@Bean注解,但此时正在执行的是创建userService实例的userService()方法,所以isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod()结果为false,会执行最后一行resolveBeanReference(),执行getBean()方法,根据方法的名字kieasar去容器中获取Kieasar对象的实例。
但是,Spring在创建Kieasar这个Bean时,如果当前执行的方法正好是kieasar()方法(也就是创建Kieasar实例的方法),此时isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod()结果为true,执行cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(),即被代理对象的方法。
@Bean的解析和推断构造方法原理一样,如果isFactoryMethodUnique属性为false,表示存在多个,则取参数最多的那个。
在由@Bean生成的BeanDefinition中,有一个重要的属性isFactoryMethodUnique,表示
factoryMethod是不是唯一的,在普通情况下@Bean生成的BeanDefinition的
isFactoryMethodUnique为true,但是如果出现了方法重载,那么就是特殊的情况,比如:
@Bean
public static AService aService(){
return new AService();
}
@Bean
public AService aService(BService bService){
return new AService();
} 虽然有两个@Bean,但是肯定只会生成一个aService的Bean,那么Spring在处理@Bean时,也只会生成一个aService的BeanDefinition,比如Spring先解析到第一个@Bean,会生成一个
BeanDefinition,此时isFactoryMethodUnique为true,但是解析到第二个@Bean时,会判断出来
beanDefinitionMap中已经存在一个aService的BeanDefinition了,那么会把之前的这个
BeanDefinition的isFactoryMethodUnique修改为false,并且不会生成新的BeanDefinition了。
并且后续在根据BeanDefinition创建Bean时,会根据isFactoryMethodUnique来操作,如果为
true,那就表示当前BeanDefinition只对应了一个方法,那也就是只能用这个方法来创建Bean了,
但是如果isFactoryMethodUnique为false,那就表示当前BeanDefition对应了多个方法,需要和推
断构造方法的逻辑一样,去选择用哪个方法来创建Bean。
9.2 有参构造方法
先进入determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors() 方法,获取当前Bean对象的有参构造函数,返回一个构造函数的数组:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Constructor[] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(@Nullable Class beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 拿到 BeanPostProcessor 的所有接口,遍历
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 获取到有 @Autowired 注解信息的构造函数
Constructor[] ctors = ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null) {
return ctors;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}- getBeanPostProcessors()方法,获取所有BeanPostProcessor接口,是AbstractBeanFactory类中的一个List beanPostProcessors = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>()容器,装载了上下文中所有的BeanPostProcessor类的实例。
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor类中的determineCandidateConstructors()方法,会调用其子类 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 中的determineCandidateConstructors()方法,来获取有@Autowired注解的构造函数。AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类会完成@Autowired和@value两个注解的扫描。
我们一般使用@Autowired注解进行依赖注入,所以会进入AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors()方法:
// 完成有@Autowied注解的有参构造函数的实例化
@Override
@Nullable
public Constructor[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class beanClass, final String beanName)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Let's check for lookup methods here...
if (!this.lookupMethodsChecked.contains(beanName)) {
// 对@Lookup注解的支撑
if (AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(beanClass, Lookup.class)) {
try {
Class targetClass = beanClass;
do {
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Lookup lookup = method.getAnnotation(Lookup.class);
if (lookup != null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
// 将当前method封装成LookupOverride,并设置到BeanDefinition的methodOverrides属性中
LookupOverride override = new LookupOverride(method, lookup.value());
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = (RootBeanDefinition)
this.beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
mbd.getMethodOverrides().addOverride(override);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Cannot apply @Lookup to beans without corresponding bean definition");
}
}
});
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Lookup method resolution failed", ex);
}
}
this.lookupMethodsChecked.add(beanName);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
Constructor[] candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
// Fully synchronized resolution now...
synchronized (this.candidateConstructorsCache) {
candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
Constructor[] rawCandidates;
try {
rawCandidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
// candidates用来装构造函数
List> candidates = new ArrayList<>(rawCandidates.length);
// 用来记录required为true的构造方法,一个类中只能有一个为true的构造方法
Constructor requiredConstructor = null;
// 用来记录默认的无参构造方法
Constructor defaultConstructor = null;
// kotlin相关,不用管
Constructor primaryConstructor = BeanUtils.findPrimaryConstructor(beanClass);
int nonSyntheticConstructors = 0;
// 遍历每个构造方法
for (Constructor candidate : rawCandidates) {
if (!candidate.isSynthetic()) {
// 记录一下普通的构造方法
nonSyntheticConstructors++;
}
else if (primaryConstructor != null) {
continue;
}
// 找@Autowired注解的过程,进入findAutowiredAnnotation()****
MergedAnnotation ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(candidate);
if (ann == null) {
// 如果beanClass是代理类,获取到被代理类的类型
Class userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanClass);
if (userClass != beanClass) {
try {
Constructor superCtor =
userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(candidate.getParameterTypes());
ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(superCtor);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Simply proceed, no equivalent superclass constructor found...
}
}
}
// 不为空,表示当前构造方法上加了@Autowired注解
if (ann != null) {
// 一个类中只能有一个required为true的构造方法,不能还有其他@Autowired的构造方法,否则会报错
if (requiredConstructor != null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructor: " + candidate +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation already: " +
requiredConstructor);
}
// 拿到 @Autowired 注解的 required 属性值,如果是 true
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
if (required) {
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructors: " + candidates +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation: " +
candidate);
}
// 记录required属性为true的构造方法
requiredConstructor = candidate;
}
// 只要加了@Autowired注解,不管有无参数,requred属性为true和false,都加入到集合中
candidates.add(candidate);
}
// 表示无参构造方法
else if (candidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
defaultConstructor = candidate;
}
}
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
// Add default constructor to list of optional constructors, as fallback.
if (requiredConstructor == null) {
if (defaultConstructor != null) {
candidates.add(defaultConstructor);
}
else if (candidates.size() == 1 && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Inconsistent constructor declaration on bean with name '" + beanName +
"': single autowire-marked constructor flagged as optional - " +
"this constructor is effectively required since there is no " +
"default constructor to fall back to: " + candidates.get(0));
}
}
// 如果只有一个required为true的构造方法,那就只有中一个是合格的
candidateConstructors = candidates.toArray(new Constructor[0]);
}
// 没有添加Autowired注解的构造方法,且只有一个、且是有参的
else if (rawCandidates.length == 1 && rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor[] {rawCandidates[0]};
}
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 2 && primaryConstructor != null &&
defaultConstructor != null && !primaryConstructor.equals(defaultConstructor)) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor[] {primaryConstructor, defaultConstructor};
}
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 1 && primaryConstructor != null) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor[] {primaryConstructor};
}
else {
// 如果有多个有参、且没有@Autowired注解的构造方法,则返回空
candidateConstructors = new Constructor[0];
}
this.candidateConstructorsCache.put(beanClass, candidateConstructors);
}
}
}
return (candidateConstructors.length > 0 ? candidateConstructors : null);
} 进入findAutowiredAnnotation()方法,找@Autowired和@value注解的过程:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
private MergedAnnotation findAutowiredAnnotation(AccessibleObject ao) {
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(ao);
// autowiredAnnotationTypes里面装了@Autowired和@Value两种类型的注解,循环这两个注解
for (Class type : this.autowiredAnnotationTypes) {
MergedAnnotation annotation = annotations.get(type);
// 判断注解是否存在,存在则返回
if (annotation.isPresent()) {
return annotation;
}
}
return null;
}determineCandidateConstructors()分支比较多,主要作用就是推断构造方法,返回一个构造器的数组(一个或多个),通过一个图归纳一下:
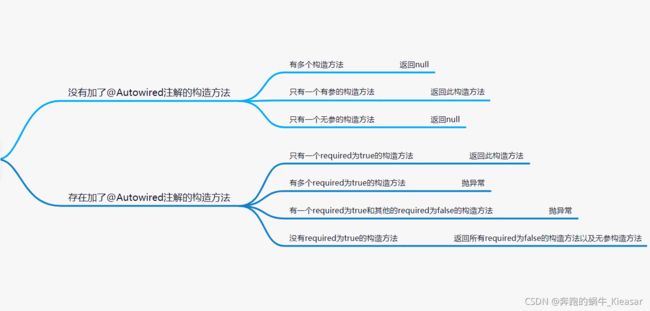
9.3 匹配构造方法
回到 createBeanInstance() 方法,找到构造方法后,Spring会选择当前BeanDefinition用哪个构造方法,进入 autowireConstructor() 方法:
protected BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Constructor[] ctors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
// 使用构造方法的实例化,进入autowireConstructor()方法
return new ConstructorResolver(this).autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, explicitArgs);
}该方法会调用到ConstructorResolver类的autowireConstructor()方法:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver
public BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
@Nullable Constructor[] chosenCtors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 选择的构造方法
Constructor constructorToUse = null;
// 构造方法的入参
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
Object[] argsToUse = null;
// explicitArgs表示getBean()方法的参数,如果有,就是构造方法的入参
if (explicitArgs != null) {
argsToUse = explicitArgs;
}
else {
Object[] argsToResolve = null;
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor) mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse != null && mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved) {
// Found a cached constructor...
argsToUse = mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments;
if (argsToUse == null) {
argsToResolve = mbd.preparedConstructorArguments;
}
}
}
if (argsToResolve != null) {
argsToUse = resolvePreparedArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, constructorToUse, argsToResolve, true);
}
}
// 如果没有对应的构造方法,或者有构造方法,但没有对应的入参
if (constructorToUse == null || argsToUse == null) {
// Take specified constructors, if any.
// 如果没有指定构造方法,则获取beanClass所有的候选构造方法
Constructor[] candidates = chosenCtors;
if (candidates == null) {
Class beanClass = mbd.getBeanClass();
try {
candidates = (mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed() ?
beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors() : beanClass.getConstructors());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
}
// 如果只有一个候选的构造方法、且没有指定入参、并且是无参的,则直接使用该无参构造进行实例化
if (candidates.length == 1 && explicitArgs == null && !mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
Constructor uniqueCandidate = candidates[0];
if (uniqueCandidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = uniqueCandidate;
mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved = true;
mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments = EMPTY_ARGS;
}
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, uniqueCandidate, EMPTY_ARGS));
return bw;
}
}
// Need to resolve the constructor.
// AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR为设置使用构造方法的模式进行初始化
boolean autowiring = (chosenCtors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
ConstructorArgumentValues resolvedValues = null;
// 确定构造方法参数个数的最小值,后续构造函数的参数个数小于minNrOfArgs,则直接pass
int minNrOfArgs;
if (explicitArgs != null) {
minNrOfArgs = explicitArgs.length;
}
else {
// 如果通过BeanDefinition传入了构造方法参数值,因为有可能是通过下标指定
ConstructorArgumentValues cargs = mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues();
resolvedValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
// 处理RuntimeBeanReference,实际上是通过getBean()方法获取Bean对象
minNrOfArgs = resolveConstructorArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, cargs, resolvedValues);
}
// 对候选构造方法进行排序,public的方法排在最前面,都是public的情况下参数越多越靠前
AutowireUtils.sortConstructors(candidates);
int minTypeDiffWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Set> ambiguousConstructors = null;
LinkedList causes = null;
// 遍历每个构造方法,进行筛选
for (Constructor candidate : candidates) {
// 参数个数
int parameterCount = candidate.getParameterCount();
// 本次遍历时,之前已经筛选出来的构造方法和参数个数,比当前的构造方法的参数个数多的话,则break
if (constructorToUse != null && argsToUse != null && argsToUse.length > parameterCount) {
// Already found greedy constructor that can be satisfied ->
// do not look any further, there are only less greedy constructors left.
break;
}
// 如果参数个数小于所要求的参数个数,则遍历下一个,(考虑了同时存在public和非public的构造方法)
if (parameterCount < minNrOfArgs) {
continue;
}
ArgumentsHolder argsHolder;
// 获取构造函数的参数类型
Class[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes();
// 没有通过getBean()指定构造方法参数值
if (resolvedValues != null) {
try {
// 如果构造方法上使用了@ConstructorProperties,那么直接取定义的值作为构造方法的参数名
String[] paramNames = ConstructorPropertiesChecker.evaluate(candidate, parameterCount);
// 获取构造方法参数名
if (paramNames == null) {
ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = this.beanFactory.getParameterNameDiscoverer();
if (pnd != null) {
paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate);
}
}
// 根据参数类型、参数名找到对应的bean对象
argsHolder = createArgumentArray(beanName, mbd, resolvedValues, bw, paramTypes, paramNames,
getUserDeclaredConstructor(candidate), autowiring, candidates.length == 1);
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
// 当前正在遍历的构造方法找不到对应的入参对象,记录一下
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Ignoring constructor [" + candidate + "] of bean '" + beanName + "': " + ex);
}
// Swallow and try next constructor.
if (causes == null) {
causes = new LinkedList<>();
}
causes.add(ex);
continue;
}
}
else {
// Explicit arguments given -> arguments length must match exactly.
if (parameterCount != explicitArgs.length) {
continue;
}
argsHolder = new ArgumentsHolder(explicitArgs);
}
// typeDiffWeight表示权重,当前遍历的构造方法所需要的入参对象找到了,根据参数类型和参数个数激素出一个权重值,值越小越匹配
int typeDiffWeight = (mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() ?
argsHolder.getTypeDifferenceWeight(paramTypes) : argsHolder.getAssignabilityWeight(paramTypes));
// Choose this constructor if it represents the closest match.
// 值越小越匹配
if (typeDiffWeight < minTypeDiffWeight) {
constructorToUse = candidate;
argsHolderToUse = argsHolder;
argsToUse = argsHolder.arguments;
minTypeDiffWeight = typeDiffWeight;
ambiguousConstructors = null;
}
// 值相等的情况下,记录一下匹配值相同的构造方法
else if (constructorToUse != null && typeDiffWeight == minTypeDiffWeight) {
if (ambiguousConstructors == null) {
ambiguousConstructors = new LinkedHashSet<>();
ambiguousConstructors.add(constructorToUse);
}
ambiguousConstructors.add(candidate);
}
}
// 循环结束
// 如果没有可用的构造方法,就取记录的最后一个异常并抛出
if (constructorToUse == null) {
if (causes != null) {
UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex = causes.removeLast();
for (Exception cause : causes) {
this.beanFactory.onSuppressedException(cause);
}
throw ex;
}
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve matching constructor " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities)");
}
// 如果有可用的构造方法,只是有多个
else if (ambiguousConstructors != null && !mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Ambiguous constructor matches found in bean '" + beanName + "' " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities): " +
ambiguousConstructors);
}
// 如果没有通过getBean()方法传入参数,并且找到了构造方法以及要用的入参对象,则缓存
if (explicitArgs == null && argsHolderToUse != null) {
argsHolderToUse.storeCache(mbd, constructorToUse);
}
}
Assert.state(argsToUse != null, "Unresolved constructor arguments");
// 确定构造方法和入参后,调用instantiate()方法进行实例化
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, constructorToUse, argsToUse));
return bw;
} ConstructorResolver类的autowireConstructor() 方法,是用来解析构造函数中的参数,最终会通过beanFactory.getBean() 方法,将参数中引用的类实例化。归纳一下:
- 先检查是否指定了具体的构造方法和构造方法参数值,或者在BeanDefinition中缓存了具体的构造方法或构造方法参数值,如果存在那么则直接使用该构造方法进行实例化;
- 如果没有确定的构造方法或构造方法参数值,那么:
- 如果没有确定的构造方法,那么则找出类中所有的构造方法;
- 如果只有一个无参的构造方法,那么直接使用无参的构造方法进行实例化;
- 如果有多个可用的构造方法或者当前Bean需要自动通过构造方法注入;
- 根据所指定的构造方法参数值,确定所需要的最少的构造方法参数值的个数;
- 对所有的构造方法进行排序,参数个数多的在前面;
- 遍历每个构造方法;
- 如果不是调用getBean方法时所指定的构造方法参数值,那么则根据构造方法参数类型找值;
- 如果时调用getBean方法时所指定的构造方法参数值,就直接利用这些值;
- 如果根据当前构造方法找到了对应的构造方法参数值,那么这个构造方法就是可用的,但是不一定这个构造方法就是最佳的,所以这里会涉及到是否有多个构造方法匹配了同样的值,这个时候就会用值和构造方法类型进行匹配程度的打分,找到一个最匹配的。
如下面的情况:(代码实例)
public void testConstruector() {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition().getBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(Teacher.class);
// 指定构造函数的入参(可以多个),前提要有对应的构造函数,Spring会找对应的构造方法,找不到则报错
beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(new Student());
beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(new Student());
beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(1, new Kieasar());
// 指定注入类型(构造器注入、根据name注入、根据类型注入)
beanDefinition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
// 指定这种方式后实例化的对象就不是最初的Bean,而是get()方法返回的对象(没卵用)
beanDefinition.setInstanceSupplier(new Supplier9.4 无参构造方法的实例化
ctors为空时表示为无参构造方法,最后会进入进入无参构造方法的实例化方法instantiateBean():
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction进入getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate()方法:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.SimpleInstantiationStrategy
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
// 判断当前BeanDefinition对应的beanClass中是否存在@Lookup注解的方法
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
// constructorToUse就是缓存的无参构造方法
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
// 如果有@Lookup注解,则生成一个代理对象
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
} 最后,我们小结一下createBeanInstance()方法的逻辑:
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中的createBeanInstance()方法会去创建一个Bean实例;
- 根据BeanDefinition加载类得到Class对象;
- 如果BeanDefinition绑定了一个Supplier,那就调用Supplier的get方法得到一个对象并直接返回;
- 如果BeanDefinition中存在factoryMethodName,那么就调用该工厂方法得到一个bean对象并返回;
- 如果BeanDefinition已经自动构造过了,那就调用autowireConstructor()自动构造一个对象;
- 调用SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的determineCandidateConstructors()方法得到哪些构造方法是可以用的;
- 如果存在可用得构造方法,或者当前BeanDefinition的autowired是AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR,或者BeanDefinition中指定了构造方法参数值,或者创建Bean的时候指定了构造方法参数值,那么就调用**autowireConstructor()**方法自动构造一个对象;
- 最后,如果不是上述情况,就根据无参的构造方法实例化一个对象。
10. applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors()
回到doCreateBean()方法,进入applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors()方法:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class beanType, String beanName) {
// 从beanFactory里拿到所有注册进去的BeanPostProcessor类型的实例
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
// postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()是钩子方法,调到对应的子类方法,收集@Autowired、@Value、@Resource、PostConstruct、@PreDestroy注解
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
} 在创建Bean的过程中,Spring会利用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的
postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()方法找出注入点并缓存,找注入点的流程为:
- 遍历当前类的所有的属性字段Field;
- 查看字段上是否存在@Autowired、@Value、@Inject中的其中任意一个,存在则认为该字段是一个注入点;
- 如果字段是static的,则不进行注入;
- 获取@Autowired中的required属性值;
- 将字段信息构造成一个AutowiredFieldElement对象,作为一个注入点对象添加到currElements集合中;
- 遍历当前类的所有方法Method;
- 判断当前Method是否是桥接方法,如果是找到原方法;
- 查看方法上是否存在@Autowired、@Value、@Inject中的其中任意一个,存在则认为该方法是一个注入点;
- 如果方法是static的,则不进行注入;
- 获取@Autowired中的required属性的值;
- 将方法信息构造成一个AutowiredMethodElement对象,作为一个注入点对象添加到currElements集合中;
- 遍历完当前类的字段和方法后,将遍历父类的,直到没有父类;
- 最后将currElements集合封装成一个InjectionMetadata对象,作为当前Bean对于的注入点集合对象,并缓存。
这里是注解的装配收集过程,由BeanPostProcessor类来处理:
首先从getBeanPostProcessors()方法的集合中拿到所有实现了BeanPostProcessor 接口的实现类,然后通过反射拿到实现类里所有属性,然后收集注解信息,主要由以下几个注解类处理:
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理@Resource 注解的解析。
- InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy 注解的解析。
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理@Autowired、@Value、@Inject(JSR-330的注解,功能和 使用方法与@Autowired相同)注解的解析。
- RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理@Required注解的解析。
接下来循环遍历包含注解元素的类以及父类,如果解析到属性上有指定注解的类(clazz),则将对应的属性元素(Field或者Method)添加到一个List elements中,然后返回new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements) ,最后把返回的InjectionMetadata放到Map injectionMetadataCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256)缓存中去,至此注解的装配收集过程全部完成。
这些注解类会调用 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()方法,以AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类为例:
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class beanType, String beanName) {
// 看findAutowiringMetadata()方法,@Autowired和@Value注解的收集过程,收集之后包装成InjectionMetadata
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}进入本类的findAutowiringMetadata() 方法:
// @Autowired和@Value注解的收集
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
// 先从缓存取,下面的代码是包装有注解的属性和方法
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// 解析注入点并缓存****
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
// TODO 收集完之后放到缓存中(beanName和InjectionMetadata的对应关系),cacheKey就是beanName
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}进入本类的buildResourceMetadata() 方法:
// 注解信息存放到 InjectionMetadata 类的具体过程
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class clazz) {
// 如果一个Bean的类型是String。。。则不需要进行依赖注入
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// 注解在属性上:反射工具类ReflectionUtils,循环类里面的field属性,然后判断属性上是否有@Autowired和@Value注解(收集过程)
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
// 回调FieldCallback.doWith()方法,MergedAnnotation封装了注解的属性
MergedAnnotation ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
// static修饰的field不是注入点,不会进行自动注入
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
// 构造注入点
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
// 把注解的required值和field包装成AutowiredFieldElement对象,并放到容器中
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
// 如果注解在方法上:对方法上的@Autowired和@Value注解进行收集
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
// set方法最好有入参
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
// 和上面的原理类似,只是包装类叫AutowiredMethodElement,包装类均继承自InjectedElement
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
// 最终把@Autowired对象的容器和Class封装成InjectionMetadata对象返回
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
} 进入本类的findAutowiredAnnotation()方法:
private MergedAnnotation findAutowiredAnnotation(AccessibleObject ao) {
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(ao);
// autowiredAnnotationTypes里面装了@Autowired和@Value两种类型的注解,循环这两个注解
for (Class type : this.autowiredAnnotationTypes) {
MergedAnnotation annotation = annotations.get(type);
// 判断注解是否存在,存在则返回
if (annotation.isPresent()) {
return annotation;
}
}
return null;
}11. addSingletonFactory()
回到 doCreateBean() 方法,进入 addSingletonFactory() 方法
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
/**
* TODO 循环依赖的解决方案,添加到三级缓存
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
// 添加到三级缓存
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}12. populateBean()
这也是doCreateBean() 中一个灰常重要的方法,IOC、DI依赖注入的核心方法。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
// IOC、DI,依赖注入的核心方法*****
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 实例化之后,属性设置之前调用。这里postProcessAfterInstantiation()可以控制让所有类都不能依赖注入
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 所有的bean都会进入这段代码
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
// MutablePropertyValues是PropertyValues的具体实现类
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
// 重点看这个if代码块,重要程度:5
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 依赖注入过程,处理@Autowired、@Resource、@Value注解(重要程度:5)*****
// 会调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor或CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类的postProcessProperties()方法
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
// 老版本用这个完成依赖注入
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 如果当前Bean的BeanDefinition中设置了PropertyValue,则最终是PropertyValue中的值,覆盖@Autowired注入
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}如果依赖注入的构造函数中的参数是引用类型,那么会触发 getBean() 方法进行引用类型的实例化。
12.1 @Autowired注解的依赖注入
@Autowired注解可以写在:
- 属性上:先根据属性类型去找Bean,如果找到多个再根据属性名确定一个
- 构造方法上:先根据方法参数类型去找Bean,如果找到多个再根据参数名确定一个
- set方法上:先根据方法参数类型去找Bean,如果找到多个再根据参数名确定一个
postProcessProperties() 方法是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的方法,这个方法很重要,主要处理@Autowired、@Resource、@Value注解的解析。
@Autowired注解由AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类负责解析,进入postProcessProperties():
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// 主要看这个findAutowiringMetadata()方法,之前已经将收集好的注解放到缓存,直接取上就可以了
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 找到注入点后进行依赖注入*****
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}进入 inject() 方法:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata
// 循环调用有注解依赖的元素的方法
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
// 收集到有注解的方法和属性集合
Collection checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
// 遍历每个注入点进行依赖注入(element表示前面收集到的属性或方法的封装类)
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
// 属性的依赖注入:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement.inject()、
// 方法的依赖注入:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredMethodElement.inject()
// 直接进来是处理@Resource注解的注入
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
} inject()方法为钩子方法,先看属性的依赖注入,AutowiredFieldElement.inject()方法,AutowiredFieldElement是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类,负责属性的依赖注入。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement
// 属性依赖注入
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
// 判断是否有缓存
if (this.cached) {
// 对于原型Bean,第一次创建时cached为false,注入完之后为true;第二次创建时,先找注入点(此时会拿到缓存好的注入点),也就是AutowiredFieldElement对象,此时cache为true,会进入这里
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
// 根据属性值field获取Bean对象*****
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
// 注册beanName依赖了autowiredBeanNames
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
// 构造一个ShortcutDependencyDescriptor作为缓存,保存当前field所匹配的autowiredBeanName
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
// 属性的依赖注入通过反射赋值
// 方法的依赖注入通过method.invoke(bean, arguments)实现
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
} // 获取Bean对象
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
// 用来获取方法的参数名称
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
// 参数的类型是Optiinal
if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
// 参数的类型是ObjectFactory或ObjectProvider
else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||
ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new Jsr330Factory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else {
// 如果属性或set方法上使用@Lazy注解,则创建一个代理对象,在真正调用时通过TargetSource获取到目标对象去调用方法
// 会调用ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver.buildLazyResolutionProxy()方法
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
if (result == null) {
// descriptor表示某个属性或某个set方法,requestingBeanName表示正在进行依赖注入的Bean
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
} 这个过程就是,一个有@Autowired注解的属性需要依赖注入,刚进来没有缓存,就会根据属性的名称找到Bean对象,然后把Bean的名称缓存起来;如果其他地方需要注入,进来该方法,就会直接从缓存中获取到beanName,然后getBean()的到Bean对象。
再看方法的依赖注入,AutowiredMethodElement.inject()方法,AutowiredMethodElement是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类,负责方法的依赖注入。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredMethodElement
// 方法的依赖注入
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
// 如果pvs中已经有当前注入点的值了,则跳过注入
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();
arguments = new Object[argumentCount];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[argumentCount];
Set autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(argumentCount);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
// 遍历每个方法参数,找到匹配的Bean对象
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
// 通过方法参数和下标构造出依赖描述符
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
// 根据方法的入参获取Bean*****
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (arguments != null) {
DependencyDescriptor[] cachedMethodArguments = Arrays.copyOf(descriptors, arguments.length);
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeans);
if (autowiredBeans.size() == argumentCount) {
Iterator it = autowiredBeans.iterator();
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
String autowiredBeanName = it.next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i])) {
cachedMethodArguments[i] = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
descriptors[i], autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i]);
}
}
}
this.cachedMethodArguments = cachedMethodArguments;
}
else {
this.cachedMethodArguments = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
// method的依赖注入通过method.invoke(bean, arguments)赋值
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
} 依赖注入的过程,拿到收集到的方法和属性的集合,field属性和method方法分别通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类AutowiredFieldElement.inject() 方法 和AutowiredMethodElement.inject() 方法,通过反射的方式最后完成依赖注入。
12.2 @Lazy注解的解析
Spring容器在启动时仅会加载单例、非懒加载的Bean,所以IOC容器并不会提前解析好@Lazy注解,只有在IOC依赖注入过程中,在DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveDependency()方法中,如果属性或set方法上使用@Lazy注解,则创建一个代理对象,在真正调用时通过TargetSource获取到目标对象去调用方法,会调用ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver.buildLazyResolutionProxy()方法:
// 判断是否依赖注入@Autowired+@Lazy,如果是则在注入时先生成一个代理对象注入给属性
public Object getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName) {
return (isLazy(descriptor) ? buildLazyResolutionProxy(descriptor, beanName) : null);
}就是通过isLazy()方法来判断当前依赖项是否是一个懒加载的:
protected boolean isLazy(DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
// 判断属性注解
for (Annotation ann : descriptor.getAnnotations()) {
Lazy lazy = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(ann, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {
return true;
}
}
// 判断方法参数(PS:在一个没有任何参数的方法上添加@Lazy注解是无效的)
MethodParameter methodParam = descriptor.getMethodParameter();
if (methodParam != null) {
Method method = methodParam.getMethod();
if (method == null || void.class == method.getReturnType()) {
Lazy lazy = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(methodParam.getAnnotatedElement(), Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}如果该方法返回true,则调用buildLazyResolutionProxy方法,会创建一个代理对象:
protected Object buildLazyResolutionProxy(final DependencyDescriptor descriptor, final @Nullable String beanName) {
Assert.state(getBeanFactory() instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory,
"BeanFactory needs to be a DefaultListableBeanFactory");
final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) getBeanFactory();
TargetSource ts = new TargetSource() {
@Override
public Class getTargetClass() {
return descriptor.getDependencyType();
}
@Override
public boolean isStatic() {
return false;
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
Object target = beanFactory.doResolveDependency(descriptor, beanName, null, null);
if (target == null) {
Class type = getTargetClass();
if (Map.class == type) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
else if (List.class == type) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
else if (Set.class == type || Collection.class == type) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(descriptor.getResolvableType(),
"Optional dependency not present for lazy injection point");
}
return target;
}
@Override
public void releaseTarget(Object target) {
}
};
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.setTargetSource(ts);
Class dependencyType = descriptor.getDependencyType();
if (dependencyType.isInterface()) {
pf.addInterface(dependencyType);
}
// 创建一个代理对象
return pf.getProxy(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader());
}buildLazyResolutionProxy()方法创建了一个TargetSource对象,该对象持有了依赖描述符以及beanName和DefaultListableBeanFactory引用,然后通过ProxyFactory来为该对象创建一个代理对象,返回该代理对象。(Spring AOP也是通过ProxyFactory来创建代理对象,后面在AOP中会详谈)
程序执行到了CglibAopProxy内部类DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的intercept方法,调用了TargetSource的getTarget方法,会执行到在ContextAannotationAutowireCandidateResolver的buildLazyResolutionProxy()方法中创建的TargetSource匿名内部类的getTarget()方法。这时候才会通过BeanFactory实例的doResolveDependency()方法真正的去解析依赖。
经过以上处理后,当Bean的依赖注入完成后,其属性注入的实际上是一个使用JDK动态代理或者CGLIB创建出来的代理对象,只有用户去调用目标对象的方法时,才会触发去真正完成依赖解析。
12.3 @Resource注解的依赖注入
进入CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties()方法:
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
} private InjectionMetadata findResourceMetadata(String beanName, final Class clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// 找注入点,即有@Resource注解的属性和方法
metadata = buildResourceMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
} private InjectionMetadata buildResourceMetadata(final Class clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, resourceAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List currElements = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(field, field, null));
}
else if (ejbClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(field, field, null));
}
// 看属性上是否有@Resource注解
else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(field.getType().getName())) {
// 封装成ResourceElement对象,也就是注入点
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(field, field, null));
}
}
});
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
if (method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (ejbClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
// 看方法上是否有@Resource注解
else if (bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(paramTypes[0].getName())) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
// 封装成ResourceElement对象,也就是注入点
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
} 我们看ResourceElement的构造方法:
private class ResourceElement extends LookupElement {
private final boolean lazyLookup;
public ResourceElement(Member member, AnnotatedElement ae, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {
super(member, pd);
Resource resource = ae.getAnnotation(Resource.class);
String resourceName = resource.name();
Class resourceType = resource.type();
// 使用@Resource没有配置name属性,则使用field的name,或setXxx()中的xxx
this.isDefaultName = !StringUtils.hasLength(resourceName);
if (this.isDefaultName) {
resourceName = this.member.getName();
if (this.member instanceof Method && resourceName.startsWith("set") && resourceName.length() > 3) {
// resourceName就是注入点需要注入的beanName
resourceName = Introspector.decapitalize(resourceName.substring(3));
}
}
// 使用@Resource时配置了name属性,进行占位符填充
else if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {
resourceName = embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(resourceName);
}
// @Resource除了设置name属性,还可以设置type,type默认为Object类型
if (Object.class != resourceType) {
// 如果指定了type,则判断是否和字段的类型、方法的参数类型是否相同
checkResourceType(resourceType);
}
else {
// No resource type specified... check field/method.
resourceType = getResourceType();
}
this.name = (resourceName != null ? resourceName : "");
this.lookupType = resourceType;
String lookupValue = resource.lookup();
this.mappedName = (StringUtils.hasLength(lookupValue) ? lookupValue : resource.mappedName());
Lazy lazy = ae.getAnnotation(Lazy.class);
this.lazyLookup = (lazy != null && lazy.value());
}
// 如果有@Lazy注解,进行属性注入时,构造代理对象,然后注入到属性或方法
@Override
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
return (this.lazyLookup ? buildLazyResourceProxy(this, requestingBeanName) :
getResource(this, requestingBeanName));
}
}
进入getResourceToInject()的getResource()方法:
所属类:org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
protected Object getResource(LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(element.mappedName)) {
return this.jndiFactory.getBean(element.mappedName, element.lookupType);
}
if (this.alwaysUseJndiLookup) {
return this.jndiFactory.getBean(element.name, element.lookupType);
}
if (this.resourceFactory == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.lookupType,
"No resource factory configured - specify the 'resourceFactory' property");
}
// 根据LookupElement从BeanFactory找到适合的Bean对象
return autowireResource(this.resourceFactory, element, requestingBeanName);
}进入本类的autowireResource()方法:
protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
Object resource;
Set autowiredBeanNames;
String name = element.name;
if (factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) factory;
DependencyDescriptor descriptor = element.getDependencyDescriptor();
// 解析@Resource找Bean的过程,resource就是获取到的Bean对象。如果@Resource没有指定name,则根据属性名找对应的Bean
// 总之,@Resource注解先byName,再byType
if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName && !factory.containsBean(name)) {
autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 根据类型找Bean
resource = beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);
if (resource == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.getLookupType(), "No resolvable resource object");
}
}
// 如果根据名称能找到对应的Bean对象,则进入这里,getBean()方法
else {
resource = beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
}
else {
resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
if (factory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) factory;
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
if (requestingBeanName != null && beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, requestingBeanName);
}
}
}
return resource;
}
进入resolveDependency()方法根据属性类型获取Bean对象:
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
// 用来获取方法的参数名称
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
// 参数的类型是Optiinal
if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
// 参数的类型是ObjectFactory或ObjectProvider
else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||
ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new Jsr330Factory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else {
// 如果属性或set方法上使用@Lazy注解,则创建一个代理对象,在真正调用时通过TargetSource获取到目标对象去调用方法
// 会调用ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver.buildLazyResolutionProxy()方法
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
if (result == null) {
// descriptor表示某个属性或某个set方法,requestingBeanName表示正在进行依赖注入的Bean
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
} 进入本类的doResolveDependency()方法:
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
// 如果当前descriptor之前已经依赖注入,则可以直接取shortcut(相当于缓存)
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
Class type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
// 获取@Vlaue指定的值,进入QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver.getSuggestedValue()方法
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
// 占位符填充(${})
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
// 解析Spring表达式(#{})
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
// 获取类型转化器,将Vlaue转化为descriptor对应的类型
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
// 如果descriptor所对应的类型是数组、Map,就获取descriptor类型所匹配的所有Bean对象
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
// 找到所有Bean,key是beanName、value可能是Bean对象,也可能是beanClass
Map matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
// required为true,抛异常
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
// 根据类型找到多个Bean,进一步筛选出某一个,@Primary-->优先级最高-->name
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
// 记录匹配过的beanName
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
// 有可能筛选出来的是某个bean的类型,此处进行实例化,调用getBean()方法
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
} 我们通过一个图总结一下@Resource的注入过程:
13. initializeBean()
回到doCreateBean()法,这个方法是Bean实例化 + IOC依赖注入完以后的调用,init-method属性和initializingBean接口方法afterPropertiesSet()调用,@PostConstruct注解方法调用,以及AOP代理对象的生成入口。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction13.1 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
/**
* TODO 初始化之前对BeanPostProcessor的处理
*/
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
/*
* TODO 着重看几个
* 1、ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:对某个Aware接口方法的调用
* 2、InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:@PostConstruct注解方法的调用
* 3、ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor:对ImportAware类型实例setImportMetadata调用
* 这个对理解springboot有很大帮助
*/
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 调用各种Aware接口实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法
// 被@Component注解修饰的事件监听在ApplicationListenerDetector中加入到Spring容器中
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}13.2 invokeInitMethods()
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
/**
* TODO 初始化方法
*/
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
// 如果当前 bean 是 InitializingBean 的实例
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 判断是否打开了安全管理器
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction在这里,说一下InitializingBean 接口的作用:
- 如果需要在一个类实例化以后去做一些事情,那么可以实现InitializingBean接口;比如Redis缓存预热、Eureka注册中心的注册、Dubbo注册中心的注册、Mybatis里的xml解析等也是通过实现InitializingBean接口来完成的。
- BeanNameAware接口的特点:获取bean名称,实现BeanNameAware接口,可以通过setBeanName(String name),得到子类的bean名称。
@PostConstruct、InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()、xml的int-method方法,这三个调用时序是依次的,功能一样,都是在bean实例化之后调用。
13.3 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
回到initializeBean()方法,进入applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()方法,这是创建代理实例,用BeanPostProcessor接口完成代理实例的生成,AOP的入口也在这。
所属类:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
// AOP的入口
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 一些validate的框架都是在这调用的
// 被@Component注解修饰的事件监听在ApplicationListenerDetector中加入到Spring容器中
// AOP的埋点入口->进入AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}到此,Spring中Bean的实例化和依赖注入、初始化的流程都执行完毕,下面用一个流程图来加深一下印象,将整个流程串起来: