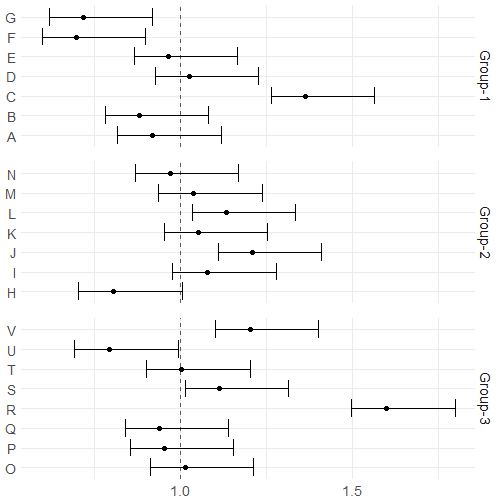R语言画森林图方法4
获取更多R语言知识,请关注公众号:医学和生信笔记
医学和生信笔记,专注R语言在临床医学中的使用,R语言数据分析和可视化。主要分享R语言做医学统计学、meta分析、网络药理学、临床预测模型、机器学习、生物信息学等。
文章目录
-
- ggplot2
- ggforestplot
今天继续学习使用R语言画森林图!
前面学习了2种通用方法,1种可视化模型的方法,今天学习使用ggplot2和ggforestplot画森林图!
不过我不喜欢,我还是最喜欢前两种通用的方法,美观,通用!
数就是图,图就是数!
ggplot2
先编造一个数据。
library(tibble)
options(digits = 2)
df <- tibble(
label = LETTERS[1:22],
mean = rnorm(22,mean = 1, sd=0.2),
lower = mean - 0.1,
upper = mean + 0.2,
group = c(rep("Group-1",7),rep("Group-2",7),rep("Group-3",8))
)
df
## # A tibble: 22 x 5
## label mean lower upper group
##
## 1 A 0.917 0.817 1.12 Group-1
## 2 B 0.880 0.780 1.08 Group-1
## 3 C 1.36 1.26 1.56 Group-1
## 4 D 1.03 0.926 1.23 Group-1
## 5 E 0.965 0.865 1.17 Group-1
## 6 F 0.697 0.597 0.897 Group-1
## 7 G 0.718 0.618 0.918 Group-1
## 8 H 0.804 0.704 1.00 Group-2
## 9 I 1.08 0.977 1.28 Group-2
## 10 J 1.21 1.11 1.41 Group-2
## # ... with 12 more rows
加载R包
library(ggplot2)
画图!
p <- ggplot(data = df)+
geom_point(aes(x=mean,y=label),size = 2)+
geom_errorbar(aes(x = mean,y=label,xmin=lower,xmax=upper))+
geom_vline(xintercept = 1, color = "black",linetype="dashed",alpha=0.6)+
labs(x=NULL,y=NULL)+
facet_grid(group ~.,scales = "free",space = "free")+
theme_minimal()+
theme(text=element_text(size=18, color="black"))+
theme(panel.spacing = unit(1, "lines"))
p
这就是一个简单的森林图了,你可以添加各种映射改变颜色和大小形状等。对于森林图中的文字部分可以通过geom_text添加。
不过确实不太好看的样子!
# 保存
ggsave(filename = "ggplot_forestplot.png",height = 26,width = 18,units = "cm")
ggforestplot
这个包是基于ggplot2系列的,看似优雅,但是颜值画出来总感觉颜值不高。
# 目前只能通过github安装
devtools::install_github("NightingaleHealth/ggforestplot")
library(ggforestplot)
library(tidyverse)
## -- Attaching packages ----------------------------- tidyverse 1.3.1 --
## v tidyr 1.2.0 v dplyr 1.0.7
## v readr 2.1.1 v stringr 1.4.0
## v purrr 0.3.4 v forcats 0.5.1
## -- Conflicts -------------------------------- tidyverse_conflicts() --
## x dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## x dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
# 筛选部分数据
df <-
ggforestplot::df_linear_associations %>%
filter(
trait == "BMI",
dplyr::row_number() <= 30
)
df
## # A tibble: 30 x 5
## name trait beta se pvalue
##
## 1 Isoleucine BMI 0.339 0.00945 1.11e-281
## 2 Leucine BMI 0.343 0.00951 1.25e-285
## 3 Valine BMI 0.287 0.00951 7.94e-200
## 4 Phenylalanine BMI 0.343 0.00862 0
## 5 Tyrosine BMI 0.261 0.00900 6.65e-185
## 6 Alanine BMI 0.179 0.00890 8.62e- 90
## 7 Glutamine BMI -0.134 0.00945 7.68e- 46
## 8 Glycine BMI -0.0296 0.00937 1.56e- 3
## 9 Histidine BMI 0.0364 0.00917 7.25e- 5
## 10 Lactate BMI 0.131 0.00911 9.20e- 47
## # ... with 20 more rows
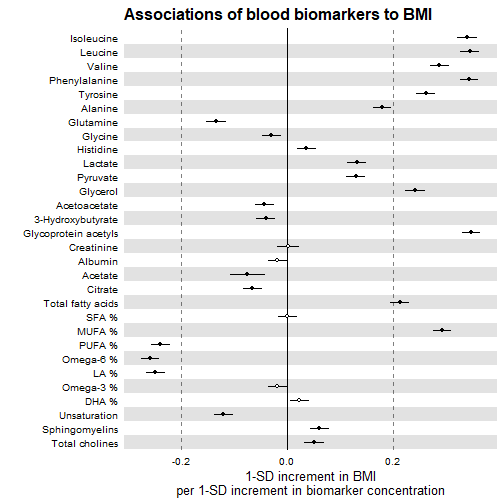
基本画图,只需要几个参数即可:
ggforestplot::forestplot(
df = df,
name = name,
estimate = beta,
se = se,
pvalue = pvalue,
psignif = 0.002, # 显著性阈值
xlab = "1-SD increment in BMI\nper 1-SD increment in biomarker concentration",
title = "Associations of blood biomarkers to BMI"
)
下面是一个多组的。
# 数据准备
selected_bmrs <- df %>% pull(name)
df_compare_traits <-
ggforestplot::df_linear_associations %>%
filter(name %in% selected_bmrs) %>%
# Set class to factor to set order of display.
mutate(
trait = factor(
trait,
levels = c("BMI", "HOMA-IR", "Fasting glucose")
)
)
画图:
# 画图ggforestplot::forestplot( df = df_compare_traits, estimate = beta, pvalue = pvalue, psignif = 0.002, xlab = "1-SD increment in cardiometabolic trait\nper 1-SD increment in biomarker concentration", title = "Biomarker associations to metabolic traits", colour = trait)
森林图一共介绍了4种,还有一种生存分析的森林图没用,因为太简单了!直接ggforest(model)就解决了,而且如果你能提取出数据,用前两种方法完全可以搞定。
获取更多R语言知识,请关注公众号:医学和生信笔记
医学和生信笔记,专注R语言在临床医学中的使用,R语言数据分析和可视化。主要分享R语言做医学统计学、meta分析、网络药理学、临床预测模型、机器学习、生物信息学等。