LTE上行链路反馈MCS(计算MCS、调制阶数、编码速率、频谱效率关系表格)
计算MCS、调制阶数、编码速率、频谱效率关系表格
参考网址:http://4g-lte-world.blogspot.tw/2012/12/transport-block-size-code-rate-protocol.html
参考网址:http://blog.richliu.com/2013/10/22/1545/
(1)前提:
因此,efficiency可简化为下式:
TBS=传输块的大小(表7.1.7.2.1-1)
CRC=附加的用于检错的比特数量=24
RE=分给PDSCH或PUSCH信道的Resource elaments数量(认为全部RE中,有90%用于共享信道)
Bits per RE=调制阶数
(2)举例
若eNB根据CQI分配该PUSCH传输的配置为:MCS index=20,2个RB。则有:
1)表7.1.7.1-1,TBS index=18
2)表7.1.7.2.1-1 计算TBS(传输块大小,单位bits)
3)计算code rate
Bits per RE=调制阶数=(MCS index=20)6阶=6
4)计算efficiency
(3)
计算RB数=12时,MCS
对应表
| MCS index |
modulation |
code rate×1024 |
efficiency |
| 0 |
QPSK |
99.329806 |
0.194003527 |
| 1 |
QPSK |
126.4197531 |
0.24691358 |
| 2 |
QPSK |
153.5097002 |
0.299823633 |
| 3 |
QPSK |
198.659612 |
0.388007055 |
| 4 |
QPSK |
243.8095238 |
0.476190476 |
| 5 |
QPSK |
297.989418 |
0.582010582 |
| 6 |
QPSK |
352.1693122 |
0.687830688 |
| 7 |
QPSK |
424.4091711 |
0.828924162 |
| 8 |
QPSK |
478.5890653 |
0.934744268 |
| 9 |
QPSK |
532.7689594 |
1.040564374 |
| 10 |
16QAM |
266.3844797 |
1.040564374 |
| 11 |
16QAM |
297.989418 |
1.164021164 |
| 12 |
16QAM |
343.1393298 |
1.340388007 |
| 13 |
16QAM |
388.2892416 |
1.51675485 |
| 14 |
16QAM |
442.4691358 |
1.728395062 |
| 15 |
16QAM |
496.64903 |
1.940035273 |
| 16 |
16QAM |
514.7089947 |
2.010582011 |
| 17 |
64QAM |
343.1393298 |
2.010582011 |
| 18 |
64QAM |
367.2192828 |
2.151675485 |
| 19 |
64QAM |
415.3791887 |
2.433862434 |
| 20 |
64QAM |
451.4991182 |
2.645502646 |
| 21 |
64QAM |
487.6190476 |
2.857142857 |
| 22 |
64QAM |
523.7389771 |
3.068783069 |
| 23 |
64QAM |
565.8788948 |
3.315696649 |
| 24 |
64QAM |
609.5238095 |
3.571428571 |
| 25 |
64QAM |
657.6837155 |
3.85361552 |
| 26 |
64QAM |
681.7636684 |
3.994708995 |
| 27 |
64QAM |
705.8436214 |
4.135802469 |
| 28 |
64QAM |
826.2433862 |
4.841269841
|
参考文章附于此处
(1)CQI and MCS
LTE UE 會使用 CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) 動態調整 MCS 以降低傳輸錯誤率.
UE 測量 PRB (Physical Resource Block)的接收功率和干擾得到 SINR 值, 在 BLER 值不超過 10%. 將測量值轉換成 CQI. eNodeB 會根據 CQI 值選擇最合適的 MCS.
CQI 報告是由 eNodeB 主動發起, 可以是定時或是不定時.
不同的 CQI Index 有不同的 Code Rate.
如下表
| CQI |
Modulation |
Bits/Symbol |
REs/PRB |
N_RB |
MCS |
TBS |
Code Rate |
| 1 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
0 |
536 |
0.101449 |
| 2 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
0 |
536 |
0.101449 |
| 3 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
2 |
872 |
0.162319 |
| 4 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
5 |
1736 |
0.318841 |
| 5 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
7 |
2417 |
0.442210 |
| 6 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
9 |
3112 |
0.568116 |
| 7 |
16QAM |
4 |
138 |
20 |
12 |
4008 |
0.365217 |
| 8 |
16QAM |
4 |
138 |
20 |
14 |
5160 |
0.469565 |
| 9 |
16QAM |
4 |
138 |
20 |
16 |
6200 |
0.563768 |
| 10 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
20 |
7992 |
0.484058 |
| 11 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
23 |
9912 |
0.600000 |
| 12 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
25 |
11448 |
0.692754 |
| 13 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
27 |
12576 |
0.760870 |
| 14 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
28 |
14688 |
0.888406 |
| 15 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
28 |
14688 |
0.88840 |
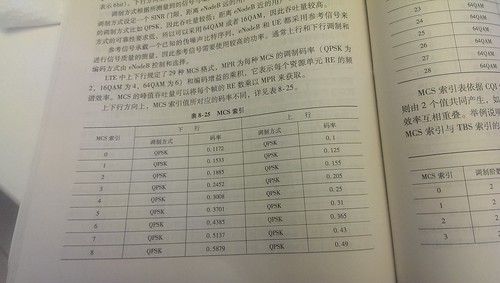
MCS
Table 7.1.7.1-1: Modulation and TBS index table for PDSCH
| MCS Index | Modulation Order | TBS Index |
| 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 |
| 7 | 2 | 7 |
| 8 | 2 | 8 |
| 9 | 2 | 9 |
| 10 | 4 | 9 |
| 11 | 4 |
10 |
| 12 | 4 | 11 |
| 13 | 4 | 12 |
| 14 | 4 | 13 |
| 15 | 4 | 14 |
| 16 | 4 | 15 |
| 17 | 6 | 15 |
| 18 | 6 | 16 |
| 19 | 6 | 17 |
| 20 | 6 | 18 |
| 21 | 6 | 19 |
| 22 | 6 | 20 |
| 23 | 6 | 21 |
| 24 | 6 | 22 |
| 25 | 6 | 23 |
| 26 | 6 | 24 |
| 27 | 6 | 25 |
| 28 | 6 | 26 |
| 29 | 2 | reserved |
| 30 | 4 | |
| 31 | 6 |
TBS Index (部份)
Table 7.1.7.2.1-1: Transport block size table (dimension 27×110)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| 0 |
16 |
32 |
56 |
88 |
120 |
152 |
176 |
208 |
224 |
256 |
| 1 |
24 |
56 |
88 |
144 |
176 |
208 |
224 |
256 |
328 |
344 |
| 2 |
32 |
72 |
144 |
176 |
208 |
256 |
296 |
328 |
376 |
424 |
| 3 |
40 |
104 |
176 |
208 |
256 |
328 |
392 |
440 |
504 |
568 |
| 4 |
56 |
120 |
208 |
256 |
328 |
408 |
488 |
552 |
632 |
696 |
| 5 |
72 |
144 |
224 |
328 |
424 |
504 |
600 |
680 |
776 |
872 |
| 6 |
328 |
176 |
256 |
392 |
504 |
600 |
712 |
808 |
936 |
1032 |
| 7 |
104 |
224 |
328 |
472 |
584 |
712 |
840 |
968 |
1096 |
1224 |
| 8 |
120 |
256 |
392 |
536 |
680 |
808 |
968 |
1096 |
1256 |
1384 |
| 9 |
136 |
296 |
456 |
616 |
776 |
936 |
1096 |
1256 |
1416 |
1544 |
| 10 |
144 |
328 |
504 |
680 |
872 |
1032 |
1224 |
1384 |
1544 |
1736 |
| 11 |
176 |
376 |
584 |
776 |
1000 |
1192 |
1384 |
1608 |
1800 |
2024 |
| 12 |
208 |
440 |
680 |
904 |
1128 |
1352 |
1608 |
1800 |
2024 |
2280 |
| 13 |
224 |
488 |
744 |
1000 |
1256 |
1544 |
1800 |
2024 |
2280 |
2536 |
| 14 |
256 |
552 |
840 |
1128 |
1416 |
1736 |
1992 |
2280 |
2600 |
2856 |
| 15 |
280 |
600 |
904 |
1224 |
1544 |
1800 |
2152 |
2472 |
2728 |
3112 |
| 16 |
328 |
632 |
968 |
1288 |
1608 |
1928 |
2280 |
2600 |
2984 |
3240 |
| 17 |
336 |
696 |
1064 |
1416 |
1800 |
2152 |
2536 |
2856 |
3240 |
3624 |
| 18 |
376 |
776 |
1160 |
1544 |
1992 |
2344 |
2792 |
3112 |
3624 |
4008 |
| 19 |
408 |
840 |
1288 |
1736 |
2152 |
2600 |
2984 |
3496 |
3880 |
4264 |
| 20 |
440 |
904 |
1384 |
1864 |
2344 |
2792 |
3240 |
3752 |
4136 |
4584 |
| 21 |
488 |
1000 |
1480 |
1992 |
2472 |
2984 |
3496 |
4008 |
4584 |
4968 |
| 22 |
520 |
1064 |
1608 |
2152 |
2664 |
3240 |
3752 |
4264 |
4776 |
5352 |
| 23 |
552 |
1128 |
1736 |
2280 |
2856 |
3496 |
4008 |
4584 |
5160 |
5736 |
| 24 |
584 |
1192 |
1800 |
2408 |
2984 |
3624 |
4264 |
4968 |
5544 |
5992 |
| 25 |
616 |
1256 |
1864 |
2536 |
3112 |
3752 |
4392 |
5160 |
5736 |
6200 |
| 26 |
712 |
1480 |
2216 |
2984 |
3752 |
4392 |
5160 |
5992 |
6712 |
7480 |
依公式
Transport block size is 776 bits for ITBS = 18 and NPRB=2
code rate = (TBS + CRC) / (RE x Bits per RE)
code rate = (776 + 24) / (302 * 6 ) = 0.4
詳情請見
http://4g-lte-world.blogspot.tw/2012/12/transport-block-size-code-rate-protocol.html
Ref.
3GPP 36.213 : 最主要的 Document.
http://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_CQI.html
(2)Transport Block Size and Code rate
Since the size of transport block is not fixed, often a question comes to mind as to how transport block size is calculated in LTE.
Back Ground
If we only consider "Uplink direction" and we assume that the UE is already attached to the network, then data is first received by PDCP (Packet data compression protocol) layer. This layer performs compression and ciphering / integrity if applicable. This layer will pass on the data to the next layer i.e. RLC Layer which will concatenate it to one RLC PDU.
RLC layer will concatenate or segment the data coming from PDCP layer into correct block size and forward it to the MAC layer with its own header. Now MAC layer selects the modulation and coding scheme configures the physical layer. The data is now in the shape of transport block size and needed to be transmitted in 1ms subframe.
Transport Block size
Now from the Table 7.1.7.2.1-1 the value of Transport block size is 776 bits for ITBS = 18 and NPRB=
Code Rate
In simple words, code rate can be defined as how effectively data can be transmitted in 1ms transport block or in other words, it is the ratio of actual amount of bits transmitted to the maximum amount of bits that could be transmitted in one transport block
code rate = (TBS + CRC) / (RE x Bits per RE)
where
TBS = Transport block size as we calculated from Table 7.1.7.2.1-1
CRC = Cyclic redundancy check i.e. Number of bits appended for error detection
RE = Resource elements assigned to PDSCH or PUSCH
Bits per RE = Modulation scheme used
While we know the values of TBS, CRC and bits per RE (modulation order), it is not easy to calculate the exact amount of RE used for PDSCH or PUSCH since some of the REs are also used by control channels like PDCCH, PHICH etc
In our case, lets assume that 10% of RE's are assigned for control channels then
TBS = 776
CRC = 24
RE = 2 (RB) x 12 (subcarriers) x 7 (assuming 7 ofdm symbols) x 2 (slots per subframe) x 0.9 (10% assumption as above) = 302 REs
Bits per RE = 6 (Modulation order from table 7.1.7.1-1)
So
code rate = (776 + 24) / (302 * 6 ) = 0.4