STL的常用算法-查找 (20221130)
STL的常用算法
概述:
算法主要是由头文件
二、查找算法
find
find_if //按条件查找元素
adjacent_find //查找相邻重复元素
binary_search //二分查找法
count //统计元素个数
count_if //按条件统计元素个数
1、find
find(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
//按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器
beg:开始迭代器
end:结束迭代器
value :查找的元素
查找自定义数据类型时报错:
error C2678: 二进制“==”: 没有找到接受“Person”类型的左操作数的运算符(或没有可接受的转换)
对自定义数据类型进行查找时,需要重载==,使底层知道如何对比
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include
#include
class Person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
//对自定义数据类型进行查找时,需要重载==,使底层知道如何对比
bool operator==(const Person&p) //避免修改 加const
{
if (p.m_name == this->m_name&&p.m_age == this->m_age)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
void test01()
{
//find
//查找内置数据类型
vectorV1;
V1.push_back(10);
V1.push_back(20);
V1.push_back(0);
V1.push_back(80);
vector::iterator pos = find(V1.begin(), V1.end(), 5); //查找是否存在5
if (pos != V1.end())
{
cout << "存在元素" << *pos << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到元素" << endl;//输出未找到元素
}
//查找自定义数据类型
vectorP;
//创建对象
Person p1("张三", 10);
Person p2("张位", 20);
Person p3("张益达", 30);
Person p4("张国伟", 50);
P.push_back(p1);
P.push_back(p2);
P.push_back(p3);
P.push_back(p4);
vector::iterator it = find(P.begin(), P.end(), p2); //查找是否存在5
if (it != P.end())
{
cout << "找到该人物" << "姓名:"<m_name<< " 年龄:"<m_age<m_name << " 年龄:" << it->m_age << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到该人" << endl;//输出未找到元素
}
}
2、find_if
find_if(iterator beg,iterator end,_Pred);
//按条件查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器
beg:开始迭代器
end:结束迭代器
_Pred:函数或谓词
class Person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
//对自定义数据类型进行查找时,需要重载==,使底层知道如何对比
bool operator==(const Person&p) //避免修改 加const
{
if (p.m_name == this->m_name&&p.m_age == this->m_age)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
class GreaterFive {
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
class AgeGreater {
public:
bool operator()(const Person&p)
{
return p.m_age > 20;
}
};
void test02()
{
//find_if
//查找内置数据类型
vectorV1;
V1.push_back(10);
V1.push_back(20);
V1.push_back(0);
V1.push_back(80);
vector::iterator pos = find_if(V1.begin(), V1.end(), GreaterFive()); //查找大于5的数 GreaterFive()匿名函数
if (pos != V1.end())
{
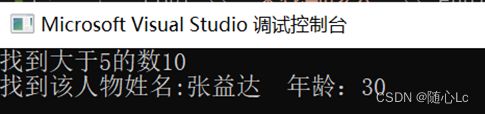
cout << "找到大于5的数" << *pos << endl;//输出第一个大于5的数 10
}
else
{
cout << "未找到元素" << endl;//输出未找到元素
}
//查找自定义数据类型
vectorP;
//创建对象
Person p1("张三", 10);
Person p2("张位", 20);
Person p3("张益达", 30);
Person p4("张国伟", 50);
P.push_back(p1);
P.push_back(p2);
P.push_back(p3);
P.push_back(p4);
vector::iterator it = find_if(P.begin(), P.end(), AgeGreater()); //查找是否存在年龄大于20的人
if (it != P.end())
{
cout << "找到该人物" << "姓名:" << it->m_name << " 年龄:" << it->m_age << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到该人" << endl;
}
} 3、adjacent_find(iterator beg,iterator end)
查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个元素的迭代器
void test03()
{
//adjacent_find
//查找内置数据类型
vectorV1;
V1.push_back(10);
V1.push_back(20);
V1.push_back(0);
V1.push_back(80);
V1.push_back(80);
vector::iterator pos = adjacent_find(V1.begin(), V1.end()); //查找大于5的数 GreaterFive()匿名函数
if (pos != V1.end())
{
cout << "找到相邻元素" << *pos << endl; //80
}
else
{
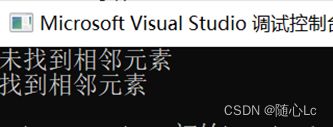
cout << "未找到相邻元素" << endl;
}
//查找自定义数据类型
vectorP;
//创建对象
Person p1("张三", 10);
Person p2("张位", 20);
Person p3("张益达", 30);
Person p4("张国伟", 50);
Person p5("张国伟", 50);
P.push_back(p1);
P.push_back(p2);
P.push_back(p3);
P.push_back(p4);
P.push_back(p5);
vector::iterator it = adjacent_find(P.begin(), P.end()); //查找是否存在信息相同的人
if (it != P.end())
{
cout << "找到该人物" << "姓名:" << it->m_name << " 年龄:" << it->m_age << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到该人" << endl;
}
}
4、binary_search
查找指定元素是否存在 底层为二分法查询;
bool binary_search(iterator beg,iterator end,value)
value:查找的元素
若指定元素查到则返回true,否则返回false
注意:在无序序列中不可用;若为无序序列,则可能找到,可能找不到,结果不准确。
void test04()
{
vectorV1;
V1.push_back(10);
V1.push_back(20);
V1.push_back(0);
V1.push_back(80);
V1.push_back(80);
bool flag = binary_search(V1.begin(), V1.end(),10); //此时序列为无序 结果不准确 打印出:未找到相邻元素
if (flag==true)
{
cout << "找到相邻元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到相邻元素" << endl;
}
vectorV2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
V2.push_back(i);
}
flag = binary_search(V2.begin(), V2.end(), 9);//为有序序列,可以找到该元素
if (flag == true)
{
cout << "找到相邻元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到相邻元素" << endl;
}
}
5、count
统计元素个数
函数原型:
count(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
value:统计的元素
class Person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
//对自定义数据类型进行统计时,需要重载==,使底层知道如何对比
bool operator==(const Person&p) //避免修改 加const
{
if (p.m_age == this->m_age)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
void test05()
{
//count
//统计内置数据类型
vectorV1;
V1.push_back(10);
V1.push_back(20);
V1.push_back(0);
V1.push_back(80);
V1.push_back(80);
int num = count(V1.begin(), V1.end(),80);
cout << "80的个数为" << num << endl; //2
//统计自定义数据类型
vectorP;
//创建对象
Person p1("张三", 10);
Person p2("张伟", 20);
Person p3("张益达", 30);
Person p4("张国伟", 50);
Person p5("张国伟", 50);
P.push_back(p1);
P.push_back(p2);
P.push_back(p3);
P.push_back(p4);
P.push_back(p5);
Person p("张哈哈", 50);
//统计与张哈哈年龄相同的人的个数 此时需要重载== ,即重新定义如何判等
int PersonNum =count(P.begin(), P.end(),p);
cout << "与张哈哈年龄相同人数为"<< PersonNum << endl;
}
6、count_if
按条件统计元素个数
count(iterator beg,iterator end,_Pred);
与count的区别为将统计value换为谓词
class Greater20 {
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 20;
}
};
class Age20 {
public:
bool operator()(const Person &p)
{
return p.m_age > 20;
}
};
void test06()
{
//count_if
//统计内置数据类型
vectorV1;
V1.push_back(10);
V1.push_back(20);
V1.push_back(0);
V1.push_back(80);
V1.push_back(80);
int num = count_if(V1.begin(), V1.end(), Greater20()); // Greater20()为匿名对象
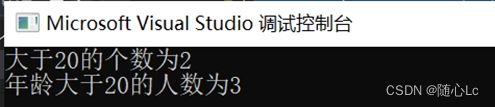
cout << "大于20的个数为" << num << endl; // 2
//统计自定义数据类型
vectorP;
//创建对象
Person p1("张三", 10);
Person p2("张伟", 20);
Person p3("张益达", 30);
Person p4("张国伟", 50);
Person p5("张国伟", 50);
P.push_back(p1);
P.push_back(p2);
P.push_back(p3);
P.push_back(p4);
P.push_back(p5);
//统计年龄大于20的人数
int PersonNum = count_if(P.begin(), P.end(), Age20());
cout << "年龄大于20的人数为" << PersonNum << endl; //3
}