脑电EEG代码开源分享 【3.可视化分析-任务态篇】
往期文章
希望了解更多的道友点这里
0. 分享【脑机接口 + 人工智能】的学习之路
1.1 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【1.前置准备-静息态篇】
1.2 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【1.前置准备-任务态篇】
2.1 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【2.预处理-静息态篇】
2.2 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【2.预处理-任务态篇】
3.1 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【3.可视化分析-静息态篇】
3.2 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【3.可视化分析-任务态篇】
4.1 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【4.特征提取-时域篇】
4.2 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【4.特征提取-频域篇】
4.3 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【4.特征提取-时频域篇】
4.4 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【4.特征提取-空域篇】
5 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【5.特征选择】
6.1 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【6.分类模型-机器学习篇】
6.2 . 脑电EEG代码开源分享 【6.分类模型-深度学习篇】
汇总. 专栏:脑电EEG代码开源分享【文档+代码+经验】
0 . 【深度学习】常用网络总结
脑电EEG代码开源分享 【3.可视化分析-任务态篇】
- 往期文章
- 一、前言
- 二、可视化 框架介绍
- 三、代码格式说明
- 三、脑电处理 代码
-
- 3.0 参数设置
- 3.1 标准输入赋值
- 3.2 可视化
-
- 3.2.1 可视化-时域
- 3.2.2 可视化-频域
- 3.2.3 可视化-空域
- 四、可视化 整体代码
- 总结
- To:新想法、鬼点子的道友:
一、前言
本文档旨在归纳BCI-EEG-matlab的数据处理代码,作为EEG数据处理的总结,方便快速搭建处理框架的Baseline,实现自动化、模块插拔化、快速化。本文以任务态(锁时刺激,如快速序列视觉呈现)为例,分享脑电EEG的分析处理方法。
脑电数据分析系列。分为以下6个模块:
- 前置准备
- 数据预处理
- 数据可视化
- 特征提取(特征候选集)
- 特征选择(量化特征择优)
- 分类模型
本文内容:【3. 数据可视化】
提示:以下为各功能代码详细介绍,若节约阅读时间,请下滑至文末的整合代码
二、可视化 框架介绍
可视化的主要功能,分为以下3部分:
- 时域波形
- 频域能谱
- 空域能量(脑地形图)
任务态可视化的代码框图、流程如下所示:
![]()
脑电信号可视化有助于对处理数据综合信息的掌握,是最直观了解数据状态的方法
同时,可视化应注重多维度、多角度分析,从不同特征域对数据进行全面了解
本文将脑电数据可视化紧邻预处理之后,放置于特征提取之前,就是为了最快速了解脑电数据情况,
同时为下一阶段的特征提取 及 分类器设计提供参考。
-
时域可视化:
脑电作为脑成像手段中时间分辨率最佳的方式,常用脑电设备采样率普遍突破1000Hz,毫秒级的采样频次可以快速记录大脑神经元放电,因此时序的分析是脑电的长板。
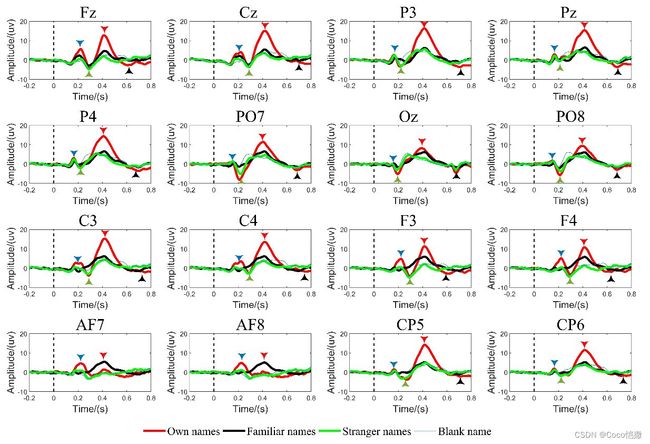
脑电信号采集后的最原始格式就是 通道数 x 时间点数 的数组,时域的时序信号是对脑电数据最直观的分析。时域可视化时任务态脑电重要观测内容,时序任务态信号最显著特点在于具有 刺激时刻(marker,triger),以刺激时间对齐并进行多试次(例如N次)叠加,理论上可将噪声降低N倍(我记得随机信号上课推导过)。由于脑电信号的低信噪比,通常采用叠加多试次的脑电信号提升数据质量。脑电随机性随着多试次的叠加在时序幅值中相互抵消,此时可以观测到单试次不易发现的重要脑电成分。例如下图任务态时域叠加信号中,不同颜色箭头标记了重要脑电成分,蓝色箭头代表3200成分,绿色箭头代表N250成分,红色箭头代表P300成分,黑色箭头代表LN(Late negativity, 晚期负性)成分。前文提到过脑电背景信号幅值在100uv,时序脑电重要成分一般在15uv以下,有效成分只占背景噪声的10%,因此如果未叠加而使用单试次信号观测是很难发现的。
以下结果来源于我做实验中对信号质量严格的要求,脑电成分才能接近20uv,一般实验中幅值不到10uv是很正常的,不仅取决于主试的要求,对环境控制、被试引导、仪器调控都是有关的。下一步会增加对脑电实验准备、采集、调试的文章。
任务态时域可视化:
-
频域可视化:
任务态信号在频域也有很多分析要点,下图展示了视觉任务刺激信号的叠加频域图,可以看到主要能量集中在10Hz,甚至5Hz以下,说明任务态脑电有效成分位于低频,从上图的P300、LN等成分的也可以看出,在1秒内大致也就1-2个周期,对应的频率就是0.5-1Hz。但从频域中也能看到不同刺激的差异性,例如红色代表自身姓名的视觉刺激 远高于 黑线和绿线代表的他人姓名,验证了时域中自身姓名的成分幅值能量也高于他人姓名。
目前研究将频域重要性略低于时域。个人认为主要原因在以下3点:1.有时间锚点的任务态叠加信号,频域重要信息在0-30Hz,常用脑电的5频带分析中高于30Hz的节律匮乏,小于静息态类长时研究的0-80Hz区间。 2.任务态刺激时长一般较短,测试的是被试瞬间的脑响应,因此刺激之后记录不会时间太长,若仅记录刺激后1秒的脑响应数据,按数字信号处理所讲的频率分辨率为1Hz,而静息态类尝试信号对几分钟甚至几小时的数据进行傅里叶变换,频率分辨率可达到0.01Hz甚至0.0001Hz。3.任务态信号的频率能量95%更集中在低频,而一般应用的去除肌电、心电伪迹的高通滤波器过渡带在0.01-1Hz,即使>1Hz的频带附近也有强烈的带内抖动(滤波导致的畸变),使得本集中在低频的任务态频域受滤波器影响较大。
任务态频域可视化:

-
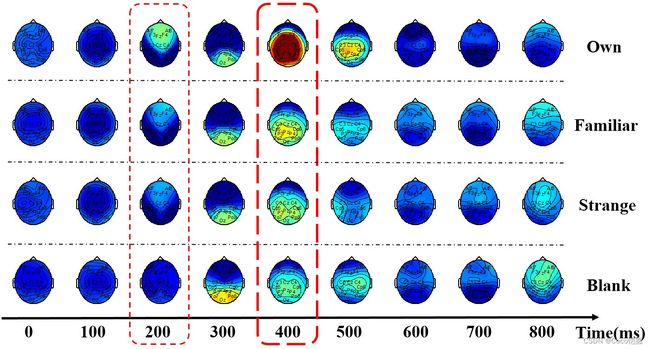
空域可视化:
任务态脑电的时空图是可视化分析中最全面的。前文提到任务态重要的特征是刺激锚点的锁时,一般以刺激开始时刻为起始,每隔0.1s绘制一幅脑电时域的空间能量分布图,可以观察脑区对刺激随时间变化的激活。同时结合时域信号可视化,可进一步分析不同脑电成分的诱发脑区。例如下午展示不同姓名视觉刺激的大脑响应,可以看出在200ms,自身姓名在额叶的激活强度就高于其他姓名,最大的差异出现在400ms,自身姓名在中央区、顶叶的激活强度远高于其他姓名的激活,对应时域可追溯P300信号是此时脑相应差异的主要成分。
大脑运行的重要特点是 多脑区协同,意思是大脑运转时时刻刻需要多个脑区的 协作和交流。脑电通过在头皮上放置大量的电极以高密度采集脑响应,通过整合电极采集的脑信号,可以绘制出大脑能量的空间分布图。
任务态空域可视化(时空地形图):
三、代码格式说明
本文任务态范例为:大脑对自身、非自身视觉刺激的认知模式分类
- **代码名称:**代码命名为Analysis_task_XXX( time\ freq\ space)
- **输入格式:**输入格式承接上阶段预处理结果文件 Proprocess_target_XX。
- **输出及保存格式:**输出为各特征域的可视化图像,代码未进行统一的图像保存,操作人员可按需求手动存储。
三、脑电处理 代码
提示:代码环境为 matlab 2018
3.0 参数设置
可视化内容可以选择,把希望可视化特征域写在analysis_content中
- 可视化内容: analysis_content=[‘time’,‘freq_mean’,‘map’]; 时域、频域、空域均分析
- 是否绘图:plot_para = [‘time’,‘freq’,‘space’]; 时域、频域、空域均绘图
- 一次进行10人次的批处理,subject_num = [1;10]
- 时域可选择使用global power方式,用方差作为权重叠加信号,本代码使用普通求均值方式,mean_para = [‘simple_mean’];
- 线宽为1:line_size = 1;
- 字体大小5:text_size = 5;
- 频域绘图横轴 1-30Hz:freq_axis = [1;30];
- 空域地形图每隔0.1秒画一张图,一行画9个,space_axis = [0:0.1:0.8];
- 空域地形图不标记电极位置:space_label = ‘off’;
%% 0.标准数据参数设置
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
data_path = 'C:\Users\Amax\Desktop\basetest_flod\save_fold\';
svae_path = 'C:\Users\Amax\Desktop\basetest_flod\save_fold\';
channel_name_path = 'F:\机制分析-128导\channel_name_128';
channel_loc_path = 'C:\Users\Amax\Desktop\ZRK_BCI_code_Summary\channel_122_loc_2d.txt';
analysis_content = ['time_mean\','freq_mean\','map\'];
plot_para = ['time\','freq\','space\'];
% mean_para = ['simple_mean\','zscore_baseline\'];
mean_para = ['simple_mean\'];
subject_num = [1 ; 10];
line_size = 1;
text_size = 5;
freq_axis = [1;30];
space_axis = [0:0.1:0.8];
space_label = 'off';
disp(['||任务态数据分析中...||']);
disp(['被试量: ' , num2str(subject_num(1,1)),'-',num2str(subject_num(2,1))]);
disp(['是否绘图: ' , num2str(plot_para)]);
disp(['绘图参数: ' , mean_para]);
disp(['频谱绘制范围: ' , num2str(freq_axis(1,1)),'-',num2str(freq_axis(2,1))]);
disp(['地形图绘制范围: ' , num2str(space_axis)]);
disp(['线条宽度:' , num2str(line_size),' ||字体大小:' , num2str(text_size)]);
3.1 标准输入赋值
导入上一步预处理-静息态阶段处理后的数据:
%% 1.标准输入赋值
disp(['||预处理后数据加载中...||']);
Proprocess_target_file = load([data_path ,'Proprocess_target_',num2str(subject_num(1,1)),'_',num2str(subject_num(2,1))]);
Proprocess_nontarget_file = load([data_path ,'Proprocess_nontarget_',num2str(subject_num(1,1)),'_',num2str(subject_num(2,1))]);
stuct_target_name = 'Proprocess_target';
stuct_nontarget_name = 'Proprocess_nontarget';
Proprocess_target_data = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).data;
Proprocess_nontarget_data = Proprocess_nontarget_file.(stuct_nontarget_name).data;
subject_num = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).subject_num;
fs_down = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).fs_down;
remain_trial_target = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).remain_trial;
remain_trial_nontarget = Proprocess_nontarget_file.(stuct_nontarget_name).remain_trial;
Baseline_reference = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).Baseline_reference ;
disp(['目标试次剩余: ' , num2str(remain_trial_target),'||平均: ', num2str(mean(remain_trial_target)),'||剩余比例: ',num2str(mean(remain_trial_target)/size(Proprocess_target_data,1))]);
disp(['非目标试次剩余: ' , num2str(remain_trial_nontarget),'||平均: ', num2str(mean(remain_trial_nontarget)),'||剩余比例: ',num2str(mean(remain_trial_nontarget)/size(Proprocess_nontarget_data,1))]);
3.2 可视化
3.2.1 可视化-时域
主体调用函数Analysis_task_time
%% 2.时域分析
disp(['||时域分析加载中...||']);
[time_target]= Analysis_task_time(Proprocess_target_data,fs_down,Baseline_reference,remain_trial_target,mean_para);
[time_nontarget]= Analysis_task_time(Proprocess_nontarget_data,fs_down,Baseline_reference,remain_trial_nontarget,mean_para);
%绘图
if contains(plot_para,'time')
load (channel_name_path);
Analysis_time_plot(time_target,time_nontarget,fs_down,Baseline_reference,channel_name,line_size,text_size)
end
主功能函数 Analysis_task_time:
function [time_analysis_out]= Analysis_task_time(Standard_input_data,fs_down,Baseline_reference,remain_trial,mean_para)
%% 1.时域均值计算
time_analysis_out = cell(1,1);
channel_mean_raw = zeros(size(Standard_input_data{1,1},1),size(Standard_input_data{1,1},2));
for channel_loop = 1:size(Standard_input_data{1,1},1)
temp_data = [];
for subject_loop = 1:size(Standard_input_data,2)
for trial_loop = 1:remain_trial(1,subject_loop)
temp_data = [temp_data ; Standard_input_data{trial_loop,subject_loop}(channel_loop,:)];
end
end
channel_mean_raw(channel_loop,:) = mean(temp_data);
end
time_analysis_out{1,1} = channel_mean_raw; %必有普通均值的选项,是最基础的分析
if contains(mean_para,'zscore_baseline')
channel_std = std(channel_mean_raw(:,1:round(fs_down * Baseline_reference(2)))');
time_analysis_out{2,1} = {time_analysis_out ;channel_mean_raw./channel_std'};
end
end
时域可视化绘图函数 Analysis_time_plot:
function Analysis_time_plot(time_target,time_nontarget,fs_down,Baseline_reference,channel_name,line_size,text_size)
figure('name','time-simple_mean');
x = (0:1/fs_down:size(time_target{1,1},2)/fs_down-1/fs_down) - Baseline_reference(2);
sub_axis_x = ceil(sqrt(size(time_target{1,1},1)));
sub_axis_y = ceil(size(time_target{1,1},1)/sub_axis_x);
for plot_loop = 1:size(time_target{1,1},1)
subplot(sub_axis_x,sub_axis_y,plot_loop);
plot(x,time_target{1,1}(plot_loop,:),'r','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
plot(x,time_nontarget{1,1}(plot_loop,:),'b','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
title([channel_name{1,plot_loop}, ' 第' num2str(plot_loop), '导联'], 'Fontsize',text_size);
hold on;
max_y = max([time_nontarget{1,1}(plot_loop,:) time_target{1,1}(plot_loop,:)]);
min_y = min([time_nontarget{1,1}(plot_loop,:) time_target{1,1}(plot_loop,:)]);
Dotted_line=plot([0,0],[min_y,max_y],'--k','LineWidth',1);
set(Dotted_line,'handlevisibility','off');
xlabel('Time/(s)', 'Fontsize',text_size);
ylabel('Amplitude/(uv)','Fontsize',text_size);
end
if size(time_target,1)>1
figure('name','time-zcore');
x = (0:1/fs_down:size(time_target{2,1},2)/fs_down-1/fs_down) - Baseline_reference(2);
sub_axis_x = ceil(sqrt(size(time_target{2,1},1)));
sub_axis_y = ceil(size(time_target{2,1},1)/sub_axis_x);
for plot_loop = 1:size(time_target{2,1},1)
subplot(sub_axis_x,sub_axis_y,plot_loop);
plot(x,time_target{2,1}(plot_loop,:),'r','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
plot(x,time_nontarget{2,1}(plot_loop,:),'b','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
title([channel_name{1,plot_loop}, ' 第' num2str(plot_loop), '导联'], 'Fontsize',text_size);
hold on;
max_y = max([time_nontarget{2,1}(plot_loop,:) time_target{2,1}(plot_loop,:)]);
min_y = min([time_nontarget{2,1}(plot_loop,:) time_target{2,1}(plot_loop,:)]);
Dotted_line=plot([0,0],[min_y,max_y],'--k','LineWidth',1);
set(Dotted_line,'handlevisibility','off');
xlabel('Time/(s)', 'Fontsize',text_size);
ylabel('Amplitude/(uv)','Fontsize',text_size);
end
end
end
3.2.2 可视化-频域
主体调用函数Analysis_task_freq
%% 3.频域分析
disp(['||频域分析加载中...||']);
% 注:fft使用采样率作为参数,因此频谱分辨率为1hz
[freq_target]= Analysis_task_freq(time_target,fs_down);
[freq_nontarget]= Analysis_task_freq(time_nontarget,fs_down);
%绘图
if contains(plot_para,'freq')
load (channel_name_path);
Analysis_freq_plot(freq_target,freq_nontarget,fs_down,channel_name,freq_axis,line_size,text_size)
end
主功能函数 Analysis_task_freq:
function [freq_analysis_out]= Analysis_task_freq(Standard_input_data,fs_down)
%% 1.频域均值计算
freq_analysis_out = [];
channel_mean_raw = [];
for channel_loop = 1:size(Standard_input_data{1,1},1)
temp_data = [];
temp_data = abs(fft(Standard_input_data{1,1}(channel_loop,:),fs_down));
channel_mean_raw(channel_loop,:) = temp_data(1,1:round(fs_down/2));
end
freq_analysis_out = channel_mean_raw; %必有普通均值的选项,是最基础的分析
channel_mean_raw = zeros(size(Standard_input_data{1,1},1),size(Standard_input_data{1,1},2));
if size(Standard_input_data,1)>1
channel_mean_raw = [];
for channel_loop = 1:size(Standard_input_data{2,1},1)
temp_data = [];
temp_data = abs(fft(Standard_input_data{2,1}(channel_loop,:),fs_down));
channel_mean_raw(channel_loop,:) = temp_data(1,1:round(fs_down/2));
end
freq_analysis_out = {freq_analysis_out ; channel_mean_raw};
end
end
频域绘图函数Analysis_freq_plot:
function Analysis_freq_plot(freq_target,freq_nontarget,fs_down,channel_name,freq_axis,line_size,text_size,freq_draw_log)
figure('name','freq-simple_mean');
x = freq_axis(1):1:freq_axis(2);
sub_axis_x = ceil(sqrt(size(freq_target{1,1},1)));
sub_axis_y = ceil(size(freq_target{1,1},1)/sub_axis_x);
for plot_loop = 1:size(freq_target{1,1},1)
subplot(sub_axis_x,sub_axis_y,plot_loop);
if freq_draw_log == 0
plot(x,freq_target{1,1}(plot_loop,freq_axis(1):freq_axis(2)),'r','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
plot(x,freq_nontarget{1,1}(plot_loop,freq_axis(1):freq_axis(2)),'b','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
end
if freq_draw_log == 1
semilogy(x,freq_target{1,1}(plot_loop,freq_axis(1):freq_axis(2)),'r','LineWidth',line_size)
hold on;
semilogy(x,freq_nontarget{1,1}(plot_loop,freq_axis(1):freq_axis(2)),'b','LineWidth',line_size)
hold on;
end
title([channel_name{1,plot_loop}, ' 第' num2str(plot_loop), '导联'], 'Fontsize',text_size);
hold on;
xlabel('freq/(s)', 'Fontsize',text_size);
ylabel('Amplitude/(uv)','Fontsize',text_size);
end
if size(freq_target,1)>1
figure('name','freq-zcore');
x = freq_axis(1):1:freq_axis(2);
sub_axis_x = ceil(sqrt(size(freq_target{1,1},1)));
sub_axis_y = ceil(size(freq_target{1,1},1)/sub_axis_x);
for plot_loop = 1:size(freq_target{2,1},1)
subplot(sub_axis_x,sub_axis_y,plot_loop);
plot(x,freq_target{2,1}(plot_loop,freq_axis(1):freq_axis(2)),'r','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
plot(x,freq_nontarget{2,1}(plot_loop,freq_axis(1):freq_axis(2)),'b','LineWidth',line_size);
hold on;
title([channel_name{1,plot_loop}, ' 第' num2str(plot_loop), '导联'], 'Fontsize',text_size);
hold on;
xlabel('freq/(s)', 'Fontsize',text_size);
ylabel('Amplitude/(uv)','Fontsize',text_size);
end
end
end
3.2.3 可视化-空域
主体调用函数Analysis_time_space_plot
%% 4.空域分析 脑地形图
disp(['||空域分析加载中...||']);
if contains(plot_para,'space')
Analysis_time_space_plot(time_target,time_nontarget,channel_loc_path,fs_down,space_axis,space_label)
end
空域绘图函数Analysis_time_space_plot:
function Analysis_time_space_plot(time_target,time_nontarget,channel_loc_path,fs_down,space_axis,space_label)
figure();
sub_axis = size(space_axis,2);
clim = [min(min(time_target{1,1})),max(max(time_target{1,1}))];
for time_loop=1:size(space_axis,2)
subplot(2,size(space_axis,2),time_loop);
topoplotEEG(time_target{1,1}(:,round((space_axis(time_loop) + 0.2)*fs_down)),channel_loc_path,'electrodes',space_label,'maplimits',clim);
title([ 'target-', num2str(space_axis(time_loop)),'s']);
end
for time_loop=1:size(space_axis,2)
subplot(2,size(space_axis,2),size(space_axis,2) + time_loop);
topoplotEEG(time_nontarget{1,1}(:,round((space_axis(time_loop) + 0.2)*fs_down)),channel_loc_path,'electrodes',space_label,'maplimits',clim);
title([ 'nontarget-',num2str(space_axis(time_loop)),'s']);
end
end
这里的地形图绘制代码topoplotEEG,源自EEGLAB软件 [https://sccn.ucsd.edu/eeglab/index.php]:
% topoplot() - plot a topographic map of an EEG field as a 2-D
% circular view (looking down at the top of the head)
% using cointerpolation on a fine cartesian grid.
% Usage:
% >> topoplot(datavector,'eloc_file');
% >> topoplot(datavector,'eloc_file', 'Param1','Value1', ...)
% Inputs:
% datavector = vector of values at the corresponding locations.
% 'eloc_file' = name of an EEG electrode position file {0 -> 'chan_file'}
%
% Optional Parameters & Values (in any order):
% Param Value
% 'colormap' - any sized colormap
% 'interplimits' - 'electrodes' to furthest electrode
% 'head' to edge of head
% {default 'head'}
% 'gridscale' - scaling grid size {default 67}
% 'maplimits' - 'absmax' +/- the absolute-max
% 'maxmin' scale to data range
% [clim1,clim2] user-definined lo/hi
% {default = 'absmax'}
% 'style' - 'straight' colormap only
% 'contour' contour lines only
% 'both' both colormap and contour lines
% 'fill' constant color between lines
% 'blank' just head and electrodes
% {default = 'both'}
% 'numcontour' - number of contour lines
% {default = 6}
% 'shading' - 'flat','interp' {default = 'flat'}
% 'headcolor' - Color of head cartoon {default black}
% 'electrodes' - 'on','off','labels','numbers'
% 'efontsize','electcolor','emarker','emarkersize' - details
%
% Note: topoplot() only works when map limits are >= the max and min
% interpolated data values.
% Eloc_file format:
% chan_number degrees radius reject_level amp_gain channel_name
% (Angle-0 = Cz-to-Fz; C3-angle =-90; Radius at edge of image = 0.5)
%
% For a sample eloc file: >> topoplot('example')
%
% Note: topoplot() will ignore any electrode with a position outside
% the head (radius > 0.5)
% Topoplot Version 2.1
% Begun by Andy Spydell, NHRC, 7-23-96
% 8-96 Revised by Colin Humphries, CNL / Salk Institute, La Jolla CA
% -changed surf command to imagesc (faster)
% -can now handle arbitrary scaling of electrode distances
% -can now handle non integer angles in eloc_file
% 4-4-97 Revised again by Colin Humphries, reformat by SM
% -added parameters
% -changed eloc_file format
% 2-26-98 Revised by Colin
% -changed image back to surface command
% -added fill and blank styles
% -removed extra background colormap entry (now use any colormap)
% -added parameters for electrode colors and labels
% -now each topoplot axes use the caxis command again.
% -removed OUTPUT parameter
% 3-11-98 changed default emarkersize, improve help msg -sm
function handle = topoplot(Vl,loc_file,p1,v1,p2,v2,p3,v3,p4,v4,p5,v5,p6,v6,p7,v7,p8,v8,p9,v9)
% User Defined Defaults:
MAXCHANS = 250;
DEFAULT_ELOC = '16channel.txt';
INTERPLIMITS = 'head'; % head, electrodes
MAPLIMITS = 'absmax'; % absmax, maxmin, [values]
GRID_SCALE = 67;
CONTOURNUM = 6;
STYLE = 'both'; % both,straight,fill,contour,blank
HCOLOR = [0 0 0];
ECOLOR = [0 0 0];
CONTCOLOR = [0 0 0];
ELECTROD = 'on'; % ON OFF LABEL
EMARKERSIZE = 6;
EFSIZE = get(0,'DefaultAxesFontSize');
HLINEWIDTH = 2;
EMARKER = '.';
SHADING = 'flat'; % flat or interp
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
nargs = nargin;
if nargs < 2
loc_file = DEFAULT_ELOC;
end
if nargs == 1
if isstr(Vl)
if any(strcmp(lower(Vl),{'example','demo'}))
fprintf(['This is an example of an electrode location file,\n',...
'an ascii file consisting of the following four columns:\n',...
' channel_number degrees arc_length channel_name\n\n',...
'Example:\n',...
' 1 -18 .352 Fp1.\n',...
' 2 18 .352 Fp2.\n',...
' 5 -90 .181 C3..\n',...
' 6 90 .181 C4..\n',...
' 7 -90 .500 A1..\n',...
' 8 90 .500 A2..\n',...
' 9 -142 .231 P3..\n',...
'10 142 .231 P4..\n',...
'11 0 .181 Fz..\n',...
'12 0 0 Cz..\n',...
'13 180 .181 Pz..\n\n',...
'The model head sphere has a diameter of 1.\n',...
'The vertex (Cz) has arc length 0. Channels with arc \n',...
'lengths > 0.5 are not plotted nor used for interpolation.\n'...
'Zero degrees is towards the nasion. Positive angles\n',...
'point to the right hemisphere; negative to the left.\n',...
'Channel names should each be four chars, padded with\n',...
'periods (in place of spaces).\n'])
return
end
end
end
if isempty(loc_file)
loc_file = 0;
end
if loc_file == 0
loc_file = DEFAULT_ELOC;
end
if nargs > 2
if ~(round(nargs/2) == nargs/2)
error('topoplot(): Odd number of inputs?')
end
for i = 3:2:nargs
Param = eval(['p',int2str((i-3)/2 +1)]);
Value = eval(['v',int2str((i-3)/2 +1)]);
if ~isstr(Param)
error('topoplot(): Parameter must be a string')
end
Param = lower(Param);
switch lower(Param)
case 'colormap'
if size(Value,2)~=3
error('topoplot(): Colormap must be a n x 3 matrix')
end
colormap(Value)
case {'interplimits','headlimits'}
if ~isstr(Value)
error('topoplot(): interplimits value must be a string')
end
Value = lower(Value);
if ~strcmp(Value,'electrodes') & ~strcmp(Value,'head')
error('topoplot(): Incorrect value for interplimits')
end
INTERPLIMITS = Value;
case 'maplimits'
MAPLIMITS = Value;
case 'gridscale'
GRID_SCALE = Value;
case 'style'
STYLE = lower(Value);
case 'numcontour'
CONTOURNUM = Value;
case 'electrodes'
ELECTROD = lower(Value);
case 'emarker'
EMARKER = Value;
case {'headcolor','hcolor'}
HCOLOR = Value;
case {'electcolor','ecolor'}
ECOLOR = Value;
case {'emarkersize','emsize'}
EMARKERSIZE = Value;
case {'efontsize','efsize'}
EFSIZE = Value;
case 'shading'
SHADING = lower(Value);
if ~any(strcmp(SHADING,{'flat','interp'}))
error('Invalid Shading Parameter')
end
otherwise
error('Unknown parameter.')
end
end
end
[r,c] = size(Vl);
if r>1 & c>1,
error('topoplot(): data should be a single vector\n');
end
fid = fopen(loc_file);
if fid<1,
fprintf('topoplot(): cannot open eloc_file (%s).\n',loc_file);
return
end
A = fscanf(fid,'%d %f %f %s',[7 MAXCHANS]);
fclose(fid);
A = A';
if length(Vl) ~= size(A,1),
fprintf(...
'topoplot(): data vector must have the same rows (%d) as eloc_file (%d)\n',...
length(Vl),size(A,1));
A
error('');
end
labels = setstr(A(:,4:7));
idx = find(labels == '.'); % some labels have dots
labels(idx) = setstr(abs(' ')*ones(size(idx))); % replace them with spaces
Th = pi/180*A(:,2); % convert degrees to radians
Rd = A(:,3);
ii = find(Rd <= 0.5); % interpolate on-head channels only
Th = Th(ii);
Rd = Rd(ii);
Vl = Vl(ii);
labels = labels(ii,:);
[x,y] = pol2cart(Th,Rd); % transform from polar to cartesian coordinates
rmax = 0.5;
ha = gca;
cla
hold on
if ~strcmp(STYLE,'blank')
% find limits for interpolation
if strcmp(INTERPLIMITS,'head')
xmin = min(-.5,min(x)); xmax = max(0.5,max(x));
ymin = min(-.5,min(y)); ymax = max(0.5,max(y));
else
xmin = max(-.5,min(x)); xmax = min(0.5,max(x));
ymin = max(-.5,min(y)); ymax = min(0.5,max(y));
end
xi = linspace(xmin,xmax,GRID_SCALE); % x-axis description (row vector)
yi = linspace(ymin,ymax,GRID_SCALE); % y-axis description (row vector)
[Xi,Yi,Zi] = griddata(y,x,Vl,yi',xi,'v4'); % Interpolate data
% Take data within head
mask = (sqrt(Xi.^2+Yi.^2) <= rmax);
ii = find(mask == 0);
Zi(ii) = NaN;
% calculate colormap limits
m = size(colormap,1);
if isstr(MAPLIMITS)
if strcmp(MAPLIMITS,'absmax')
amin = -max(max(abs(Zi)));
amax = max(max(abs(Zi)));
elseif strcmp(MAPLIMITS,'maxmin')
amin = min(min(Zi));
amax = max(max(Zi));
end
else
amin = MAPLIMITS(1);
amax = MAPLIMITS(2);
end
delta = xi(2)-xi(1); % length of grid entry
% Draw topoplot on head
if strcmp(STYLE,'contour')
contour(Xi,Yi,Zi,CONTOURNUM,'k');
elseif strcmp(STYLE,'both')
surface(Xi-delta/2,Yi-delta/2,zeros(size(Zi)),Zi,'EdgeColor','none',...
'FaceColor',SHADING);
% colorbar;
contour(Xi,Yi,Zi,CONTOURNUM,'k');
elseif strcmp(STYLE,'straight')
surface(Xi-delta/2,Yi-delta/2,zeros(size(Zi)),Zi,'EdgeColor','none',...
'FaceColor',SHADING);
% colorbar
elseif strcmp(STYLE,'fill')
contourf(Xi,Yi,Zi,CONTOURNUM,'k');
else
error('Invalid style')
end
caxis([amin amax]) % set coloraxis
end
set(ha,'Xlim',[-rmax*1.3 rmax*1.3],'Ylim',[-rmax*1.3 rmax*1.3])
% %%% Draw Head %%%%
l = 0:2*pi/100:2*pi;
basex = .18*rmax;
tip = rmax*1.15; base = rmax-.004;
EarX = [.497 .510 .518 .5299 .5419 .54 .547 .532 .510 .489];
EarY = [.0555 .0775 .0783 .0746 .0555 -.0055 -.0932 -.1313 -.1384 -.1199];
% Plot Electrodes
if strcmp(ELECTROD,'on')
hp2 = plot(y,x,EMARKER,'Color',ECOLOR,'markersize',EMARKERSIZE);
elseif strcmp(ELECTROD,'labels')
for i = 1:size(labels,1)
text(y(i),x(i),labels(i,:),'HorizontalAlignment','center',...
'VerticalAlignment','middle','Color',ECOLOR,...
'FontSize',EFSIZE)
end
elseif strcmp(ELECTROD,'numbers')
whos y x
for i = 1:size(labels,1)
text(y(i),x(i),int2str(i),'HorizontalAlignment','center',...
'VerticalAlignment','middle','Color',ECOLOR,...
'FontSize',EFSIZE)
end
end
% Plot Head, Ears, Nose
plot(cos(l).*rmax,sin(l).*rmax,...
'color',HCOLOR,'Linestyle','-','LineWidth',HLINEWIDTH);
plot([.18*rmax;0;-.18*rmax],[base;tip;base],...
'Color',HCOLOR,'LineWidth',HLINEWIDTH);
plot(EarX,EarY,'color',HCOLOR,'LineWidth',HLINEWIDTH)
plot(-EarX,EarY,'color',HCOLOR,'LineWidth',HLINEWIDTH)
hold off
axis off
四、可视化 整体代码
任务态信号-可视化 整体代码:
%% 0.标准数据参数设置
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
data_path = 'C:\Users\Amax\Desktop\basetest_flod\save_fold\';
svae_path = 'C:\Users\Amax\Desktop\basetest_flod\save_fold\';
channel_name_path = 'F:\机制分析-128导\channel_name_128';
channel_loc_path = 'C:\Users\Amax\Desktop\ZRK_BCI_code_Summary\channel_122_loc_2d.txt';
analysis_content = ['time_mean\','freq_mean\','map\'];
plot_para = ['time\','freq\','space\'];
% mean_para = ['simple_mean\','zscore_baseline\'];
mean_para = ['simple_mean\'];
subject_num = [1 ; 10];
line_size = 1;
text_size = 5;
freq_axis = [1;30];
space_axis = [0:0.1:0.8];
space_label = 'off';
disp(['||任务态数据分析中...||']);
disp(['被试量: ' , num2str(subject_num(1,1)),'-',num2str(subject_num(2,1))]);
disp(['是否绘图: ' , num2str(plot_para)]);
disp(['绘图参数: ' , mean_para]);
disp(['频谱绘制范围: ' , num2str(freq_axis(1,1)),'-',num2str(freq_axis(2,1))]);
disp(['地形图绘制范围: ' , num2str(space_axis)]);
disp(['线条宽度:' , num2str(line_size),' ||字体大小:' , num2str(text_size)]);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% 1.标准输入赋值
disp(['||预处理后数据加载中...||']);
Proprocess_target_file = load([data_path ,'Proprocess_target_',num2str(subject_num(1,1)),'_',num2str(subject_num(2,1))]);
Proprocess_nontarget_file = load([data_path ,'Proprocess_nontarget_',num2str(subject_num(1,1)),'_',num2str(subject_num(2,1))]);
stuct_target_name = 'Proprocess_target';
stuct_nontarget_name = 'Proprocess_nontarget';
Proprocess_target_data = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).data;
Proprocess_nontarget_data = Proprocess_nontarget_file.(stuct_nontarget_name).data;
subject_num = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).subject_num;
fs_down = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).fs_down;
remain_trial_target = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).remain_trial;
remain_trial_nontarget = Proprocess_nontarget_file.(stuct_nontarget_name).remain_trial;
Baseline_reference = Proprocess_target_file.(stuct_target_name).Baseline_reference ;
disp(['目标试次剩余: ' , num2str(remain_trial_target),'||平均: ', num2str(mean(remain_trial_target)),'||剩余比例: ',num2str(mean(remain_trial_target)/size(Proprocess_target_data,1))]);
disp(['非目标试次剩余: ' , num2str(remain_trial_nontarget),'||平均: ', num2str(mean(remain_trial_nontarget)),'||剩余比例: ',num2str(mean(remain_trial_nontarget)/size(Proprocess_nontarget_data,1))]);
%% 2.时域分析
disp(['||时域分析加载中...||']);
[time_target]= Analysis_task_time(Proprocess_target_data,fs_down,Baseline_reference,remain_trial_target,mean_para);
[time_nontarget]= Analysis_task_time(Proprocess_nontarget_data,fs_down,Baseline_reference,remain_trial_nontarget,mean_para);
%绘图
if contains(plot_para,'time')
load (channel_name_path);
Analysis_time_plot(time_target,time_nontarget,fs_down,Baseline_reference,channel_name,line_size,text_size)
end
%% 3.频域分析
disp(['||频域分析加载中...||']);
% 注:fft使用采样率作为参数,因此频谱分辨率为1hz
[freq_target]= Analysis_task_freq(time_target,fs_down);
[freq_nontarget]= Analysis_task_freq(time_nontarget,fs_down);
%绘图
if contains(plot_para,'freq')
load (channel_name_path);
Analysis_freq_plot(freq_target,freq_nontarget,fs_down,channel_name,freq_axis,line_size,text_size)
end
%% 4.空域分析 脑地形图
disp(['||空域分析加载中...||']);
if contains(plot_para,'space')
Analysis_time_space_plot(time_target,time_nontarget,channel_loc_path,fs_down,space_axis,space_label)
end
disp(['||数据分析完毕||']);
总结
任务态的可视化突出刺激诱发时刻的锁时特性(时间锚点),
对比刺激前后的脑模式,可分析大脑对任务刺激的响应,
脑响应分析常涉及到时域成分、空域脑区等
可视化是对脑电数据状态的直观呈现,既是对已处理信号的检查回顾,也是为下一步处理提供借鉴
通过时域抖动观察时序成分,频域能谱分析节律特征,空域分布了解脑区激活
避免从数据输入 到结果输出全程 端到端黑盒,中间缺少对数据的把控
当然,本文只介绍了最基础的时域、频域、空域可视化
还有多种可视化方法如PCA降维分布可视化、直方图统计可视化、脑网络连接可视化等
如有需要可以联系我,写新文章介绍进阶的脑电数据可视化方式
囿于能力,挂一漏万,如有笔误请大家指正~
感谢您耐心的观看,本系列更新了约30000字,约3000行开源代码,体量相当于一篇硕士工作。
往期内容放在了文章开头,麻烦帮忙点点赞,分享给有需要的朋友~
坚定初心,本博客永远:
免费拿走,全部开源,全部无偿分享~
To:新想法、鬼点子的道友:
自己:脑机接口+人工智领域,主攻大脑模式解码、身份认证、仿脑模型…
在读博士第3年,在最后1年,希望将代码、文档、经验、掉坑的经历分享给大家~
做的不好请大佬们多批评、多指导~ 虚心向大伙请教!
想一起做些事情 or 奇奇怪怪点子 or 单纯批评我的,请至[email protected]
