R语言基础学习——D01
20190410内容纲要:
1、R的下载与安装
2、R包的安装与使用方法
(1)查看已安装的包
(2)查看是否安装过包
(3)安装包
(4)更新包
3、结果的重用
4、R处理大数据集
5、R的数据结构
(1)向量
(2)矩阵
(3)数组
(4)数据框
(5)列表
6、实例演练
7、小结
1 R的下载与安装
R是用于统计分析、绘图的语言和操作环境。R是属于GNU系统的一个自由、免费、源代码开放的软件,它是一个用于统计计算和统计制图的优秀工具。
学习它那就先下载它!话不多说看链接:
Windows镜像: http://mirror.fcaglp.unlp.edu.ar/CRAN/
当然也有Linux和Mac版本。
安装,就不多少,直接下一步,下一步,下一步。别忘了更改安装路径就行!!!
先随便玩点什么?
>demo() >demo(graphics) >help.start() >help("mean") >?mean >getwd() >setwd("path") >history()
看完这些,觉得R跟linux和Matlab有点像。据说R的前身是S语言。S语言是什么?https://baike.baidu.com/item/S%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80
2 R包的安装与使用方法
(1)查看已安装的包。
首先,如果照1方法安装完成之后打开软件。在R console中输入library()就能查看当前已经安装的包。
>library()
1 图书馆‘F:/R/R-3.5.3/library’里有个程辑包: 2 3 abind Combine Multidimensional Arrays 4 assertthat Easy Pre and Post Assertions 5 base The R Base Package 6 BH Boost C++ Header Files 7 boot Bootstrap Functions (Originally by Angelo Canty for S) 8 car Companion to Applied Regression 9 carData Companion to Applied Regression Data Sets 10 cellranger Translate Spreadsheet Cell Ranges to Rows and Columns 11 class Functions for Classification 12 cli Helpers for Developing Command Line Interfaces 13 clipr Read and Write from the System Clipboard 14 cluster "Finding Groups in Data": Cluster Analysis Extended Rousseeuw et al. 15 codetools Code Analysis Tools for R 16 compiler The R Compiler Package 17 crayon Colored Terminal Output 18 curl A Modern and Flexible Web Client for R 19 data.table Extension of `data.frame` 20 datasets The R Datasets Package 21 ellipsis Tools for Working with ... 22 fansi ANSI Control Sequence Aware String Functions 23 forcats Tools for Working with Categorical Variables (Factors) 24 foreign Read Data Stored by 'Minitab', 'S', 'SAS', 'SPSS', 'Stata', 'Systat', 'Weka', 'dBase', ... 25 graphics The R Graphics Package 26 grDevices The R Graphics Devices and Support for Colours and Fonts 27 grid The Grid Graphics Package 28 haven Import and Export 'SPSS', 'Stata' and 'SAS' Files 29 hms Pretty Time of Day 30 KernSmooth Functions for Kernel Smoothing Supporting Wand & Jones (1995) 31 lattice Trellis Graphics for R 32 lme4 Linear Mixed-Effects Models using 'Eigen' and S4 33 magrittr A Forward-Pipe Operator for R 34 maptools Tools for Handling Spatial Objects 35 MASS Support Functions and Datasets for Venables and Ripley's MASS 36 Matrix Sparse and Dense Matrix Classes and Methods 37 MatrixModels Modelling with Sparse And Dense Matrices 38 methods Formal Methods and Classes 39 mgcv Mixed GAM Computation Vehicle with Automatic Smoothness Estimation 40 minqa Derivative-free optimization algorithms by quadratic approximation 41 nlme Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models 42 nloptr R Interface to NLopt 43 nnet Feed-Forward Neural Networks and Multinomial Log-Linear Models 44 openxlsx Read, Write and Edit XLSX Files 45 parallel Support for Parallel computation in R 46 pbkrtest Parametric Bootstrap and Kenward Roger Based Methods for Mixed Model Comparison 47 pillar Coloured Formatting for Columns 48 pkgconfig Private Configuration for 'R' Packages 49 prettyunits Pretty, Human Readable Formatting of Quantities 50 progress Terminal Progress Bars 51 quantreg Quantile Regression 52 R6 Encapsulated Classes with Reference Semantics 53 Rcpp Seamless R and C++ Integration 54 RcppEigen 'Rcpp' Integration for the 'Eigen' Templated Linear Algebra Library 55 readr Read Rectangular Text Data 56 readxl Read Excel Files 57 rematch Match Regular Expressions with a Nicer 'API' 58 rio A Swiss-Army Knife for Data I/O 59 rlang Functions for Base Types and Core R and 'Tidyverse' Features 60 rpart Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees 61 sp Classes and Methods for Spatial Data 62 SparseM Sparse Linear Algebra 63 spatial Functions for Kriging and Point Pattern Analysis 64 splines Regression Spline Functions and Classes 65 stats The R Stats Package 66 stats4 Statistical Functions using S4 Classes 67 survival Survival Analysis 68 tcltk Tcl/Tk Interface 69 tibble Simple Data Frames 70 tools Tools for Package Development 71 translations The R Translations Package 72 utf8 Unicode Text Processing 73 utils The R Utils Package 74 zip Cross-Platform 'zip' Compression
(2)查看当前是否安装过包
>help(package="car") #car就是具体的某个包的名称
如果已经安装过,会自动跳转本机的12569端口查看网页版的详细介绍。如果没有那就装吧~
(3)安装包
安装包的时候会提示选择镜像源,选中国的就行,剩下的就看网络给不给力了~
install.packages("car")
(4)更新包
update.packages() #不生命的话就默认更新全部
3 结果的重用
>head(mtcars) #mtcars是一个数据集 >lm(mpg~wt, data=mtcars #lm是线性拟合的命令 >Result = lm(mpg~wt, data=mtcars) >summary(Result) >plot(Result) >predict(Result, mynewdata) #mynewdata是自己要预测的值
有很多东西看不懂没事,后面还会有详细说明。~~
4 R处理大数据集
(1)R有专门用于大数据分析的包。如biglm()能以内存高效的方式实现大型数据的线性模型拟合。
(2)R与大数据平台的结合。如Rhadoop、RHive、RHipe。
R的数据集通常是由数据构成的一个矩形数组,行表示记录,列表示属性(字段)。形式可以使Excel、txt、SAS、Mysql
对数据库有兴趣的话可以看看:2019最受欢迎的数据库是? https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9fhPicVCjMpfMmjbhZUoFA
5 R的数据结构
话不多说,还是通过代码比较容易理解。。
(1)向量
向量中的元素可以是数字型、字符型、也可以是布尔型。但是当数组型和字符型混一起时,有没有什么说法自己动手试试吧!!
>a <- c(1,3,5,7,2,-4) >b <- c("one","two","three") >c <- c(TRUE,TRUE,FALSE) >d <- c(1,3,5,"ONE")
此外,关于切片其实跟python有点类似
>d[c(1,3,4)] >d[3] >d[1:3]
(2)矩阵 matrix
>?matrix >y <- matrix(5:24, nrow=4, ncol=5) >x <- c(2,45,68,94) >rnames <- c("R1","R2") >cnames <- c("C1","C2") >newMatrix <- matrix(x, nrow=2, ncol=2, byrow=TRUE, dimnames=list(rnames,cnames)) >>newMatrix <- matrix(x, nrow=2, ncol=2,dimnames=list(rnames,cnames)) #默认按列填充
>x[3,] >x[2,3] >x[,4]
(3)数组 array
>?array >dim1 <- c("A1","A2", "A3") >dim2 <- c("B1", "B2") >dim3 <- c("C1","C2", "C3") >d <- array(1:24, c(3,2,4), dimnames=list(dim1,dim2,dim3)) >d[1,2,3]
1 #输出结果 2 > d 3 , , C1 4 5 B1 B2 6 A1 1 4 7 A2 2 5 8 A3 3 6 9 10 , , C2 11 12 B1 B2 13 A1 7 10 14 A2 8 11 15 A3 9 12 16 17 , , C3 18 19 B1 B2 20 A1 13 16 21 A2 14 17 22 A3 15 18 23 24 , , C4 25 26 B1 B2 27 A1 19 22 28 A2 20 23 29 A3 21 24 30 31 > d[1,2,3] 32 [1] 16
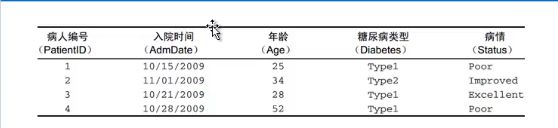
(4)数据框 data.frame()
>patientID <- c(1,2,3,4) >age <- c(25,34,28,52) >diabetes <- c("Type1", "Type2", "Type3", "Type2") >status <- c("poor", "Improved, "Excllent", "poor") >patientData <- data.frame(patientID, age, diabetes, status)
> patientData patientID age diabetes status 1 1 25 Type1 poor 2 2 34 Type2 Improved 3 3 28 Type3 Excllent 4 4 52 Type2 poor
>patientData[1:2] >patientData[c("diabetes","status")] >patientData$age
#虽然age直接输入age也能调出,但是这是因为前面创建数据帧的时候包含age。如果没有呢?
#下面举个例子 >head(mtcars) >mtcars$mpg >mpg #为什么会报错呢,这个时候是因为mpg并没有关联到R中。这个时候可以用attach这个命令进行关联,解除用detach
>attach(mtcars) >mpg >detach(mtcars) >mpg
#因子 > diabetes <- factor(diabetes) > diabetes [1] Type1 Type2 Type3 Type2 Levels: Type1 Type2 Type3
(5)列表 list
> g <- "My first list" > h <- c(12,23,34) > j <- c("one","two","there") > k <- matrix(1:10, nrow=2)
> mylist <- list(g,h,j,k
> mylist [[1]] [1] "My first list" [[2]] [1] 12 23 34 [[3]] [1] "one" "two" "there" [[4]] [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [1,] 1 3 5 7 9 [2,] 2 4 6 8 10
但是,列表的切片方式略有不同。双中括号!!!
>mylist[[2]]
6 实例演练
>age <- c(1,3,5,2,11,9,3,9,12,3) >weight <- c(4.4, 5.3, 7.2, 5.2, 8.5, 7.3, 6.0, 10.4, 10.2, 6.1) >mean(weight) #求均值 >sd(weight) #求方差 >cor(age, weight) #求相关性 >plot(age,weight)
7 推荐
推荐1: 数据分析从零开始实战 | 基础篇 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/4ESKjlF4B63IveiIlfCdDA
推荐2:给入行数据分析的8个建议 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FYQ192iwstn2J2QejDvNhA
我是尾巴~
数据分析必将大有所为!!!