深圳大学移动互联网应用期末大作业——垃圾分类app
文章目录
-
- 一、期末大作业的目的与要求:
-
- 1. 垃圾分类界面
- 2.具体要求
- 3.部分参考
- 4.其他要求
- 二、实验过程和代码与结果
-
- 1.“我的垃圾分类APP”的构建过程及结果
-
- (1)启动页面的实现
- (2)登陆界面
- (3)主界面的实现
- (4)首页界面逻辑编写
- (5)指南界面编写
- (6)设置界面编写
- 2. 请详细说明“我的垃圾分类APP”的功能、出现的关键问题及解决方案
-
- 功能展示
- 问题和解决方案
-
- (1)fragment加载问题
- (2)设置按钮背景透明
- (3)TabLayout界面的缓存
- (4)权限的声明
- (5)不重复随机数的生成
- (6)对象列表的传值
- (7)EditText焦点失去
- (8)百度语音识别api的申请以及调用
- 三、实验总结
一、期末大作业的目的与要求:
1. 垃圾分类界面
请尽量模拟如下垃圾分类APP的功能,即参考如下的界面展示形式及功能模块。
2.具体要求
模拟图1所示垃圾分类APP,介绍垃圾分类与回收相关的一些知识点并能提供相应服务:
1) 建议包含的一些功能:活动之间的转换与数据传递;能适应不同的展示界面;有登录功能,强制下线功能;数据有多样化的持久化功能;能跨程序提供与共享数据;有展示一些多媒体的功能;
2) 较好的实现了书本上介绍的一些较成熟的功能,并能较好的把这些功能融合在一个完整且无大bug的APP里;
3) 能在此基础上构建自己的报告亮点,如实现了书本不一样的功能模块,或者为某个知识点找到一些新的应用场景,或者能解决同学们普遍存在的一些问题等;
4) 模拟的APP不局限于所参照APP的功能,即尽量模拟这些功能,不要求将每个功能都实现,如果某个功能不能体现已学知识点,可以不用考虑,当然如果能想办法实现出来,可以作为报告亮点;即不必与这些功能完全一样,可在这些功能基础上进行变通,达到类似的效果就可以;可以设计一些该APP没有的功能,并能清楚说明这些功能的实现方式、潜在的用途等;同时布局的设计也不必与参考APP完全一样,可根据自己需要适当调整;
5) 总体目标是灵活利用所学的知识点,做到每个功能各种实现方式的丰富化(如数据的持久化的三种实现方式都能在APP中有所体现),并且能体现不同实现方式的优劣,如果能在APP上体现会更好;
3.部分参考
1)功能实现参考:图1第3列图尽量参考第6章数据持久化技术的各个知识点;第1,4列尽量参考布局及活动之间的跳转,碎片的实现,多媒体展示功能;第5列可以利用数据持久化技术;
2)潜在的扩展功能:图1第1列尽量参考并利用Android基于位置的服务,比如能根据用户所在位置查找最近的垃圾投放点;添加一个小功能,整合网络技术的应用,即将一个HTML网页文件中的文本与图片网址进行分离,并将文本与图片用不同文件夹分开保持;利用数据后台下载的功能;
3)可以借鉴的部分章节内容,第12章可以让你的APP界面变得更美观;第14章展示了一个大型的工程,可以学习下多个功能怎样在一个工程里体现;
4.其他要求
1)构建的APP要格式工整,美观;
2)实验报告中需要有功能的描述、实验结果的截屏图像及详细说明;结果展示要具体,图文交叉解释;代码与文本重点要突出;
3)也欢迎采用课程后续章节的知识点完成本次大作业,如果实现的功能言之合理,会考虑酌情加分;
4)每位同学在最后一次课都需要上台报告,并且最好能现场演示APP的功能等,没上台报告的同学分数会受一定的影响;
5)报告由个人独立完成。
###5.评分标准
- APP协议完成度高,与参考APP有一定的相似度,功能完善、丰富。能实现活动的编写、自定义用户界面的开发、碎片开发、广播机制、数据持久化与共享技术、网络技术、后台服务的应用等。-------------(60分)
- 模拟APP结构合理,代码规范,界面美观易用。项目报告撰写规范、美观整齐,内容详实且能准备描述项目内容和设计思想、原理、框架等,项目报告要求5号字、除前两页外A4版面不低于10页的长度。-------------(15分)
- 提供程序源代码和可执行程序(或安装程序);报告文档采用单独的word文档,项目所有代码(不是整个工程文件,应该总共不超过5M)在第17周之前打包作为附件进行上传blackboard系统;纸质版交到任课老师处。-------------(10分)
- 项目报告能够详细,准确的描述项目内容,并在最后一堂课有较好的展示效果。
-------------(15分)
二、实验过程和代码与结果
1.“我的垃圾分类APP”的构建过程及结果
(1)启动页面的实现
首先新建活动StartActivity,编写碎片文件frag_start.xml,在该碎片布局中采用了相对布局RelativeLayout,碎片中只包含一个TextView控件,使用layout_alignParentTop和layout_alignParentRight将其显示在屏幕右上角,并设置文字“跳过 (3s)”使用layout_margin控制边缘的距离,便于美观。
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/skip"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="跳过 (3s)"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp" />
RelativeLayout>
新建一个文件StartFragment作为碎片的适配器,并在onCreateView中将其加载进来。
public class StartFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_start, container, false);
return view;
}
}
新建文件夹layout-sw600dp作为平板的碎片文件夹,在layout文件夹和这一文件夹编写activity_start,将碎片包含进来。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/welcome_small">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/start_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:name="com.example.refuseclassification.StartFragment" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/welcome_large">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/start_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:name="com.example.refuseclassification.StartFragment" />
LinearLayout>
可以看到,手机和平板的activity_start都是直接使用刚刚写的碎片文件,并加载相应大小的图片。因为屏幕尺寸的原因,一张图片无法同时适配平板和手机,会导致图片被压缩或者拉伸,使得欢迎界面很难看,于是对于不同屏幕大小,布局文件加载了不同的照片。
接着编写StartActivity.java。首先定义TextView对象skip,用于后面获取欢迎界面的TextView实例,然后设置倒计时为3s,定义处理信息的handler和线程runnable,定义计时器timer。
首先编写任务类TimerTask,在task中新建一个线程用于计时,之所以这样是为了防止线程堵塞,主线程用于更新UI显示,子线程用来计时,最后更新skip,当倒计时为0的时候,把skip的字体隐藏起来。
public class StartActivity extends BaseActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
private TextView skip;
private int TIME = 3;
private Handler handler;
private Runnable runnable;
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
TIME--;
skip.setText("跳过 " + "(" + TIME + "s)");
if (TIME < 0) {
// 小于0时隐藏字体
timer.cancel();
skip.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
});
}
};
接着编写活动的onCreate方法。首先通过下面这一语句将标题栏隐藏,保证欢迎页面全屏显示。
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
接着获取TextView实例并设置点击事件的监听器。然后使用timer这一计时器工具,执行前面定义的task任务,每隔1s执行一次该任务。我们使用handler来实现计时器,当计时结束时再过2s,跳转到登录界面。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 去掉app标题栏
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_start);
skip = findViewById(R.id.skip);
skip.setOnClickListener(this);// 设置点击跳过
timer.schedule(task, 1000, 1000);// 等待时间1s,停顿时间1s
// 设置不点击跳过
handler = new Handler();
handler.postDelayed(runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//从闪屏界面跳转到首界面
Intent intent = new Intent(StartActivity.this, LoginActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
}
}, 5000);//延迟5S后发送handler信息
}
最后实现TextView的点击事件。用switch……case……语句来判断点击的View的id,若是skip,则跳转到登录界面,然后将runnable线程结束。
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.skip:
// 跳转到登录页面
Intent intent = new Intent(StartActivity.this, LoginActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
if (runnable != null) {
handler.removeCallbacks(runnable);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
最后,在Manifest中将启动活动修改为StartActivity。
<activity android:name=".StartActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
(2)登陆界面
新建活动LoginActivity,编写碎片活动frag_login.xml。该界面总体是LinearLayout布局,其中包含了四个横向分布的LinearLayout。前两个布局包含了一个TextView和一个EditText,用来设置输入账号和密码;第三个布局设置记住密码的选项;最后一个设置两个按钮,一个用于登录,一个用于注册;最后加一个提示,使用户可以按照正确的方式进行注册。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:text="账户:"
android:padding="10dp"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/account"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:text="密码:"
android:padding="10dp"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/password"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:inputType="textPassword" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/remember_pass"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:text="记住密码" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/login"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="登录" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/register"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="注册" />
LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="提示:若要进行注册,请填写账户和密码然后点击注册"
android:textSize="16dp" />
LinearLayout>
新建一个LoginFragment作为碎片的适配器,在onCreateView中将其加载进来。
public class LoginFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_login, container, false);
return view;
}
}
和之前的欢迎界面一样,登陆界面也要适应平板和手机这些不同大小屏幕的需求,所以在layout文件夹和layout-sw600dp文件夹中编写activity_login.xml文件,用于适配不同屏幕。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/login_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/login_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:name="com.example.refuseclassification.LoginFragment" />
LinearLayout>
小屏幕的布局这里使用了Toolbar来代替系统的ActionBar,设置为自己的颜色。然后直接用fragment将之前的登录碎片包含进来。
而大屏幕的布局同样使用了Toolbar,然后使用一个横向排列的线性布局,将登录的控件控制在屏幕的中央。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/login_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/login_fragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:name="com.example.refuseclassification.LoginFragment" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
实现注册和登录功能,自然要使用数据持久化技术,来储存用户名的账号和密码,这里使用SQLite来实现。首先新建MyDatabaseHelper,使用MYSQL语言建立Account数据表。
public class MyDatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public static final String CREATE_ACCOUNT = "create table Account (" +
"id integer primary key autoincrement, " +
"account text, " +
"password text)";
private Context mContext;
public MyDatabaseHelper(Context context, String name,
SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
mContext = context;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL(CREATE_ACCOUNT);
Toast.makeText(mContext, "注册成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL("drop table if exists Account");
onCreate(db);
}
}
最后编写LoginActivity。首先调用findViewById()方法获得账号输入框、密码输入框和登陆按钮的实例。先判断是否有选择“记住密码”这一选项,如果有,就将账号和密码再次设置在输入框内。
public class LoginActivity extends BaseActivity {
private SharedPreferences pref;
private SharedPreferences.Editor editor;
private EditText accountEdit;
private EditText passwordEdit;
private Button login;
private Button register;
private CheckBox rememberPass;
private Toolbar toolbar;
private MyDatabaseHelper dbhelper;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_login);
pref = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(this);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.login_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("登录");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
accountEdit = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.account);
passwordEdit = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.password);
rememberPass = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.remember_pass);
login = (Button) findViewById(R.id.login);
dbhelper = new MyDatabaseHelper(this, "Account password", null, 2);
register = (Button) findViewById(R.id.register);
boolean isRemember = pref.getBoolean("remember_password", false);
if (isRemember) {
// 将账号和密码都设置到文本框中
String account = pref.getString("account", "");
String password = pref.getString("password", "");
accountEdit.setText(account);
passwordEdit.setText(password);
rememberPass.setChecked(true);
}
然后在登陆按钮的点击事件中,获取account和password的内容并获得数据库的实例以便读写数据库,先判断是否有已经创建了数据库,如果没有就先创建。接着调用SQLiteDatabase的query()方法,使用第一个参数指明去查询Account表,后面参数全部为null。查询完后获得一个Cursor对象,接着调用它的moveToFirst()方法将数据的指针移动到第一行的数据,然后进去一个循环,遍历每一行数据,如果有匹配输入的,则成功登陆,进入下一个活动。如果没有,则弹窗显示账号或密码输入错误。
login.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int flag = 1; //表示账号和密码是否正确
String account = accountEdit.getText().toString();
String password = passwordEdit.getText().toString();
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query("Account", null, null,
null, null, null, null);
if (cursor.moveToFirst()) {
do {
String hadaccount = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("account"));
String hadpassword = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("password"));
if (account.equals(hadaccount) && password.equals(hadpassword)) {
editor = pref.edit();
if (rememberPass.isChecked()) {
editor.putBoolean("remember_password", true);
editor.putString("account", account);
editor.putString("password", password);
}
else {
editor.clear();
}
editor.apply();
Intent intent = new Intent(LoginActivity.this, MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
flag = 0;
}
} while (cursor.moveToNext());
}
cursor.close();
if (flag == 1) {
Toast.makeText(LoginActivity.this, "账号或密码错误", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
而在注册的按钮的点击事件中,则是将输入在账号框和密码框中的内容加入到数据库中,完成注册的功能。
register.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getWritableDatabase();
String account = accountEdit.getText().toString();
String password = passwordEdit.getText().toString();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("account", account);
values.put("password", password);
db.insert("Account", null, values);
Toast.makeText(LoginActivity.this, "注册成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
对于Toolbar,我们需要让它可以显示标题,并且居中,由于后面要写很多活动,因此将标题居中的方法封装到一个类setTitleCenter中。
public class setTitleCenter {
public void setTitleCenter(Toolbar toolbar) {
String title = "title";
final CharSequence originalTitle = toolbar.getTitle();
toolbar.setTitle(title);
for (int i = 0; i < toolbar.getChildCount(); i++) {
View view = toolbar.getChildAt(i);
if (view instanceof TextView) {
TextView textView = (TextView) view;
if (title.equals(textView.getText())) {
textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
Toolbar.LayoutParams params = new Toolbar.LayoutParams
(Toolbar.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, Toolbar.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
params.gravity = Gravity.CENTER;
textView.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
toolbar.setTitle(originalTitle);
}
}
}
这样子只需要在每个活动主函数中获得Toolbar实例,设置标题并调用这个函数。
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.login_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("登录");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
最后登录界面结果如下,若为进行注册,登录的时候会显示账号和密码错误。


若已经注册,则可以成功登录

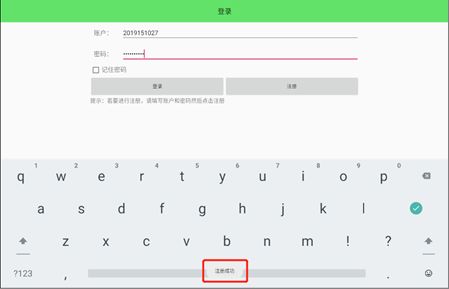
(3)主界面的实现
首先分析下样例的主界面。1标题栏可以使用Toolbar来实现;2可以使用一张图片;这里使用ImageView实现;3是一个横向的LinearLayout,分布着四对Button和TextView;4、5同在一个横向的LinearLayout中,每个控件都可以使用LinearLayout来排列,也是由Button1和TextView组成的;6是一个搜索框,可以使用EditText来实现;7是一个Button,用于识别语音;8则是底部导航栏Bottom navigation。

首先实现底部导航栏Bottom navigation。需要先添加依赖:
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.0.0'
然后编写activity_main.xml。同样的,这里使用线性布局,使控件垂直排列。这里还是有个标题栏Toolbar。然后使用ViewPager容器占满其余屏幕,用于显示碎片。底下则是BottomNavigationView的底部导航栏。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.viewpager.widget.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewPager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView
android:id="@+id/nav_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="0dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="0dp"
android:background="?android:attr/windowBackground"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
app:menu="@menu/bottom_nav_menu" />
LinearLayout>
接着我们需要编写底部导航栏所需要的菜单bottom_nav_menu.xml,给底部导航栏添加合适的图标和相应的标题。
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:id="@+id/navigation_home"
android:icon="@drawable/home"
android:title="首页" />
<item
android:id="@+id/navigation_guide"
android:icon="@drawable/menu"
android:title="指南" />
<item
android:id="@+id/navigation_setting"
android:icon="@drawable/setting"
android:title="设置" />
menu>
前面提到了BottomNavigationView用ViewPager容器存放Fragment,所以我们需要一个Adapter适配器。编写PagerAdapter.java,可以初始化适配器,这边getItem()方法你需要返回你当前List中和当前position对应的元素(也就是Fragment页面),getCount()就比较简单了,直接返回List的大小就行了。
public class PagerAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter {
Context context;
private List<Fragment> fragmentList;
public PagerAdapter(@NonNull FragmentManager fragmentManager, Context context, List<Fragment> list) {
super(fragmentManager);
fragmentList = list;
this.context = context;
}
public PagerAdapter(@NonNull FragmentManager fragmentManager, GuideFragment guideFragment, List<Fragment> list) {
super(fragmentManager);
fragmentList = list;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int position) {
return fragmentList.get(position);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return fragmentList.size();
}
}
最后编写MainActivity.java。在主类中,首先定义ViewPager和BottomNavigationView对象,以及Fragment列表,用于初始化。然后在onCreate方法中初始化主界面,然后调用initView方法。
public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity {
private ViewPager viewPager;
private BottomNavigationView navigation;
private List<Fragment> fragmentList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
在initView方法中首先获得布局文件中的ViewPager和BottomNavigationView实例。然后在列表中加入三个对应菜单的fragment,然后实例化adapter,最后ViewPager调用 .setAdapter() 方法传入PagerAdapter即可实现一个可以左右侧滑切换界面的效果。
private void initView() {
viewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.viewPager);
navigation = (BottomNavigationView) findViewById(R.id.nav_view);
//添加Fragment
fragmentList.add(new HomeFragment());
fragmentList.add(new GuideFragment());
fragmentList.add(new SettingFragment());
PagerAdapter adapter = new PagerAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager(), this, fragmentList);
//ViewPager设置adpater
viewPager.setAdapter(adapter);
接着实现底部按钮带动界面的功能。我们需要给BottomNavigationView加上一个ItemSelectedListener(子项选择监听器),然后根据子项的改变,然后ViewPager调用.setCurrentItem()方法对当前显示的页面进行更改;点击按钮以后,页面跟着动的效果也就实现了。
//导航栏点击事件和ViewPager滑动事件,让两个控件相互关联
navigation.setOnNavigationItemSelectedListener(new BottomNavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem item) {
//这里设置为:当点击到某子项,ViewPager就滑动到对应位置
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.navigation_home:
viewPager.setCurrentItem(0);
return true;
case R.id.navigation_guide:
viewPager.setCurrentItem(1);
return true;
case R.id.navigation_setting:
viewPager.setCurrentItem(2);
return true;
default:
break;
}
return false;
}
});
最后实现ViewPager侧滑改变底部BottomNavigationView的当前选项的功能。只需给你的ViewPager加上一个PageChangeListener(页面改变监听器),然后在页面改变以后,BottomNavigationView调用.setChecked ()方法,手动对当前选项作出对应的改变,就实现了。
viewPager.addOnPageChangeListener(new ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int position, float positionOffset, int positionOffsetPixels) {
}
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int position) {
//该方法只在滑动停止时调用,position滑动停止所在页面位置
// 当滑动到某一位置,导航栏对应位置被按下
navigation.getMenu().getItem(position).setChecked(true);
}
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int state) {
}
});
}
}
然后我们按照刚才对主界面元素的分析,编写frag_home.xml,实现主界面(菜单第一个选项)的内容。该界面主要还是采用LinearLayout布局,里面所有的界面都是垂直排列。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
最开始排列到的是一张图片,这里使用了scaleType进行了拉伸。
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/home_image"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/home_image" />
接着就是存放了四个按钮的横向的线性布局。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
在该布局中,存放着如下四个纵向的现场布局,每个布局包含一个ImageButton和一个TextView,其中ImageButton也使用了scaleType进行了拉伸,防止图片变形。两个元素都使用layout_gravity来保证居中。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/recyclable_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/recyclable"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="可回收"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/harmful_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/harmful"
android:background="#00000000" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="有害垃圾"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/wet_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/wet"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="湿垃圾"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/dry_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/dry"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="干垃圾"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
在该布局下面有这一段布局,用以设置分割线,使界面更加美观。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
接着又是一段横向的线性布局,用来存放两块线性布局、五个按钮。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:orientation="horizontal">
第一块以一个线性布局来存放一个ImageButton和TextView,和之前差不多,不同的是padding的值比较大,这样子将控件缩放在中央位置。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="40dp">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/test_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/test"
android:background="#00000000"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:padding="5dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="模拟考试"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
第二块又分成两块以纵向排列的线性布局。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
而每一块又分成两块横向排列的线性布局。这样子,我们就将一大块区域分成四块。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
然后就是设置ImageView和TextView,这里不再赘述。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/exercise_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/exercise"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="练习"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/errorProne_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/errorprone"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="易错"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:background="#00000000"/>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/common_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/common"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="常见"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/special_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/special"
android:background="#00000000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="专项"
android:textSize="15sp" />
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
这里同样是加了分割线。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
最后这里设置了一个SearchView搜索框和一个ImageButton。其中设置了搜索框的内容,并在background中引入编写的circle文件使搜索框的边缘呈现圆形。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/searchHome"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:hint=" 请输入搜索内容"
android:paddingLeft="20dp"
android:background="@drawable/searchview_circle"/>
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/recording_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:src="@drawable/recording"
android:background="#00000000"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:padding="20dp"/>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
circle文件如下,设置了形状以及颜色,利用color设置绿色,用radius设置边缘为圆形。
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle">
<stroke
android:width="1dp"
android:color="#57A81C" />
<corners android:radius="20dp" />
shape>
(4)首页界面逻辑编写
首先,我们给app内置一个数据库,用以储存垃圾以及对应的分类。这里使用LitePal数据库来储存数据。
配置litepal.xml文件(在app/src/main目录下新建一个litepal.xml文件),并编辑内容为:
<litepal>
<dbname value="KnowledgeStore">dbname>
<version value="1">version>
<list>
<mapping class="com.example.refuseclassification.Database.Knowledge">mapping>
list>
litepal>
然后配置LitePalApplication,修改Manifest.xml文件中的代码,如下所示:
定义一个类Knowledge类,继承自LitePalSupport,声明属性id、name、kind和answer,并实现其getter和setter方法。然后在上面的litepal.xml文件添加该类的映射模型。
public class Knowledge extends LitePalSupport implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String kind;
private String answer;
public Knowledge() {
}
public Knowledge(int id, String name, String kind, String answer) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.kind = kind;
this.answer = answer;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setKind(String kind) {
this.kind = kind;
}
public void setAnswer(String answer) {
this.answer = answer;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getKind() {
return kind;
}
public String getAnswer() {
return answer;
}
}
配置工作完成了,开始进行数据库的创建的插入。首先用两个数组储存要插入的name和kind。
public class KnowledgeDatabase {
String[] name = {"菠萝", "鸭脖", "鸭脖子", "萝卜", "胡萝卜", "萝卜干", "草", "草莓",
"红肠", "香肠", "鱼肠", "过期食品", "剩菜剩饭", "死老鼠", "麦丽素", "果粒",
"巧克力", "芦荟", "落叶", "乳制品", "鲜肉月饼", "炸鸡腿", "药渣", "毛毛虫", "蜗牛",
"安全套", "按摩棒", "肮脏塑料袋", "旧扫把", "旧拖把", "搅拌棒", "棒骨", "蚌壳",
"保龄球", "爆竹", "纸杯", "扇贝", "鼻毛", "鼻屎", "笔", "冥币",
"尿不湿", "餐巾", "餐纸", "一次性叉子", "掉下来的牙齿", "丁字裤", "耳屎", "飞机杯", "碱性无汞电池",
"安全帽", "棉袄", "白纸", "手办", "包包", "保温杯", "报纸", "电脑设备",
"被单", "本子", "手表", "玻璃", "尺子", "充电宝", "充电器", "空调",
"耳机", "衣服", "乐高", "公仔", "可降解塑料", "酒瓶", "篮球", "红领巾", "泡沫箱",
"阿司匹林", "浴霸灯泡", "避孕药", "温度计", "杀毒剂", "感冒药", "药瓶", "止咳糖浆",
"胶囊", "灯泡", "农药", "油漆", "维生素", "酒精", "指甲油", "铅蓄电池",
"废电池", "打火机", "医用纱布", "医用棉签", "相片", "干电池", "钙片", "针管", "针筒"};
String[] kind = {"湿垃圾", "干垃圾", "可回收物", "有害垃圾"};
接着开始数据库的配置。首先获取数据库的实例,然后循环插入数据,先用where子句来查询是否已经有此数据id,若无则用类方法insert插入该数据,否则跳过插入,以防止数据的重复插入。
public void setKnowledgeDatabase() {
LitePal.getDatabase();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// 获取数据表数据,查询是否有相同数据,防止重复插入
List<Knowledge> knowledges = LitePal.where("id = ?", String.valueOf(i + 1))
.find(Knowledge.class);
if (knowledges == null || knowledges.size()== 0)
if (i < 25)
insert(i + 1, name[i], kind[0]);
else if (i < 50)
insert(i + 1, name[i], kind[1]);
else if (i < 75)
insert(i + 1, name[i], kind[2]);
else
insert(i + 1, name[i], kind[3]);
else
continue;
}
}
这里是insert方法。这里先创造出一个Knowledge实例,然后调用set方法进行设置,最后用save将数据保存到数据库中。
public void insert(int id, String name, String kind) {
Knowledge knowledge = new Knowledge();
knowledge.setId(id);
knowledge.setName(name);
knowledge.setKind(kind);
knowledge.save();
}
}
这样,app中重要的垃圾数据我们就成功嵌入到app的数据库中。
该界面中,这四个按钮的界面和功能类似,我们用其中的“可回收”按钮进行分析。

新建活动RecyclableActivity和布局activity_recyclable,首先编写布局。该布局是一个线性布局,首先包含的是一个用于显示标题的toolbar。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/recyclable_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
接下来是个横向排列的线性布局,先放置一张ImageView,使用scaleType来保证图片不被拉伸。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:src="@drawable/recyclable"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="5"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_margin="5dp">
该图片的右侧,是一个纵向排列的线性布局,该布局由两个TextView组成,内容是标题已经可回垃圾的定义。
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#D8000000"
android:text="可回收垃圾"
android:textSize="15sp"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#45000000"
android:text="可回收物指适宜回收利用和资源化利用的生活废弃物。主要包括:废纸、废弃塑料瓶、废金属、废包装物、废旧纺织物、废弃电器电子产品、废玻璃、废纸塑铝复合包装等。" />
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
在这个线性布局下面,又是一个纵向排列的线性布局,也是由两个TextView组成内容是投放要求和投放要求的具体内容。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_margin="5dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#D8000000"
android:text="投放要求"
android:textSize="15sp"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#45000000"
android:text="鼓励居民直接将可回收物纳入再生资源回收系统,如需分类投放应尽量保持清洁干燥,避免污染,轻投轻放。其中:1、废纸应保持平整,立体包装物应清空内容物,清洁后压扁投放。2、废玻璃有尖锐边角的,应包裹后投放。" />
LinearLayout>
最后还是一个纵向排列的线性布局,该布局由一个标题和一个RecyclerView组成,RecyclerView用于储存常见的可回收垃圾。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="4"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#D8000000"
android:text="常见可回收垃圾"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclable_recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
RecyclerView由子项item组成,所以需要对子项布局进行编写,这里采用相对布局,将垃圾名放置在子项左边,种类放在子项右边,最下边是一条分割线。
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/kind"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#1B000000"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/>
RelativeLayout>
接下来编写RecyclableActivity。首先我们定义一些需要用到的控件以及RecyclerView的适配器,然后在主方法中设置标题栏内容,用litepal调用where查询语句获取数据库内容,得到knowledges列表。然后我们实例化适配器,给RecyclerView适配适配器和布局管理器。
public class RecyclableActivity extends BaseActivity {
private Toolbar toolbar;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private List<Knowledge> knowledges = new ArrayList<>();
private MyAdapter myAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_recyclable);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.recyclable_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("可回收垃圾");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
// 编写列表内容
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclable_recyclerView);
knowledges = LitePal.where("kind = ?", "可回收物").find(Knowledge.class);
myAdapter = new MyAdapter();
recyclerView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
LinearLayoutManager manager = new LinearLayoutManager(RecyclableActivity.this);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(manager);
}
如图,我们在该活动的主类中创建适配器内部类,在onCreateViewHolder方法中将item布局加载进来,然后创建一个ViewHolder实例并返回;onBindViewHolder方法中,我们对子项进行赋值;最后在getItemCount中返回有多少子项。
private class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyViewHolder> {
@NonNull
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = View.inflate(RecyclableActivity.this, R.layout.item_recyclerview, null);
MyViewHolder myViewHolder = new MyViewHolder(view);
return myViewHolder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, int position) {
Knowledge knowledge = knowledges.get(position);
holder.name.setText(knowledge.getName());
//holder.kind.setText((knowledge.getKind()));
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return knowledges.size();
}
}
这个类是用于适配ViewHolder,实例化name和kind。
private class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView name;
TextView kind;
public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
name = itemView.findViewById(R.id.name);
kind = itemView.findViewById(R.id.kind);
}
}
}
最后效果如下:

首页中,这五个按钮对应的活动的功能也是相似的,这里以模拟考试来分析。

新建活动activity_test.xml,编写界面。该界面首先是一个纵向排列的线性布局,第一个控件时toolbar,这个已经提到很多次了,用于设置标题栏。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/test_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
接下来是一个横向排列的线性布局,该布局由两个TextView组成,用于显示题目的数量,其中question_num会在活动的方法中动态改变值,达到答题然后题目数改变的效果。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_margin="10dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/question_num"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1"
android:textColor="#000000" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="/10"
android:textColor="#88000000" />
LinearLayout>
接下来的布局由一个大的纵向排列的线性布局组成。
首先是一个醒目的TextView,用于显示当前的题目,它也会在方法进行刷新,以显示不同的题目。然后是一个RadioGroup,它包含四个RadioButton,分别表示四个选项:可回收物、有害垃圾、湿垃圾、干垃圾。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/question"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="30dp"
android:textSize="35sp" />
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/radioGroup"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp">
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/answer1"
android:text="可回收物"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/answer2"
android:text="有害垃圾"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checked="false"/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/answer3"
android:text="湿垃圾 "
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/answer4"
android:text="干垃圾 "
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
RadioGroup>
最后是一个Button,用于提示用户开始答题,当用户点击按钮之后,会变成“提交答案”,以提示用户作答。
<Button
android:id="@+id/submit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="开始答题"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:background="@drawable/button_circle"
android:padding="20dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
接下来编写TextActivity的代码。这里还是先定义一些控件和垃圾知识列表,以及分数和计数器。
public class TestActivity extends BaseActivity{
private Toolbar toolbar;
private TextView question_num;
private TextView question;
private Button submit;
private RadioGroup radiogroup;
private RadioButton answer1;
private RadioButton answer2;
private RadioButton answer3;
private RadioButton answer4;
private List<Knowledge> knowledges = new ArrayList<>();
private String answer = "";
private int score = 0;
private int count;
这里是引入布局和初始化toolbar以及计数器然后使用Math.random()方法来获取随机数,并加入到一个集合中。之所以使用集合来储存随机数,是因为集合中的元素不重复,这样子我们就可以得到不重复的10个0~99的数字,以此从数据库中随机选择题目。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.test_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("模拟考试");
count = -1;
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);// 初始化ToolBar
// 初始化随机数列表,10个1~100的数
Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
while (hashSet.size() != 10) {
int number = (int) (Math.random() * 100);
hashSet.add(number);
}
这里使用到了前面所说的随机数集合hashSet,我们使用迭代器,将里面的数据转化为int型的id,按照这个随机的id,使用LitePal的查询语句获取数据库中相应id的knowledge对象,并把这个对象加入到该活动的knowledge对象列表中。然后就是对控件的实例化。
// 初始化问题列表
Iterator it = hashSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
int id = Integer.parseInt(it.next().toString());
Knowledge knowledge = LitePal.find(Knowledge.class, id);
knowledges.add(knowledge);
}
// 设置题目
question = findViewById(R.id.question);
question_num = findViewById(R.id.question_num);
radiogroup = findViewById(R.id.radioGroup);
answer1 = findViewById(R.id.answer1);
answer2 = findViewById(R.id.answer2);
answer3 = findViewById(R.id.answer3);
answer4 = findViewById(R.id.answer4);
submit = findViewById(R.id.submit);
这里我们对radioGroup设置一个监听器,监听用户的选择,选择相应的答案,answer会赋值为相应的答案,用以存储用户的答案,并设置用户选择选项时,选项的颜色为红色。
radiogroup.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
// 选中文字显示红色,没有选中显示黑色
if(answer1.isChecked()) {
answer = "可回收物";
answer1.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FF0033"));
}else{
answer1.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#000000"));
}
if(answer2.isChecked()) {
answer = "有害垃圾";
answer2.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FF0033"));
}else{
answer2.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#000000"));
}
if(answer3.isChecked()) {
answer = "湿垃圾";
answer3.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FF0033"));
}else{
answer3.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#000000"));
}
if(answer4.isChecked()) {
answer = "干垃圾";
answer4.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FF0033"));
}else{
answer4.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#000000"));
}
}
});
接下来设置按钮的监听器。当用户还未点击时,count为-1,此时按钮文字未改变,只有当点击之后,才会变成“提交答案”。用户每点击一次按钮,count++,并将answer与正确答案做对比,记录分数并储存用户答案。
submit.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
radiogroup.clearCheck();
if (count == -1) {
count++;
question_num.setText(Integer.toString(count + 1));
question.setText(knowledges.get(count).getName());
submit.setText("提交答案");
}
else if (count < 10) {
if (!answer.equals("")) {
if (answer.equals(knowledges.get(count).getKind())) {
score += 10;
}
Knowledge knowledge = knowledges.get(count);
knowledge.setAnswer(answer);
knowledges.set(count, knowledge);
}
当用户答到最后一题时,按钮变成查看结果。
count = count + 1;
if (count != 10)
{
question_num.setText(Integer.toString(count + 1));
question.setText(knowledges.get(count).getName());
}
else {
submit.setText("查看结果");
}
}
最后点击按钮时,我们跳转到一个新的活动,使用intent和bundle传递数据knowledges列表和分数score。由于我们需要将answer储存到列表中,所以修改Knowledge类,新增answer元素以及相应的set和get方法。因为使用bundle传递对象列表与传递一般的数据不一样,需要对列表进行序列,只要让类继承接口Serializable就行了。然后就是启动新活动并结束该活动。
else {
Intent intent = new Intent(TestActivity.this,
AnswerActivity.class);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putSerializable("knowledges", (Serializable) knowledges);
bundle.putInt("score", score);
intent.putExtra("message", bundle);
startActivity(intent);
finish();// 销毁活动
}
}
});
}
}
我们来编写答题完成之后跳转的活动AnswerActivity。这里首先依然是纵向排列的线性布局以及toolbar。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/test_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
然后就是一个横向排列的线性布局,包含一个ImageView和一个TextView,用于提示用户和显示最后的得分。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_margin="40dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/score"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/score"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:textSize="70sp"
android:textColor="#F73C2E"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_margin="10dp" />
LinearLayout>
接下来是一个纵向的布局,用于显示用户答题的结果。包含的第一个横向的线性布局是答题的表头,里面就是使用相对布局居中的TextView和分割线。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="4"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="题目"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#1B000000" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我的答案"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#1B000000" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="正确答案"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
RelativeLayout>
LinearLayout>
最后就是显示最终答题情况的RecyclerView。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#1B000000" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/answer_recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
既然有了RecyclerView,那我们就需要编写子项布局。编写item_answer.xml,该布局和上一个布局中显示答案的表头差不多。主要是分割线和利用RelativeLayout居中显示的TextView。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/question_done"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#1B000000" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/my_answer"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#1B000000" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/right_answer"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
RelativeLayout>
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#1B000000" />
LinearLayout>
最后我们来编写AnswerActivity。这里依然还是定义控件。
public class AnswerActivity extends BaseActivity {
private Toolbar toolbar;
private TextView score_view;
private List<Knowledge> knowledges = new ArrayList<>();
private int score;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private MyAdapter myAdapter;
主方法这里我们先初始化控件,然后使用Intent和Bundle获取来自上个活动用户的答题情况以及分数,然后显示、适配到控件中。给RecyclerView适配数据以及适配器,这里就不在赘述了。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_answer);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.test_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("考试结果");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);// 初始化ToolBar
score_view = findViewById(R.id.score);
// 获取数据
Intent intent = getIntent();
Bundle bundle = intent.getBundleExtra("message");
knowledges = (List<Knowledge>) bundle.getSerializable("knowledges");
score = bundle.getInt("score");
score_view.setText(String.valueOf(score));
// 适配
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.answer_recyclerView);
myAdapter = new MyAdapter();
recyclerView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
LinearLayoutManager manager = new LinearLayoutManager(AnswerActivity.this);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(manager);
}
private class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyViewHolder> {
@NonNull
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = View.inflate(AnswerActivity.this, R.layout.item_answer, null);
MyViewHolder myViewHolder = new MyViewHolder(view);
return myViewHolder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, int position) {
Knowledge knowledge = knowledges.get(position);
holder.question_done.setText(knowledge.getName());
holder.right_answer.setText(knowledge.getKind());
holder.my_answer.setText(knowledge.getAnswer());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return knowledges.size();
}
}
private class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView question_done;
TextView my_answer;
TextView right_answer;
public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
question_done = itemView.findViewById(R.id.question_done);
my_answer = itemView.findViewById(R.id.my_answer);
right_answer = itemView.findViewById(R.id.right_answer);
}
}
}
结果如图所示:

最后,我们对这首页中剩下的两个功能:搜索框和语音识别,进行实现。

首先,我们在主页界面设置搜索框EditText失去焦点并设置点击事件,使得用户点击搜索框就可以跳转到搜索活动SearchActivity中。
search = (EditText) view.findViewById(R.id.searchHome);
search.setFocusable(false);//失去焦点
search.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), SearchActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
首先编写搜索活动的布局activity_search.xml。该布局是线性排列,顶部是标题栏Toolbar,然后就是搜索栏EditText,搜索栏下方则是展现搜索结果的RecyclerView。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/search_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/search"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:hint=" 请输入搜索内容"
android:paddingLeft="20dp"
android:background="@drawable/searchview_circle"/>
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/search_recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="20dp"/>
LinearLayout>
然后我们编写搜索活动SearchActivity。首先在主函数定义需要使用到的控件、知识列表以及一个适配器。
public class SearchActivity extends BaseActivity {
private Toolbar toolbar;
private EditText editText;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
List<Knowledge> knowledges = new ArrayList<>();
private MyAdapter myAdapter;
接着在主函数onCreate中加载刚才写好的布局,并且设置标题栏为搜索然后设置其居中显示;然后初始化数据列表,利用SQLite语句将数据库中的所有数据加载到knowledges列表当中,并初始化recyclerView和适配器myAdapter,最后再用LinearLayoutManager将布局指定为线性布局。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_search);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.search_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("搜索");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
// 初始化数据列表
knowledges = LitePal.findAll(Knowledge.class);
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.search_recyclerView);
myAdapter = new SearchActivity.MyAdapter();
recyclerView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
LinearLayoutManager manager = new LinearLayoutManager(SearchActivity.this);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(manager);
然后我们实例化EditText,由于我们要使用语音识别功能,这里要将语音识别的结果利用intent传到当前的活动中。先用if语句判断是否有传入识别结果,如果是,则将识别到的结果显示在EditText中;然后清空列表,重新利用SQLite语句获取数据库中包含识别结果的内容,然后更新适配器,从而刷新recyclerView显示的搜索结果。
// 实例化EditText
editText = findViewById(R.id.search);
Intent intent = getIntent();
String record = intent.getStringExtra("record");
if (record != null) {
editText.setText(record);
knowledges.clear();
knowledges = LitePal.where("name like ?", "%" + record + "%").
find(Knowledge.class);
myAdapter = new SearchActivity.MyAdapter();
recyclerView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
}
我们给EditText设置一个监听器,监听用户的输入。在用户输入文本前,设置好适配器;当用户开始输入的时候,EditText获取当前输入框中的内容,然后使用SQLite语句,在数据库中获取含有输入框内容的搜索结果,以此来实现动态的模糊搜索。
editText.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
// 输入文本前的状态
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
if(myAdapter != null){
recyclerView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
}
}
// 输入文本时的状态
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
String str = s.toString();
knowledges.clear();
knowledges = LitePal.where("name like ?", "%" + str + "%").
find(Knowledge.class);
myAdapter = new SearchActivity.MyAdapter();
recyclerView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
}
// 输入文本之后的状态
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
}
});
}
剩下的就是适配器类和ViewHolder的实现,这个在前面已经介绍过作用了,这里不予赘述。
private class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyViewHolder> {
@NonNull
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = View.inflate(SearchActivity.this, R.layout.item_recyclerview, null);
MyViewHolder myViewHolder = new MyViewHolder(view);
return myViewHolder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, int position) {
Knowledge knowledge = knowledges.get(position);
holder.name.setText(knowledge.getName());
holder.kind.setText((knowledge.getKind()));
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return knowledges.size();
}
}
private class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView name;
TextView kind;
public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
name = itemView.findViewById(R.id.name);
kind = itemView.findViewById(R.id.kind);
}
}
}
结果如下,用户输入一个字就会进行刷新,展示搜索内容,实现了动态搜索;内容是包含用户搜索内容的所有内容,以此实现模糊搜索。



编写主角界面的最后一个按钮——语音识别。如何导入api我是参考了这篇博客https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38436214/article/details/106636277#comments_19582555。
按照上面的博客将百度语音识别库api导入完成之后,首先在HomeFragment中定义语音识别核心库。
private EventManager asr;//语音识别核心库
private String result;
接下来开始编写语音识别功能。首先在Manifest中添加以下权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.GET_TASKS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BROADCAST_STICKY" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
然后在core文件夹中的Manifest文件中添加id和密钥,value对应的值是自己注册之后生成的,每个人都不一样,这样才可以使用该api。
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="com.baidu.speech.APP_ID"
android:value="25415468"/>
<meta-data
android:name="com.baidu.speech.API_KEY"
android:value="iCYsEmwScqNGAlzDbZcl7vh4"/>
<meta-data
android:name="com.baidu.speech.SECRET_KEY"
android:value="WakD4dM6hykhHreHjQ5uNayIXnP3BSSp"/>
application>
首先在HomeFragment的主函数中,初始化待会儿要用到的权限。
// 初始化权限
initPermission();
语音识别自然要用到这个麦克风,这个权限是需要动态申请的,initPermission方法如下。
private void initPermission() {
String permissions[] = {Manifest.permission.RECORD_AUDIO,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE,
Manifest.permission.INTERNET,
Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
};
ArrayList<String> toApplyList = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String perm : permissions) {
if (PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED != ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(getContext(), perm)) {
toApplyList.add(perm);
}
}
String tmpList[] = new String[toApplyList.size()];
if (!toApplyList.isEmpty()) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(getActivity(), toApplyList.toArray(tmpList), 123);
}
}
接下来给录音按钮绑定按下和松开事件,当按下按钮时开始录音,松开按钮时录音结束。
recording_button = (ImageButton) view.findViewById(R.id.recording_button);
recording_button.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// 按下 处理相关逻辑
asr.send(SpeechConstant.ASR_START, "{}", null, 0, 0);
} else if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
// 松开 处理相关逻辑
asr.send(SpeechConstant.ASR_STOP, "{}", null, 0, 0);
}
return false;
}
});
然后还要初始化语音识别核心库对象,并设置监听器。
//初始化EventManager对象
asr = EventManagerFactory.create(getContext(), "asr");
//注册自己的输出事件类
asr.registerListener(this); // EventListener 中 onEvent方法
由于解析之后得到的语音识别结果是JSON字符串,无法直接对其进行搜索,我们需要对结果进行处理,转化成可以直接搜索的文字识别结果。定义ASRresponse实体bean,如下。
package com.example.refuseclassification;
import java.util.List;
public class ASRresponse {
/**
* results_recognition : ["你好,"]
* result_type : final_result
* best_result : 你好,
* origin_result : {"asr_align_begin":80,"asr_align_end":130,"corpus_no":6835867007181645805,"err_no":0,"raf":133,"result":{"word":["你好,"]},"sn":"82d975e0-6eb4-43ac-a0e7-850bb149f28e"}
* error : 0
*/
private String result_type;
private String best_result;
private OriginResultBean origin_result;
private int error;
private List<String> results_recognition;
public String getResult_type() {
return result_type;
}
public void setResult_type(String result_type) {
this.result_type = result_type;
}
public String getBest_result() {
return best_result;
}
public void setBest_result(String best_result) {
this.best_result = best_result;
}
public OriginResultBean getOrigin_result() {
return origin_result;
}
public void setOrigin_result(OriginResultBean origin_result) {
this.origin_result = origin_result;
}
public int getError() {
return error;
}
public void setError(int error) {
this.error = error;
}
public List<String> getResults_recognition() {
return results_recognition;
}
public void setResults_recognition(List<String> results_recognition) {
this.results_recognition = results_recognition;
}
public static class OriginResultBean {
/**
* asr_align_begin : 80
* asr_align_end : 130
* corpus_no : 6835867007181645805
* err_no : 0
* raf : 133
* result : {"word":["你好,"]}
* sn : 82d975e0-6eb4-43ac-a0e7-850bb149f28e
*/
private int asr_align_begin;
private int asr_align_end;
private long corpus_no;
private int err_no;
private int raf;
private ResultBean result;
private String sn;
public int getAsr_align_begin() {
return asr_align_begin;
}
public void setAsr_align_begin(int asr_align_begin) {
this.asr_align_begin = asr_align_begin;
}
public int getAsr_align_end() {
return asr_align_end;
}
public void setAsr_align_end(int asr_align_end) {
this.asr_align_end = asr_align_end;
}
public long getCorpus_no() {
return corpus_no;
}
public void setCorpus_no(long corpus_no) {
this.corpus_no = corpus_no;
}
public int getErr_no() {
return err_no;
}
public void setErr_no(int err_no) {
this.err_no = err_no;
}
public int getRaf() {
return raf;
}
public void setRaf(int raf) {
this.raf = raf;
}
public ResultBean getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(ResultBean result) {
this.result = result;
}
public String getSn() {
return sn;
}
public void setSn(String sn) {
this.sn = sn;
}
public static class ResultBean {
private List<String> word;
public List<String> getWord() {
return word;
}
public void setWord(List<String> word) {
this.word = word;
}
}
}
}
然后在gradle中加入GSON依赖,我们使用GSON对JSON数据进行处理。
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.4.0'
后面我们在处理之后的结果中就可以直接使用GSON来进行解析了。
接下来我们实现核心库接口EventListener。
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment implements EventListener {...}
我们重写接口的回调方法。参数params是识别之后未经处理的json字符串,如果params为空,表示未识别,我们跳过处理;否则,我们使用GSON解析参数,并去掉其中的“,”,保证字符串的连续;最后使用intent将结果传递到下一个活动SearchActivity。
@Override
public void onEvent(String name, String params, byte[] data, int offset, int length) {
if (name.equals(SpeechConstant.CALLBACK_EVENT_ASR_PARTIAL)) {
// 识别相关的结果都在这里
if (params == null || params.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (params.contains("\"final_result\"")) {
// 一句话的最终识别结果
Gson gson = new Gson();
ASRresponse asRresponse = gson.fromJson(params, ASRresponse.class);//数据解析转实体bean
if(asRresponse.getBest_result().contains(",")){
// 包含逗号 则将逗号替换为空格
// 替换为空格之后,通过trim去掉字符串的首尾空格
setResult(asRresponse.getBest_result().replace(',',' ').trim());
}else {// 不包含
setResult(asRresponse.getBest_result().trim());
}
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), SearchActivity.class);
if (result.contains("。")) {
setResult(result.replaceAll("。", ""));
}
intent.putExtra("record", result);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
}
最后,我们还要重写结束事件,退出监听。
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
//发送取消事件
asr.send(SpeechConstant.ASR_CANCEL, "{}", null, 0, 0);
//退出事件管理器
// 必须与registerListener成对出现,否则可能造成内存泄露
asr.unregisterListener(this);
}
结果如下,按下录音键开始语音识别,松开录音键则跳转到搜索界面,显示搜索结果。


(5)指南界面编写
接下来进行第二个界面(指南界面)的编写。打开之前创建的碎片布局frag_guide.xml,编写其中的布局。和前面home碎片一样,需要一个Toolbar作为标题栏;紧接着是一个顶端导航栏,这里使用了TabLayout作为顶部导航栏;最后就是一个ViewPager容器占满其余屏幕,用于显示碎片。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/guide_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/guide_tab"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<androidx.viewpager.widget.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewPagerGuide"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
LinearLayout>
和前面提到的BottomNavigationView用ViewPager容器存放Fragment一样,TabLayout也是,两者都需要一个Adapter适配器,由于前面编写了PagerAdapter.java,这里直接重用就行,就不需要再重新编写。
我们直接编写GuideFragmet.java。和前面BottomNavigationView一样,这里先定义一些需要使用的构件。
public class GuideFragment extends Fragment {
private TabLayout tabLayout;
private List<Fragment> fragmentList;
private ViewPager viewPager;
private PagerAdapter adapter;
private Toolbar toolbar;
接着,我们初始化碎片界面之后,实例化toolbar并调用方法设置标题栏为“指南”,然后调用类方法来实例化TabLayout和viewPager,并实现点击和滑动事件。
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_guide, container, false);
toolbar = (Toolbar) view.findViewById(R.id.guide_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("指南");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
// 初始化tabLayout和viewPager并绑定滑动和点击事件
initMenuTabs(view);
initViewPager(view);
bindTabAndPager(view);
return view;
}
initMenuTabs方法中,实例化tabLayout并设置了相应的tab标题。
public void initMenuTabs(View view) {
tabLayout = (TabLayout) view.findViewById(R.id.guide_tab);
tabLayout.setSelectedTabIndicatorColor(0);
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("可回收物"));
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("有害垃圾"));
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("湿垃圾"));
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("干垃圾"));
}
这个方法和前面的BottomNavigationView一样,在列表中加入四个对应菜单的fragment,然后实例化adapter,最后ViewPager调用 .setAdapter() 方法传入PagerAdapter即可实现一个可以左右侧滑切换界面的效果。
public void initViewPager(View view) {
viewPager = (ViewPager) view.findViewById(R.id.viewPagerGuide);
fragmentList = new ArrayList<>();
fragmentList.add(new RecyclableFragment());
fragmentList.add(new HarmfulFragment());
fragmentList.add(new WetFragment());
fragmentList.add(new DryFragment());
adapter = new PagerAdapter(getFragmentManager(), this, fragmentList);
viewPager.setAdapter(adapter);
}
这个bindTabAndPager是完成ViewPager和TabLayout的联动。我们给ViewPager设置了监听器,监听TabLayout菜单的改变,当TabLayout改变时,ViewPager也随之改变。最后一个很重要的点,就是设置ViewPager的缓存页面为3,因为我们有四个fragment,而ViewPager的默认缓存页面为1,导致连续跳转fragment要重新加载。
public void bindTabAndPager(View view) {
tabLayout = (TabLayout) view.findViewById(R.id.guide_tab);
viewPager = (ViewPager) view.findViewById(R.id.viewPagerGuide);
viewPager.addOnPageChangeListener(new TabLayout.TabLayoutOnPageChangeListener(tabLayout));
viewPager.setOffscreenPageLimit(3); // 设置缓存页面为3
tabLayout.addOnTabSelectedListener(new TabLayout.OnTabSelectedListener() {
@Override
public void onTabSelected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
int position = tab.getPosition();
viewPager.setCurrentItem(position);
}
@Override
public void onTabUnselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
}
@Override
public void onTabReselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
}
});
}
}
接下来实现里面的碎片,四个碎片功能都一样,都是用来科普四种垃圾,这里举例可回收垃圾的界面,首先编写frag_recyclable.xml文件,该文件很简单,里面只包含了一个WebView。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<WebView
android:id="@+id/recyclable_web"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
LinearLayout>
接着编写RecyclableFragment.java,将刚刚编写的碎片布局加载进来,并实例化WebView,调用getSettings方法和setJavaScriptEnabled(true)来让WebView支持JavaScript脚本,然后使用setWebViewClient方法保证网页在app中显示,最后传入百度百科可回收垃圾的地址url。
public class RecyclableFragment extends Fragment {
private WebView webView;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_recyclable, container, false);
webView = (WebView) view.findViewById(R.id.recyclable_web);
webView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
webView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient());
// 百度百科
webView.loadUrl("https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8F%AF%E5%9B%9E%E6%94%B6%E7%89%A9");
return view;
}
}
其他文件也一样。
最后在Manifest申请网络权限,才可以访问网络。
结果如下:




(6)设置界面编写
接下来进行最后一个界面(设置界面)的编写。打开之前创建的碎片布局frag_setting.xml,编写其中的布局。和前面home和guide碎片一样,需要一个Toolbar作为标题栏;然后是一个包含着ImageButton的线性布局,由于更换头像;最后就是六个居中显示的TextView,用于查看通知、联系、退出登录等功能。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/setting_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="140dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/person_photo"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:background="@drawable/image_circle"
android:src="@drawable/person_default" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_notification"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="查看通知"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="15dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_contact"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="联系我们"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="15dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_about"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="关于我们"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="15dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_agreement"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="用户协议与隐私"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="15dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_version"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="当前版本"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="15dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_logout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="退出登录"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="15dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#A3DD53" />
LinearLayout>
最后设置界面如下。

首先在SettingFragment中定义需要使用的控件。然后在主函数中设置toolbar。
public class SettingFragment extends Fragment {
private Toolbar toolbar;
private ImageButton imageButton;
private TextView notification;
private TextView contact;
private TextView about;
private TextView agreement;
private TextView version;
private TextView logout;
private Bitmap head;// 头像Bitmap
private static String path = "/sdcard/myHead/";// sd路径
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_setting, container, false);
toolbar = (Toolbar) view.findViewById(R.id.setting_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("设置");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
首先,我们来实现更换头像功能。先实例化imageButton,然后将相册中的头像文件转化为bitmap,显示在imageButton上。然后给imageButton设置监听器,点击的时候就调用showTypeDialog()方法。
//API24以上系统分享支持file:///开头
StrictMode.VmPolicy.Builder builder = new StrictMode.VmPolicy.Builder();
StrictMode.setVmPolicy(builder.build());
builder.detectFileUriExposure();
imageButton = (ImageButton) view.findViewById(R.id.person_photo);
Bitmap bt = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path + "head.jpg");// 从SD卡中找头像,转换成Bitmap
if (bt != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
Drawable drawable = new BitmapDrawable(bt);// 转换成drawable
imageButton.setImageDrawable(drawable);
} else {
/**
* 如果SD里面没有则需要从服务器取头像,取回来的头像再保存在SD中
*
*/
}
imageButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.person_photo:// 更换头像
showTypeDialog();
break;
}
}
});
showTypeDialog()方法的实现如下。首先显示一个对话框,对话框的布局在dialog_select_photo.xml中实现。然后分别获得对话框TextView的实例,并分别设置点击事件。一个设置打开相册,另外一个则是设置打开相机。
private void showTypeDialog() {
//显示对话框
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
final AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
View view = View.inflate(getActivity(), R.layout.dialog_select_photo, null);
TextView tv_select_gallery = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_select_gallery);
TextView tv_select_camera = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_select_camera);
tv_select_gallery.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {// 在相册中选取
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent1 = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_PICK, null);
//打开文件
intent1.setDataAndType(MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, "image/*");
startActivityForResult(intent1, 1);
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
tv_select_camera.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {// 调用照相机
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent2 = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
intent2.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT,
Uri.fromFile(new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), "head.jpg")));
startActivityForResult(intent2, 2);// 采用ForResult打开
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
dialog.setView(view);
dialog.show();
}
对话框的布局在dialog_select_photo.xml。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="60dp"
android:paddingRight="60dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_select_gallery"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="20dp"
android:padding="20dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="从相册中选取" />
<TextView
android:layout_below="@id/tv_select_gallery"
android:id="@+id/tv_select_camera"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom="20dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="拍摄照片" />
RelativeLayout>
接下来我们重写onActivityResult()方法,在选择好图片之后执行cropPhoto()方法。
@Override
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
switch (requestCode) {
case 1:
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
cropPhoto(data.getData());// 裁剪图片
}
break;
case 2:
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
File temp = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() + "/head.jpg");
cropPhoto(Uri.fromFile(temp));// 裁剪图片
}
break;
case 3:
if (data != null) {
Bundle extras = data.getExtras();
head = extras.getParcelable("data");
if (head != null) {
/**
* 上传服务器代码
*/
imageButton.setImageBitmap(head);// 用ImageButton显示出来
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
}
这里调用了系统的裁剪功能,指定宽和高,达到裁剪的效果。
/**
* 调用系统的裁剪功能
*
* @param uri
*/
public void cropPhoto(Uri uri) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.android.camera.action.CROP");
intent.setDataAndType(uri, "image/*");
intent.putExtra("crop", "true");
// aspectX aspectY 是宽高的比例
intent.putExtra("aspectX", 1);
intent.putExtra("aspectY", 1);
// outputX outputY 是裁剪图片宽高
intent.putExtra("outputX", 250);
intent.putExtra("outputY", 250);
intent.putExtra("return-data", true);
startActivityForResult(intent, 3);
}
}
效果如下。






接着,我们来实现查看通知功能。实例化通知的TextView之后,我们给它绑定了监听事件,首先新建一个活动NotificationActivity,点击通知栏之后可以跳转到该活动;然后用NotificationManager对通知进行管理,最后对通知进行一些设置,设置标题、内容图标以及活动等等就可以了。
notification = view.findViewById(R.id.text_notification);
notification.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), NotificationActivity.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivities(getContext(),
0, new Intent[]{intent}, 0);
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager)
getContext().getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
//需添加的代码
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O){
String channelId = "default";
String channelName = "默认通知";
manager.createNotificationChannel(new NotificationChannel
(channelId, channelName, NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH));
}
Notification notification = new NotificationCompat.
Builder(getContext(), "default")
.setContentTitle("通知")
.setContentText("点击查看消息内容")
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher))
.setContentIntent(pi)
.setAutoCancel(true)
.build();
manager.notify(1, notification);
}
});
NotificationActivity的活动和布局文件如下,很简单所以不予赘述。
public class NotificationActivity extends BaseActivity {
private Toolbar toolbar;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_notification);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.notification_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("通知");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
}
}
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/notification_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:text="无通知" />
RelativeLayout>
效果如下。


接下来我们来实现“联系我们”、“关于我们”和“用户协议与隐私”。首先实例化contact,当用户点击的时候就会跳转到拨打电话号码的界面,这里传入了一个uri,是一个手机号,用户跳转到拨打页面就可以直接拨打改电话;about则是点击之后跳转到一个AboutActivity;agreement也是跳转到AgreementActivity。
contact = view.findViewById(R.id.text_contact);
contact.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:15767064234"));
startActivity(intent);
}
});
about = view.findViewById(R.id.text_about);
about.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), AboutActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
agreement = view.findViewById(R.id.text_agreement);
agreement.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), AgreementActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
AboutActivity的活动和布局如下。
public class AboutActivity extends BaseActivity {
private Toolbar toolbar;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_about);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.about_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("关于我们");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
}
}
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".AboutActivity">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/about_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="30dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="陈泓龙"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:padding="15dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2019151027"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:padding="15dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="计算机与软件学院软件工程"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:padding="15dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2019级软工三班"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:padding="15dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
LinearLayout>
AgreementActivity的活动和布局如下。其中隐私与协议的内容直接以TextView的文本内容呈现。
public class AgreementActivity extends BaseActivity {
private Toolbar toolbar;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_agreement);
toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.agreement_toolbar);
toolbar.setTitle("用户协议与隐私");
new setTitleCenter().setTitleCenter(toolbar);
}
}
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".AgreementActivity">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/agreement_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#64E269" />
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
ScrollView>
LinearLayout>
效果如下。


接着,我们来实现查看当前版本的功能。这里给version设置的点击事件是用一个Toast显示“当前已是最新版本”。
version = view.findViewById(R.id.text_version);
version.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getContext(), "当前已是最新版本", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
效果如下。

最后,我们实现强制下线的功能。给logout设置点击事件,当用户点击的时候,就会发送一条广播。
logout = view.findViewById(R.id.text_logout);
logout.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.refuseclassification.FORCE_OFFLINE");
getActivity().sendBroadcast(intent);
}
});
然后我们编写一个BaseActivity继承自AppCompatActivity,所有的活动都使用重写后的BaseActivity而不是AppCompatActivity。在BaseActivity中注册广播监听器,用于接收用户发送的广播。当用户发送广播之后,就会弹出一个提示框,用户点击之后就会跳转到登录界面。最后我们将广播取消注册。
package com.example.refuseclassification;
import android.app.ActivityManager;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.net.ConnectivityManager;
import android.net.NetworkInfo;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class BaseActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ForceOfflineReceiver receiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ActivityCollector.addActivity(this);
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction("com.example.refuseclassification.FORCE_OFFLINE");
receiver = new ForceOfflineReceiver();
registerReceiver(receiver, intentFilter);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
if (receiver != null) {
unregisterReceiver(receiver);
receiver = null;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
ActivityCollector.removeActivity(this);
}
class ForceOfflineReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(final Context context, Intent intent) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
builder.setTitle("Warning");
builder.setMessage("您已退出,请重新登录");
builder.setCancelable(false);
builder.setPositiveButton("OK", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
ActivityCollector.finishAll(); //销毁所有活动
Intent i = new Intent(context, LoginActivity.class);
context.startActivity(i); //重新启动LoginActivity
}
});
builder.show();
}
}
}
2. 请详细说明“我的垃圾分类APP”的功能、出现的关键问题及解决方案
功能展示
可以点击此处下载,浏览功能。
问题和解决方案
(1)fragment加载问题
如果用BottomNavigation直接加载Fragment,会导致Fragment无法正常显示,需要使用ViewPager来缓存Fragment。
(2)设置按钮背景透明
在缩放按钮图标时,我发现按钮周围呈现灰色,一时不知道怎么解决,后来发现直接设置背景色为白色就可以达到透明效果。

(3)TabLayout界面的缓存
一开始没有缓存的时候,我发现把界面活动走再滑动回来会导致界面重新加载,刚刚看到的地方就没有了,所以使用设置缓存界面为3,保证不用再重新加载。

(4)权限的声明
(5)不重复随机数的生成
在随机生成题目的时候,为了保证题目不重复,使用了java类对象Set,它是一个集合,而集合中的元素是不重复的,以此保证题目不重复。

(6)对象列表的传值
intent传递对象列表的时候,无法像一般地传值,需要先把对象序列化之后才可以正常传值。

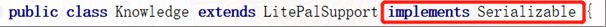
(7)EditText焦点失去
若不失去焦点,用户在点击首页的输入框的时候,会跳出输入法;失去焦点之后就可以顺利跳转到下个页面。

(8)百度语音识别api的申请以及调用
参考了https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38436214/article/details/106636277#comments_19582555,成功实现了语音识别功能。
三、实验总结
本次实验是我做过的最难的实验,该实验综合运用到了课堂上学习到的很多知识,基本上涵盖了老师所讲的,以及还需要自己去探索学习一些新知识,运用到实验中。虽然本次实验难度较大,但是由于前面的几次实验给我打了些许基础,让我开始这个实验的时候不至于不知所措。构建app的过程是顺利的,遇到的困难在网上找一找、自己钻研一下就可以顺利解决。由于时间问题,我只花了不到一个星期去完成这个实验,最后可以达到这样的效果,我是很满意的。在这里也感谢老师和同学们,感谢他们也教会了我许多东西,让我基本上手安卓,并做出这样的项目。





