Spring--扩展
一、 前言
对于入行四五年的JAVA程序员来说,通过学习开源项目的源码来提升自身编码设计能力是不可或缺的途径。楼主自认为热爱编程,有时心血来潮就会断点跟下Tomcat或者Spring,BUT:我会发现越跟到后来,自己都不晓得看到什么,学到了什么!
一年前买了本spring源码的书籍,到目前为止也仅把spring的IOC看了一遍,感觉不到有多少收获。
近段时间,因工作需要,需要用到Mybatis的拦截器,于是又开始了一遍Spring的源码查看学习之旅。
二、 学习方法
对于源码的学习,我觉得应该遵循以下步骤才会更容易学习:
A. 知道Spring是干什么的,理解IOC和AOP的理论,推荐下这篇文章
B. 使用Spring的XML配置方式做过例子或者项目
C. 理解Spring Bean的生命周期,至少知道几个常用的对象的作用,BeanDefinition,BeanFactory,Aware,InitializingBean等
D. 查看Spring插件(你比较熟悉的插件)的源码,如:mybatis-spring,spring-data-redis等源码,因为插件基本上只有在XML配置那几个类中才会与Spring有关系,所以可重点学习那几个类或者接口,再者,学习源码主要作用也是扩展Spring或者写Spring的插件,一举两得。
E. 总结设计模式,设计思想
三、 核心类介绍
A. Bean从XML配置文件转换成BeadDefinition相关接口
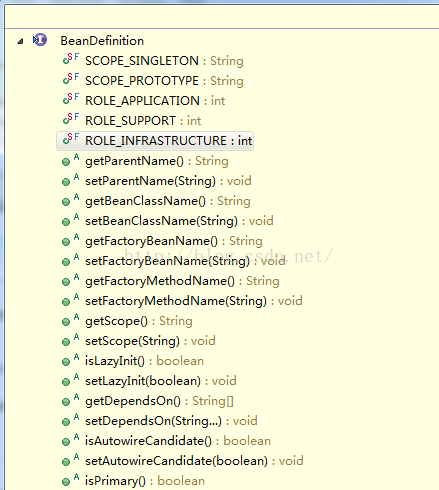
1. BeanDefinition:我们配置的每一个Bean都会生成一个BeanDefinition对象,该对象保存了配置Bean的信息,如属性,类名等等,我们可以理解为这是个实体域接口,里面保存了很多属性供使用
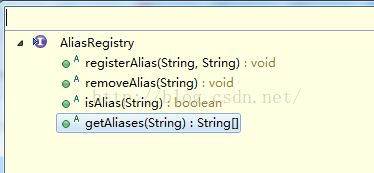
2. AliasRegistry:这个接口相对很简单,一个管理别名的接口,可以理解为使用一个Map来管理name和alias的RUID
3. BeanDefinitionRegistry:这个接口继承了AliasRegistry接口,是一个管理BeanDefinition的注册接口,可以理解为使用一个Map来管理name和BeanDefination的RUID
4. Resource:类是File,一个资源对象的实体域接口
5. ResourceLoader:定义资源加载器,主要应用于根据给定的资源文件地址返回对应的Resource,类似于通过FileStr获取File
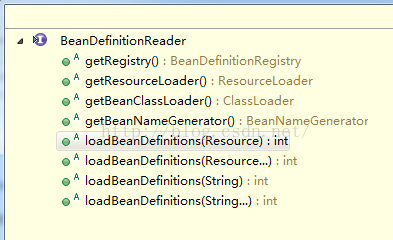
6. BeanDefinitionReader:从资源文件(或路径)中读取出BeanDefinitions,并把BeanDefinitions放入BeanDefinitionRegistry中,这样就可以直接通过getRegistry拿到BeanDefinitionRegistry,就可以从这拿到所有用户XML配置的Bean属性信息了。这段源码看的比较费劲,耐心点看
B. BeanDefinitions转换成具体对象相关接口
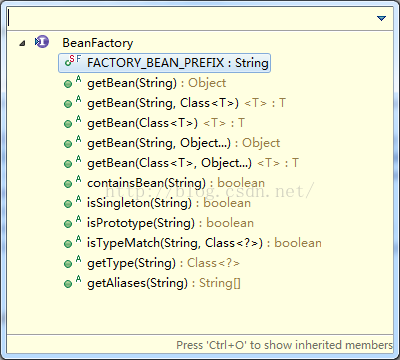
1. BeanFactory:主要是从容器中获取Bean,以及查看Bean的属性,我们可以理解为这是一个服务域接口。一个Web容器只有一个BeanFactory?
2. DefaultListableBeanFactory:
C. 其他接口
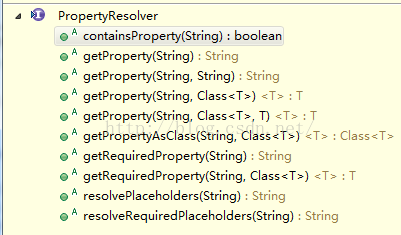
1. PropertyResolver:一个获取属性的接口
2. Environment:管理profile的
3. FactoryBean:使用编程方式生成的Bean,后面会有一个例子简单说明
四、 Spring Bean的生命周期
A. AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法简介
public void refresh() throws BeansException,IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识
prepareRefresh();
//告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,Bean定义资源文件的载入从子类的refreshBeanFactory()方法启动,这个方法完成了从XML配置文件到BeanDefinition的转换,并把最终引用对象BeanDefinitionRegister对象set到BeanFactory的属性中
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory =obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try{
//为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPost事件处理器
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//调用所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//为BeanFactory注册BeanPost事件处理器.BeanPostProcessor是Bean后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//初始化信息源,和国际化相关.
initMessageSource();
//初始化容器事件传播器.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法
onRefresh();
//为事件传播器注册事件监听器.
registerListeners();
//初始化所有非懒加载Bean. 此处会调用doGet方法
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch(BeansException ex) {
//销毁以创建的单态Bean
destroyBeans();
//取消refresh操作,重置容器的同步标识.
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
}
}B. 测试例子
StudentVO与StudentVO1类,初始化两个相同的类是为了更清楚的看到Spring容器的加载顺序,HashCode可看出对象事都是同一个
package com.code.tate.core.web.spring;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public classStudentVO implementsBeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean,
BeanFactoryPostProcessor,DisposableBean, BeanPostProcessor {
private Long id;
private String Name;
private Date birthday;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
// 1
public StudentVO() {
System.out.println("StudentVO Construct");
}
// 2
public void setId(Long id) {
System.out.println("StudentVO setId method");
this.id = id;
}
// 3 BeanNameAware
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("StudentVO implements BeanNameAware method:setBeanName");
}
// 4 BeanFactoryAware
@Override
public voidsetBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throwsBeansException {
System.out.println("StudentVO implements BeanFactoryAware method:setBeanFactory;beanFactory.hashcode:"
+beanFactory.hashCode());
}
// 5 ApplicationContextAware
@Override
public voidsetApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("StudentVO implements ApplicationContextAwaremethod: setApplicationContext;applicationContext.hashcode:"
+applicationContext.hashCode());
this.applicationContext= applicationContext;
}
// 6 InitializingBean
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("StudentVO implements InitializingBean method:afterPropertiesSet");
}
// 7
public void init() {
System.out.println("StudentVO init method");
}
// 8 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
@Override
public voidpostProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("StudentVO implements BeanFactoryPostProcessormethod: postProcessBeanFactory;beanFactory.hashcode:"
+beanFactory.hashCode());
}
// 9 DisposableBean
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("StudentVO implements DisposableBean method:destroy");
}
// 10
private void destory() {
System.out.println("StudentVO destory method");
}
// BeanPostProcessor
@Override
public ObjectpostProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)throwsBeansException {
System.out
.println("StudentVO implements BeanPostProcessor method:postProcessAfterInitialization;bean.hashcode:"
+bean.hashCode());
return bean;
}
// BeanPostProcessor
@Override
public ObjectpostProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("StudentVO implements BeanPostProcessor method:postProcessBeforeInitialization;bean.hashcode:"
+bean.hashCode());
return bean;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentVO [id="+ id + ", Name="+ Name+ ", birthday=" + birthday+ "]";
}
}
Start.java
package com.code.tate.core.web.spring;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public classStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContextfactory= newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-spring.xml");
System.out.println("StartClassPathXmlApplicationContext.hashcode:"+ factory.hashCode());
StudentVOstudent= factory.getBean("studentVO",StudentVO.class);
// System.out.println(student);
// System.out.println(factory.getBeanDefinitionNames());
factory.destroy();
}
}StudentVO Construct
StudentVO setId method
StudentVO implements BeanNameAwaremethod: setBeanName
StudentVO implementsBeanFactoryAware method: setBeanFactory;beanFactory.hashcode:1376400422
StudentVO implementsApplicationContextAware method:setApplicationContext;applicationContext.hashcode:766572210
StudentVO implementsInitializingBean method: afterPropertiesSet
StudentVO init method
StudentVO1 Construct
StudentVO1 setId method
StudentVO1 implements BeanNameAwaremethod: setBeanName
StudentVO1 implementsBeanFactoryAware method: setBeanFactory;beanFactory.hashcode:1376400422
StudentVO1 implementsApplicationContextAware method:setApplicationContext;beanFactory.hashcode:766572210
StudentVO1 implementsInitializingBean method: afterPropertiesSet
StudentVO1 init method
StudentVO implements BeanFactoryPostProcessormethod: postProcessBeanFactory;beanFactory.hashcode:1376400422
StudentVO1 implementsBeanFactoryPostProcessor method:postProcessBeanFactory;beanFactory.hashcode:1376400422
StartClassPathXmlApplicationContext.hashcode:766572210
StudentVO1 implements DisposableBeanmethod: destroy
StudentVO1 destory method
StudentVO implements DisposableBeanmethod: destroy
StudentVO destory method五、 FactoryBean扩展
A. Spring FactoryBean是创建复杂的bean,一般的bean直接用xml配置即可,如果一个bean的创建过程中涉及到很多其他的bean和复杂的逻辑,用xml配置比较困难,这时可以考虑用FactoryBean
B. 例子:
FactoryBeanDemo:实现了FactoryBean
package com.code.tate.core.web.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
/**
* FactoryBean创建Bean
*
*/
public class FactoryBeanDemo implements FactoryBean {
private StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
@Override
public StudentVO getObject() throws Exception {
return studentVO;
}
@Override
public Class getObjectType() {
return StudentVO.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
}
package com.code.tate.core.web.spring;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class FactoryBeanTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext-factoryBean.xml");
// FactoryBeanDemo,使用&studentVO可获取
FactoryBeanDemo FactoryBeanDemo = factory.getBean("&studentVO", FactoryBeanDemo.class);
System.out.println(FactoryBeanDemo);
// FactoryBeanDemo.getObject返回的Bean
StudentVO student = factory.getBean("studentVO", StudentVO.class);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
StudentVO Construct
com.code.tate.core.web.spring.FactoryBeanDemo@5e5d171f
StudentVO [id=null, Name=null, birthday=null]六、 mybatis-spring源码解读
待续