飞桨深度学习7日入门CV - Day06 - 初识PaddleSlim
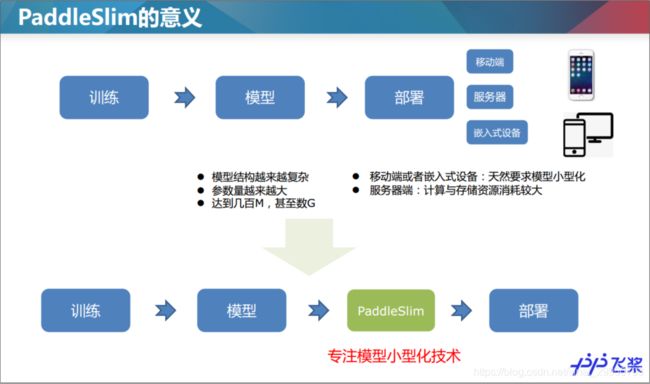
1.PaddleSlim与模型压缩
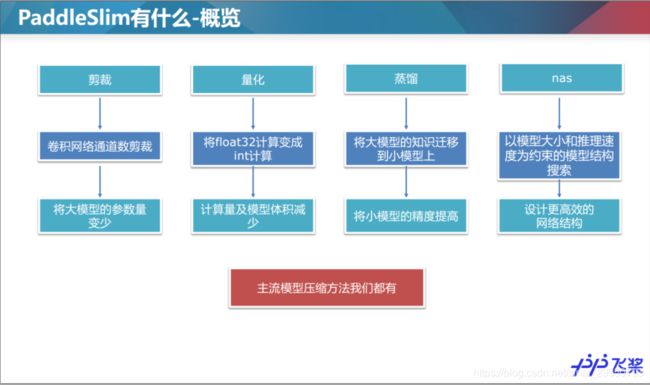
1.1裁剪
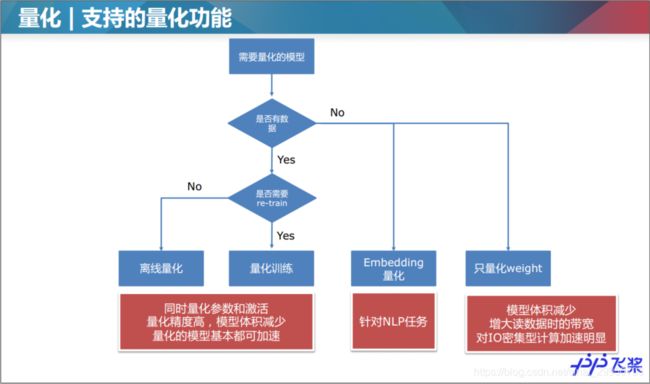
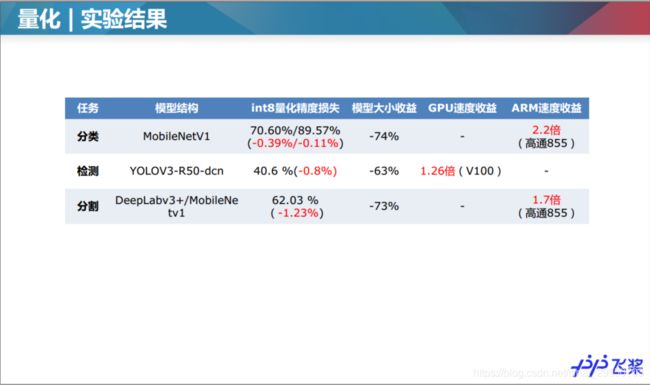
1.2量化
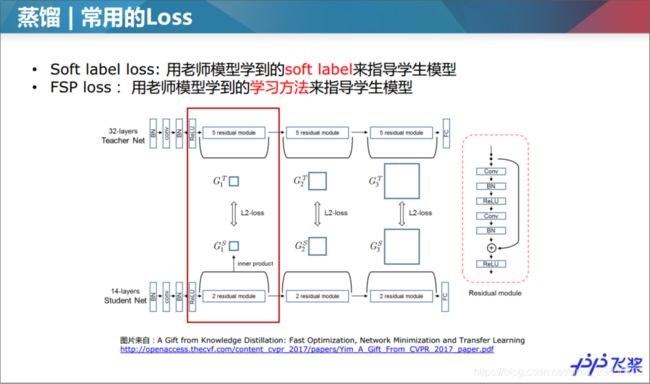
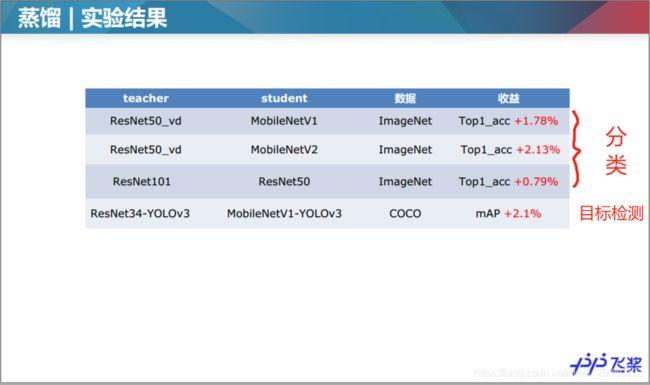
1.3蒸馏
1.4NAS
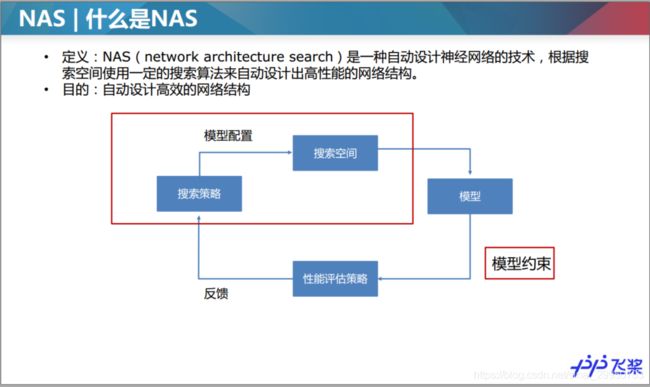


查了NAS是什么,简书上这篇文章写到

至少目前我接触不到这个级别的设备,咱普通用户只能先了解其理论层面

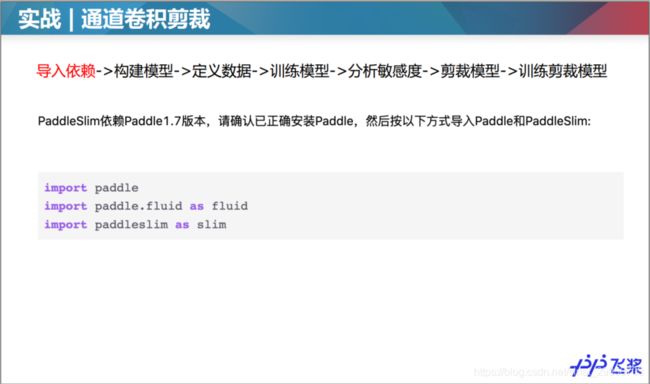
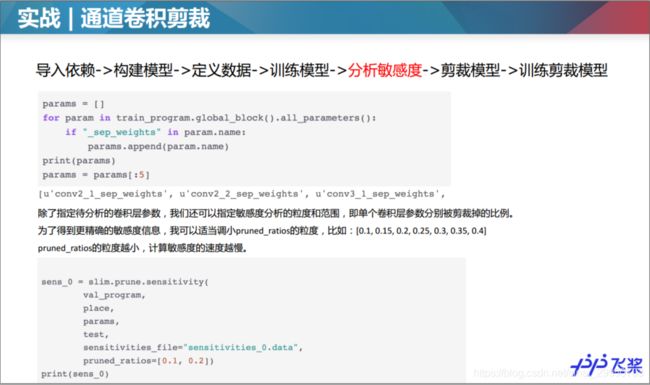
2.Paddle实战-裁剪
3.Paddle-Lite快速部署
github: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSlim
gitee: https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleSlim
PaddleSlim文档: https://paddlepaddle.github.io/PaddleSlim
Paddle Lite:
github: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite
Gitee: https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/paddle-lite
Paddle Lite文档: https://paddle-lite.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/
4.【作业】Paddle实战-量化
图像分类模型量化教程
该教程以图像分类模型MobileNetV1为例,说明如何快速使用量化训练接口。 该示例包含以下步骤:
- 导入依赖
- 构建模型
- 定义输入数据
- 训练模型
- 量化模型
- 训练和测试量化后的模型
4.1 安装与导入依赖
!pip install paddleslim
'''
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/
Collecting paddleslim
Downloading https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/69/3c/880afac020e3393da5a55b4e0b504d2b644a7ebe91092d953185f09660d1/paddleslim-1.0.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (103kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 112kB 2.4MB/s ta 0:00:01
Requirement already satisfied: tqdm in /opt/conda/envs/python27-paddle120-env/lib/python2.7/site-packages (from paddleslim) (4.36.1)
Installing collected packages: paddleslim
Successfully installed paddleslim-1.0.1
'''
PaddleSlim依赖Paddle1.7版本,请确认已正确安装Paddle,然后按以下方式导入Paddle和PaddleSlim:
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import paddleslim as slim
import numpy as np
4.2 构建模型
该章节构造一个用于对MNIST数据进行分类的分类模型,选用MobileNetV1,并将输入大小设置为[1, 28, 28],输出类别数为10。 为了方便展示示例,我们在paddleslim.models下预定义了用于构建分类模型的方法,执行以下代码构建分类模型:
use_gpu = fluid.is_compiled_with_cuda()
exe, train_program, val_program, inputs, outputs = slim.models.image_classification("MobileNet", [1, 28, 28], 10, use_gpu=use_gpu)
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if fluid.is_compiled_with_cuda() else fluid.CPUPlace()
4.3 定义输入数据
为了快速执行该示例,我们选取简单的MNIST数据,Paddle框架的paddle.dataset.mnist包定义了MNIST数据的下载和读取。 代码如下:
import paddle.dataset.mnist as reader
train_reader = paddle.batch(
reader.train(), batch_size=128, drop_last=True)
test_reader = paddle.batch(
reader.test(), batch_size=128, drop_last=True)
data_feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(inputs, place)
'''
Cache file /home/aistudio/.cache/paddle/dataset/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz not found, downloading https://dataset.bj.bcebos.com/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Begin to download
....................
Download finished
Cache file /home/aistudio/.cache/paddle/dataset/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz not found, downloading https://dataset.bj.bcebos.com/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Begin to download
........
Download finished
Cache file /home/aistudio/.cache/paddle/dataset/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz not found, downloading https://dataset.bj.bcebos.com/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Begin to download
....................
Download finished
Cache file /home/aistudio/.cache/paddle/dataset/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz not found, downloading https://dataset.bj.bcebos.com/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Begin to download
..
Download finished
'''
4.4 训练模型
先定义训练和测试函数,正常训练和量化训练时只需要调用函数即可。在训练函数中执行了一个epoch的训练,因为MNIST数据集数据较少,一个epoch就可将top1精度训练到95%以上。
def train(prog):
iter = 0
for data in train_reader():
acc1, acc5, loss = exe.run(prog, feed=data_feeder.feed(data), fetch_list=outputs)
if iter % 100 == 0:
print('train iter={}, top1={}, top5={}, loss={}'.format(iter, acc1.mean(), acc5.mean(), loss.mean()))
iter += 1
def test(prog):
iter = 0
res = [[], []]
for data in test_reader():
acc1, acc5, loss = exe.run(prog, feed=data_feeder.feed(data), fetch_list=outputs)
if iter % 100 == 0:
print('test iter={}, top1={}, top5={}, loss={}'.format(iter, acc1.mean(), acc5.mean(), loss.mean()))
res[0].append(acc1.mean())
res[1].append(acc5.mean())
iter += 1
print('final test result top1={}, top5={}'.format(np.array(res[0]).mean(), np.array(res[1]).mean()))
调用train函数训练分类网络,train_program是在第2步:构建网络中定义的
train(train_program)
'''
train iter=0, top1=0.09375, top5=0.453125, loss=2.7742357254
train iter=100, top1=0.90625, top5=1.0, loss=0.282765984535
train iter=200, top1=0.953125, top5=1.0, loss=0.216699957848
train iter=300, top1=0.953125, top5=0.984375, loss=0.154857292771
train iter=400, top1=0.9296875, top5=1.0, loss=0.257796555758
'''
调用test函数测试分类网络,val_program是在第2步:构建网络中定义的。
test(val_program)
'''
test iter=0, top1=0.9921875, top5=1.0, loss=0.0288050789386
final test result top1=0.973858177662, top5=0.99919873476
'''
4.5 量化模型
place = exe.place
quant_program = slim.quant.quant_aware(train_program, exe.place, for_test=False)
val_quant_program = slim.quant.quant_aware(val_program, exe.place, for_test=True)
'''
2020-04-11 19:13:28,234-INFO: quant_aware config {'moving_rate': 0.9, 'weight_quantize_type': 'channel_wise_abs_max', 'is_full_quantize': False, 'dtype': 'int8', 'weight_bits': 8, 'window_size': 10000, 'activation_bits': 8, 'quantize_op_types': ['conv2d', 'depthwise_conv2d', 'mul'], 'not_quant_pattern': ['skip_quant'], 'activation_quantize_type': 'moving_average_abs_max', 'for_tensorrt': False}
2020-04-11 19:13:29,174-INFO: quant_aware config {'moving_rate': 0.9, 'weight_quantize_type': 'channel_wise_abs_max', 'is_full_quantize': False, 'dtype': 'int8', 'weight_bits': 8, 'window_size': 10000, 'activation_bits': 8, 'quantize_op_types': ['conv2d', 'depthwise_conv2d', 'mul'], 'not_quant_pattern': ['skip_quant'], 'activation_quantize_type': 'moving_average_abs_max', 'for_tensorrt': False}
'''
此处参考该博客
4.6 训练和测试量化后的模型
微调量化后的模型,训练一个epoch后测试。
train(quant_program)
'''
train iter=0, top1=0.96875, top5=1.0, loss=0.166143000126
train iter=100, top1=0.9765625, top5=1.0, loss=0.0825310945511
train iter=200, top1=0.9921875, top5=1.0, loss=0.0762285068631
train iter=300, top1=0.9609375, top5=0.9921875, loss=0.120382666588
train iter=400, top1=0.953125, top5=1.0, loss=0.141556233168
'''
测试量化后的模型,和3.2 训练和测试中得到的测试结果相比,精度相近,达到了无损量化。
test(val_quant_program)
'''
test iter=0, top1=1.0, top5=1.0, loss=0.0112342201173
final test result top1=0.979066491127, top5=0.999499201775
'''
5.【作业】选择题
【1】定点化量化的优点有哪些?
A. 存内存带宽 B. 低功耗 C. 低计算资源 D. 低存储体积
【2】在常规蒸馏任务中,以下说法正确的是:
A. 只有teacher model的参数需要更新
B. 只有student model的参数需要更新
C. teacher model和student model 的参数都需要更新
D.teacher model和student model 的参数都不需要更新
【3】是否能用MobileNetv1蒸馏ResNet50?
A: 能
B: 不能
【4】下面方法哪些可以减少模型推理时间?
A. 只对权重weight进行量化
B. 对ResNet50模型进行蒸馏提高精度
C. 对模型进行裁剪,减少通道数
D. 对权重weight和激活进行量化,预测采用INT8计算
【5】NAS的三个关键要素是:
A. 搜索空间
B. 搜索算法
C. 模型优化
D. 模型评估
答案
【1】A、B、C、D
【2】C
【3】A
【4】A、B、C、D
【5】A、B、D