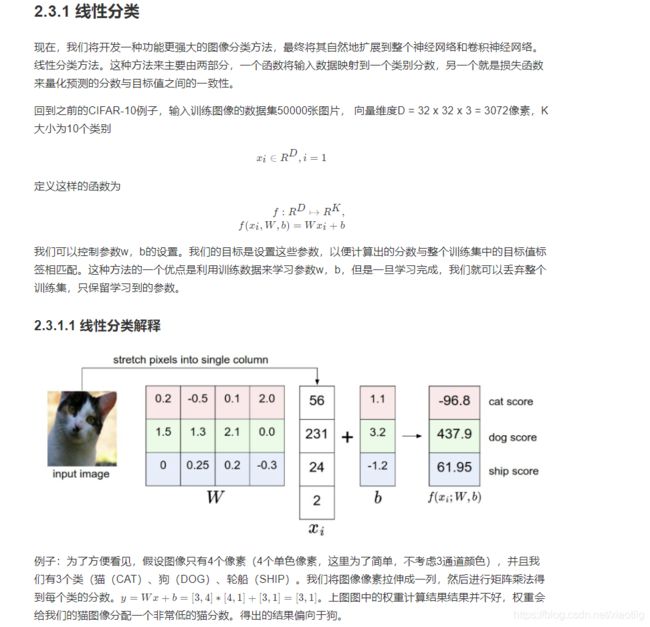
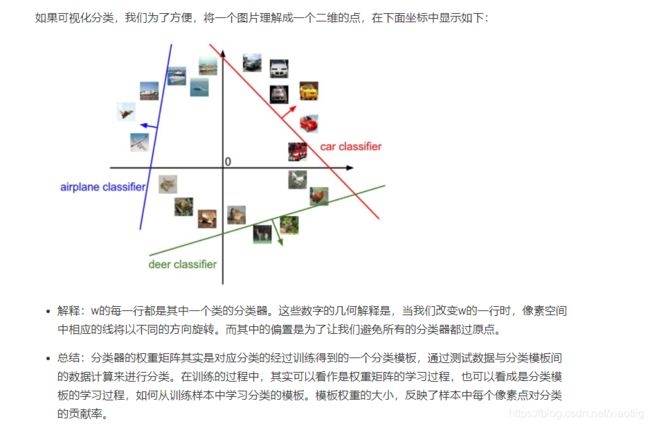
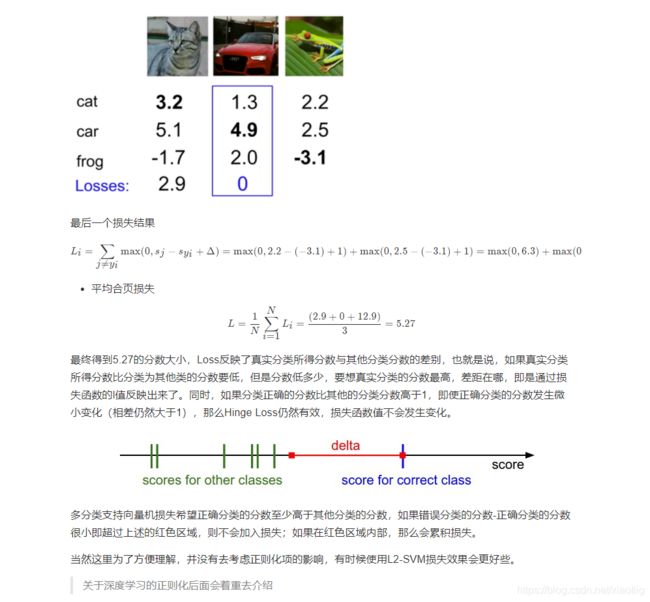
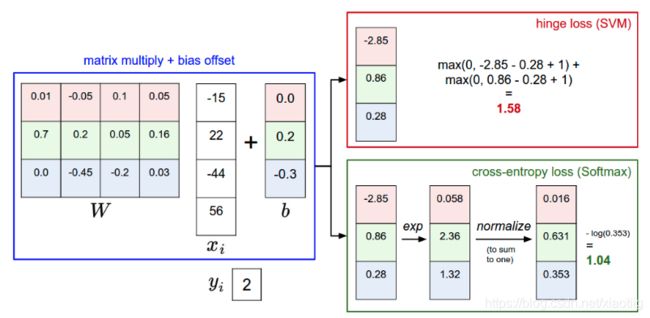
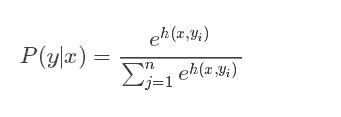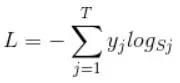深度学习原理24——损失函数与优化过程
损失函数
- 1 损失函数的作用
-
- 1.1 损失函数的作用就是调整权重
- 1.2 不同损失函数对应不同的分类器
- 2 各种损失函数
-
- 2.1 SVM平均合页损失
- 2.2 交叉熵损失(softmax分类后)
- 2.3 SVM与Softmax对比
- 2.4 L1损失:
- 2.5 L2损失:
- 2.6 均方误差
- 2.7 sigmoid和softmax
- 1 深度学习的交叉熵损失函数
-
- 2 sigmoid对应binary_cross_entropy
- 3 softmax对应
-
- 2.8 损失函数大全
- 3 网络最优化
-
- 3.1 梯度下降
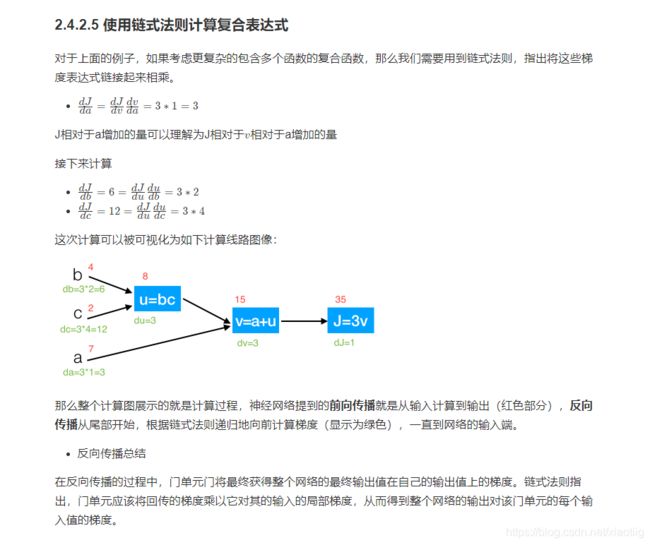
- 3.2 链式求导与反向传播
-
- 3.2.1 导数与链式求导
- 3.2.2 反向传播
- 4 反向传播的代码
1 损失函数的作用
1.1 损失函数的作用就是调整权重
损失函数是用来告诉我们当前分类器性能好坏的评价函数,是用于指导分类器权重调整的指导性函数,通过该函数可以知道该如何改进权重系数。
1.2 不同损失函数对应不同的分类器
在图像识别中最常用的两个损失——多类别SVM损失(合页损失hinge loss)和交叉熵损失,分别对应多类别SVM分类器和Softmax分类器。
2 各种损失函数
2.1 SVM平均合页损失
2.2 交叉熵损失(softmax分类后)
2.3 SVM与Softmax对比
2.4 L1损失:
就是两个值的差的绝对值
2.5 L2损失:
2.6 均方误差
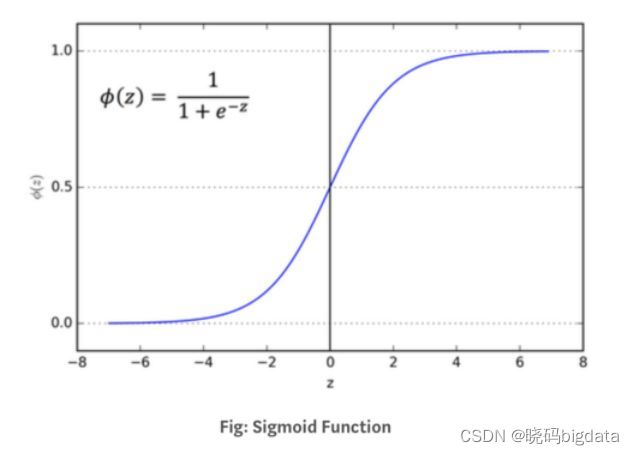
2.7 sigmoid和softmax
1 深度学习的交叉熵损失函数
首先明确一点,进入sigmoid或者softmax的值是多少维度,通过sigmoid或者softmax维度不变,比如sigmoid或者softmax输入前的维度是(256,256,10),通过它们以后输出的维度也是(256,256,10)。 跟给每个数加1的道理一样,只不过对每个数进行了函数变化
在深度学习中,一般来说,无论是用sigmoid和softmax,对应的都是交叉熵损失函数,一个对应
二分类和多分类都叫交叉熵损失函数,一个是sigmoid交叉熵损失函数,一个是softmax交叉熵损失函数
用的是sigmoid,就用binary_cross_entropy
用的是softmax,就用softmax_cross_entropy
2 sigmoid对应binary_cross_entropy
binary_cross_entropy
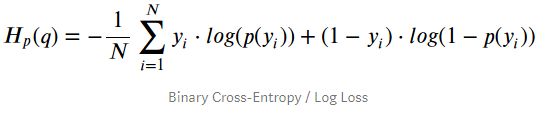
上面的yi表示真实标签,p(yi)表示经过sigmoid后的预测值。
举例:
举个例子,假设一个2分类问题,假如一个batch包含两个样本,第一个样本是类别0,第二个样本是类别1,那么标签要制成一维,形如:
y=[0,1 ],
模型预测输出也为一维,形如p=[ 0.2,0.6 ] #sigmoid的输出,这里一定要预先用sigmod处理,将预测结果限定在0~1之间。
对应的损失函数值计算:
L=( - 0*log(0.2) - (1 - 0)*log(1- 0.2) - log(0.6) - (1 -1)*log(1 - 0.6) ) / 2 = ( -log(0.8) - log(0.6) ) / 2
极端情况:
L = - 0*log(0.5) - (1 - 0)*log(1- 0.5)=-ln0.5 = ln2
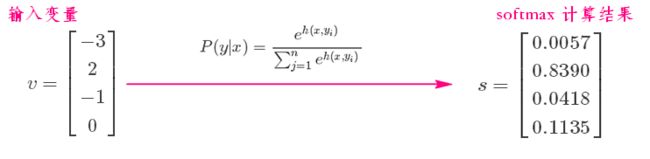
3 softmax对应
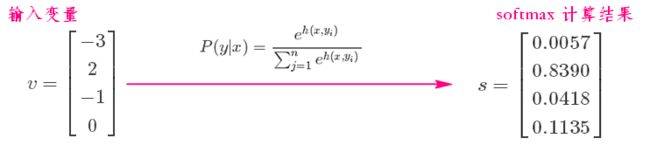
softmax计算步骤:

假设你的输入S=[1,2,3],那么经过softmax层后就会得到[0.09,0.24,0.67],这三个数字表示这个样本属于第1,2,3类的概率分别是0.09,0.24,0.67。
举例:
**举例1,**softmax计算二分类问题中用了softmax的输出,每个样本输出维2,用sigmoid的时候才为1
假设一个2分类问题,假如一个batch包含两个样本,那么标签要制成二维,
形如y=[ [1, 0],[0, 1] ],
模型预测输出也为二维,形如p=[ [0.8,0.2],[0.4,0.6] ] #(softmax的输出)
那么对应的损失L=( -log(0.8) - log(0.6) ) / 2
**举例2,**多分类,和上面例子计算过程一样
如果3分类问题某个样本预测的logits经过softmax或者sigmoid之后是(0.1, 0.8, 0.1)(这是softmax的结果,sigmoid不保证分量和为1),而labels的one hot形式是(0, 1, 0),那么该样本贡献的损失就是-(0ln0.1+1ln0.8+0*ln0.1)/3,batch loss就是一个batch的平均值。可以看出,全预测对,且正确项置信度为1,则loss为0,预测错误损失相当大。
2.8 损失函数大全
语义分割中的 loss function 最全面汇总 - 知乎
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/101773544
3 网络最优化
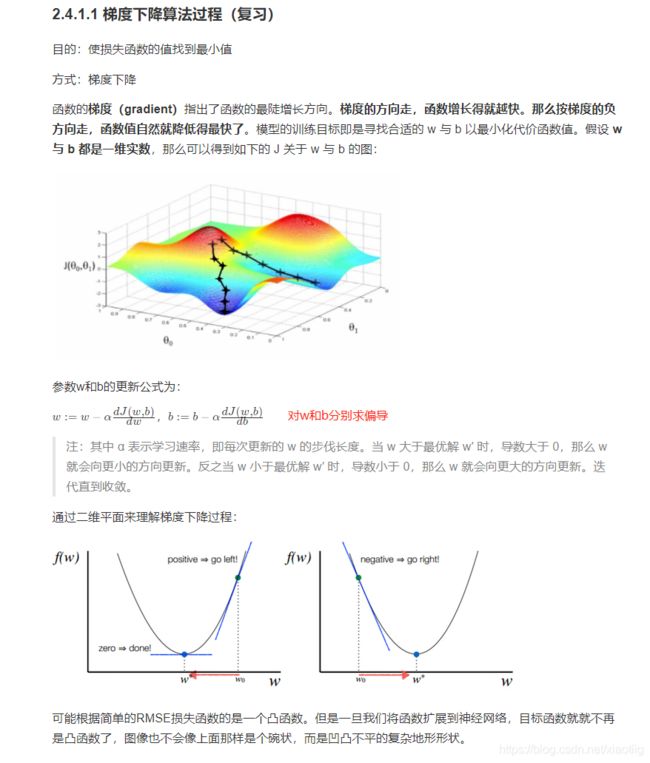
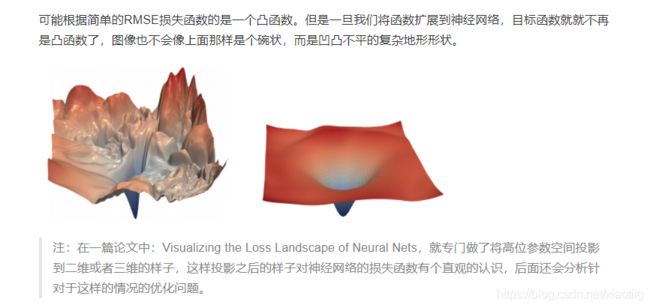
最优化是寻找能使得损失函数值最小化的参数W的过程
目的就是使损失函数最小
转换为更新参数W
方法就是求函数的梯度
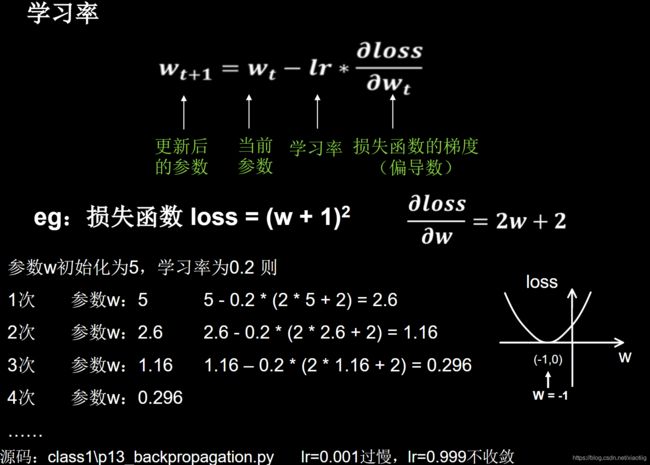
3.1 梯度下降
3.2 链式求导与反向传播
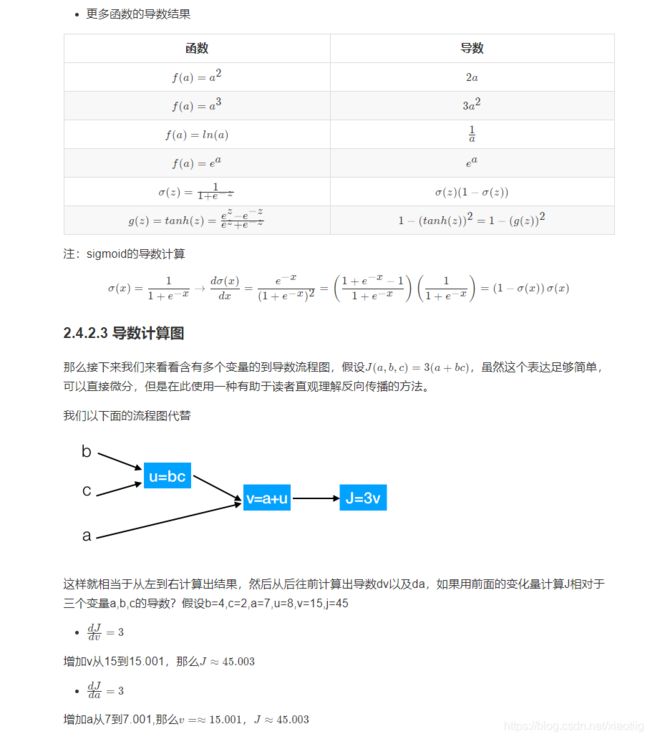
3.2.1 导数与链式求导
3.2.2 反向传播
反向传播就是利用链式求导法则进行反向计算
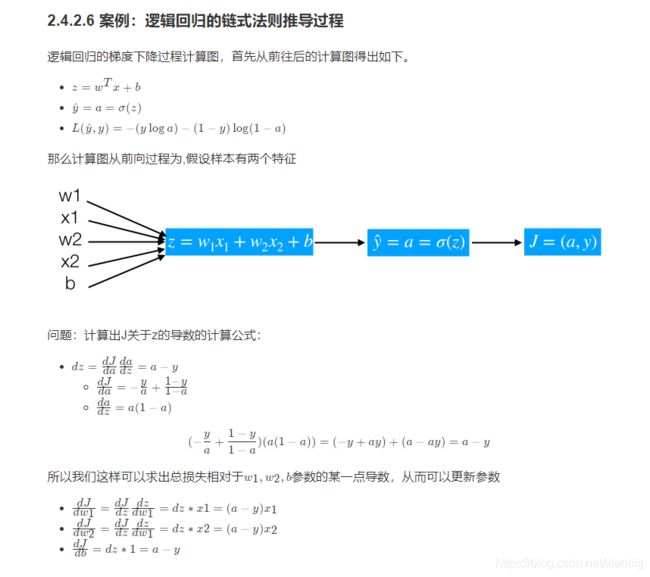
(1)案例:逻辑回归前向与反向传播简单计算
假设简单的模型为y =sigmoid(w1x1+w2x2+b), 我们在这里给几个随机的输入的值和权重,带入来计算一遍,其中在点x1,x2 = (-1 -2),目标值为1,假设给一个初始化w1,w2,b=(2, -3, -3),由于中间有sigmoid的计算过程,所以我们用代码来呈现刚才的过程。
# 假设一些随机数据和权重,以及目标结果1
w = [2,-3,-3]
x = [-1, -2]
y = 1
# 前向传播
z = w[0]*x[0] + w[1]*x[1] + w[2]
a = 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
cost = -np.sum(y * np.log(a) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - a))
# 对神经元反向传播
# 点积变量的梯度, 使用sigmoid函数求导
dz = a - y
# 回传计算x梯度
dx = [w[0] * dz, w[1] * dz]
# #回传计算w梯度
dw = [x[0] * dz, x[1] * dz, 1.0 * dz]
我们可以看出来w1,w2,b是在这次更新是收到x的输入的影响梯度的计算的。
# 随机初始化权重
# w1,w2
W = np.random.random([2, 1])
X = np.random.random([2, 10])
b = 0.0
Y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0])
Z = np.dot(W.T, X) + b
A = 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-Z))
cost = -1 / 10 * np.sum(Y * np.log(A) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - A))
# 形状:A:[1, 10] , Y:[1, 10]
dZ = A - Y
# [2, 10] * ([1, 10].T) = [2, 1]
dW = (1.0 / 10) * np.dot(X, dZ.T)
db = (1.0 / 10) * np.sum(dZ)
4 反向传播的代码
一共包括1个文件夹,(datasets文件夹存放了两个h5数据文件)
两个文件

data.py
# 进行数据的读取
import numpy as np
import h5py
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
print("原始训练数据x的shape:", train_set_x_orig.shape)
print("原始训练数据y的shape:", train_set_y_orig.shape)
print("原始测试数据x的shape:", test_set_x_orig.shape)
print("原始测试数据y的shape:", test_set_y_orig.shape)
# 把列转换为行
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
print("数据转换后训练数据y的shape:", train_set_y_orig.shape)
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
single_unit_nn
## 实现模型的训练
import numpy as np
import data
def main():
# 1、读取样本数据
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, classes = data.load_dataset()
print("训练集的样本数: ", train_x.shape[0])
print("测试集的样本数: ", test_x.shape[0])
# train_x形状: (209, 64, 64, 3)
print("train_x形状: ", train_x.shape)
# train_y形状: (1, 209)
print("train_y形状: ", train_y.shape)
print("test_x形状: ", test_x.shape)
print("test_y形状: ", test_y.shape)
# 输入数据的形状修改以及归一化
train_x = train_x.reshape(train_x.shape[0], -1).T
# 这里train_x.shape为(12288, 209)
test_x = test_x.reshape(test_x.shape[0], -1).T
train_x = train_x / 255.
test_x = test_x / 255.
# 2、模型训练以及预测
d = model(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, num_iterations=2000, learning_rate=0.005)
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, num_iterations=2000, learning_rate=0.5):
"""
"""
# 初始化参数
w, b = initialize_with_zeros(X_train.shape[0])
# 梯度下降
# params:更新后的网络参数
# grads:最后一次梯度
# costs:每次更新的损失列表
params, grads, costs = optimize(w, b, X_train, Y_train, num_iterations, learning_rate)
# 获取训练的参数
# 预测结果
w = params['w']
b = params['b']
Y_prediction_train = predict(w, b, X_train)
Y_prediction_test = predict(w, b, X_test)
print("预测结果是什么:",Y_prediction_test)
# 打印准确率
print("训练集准确率: {} ".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_train - Y_train)) * 100))
print("测试集准确率: {} ".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_test - Y_test)) * 100))
d = {"costs": costs,
"Y_prediction_test": Y_prediction_test,
"Y_prediction_train": Y_prediction_train,
"w": w,
"b": b,
"learning_rate": learning_rate,
"num_iterations": num_iterations}
return d
def basic_sigmoid(x):
"""
计算sigmoid函数
"""
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return s
def initialize_with_zeros(shape):
"""
创建一个形状为 (shape, 1) 的w参数和b=0.
return:w, b
"""
# 本例中shape是209
w = np.zeros((shape, 1))
b = 0
return w, b
def optimize(w, b, X, Y, num_iterations, learning_rate):
"""
参数:
w:权重,b:偏置,X特征,Y目标值,num_iterations总迭代次数,learning_rate学习率
Returns:
params:更新后的参数字典
grads:梯度
costs:损失结果
"""
costs = []
for i in range(num_iterations):
# 梯度更新计算函数
grads, cost = propagate(w, b, X, Y)
# 取出两个部分参数的梯度
# dw的形状是(12288, 1),每行dw的值是不一样的
dw = grads['dw']
db = grads['db']
# 按照梯度下降公式去计算
w = w - learning_rate * dw
b = b - learning_rate * db
# 每100次输出一次损失
if i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
if i % 100 == 0:
print("损失结果 %i: %f" % (i, cost))
print(b)
params = {"w": w,
"b": b}
grads = {"dw": dw,
"db": db}
return params, grads, costs
def propagate(w, b, X, Y):
"""
参数:w,b,X,Y:网络参数和数据
Return:
损失cost、参数W的梯度dw、参数b的梯度db
"""
m = X.shape[1]
# w.t的形状 (1, 12288)
# x的形状: (12288, 209)
# b就是0:
# Y的形状: (1, 209)
# m是个209
# np.dot(w.T, X)是什么: (1, 209)
# 前向传播
# w (n,1), x (n, m)
A = basic_sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)
# 计算损失
cost = -1 / m * np.sum(Y * np.log(A) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - A))
# 反向传播
dz = A - Y
dw = 1 / m * np.dot(X, dz.T)
db = 1 / m * np.sum(dz)
grads = {"dw": dw,
"db": db}
return grads, cost
def predict(w, b, X):
'''
利用训练好的参数预测
return:预测结果
'''
m = X.shape[1]
Y_prediction = np.zeros((1, m))
# 计算结果
A = basic_sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)
# 得分小于0.5归为第一类,大于0.5归为第二类
for i in range(A.shape[1]):
if A[0, i] <= 0.5:
Y_prediction[0, i] = 0
else:
Y_prediction[0, i] = 1
assert (Y_prediction.shape == (1, m))
return Y_prediction
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()