基于Kmeans聚类算法实现图像分割(从原理开始实现)
一、Kmeans聚类算法基本原理
K-Means算法的思想很简单,对于给定的样本集,按照样本之间的距离大小,将样本集划分为K个簇。让簇内的点尽量紧密的连在一起,而让簇间的距离尽量的大。
以彩色图像为例:基于彩色图像的RGB三通道为xyz轴建立空间直角坐标系,那么一副图像上的每个像素点与该空间直角坐标系建立了一 一映射(双射)的关系。
从空间直角坐标系中随机取 k 个点,作为 k 个簇的各自的中心。计算所有像素点到k个簇心的距离,并将所有像素点划分至与其距离最小的簇类。自此聚类完成。其中,距离定义为欧氏距离:
![]()
其中r,g,b分别表示红绿蓝三通道,r1,g1,b1为彩色图片中某像素点;r0,g0,b0表示某簇类的簇心。
二、基于Kmeans图像分割算法流程
Note:彩色图像的操作是基于一个三维空间
1、加载图像,获取图像的所有像素点并将其转换为样本数据。
2、开始迭代
a)、初始化簇心坐标。
a)、更新簇心坐标,遍历样本数据中的数据点并计算数据点与所有簇心的距离。对于某数据点计算得到的与所有簇类的欧氏距离中,取欧氏距离最小所对应的簇类作为该数据点对应的类。
c)、计算更新后的簇心坐标与更新前的簇心坐标的均方误差。若均方误差仍大于某阈值,则重复b),反之结束迭代。
Kmeans的详细算法流程参考博文:
https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6164214.html
三、代码主函数部分
1、加载图片
Mat src, dst;
src = imread("J20.jpg");
namedWindow("输入图像", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("输入图像", src);
2、初始化颜色(图像分割后需要上色)
Scalar colorTab[] = {
Scalar(0,0,255),
Scalar(0,255,0),
Scalar(255,0,0),
Scalar(0,255,255),
Scalar(255,0,255),
};
3、初始化簇类数,并将所有的像素点全部转换为样本数据
int sampleCount = width*height;
int clusterCount = 5;
Mat points(sampleCount, dims, CV_32F, Scalar(10));
//将彩色图像的像素点转换为样本数据
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
index = row*width + col;
Vec3b bgr = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col);
points.at<float>(index, 0) = static_cast<int>(bgr[0]);//b
points.at<float>(index, 1) = static_cast<int>(bgr[1]);//g
points.at<float>(index, 2) = static_cast<int>(bgr[2]);//r
}
}
4、利用Kmeans算法对样本数据分类
centers, feature = Kmeans(points, clusterCount, sampleCount);
5、
显示图像分割后的结果
//显示图像分割结果
Mat result = Mat::zeros(src.size(), src.type());
int index1 = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
index1 = row*width + col;
int label = feature.at<float>(index1, 3);
result.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[0] = colorTab[label][0];
result.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[1] = colorTab[label][1];
result.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[2] = colorTab[label][2];
}
}
imshow("基于Kmeans聚类的图像分割", result);
四、代码子函数部分
1、初始化聚类中心
//初始化簇心
Mat centers = Mat::zeros(clusterCount, 1, CV_32FC3);//4行3列
centers.at<float>(0, 0) = 150;
centers.at<float>(0, 1) = 180;
centers.at<float>(0, 2) = 200;
centers.at<float>(1, 0) = 20;
centers.at<float>(1, 1) = 25;
centers.at<float>(1, 2) = 37;
centers.at<float>(2, 0) = 80;
centers.at<float>(2, 1) = 100;
centers.at<float>(2, 2) = 140;
centers.at<float>(3, 0) = 226;
centers.at<float>(3, 1) = 234;
centers.at<float>(3, 2) = 235;
2、利用Kmeans算法进行迭代
Mat feature = Mat::zeros(sampleCount, 1, CV_32FC4);
float *distance = new float[sampleCount];
int epoch = 0;
while (true)
{
for (int row = 0; row < points.rows; row++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < centers.rows; i++)
{
distance[i] = pow((points.at<float>(row, 0) - centers.at<float>(i, 0)), 2) + pow((points.at<float>(row, 1) - centers.at<float>(i, 1)), 2)
+ pow((points.at<float>(row, 2) - centers.at<float>(i, 2)), 2);
}
float min = distance[0];
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < clusterCount; i++)
{
if (min > distance[i])
{
min = distance[i];
flag = i;
}
}
feature.at<float>(row, 0) = points.at<float>(row, 0);
feature.at<float>(row, 1) = points.at<float>(row, 1);
feature.at<float>(row, 2) = points.at<float>(row, 2);
feature.at<float>(row, 3) = flag;
}
float new_center_r = 0, new_center_g = 0, new_center_b = 0;
float *temp = new float[clusterCount];
for (int i = 0; i < clusterCount; i++)
{
int num = 0;
float sum_center_r = 0, sum_center_g = 0, sum_center_b = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < sampleCount; row++)
{
if (feature.at<float>(row, 3) == i)
{
sum_center_b = sum_center_b + feature.at<float>(row, 0);
sum_center_g = sum_center_g + feature.at<float>(row, 1);
sum_center_r = sum_center_r + feature.at<float>(row, 2);
num++;
}
}
new_center_b = sum_center_b / num;
new_center_g = sum_center_g / num;
new_center_r = sum_center_r / num;
temp[i] = pow((new_center_b - centers.at<float>(i, 0)), 2) + pow((new_center_g - centers.at<float>(i, 1)), 2)
+ pow((new_center_r - centers.at<float>(i, 2)), 2);
centers.at<float>(i, 0) = new_center_b;
centers.at<float>(i, 1) = new_center_g;
centers.at<float>(i, 2) = new_center_r;
}
float total = 0;
float mean_square_error = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < clusterCount; i++)
{
total = total + temp[i];
}
mean_square_error = total / 4;
if (epoch % 1 == 0)
cout << "epoch:" << epoch << "\terror of mean square:" << mean_square_error << endl;
if (mean_square_error < 0.01)
break;
epoch++;
}
五、代码运行结果及评价
输入图片:

2、迭代过程
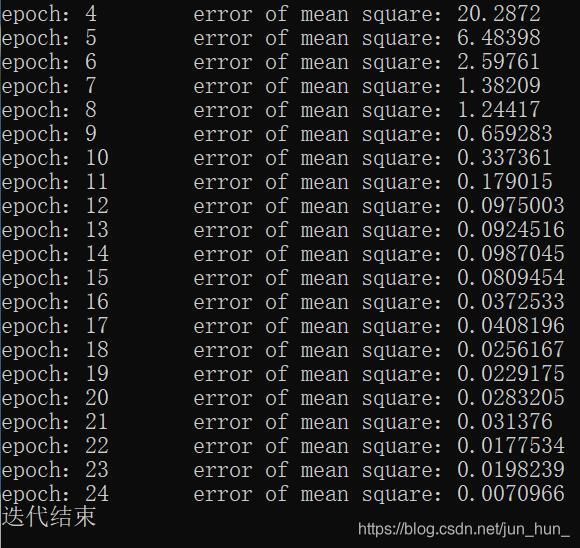
3、聚类结果

如上图,从左至右分别为Blue、Green、Red通道;从上之下分别是五个簇心的坐标(像素值)。
4、图像分割结果
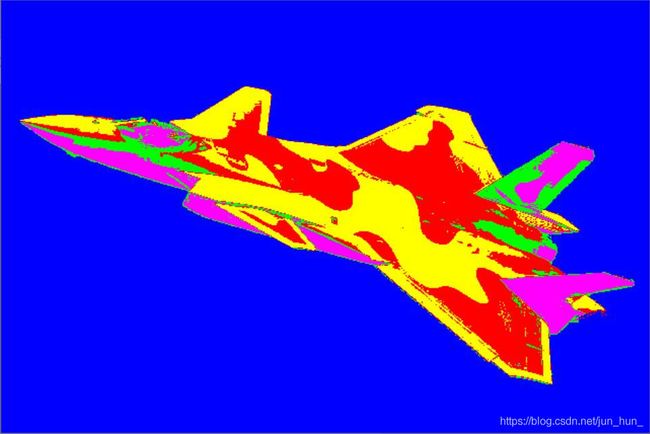
如上图,图像被清晰的分为了五个部分:背景为蓝色、歼20的迷彩涂装分为了红黄两色,颜色最暗的地方为紫色,颜色次暗的地方为绿色。
另外,对于大数据,经典的Kmeans算法显然处理速度太慢,但对于彩色图像,使用经典Kmeans算法对其进行分割,其所耗时长在可接受的范围内。
至此完全实现了基于Kmeans聚类算法的图像分割,经验证,其结果与利用OpenCV提供的API得到的效果完全一致!
六、最后附上所有代码
#include