【MMDet Note】MMDetection中Loss之FocalLoss代码理解与解读
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、FocalLoss计算原理介绍
- 二、FocalLoss代码解读
-
- 1. class FocalLoss
- 2. def py_focal_loss_with_prob
- 总结
前言
mmdetection/mmdet/models/losses/focal_loss.py中的FocalLoss类的个人理解与代码解读。
一、FocalLoss计算原理介绍
Focal loss最先在RetinaNet一文中被提出。论文链接
其在目标检测算法中主要用以前景(foreground)和背景(background)的分类,是一个分类损失。由于现在已经有很多文章详细地介绍了Focal loss,我就不再介绍了,想详细了解的可以直接阅读RetinaNet论文,我这里简单地以举例子的形式来介绍一下这一种损失函数。下面将用6个模拟的样本数据的例子来解释该损失函数具体是如何计算的(不考虑 α \alpha α)。

以上计算过程只对目标类别对应下的损失进行计算,可以看到例如第5个样本的真实标签为0,但预测其为1的概率为0.9,显然十分错误,因此便给予其标签0对应损失更高的权重 ( 1 − p t ) γ = 0.9 (1-p_t)^\gamma=0.9 (1−pt)γ=0.9。
总而言之,Focal loss可以简单看作是在原本的Cross Entropy Loss之上加了一个权重,使得难例样本(hard examples)的损失有更高的权重,从而模型更加关注这些样本的学习。
二、FocalLoss代码解读
1. class FocalLoss
这里我将Class FocalLoss的构成情况总结为下图:
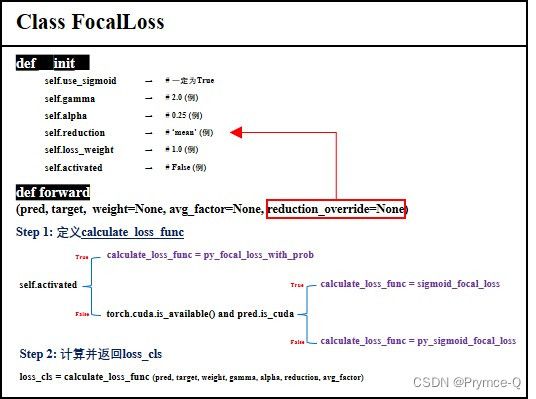
FocalLoss类由两个方法构成:def __init__与def forward。其中,def __init__定义了一系列相关的变量。def forward用来进行计算分类损失。
def forward中,首先,会指定reduction变量,优先为reduction_override,若其为空则为self.reduction。接着,根据一些条件来确定用来计算损失的具体函数calculate_loss_func为[1.py_focal_loss_with_prob, 2.sigmoid_focal_loss, 3.py_sigmoid_focal_loss]中的哪个,最后,调用calculate_loss_func与相关变量进行具体计算。
代码解读如下:
@LOSSES.register_module()
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
use_sigmoid=True,
gamma=2.0,
alpha=0.25,
reduction='mean',
loss_weight=1.0,
activated=False):
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
assert use_sigmoid is True, 'Only sigmoid focal loss supported now.'
# 定义一些变量
self.use_sigmoid = use_sigmoid
self.gamma = gamma # 2.0
self.alpha = alpha # 0.25
self.reduction = reduction # 'mean'
self.loss_weight = loss_weight # 1.0
self.activated = activated # False
def forward(self,
pred,
target,
weight=None,
avg_factor=None,
reduction_override=None):
assert reduction_override in (None, 'none', 'mean', 'sum')
reduction = ( # 为reduction重新赋值,优先为foward方法中的reduction_override值
reduction_override if reduction_override else self.reduction)
if self.use_sigmoid: # 一定为True
# Step1 根据条件选择calculate_loss_func
if self.activated:
calculate_loss_func = py_focal_loss_with_prob
else:
if torch.cuda.is_available() and pred.is_cuda:
calculate_loss_func = sigmoid_focal_loss
else:
# 提前将target处理为one-hot编码格式
num_classes = pred.size(1)
target = F.one_hot(target, num_classes=num_classes + 1)
target = target[:, :num_classes]
calculate_loss_func = py_sigmoid_focal_loss
# Step2 使用指定的calculate_loss_func计算并返回loss_cls
loss_cls = self.loss_weight * calculate_loss_func(
# 以下变量在介绍具体的方法中会更详细地介绍
pred, # 预测值
target, # 目标值
weight,
gamma=self.gamma, # 2.0
alpha=self.alpha, # 0.25
reduction=reduction, # 'mean'
avg_factor=avg_factor)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return loss_cls
下面介绍py_focal_loss_with_prob的损失计算代码。其余两种方法类似,主要区别为数据格式的处理。
2. def py_focal_loss_with_prob
def py_focal_loss_with_prob(pred,
target,
weight=None,
gamma=2.0,
alpha=0.25,
reduction='mean',
avg_factor=None):
"""
假设:
1. 只有0和1这两个类
2. pred (torch.Tensor) = [[p00,p01],
[p10,p11],
[p20,p21]]
pred.shape = (N=3, C=2) 3个样本,2种类别
3. target (torch.Tensor) = [0,1,1]
"""
# STEP1:将target转化为one-hot编码格式
num_classes = pred.size(1) # num_class = 2
target = F.one_hot(target, num_classes=num_classes + 1)
target = target[:, :num_classes] # target = tensor([[1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]]) 也就是3个样本的所属类别的one-hot编码
target = target.type_as(pred)
# STEP2:计算CrossEntropyLoss前的权重
pt = (1 - pred) * target + pred * (1 - target) # pt = [[1-p00, p01], [p10,1-p11], [p20, 1-p21]]
focal_weight = (alpha * target + (1 - alpha) *
(1 - target)) * pt.pow(gamma)
# Step3: 基于pred与target计算CrossEntropyLoss, 同时乘以上面计算的权重focal_weight
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(
pred, target, reduction='none') * focal_weight
if weight is not None:
if weight.shape != loss.shape:
if weight.size(0) == loss.size(0):
# For most cases, weight is of shape (num_priors, ),
# which means it does not have the second axis num_class
weight = weight.view(-1, 1)
else:
# Sometimes, weight per anchor per class is also needed. e.g.
# in FSAF. But it may be flattened of shape
# (num_priors x num_class, ), while loss is still of shape
# (num_priors, num_class).
assert weight.numel() == loss.numel()
weight = weight.view(loss.size(0), -1)
assert weight.ndim == loss.ndim
# Step4: 求loss的平均值为最终loss
loss = weight_reduce_loss(loss, weight, reduction, avg_factor) # reduction='mean'
return loss
总结
本文仅代表个人理解,若有不足,欢迎批评指正。