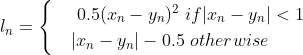深度学习损失函数numpy实现并与torch对比
用numpy实现L1损失、MSE损失、KL损失、NLL损失、交叉熵损失、BCE损失、SmoothL1损失,并和torch的计算结果对比。
目录
一、L1损失
1、公式
2、实现及对比
二、MSE损失
1、公式
2、实现及对比
三、 交叉熵损失
1、公式
2、实现及对比
四、NLL损失
1、公式
2、实现及对比
五、Kullback-Leibler divergence 损失
1、公式
2、实现及对比
六、BCE损失
一、公式
2、实现及对比
七、SMOOTHL1损失
一、公式
2、实现及对比
若无特殊声明,文中![]() 表示预测值,
表示预测值,![]() 表示目标值。
表示目标值。
一、L1损失
1、公式
L1损失函数又被称为最小绝对值偏差(LAD),最小绝对值误差(LAE),它的公式如下:
![]()
![]()
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def l1_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
dif = np.abs(x - y)
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, 3, 100)
y = np.random.rand(4, 3, 100)
np_loss = l1_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 输出:0.3279294731209465 0.3279294731209465
二、MSE损失
1、公式
均方差损失是预测数据和原始数据对应点误差的平方和的均值,它的公式如下:
![]()
![]()
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def mse_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
dif = np.square(x - y)
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, 3, 100)
y = np.random.rand(4, 3, 100)
np_loss = mse_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 输出:0.16281742957744108 0.16281742957744105
三、 交叉熵损失
1、公式
交叉熵损失函数常用于解决分类问题,在构建深度学习模型是,为了数值计算稳定,一般将logits(sigmoid或者softmax的输入)送入损失函数计算损失。
![]()
![]()
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def one_hot(x, num_class=None):
if not num_class:
num_class = np.max(x) + 1
ohx = np.zeros((len(x), num_class))
ohx[range(len(x)), x] = 1
return ohx
def cross_entropy_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
loss = []
for i in range(y.shape[0]):
loss_i = -x[i, y[i]] + np.log(np.sum(np.exp(x[i])))
loss.append(loss_i)
dif = np.array(loss).reshape([y.shape[0], 1])
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, 100).astype('float32')
y = np.random.randint(0, 100, (4,))
np_loss = cross_entropy_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y).to(torch.long))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 输出:4.8294697 4.829469
四、NLL损失
1、公式
负对数似然损失的思想就是使预测类别的概率最大,他的输入是概率值(sigmoid或者softmax层的输出),公式如下:
![]()
![]()
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def log_softmax(x):
m = np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1, keepdims=True)
x = np.log(x / m)
return x
def nll_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
loss = []
for i in range(y.shape[0]):
loss_i = -x[i, y[i]]
loss.append(loss_i)
dif = np.array(loss)
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, 100).astype('float32')
x = log_softmax(x)
y = np.random.randint(0, 100, (4,))
np_loss = nll_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.NLLLoss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y).to(torch.long))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 6.5572305 6.55723
五、Kullback-Leibler divergence 损失
1、公式
KL散度衡量不同分布的差异性,公式如下,它计算了预测概率和标签的分布差异:
![]()
![]()
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def log_softmax(x):
m = np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1, keepdims=True)
x = np.log(x / m)
return x
def kldiv_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
y_log = np.log(np.where(y < 1e-3, 1e-3, y))
dif = y * (y_log - x)
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, 100).astype('float32')
x = log_softmax(x)
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, (4, 100))
np_loss = kldiv_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y).to(torch.long))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 输出:2.879388073682785 2.879388
六、BCE损失
一、公式
BCE(Binary Cross Entropy Loss)用于二分类问题,该损失函数和交叉熵损失函数原理一致,公式如下:
![]()
![]()
BCEWithLogitsLoss和BCELoss原理相同,只是函数的输入有区别,本文不再验证该函数。
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def binary_cross_entropy_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
dif = -(y * np.log(x) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - x))
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, ).astype('float32')
y = np.random.randint(0, 1, (4, )).astype('float32')
np_loss = binary_cross_entropy_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.BCELoss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 输出:0.9325159 0.9325159七、SMOOTHL1损失
一、公式
L1损失的导数处处相等,在网络训练时较为稳定,但是在中心值处无法求导,不方便求解。
L2损失函数处处可导,函数连续光滑,但是当输入距离中心值较远的时候,梯度较大,从而可能导致梯度下降求解过程中发生梯度爆炸,导致模型不收敛。
结合L1和L2损失函数的优点,可以得到SMOOTHL1损失函数:
![]()
2、实现及对比
import torch
import numpy as np
def smooth_l1_loss(x, y, reduction='mean'):
rel = np.abs(x - y)
dif = rel - 0.5
dif[rel < 1] = 0.5 * np.square(rel)[rel < 1]
if reduction == 'mean':
return np.mean(dif)
elif reduction == 'sum':
return np.sum(dif)
return dif
np.random.seed(10001)
x = np.random.rand(4, 3, 100)
y = np.random.rand(4, 3, 100)
np_loss = smooth_l1_loss(x, y, 'mean')
torch_loss_fn = torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='mean')
torch_loss = torch_loss_fn(torch.from_numpy(x), torch.from_numpy(y))
print(np_loss, torch_loss.numpy())
# 输出:0.08140871478872054 0.08140871478872053