深入理解CV中的Attention机制之CBAM
CV中的Attention机制汇总(二):CBAM
CBAM:Convolutional Block Attention Module
论文链接:CBAM(ECCV 2018)
一、 摘要
1.1 CBAM概要
Given an intermediate feature map, our module sequentially infers attention maps along two separate dimensions, channel and spatial, then the attention maps are multiplied to the input feature map for adaptive feature refinement.
与SE模块不同,CBAM结合了使用了通道 与 空间注意力机制。作者认为通道注意力决定了“what is important",空间注意力决定了"where is important".
1.2 CV中Attention机制的作用
此外,作者在Introduction中简明阐述了Attention机制的作用,即:
Attention not only tells where to focus, it also improves the representation of interests.
Our goal is to increase representation power by using attention mechanism: focusing on important features and suppressing unnecessary ones.
使用注意力机制可以提高网络的特征表达能力。
1.3 CBAM模块的优势
CBAM具有以下两点优势:
- 与SE相比,改进了通道注意力模块,增加了空间注意力模块;
- 与BAM相比,不只是用在bottleneck中,而是可以用在任何中间卷积层模块中,是一个plug-and-play(即插即用)的注意力模块。
二、模块详解
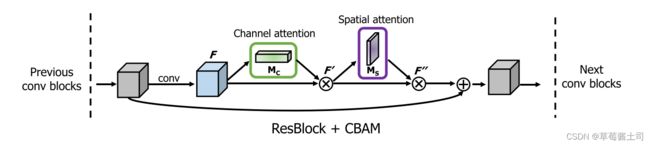
文中给出的CBAM模块如下图所示:

下面结合论文第3节详细阐述CBAM模块的实现细节。
2.1 Channel Attention Module:focusing on “what”
与SE模块的区别在于,作者添加了max-pooling操作,并且AvgPool与MaxPool共用同一个多层感知机(multi-layer perceptron, MLP)减少可学习参数。
因此,CBAM的通道注意力提取可使用以下公式表示:
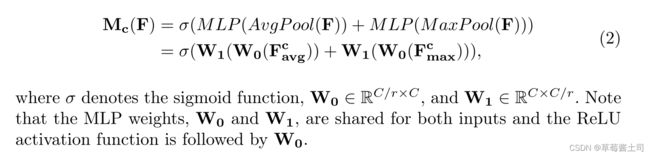
2.2 Spatial Attention Module: focusing on “where”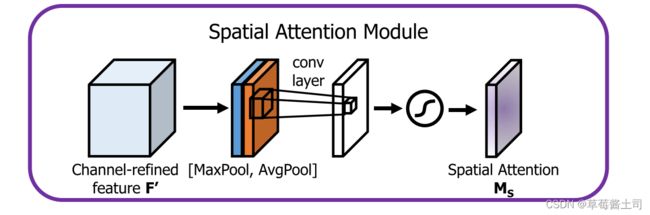
首先,分别在通道维度上执行最大值汇聚与平均汇聚操作,得到大小为 H × W H\times W H×W
的特征图,然后使用输入通道数为2, 输出通道数为1的卷积层提取空间注意力,公式表示如下:
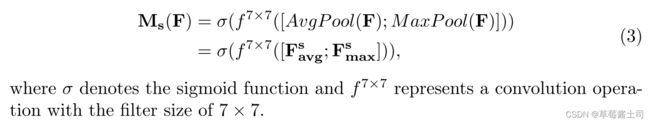
2.3 Arrangement of attention modules
将通道注意力与空间注意力结合,得到被加权后的特征。
通道注意力与空间注意力的结合顺序与方式(如图1所示):
- 通道在前,空间在后
- 空间在前,通道在后
- 串行
- 并行
针对结合顺序与方式,作者通过消融实验予以了证明。
2.4 使用方式
三、PyTorch实现
import torch
from torch import nn
class ChannelAttentionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(ChannelAttentionModule, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1, 1))
self.shared_MLP = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.shared_MLP(self.avg_pool(x))
max_out = self.shared_MLP(self.max_pool(x))
out = avg_out + max_out
return self.sigmoid(out)
class SpatialAttentionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7, padding=3):
super(SpatialAttentionModule, self).__init__()
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2, out_channels=1,
kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True) # torch.max returns (values, indices)
out = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
out = self.conv2d(out)
return self.sigmoid(out)
class CBAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction, kernel_size, padding):
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttentionModule(channel, reduction)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttentionModule(kernel_size, padding)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.channel_attention(x) * x
out = self.spatial_attention(out) * out
return out