1. 数据集
- 由美国高中生和人口调查局员工手写的70000个数字的图片。
- 数据集获取
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
mnist = fetch_openml('mnist_784', version=1, cache=True, as_frame=False)
mnist
- 查看X和Y

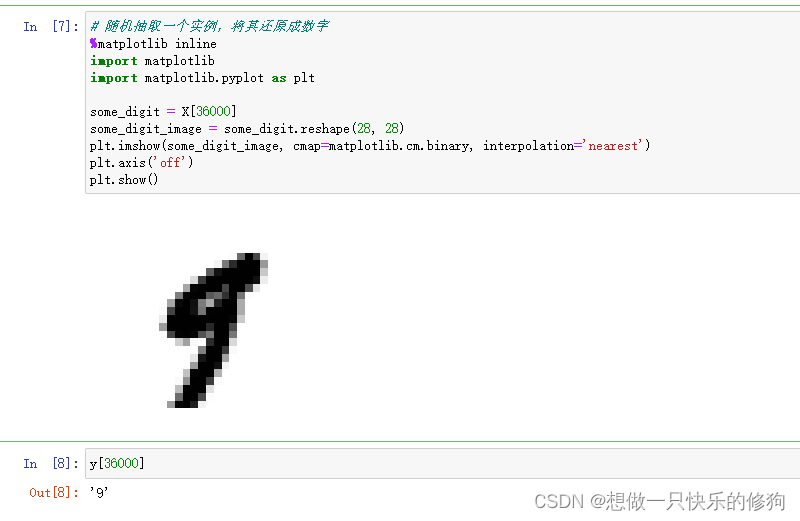
- 找索引为36000的实例,并将其还原成数字(书中是还原成了5,但是我这么获取数据集还原的数字是9,不知道什么原因)
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
some_digit = X[36000]
some_digit_image = some_digit.reshape(28, 28)
plt.imshow(some_digit_image, cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary, interpolation='nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
2. 划分数据集
- 因为有些机器学习算法对训练实例的顺序敏感,如果连续输入许多相似的实例,可能导致执行性能不佳,所以对训练集进行洗牌。
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = X[:60000], X[60000:], y[:60000], y[60000:]
import numpy as np
shuffle_index = np.random.permutation(60000)
X_train, y_train = X_train[shuffle_index], y_train[shuffle_index]
3. 重新创建目标向量(以是5和非5作为二分类标准)
y_train_5 = (y_train == '5')
y_test_5 = (y_test == '5')
4. 训练SGD分类器
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
sgd_clf = SGDClassifier(random_state=42)
sgd_clf.fit(X_train, y_train_5)
4.1 使用准确率进行评估
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.base import clone
skfolds = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3, random_state=42, shuffle=True)
for train_index, test_index in skfolds.split(X_train, y_train_5):
clone_clf = clone(sgd_clf)
X_train_folds = X_train[train_index]
y_train_folds = y_train_5[train_index]
X_test_folds = X_train[test_index]
y_test_folds = y_train_5[test_index]
clone_clf.fit(X_train_folds, y_train_folds)
y_pred = clone_clf.predict(X_test_folds)
n_correct = sum(y_pred == y_test_folds)
print('预测正确的数量比例:', n_correct / len(y_pred))

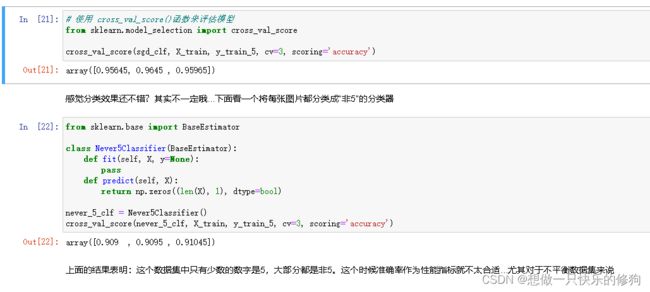
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
cross_val_score(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, scoring='accuracy')
4.2 使用混淆矩阵进行评估(精度、召回率和F1分数)
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_predict
y_train_pred = cross_val_predict(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3)
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_matrix(y_train_5, y_train_pred)
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score
precision_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred)
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
f1_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred)

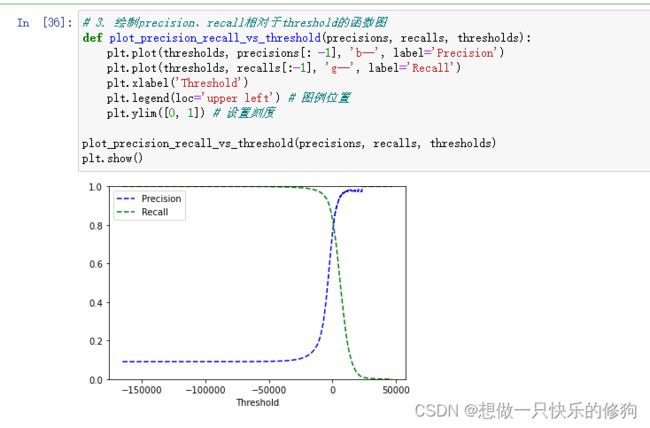
4.3 绘制precision、recall相对于threshold的函数图
y_scores = cross_val_predict(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, method='decision_function')
y_scores
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
precisions, recalls, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_train_5, y_scores)
def plot_precision_recall_vs_threshold(precisions, recalls, thresholds):
plt.plot(thresholds, precisions[: -1], 'b--', label='Precision')
plt.plot(thresholds, recalls[:-1], 'g--', label='Recall')
plt.xlabel('Threshold')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylim([0, 1])
plot_precision_recall_vs_threshold(precisions, recalls, thresholds)
plt.show()
4.4 精度-召回率(PR曲线)
plt.plot(recalls[:-1], precisions[: -1], 'r--')
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.show()

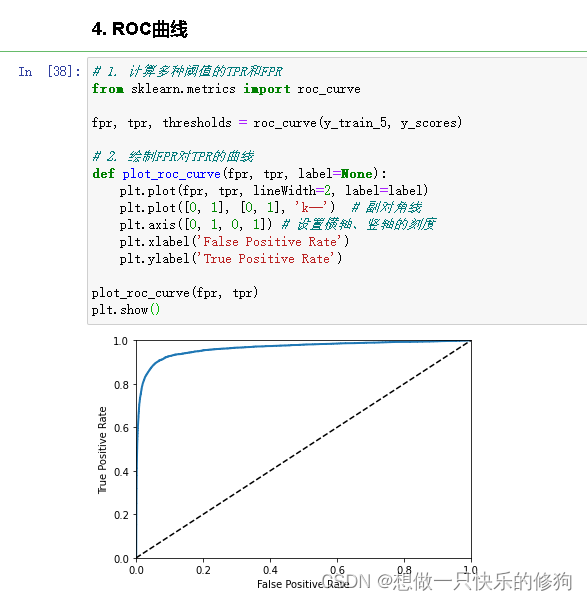
4.5 ROC曲线、AUC值
4.5.1 ROC曲线
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_train_5, y_scores)
def plot_roc_curve(fpr, tpr, label=None):
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, lineWidth=2, label=label)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--')
plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 1])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plot_roc_curve(fpr, tpr)
plt.show()
4.5.2 AUC值
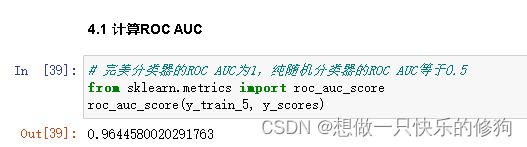
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
roc_auc_score(y_train_5, y_scores)
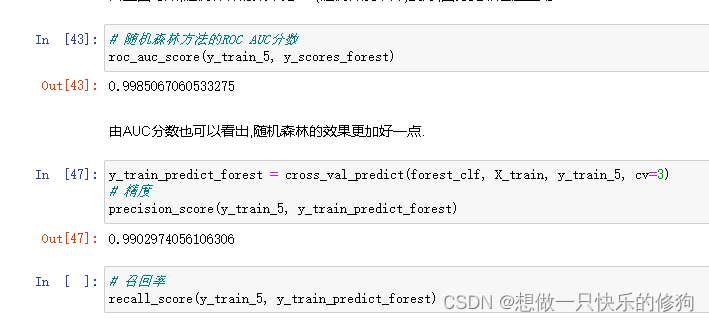
5. 使用随机森林训练、评估
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
forest_clf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
y_probas_forest = cross_val_predict(forest_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, method='predict_proba')
y_probas_forest
y_scores_forest = y_probas_forest[:, 1]
y_scores_forest
fpr_forest, tpr_forest, thresholds_forest = roc_curve(y_train_5, y_scores_forest)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, "b:", label="SGD")
plot_roc_curve(fpr_forest, tpr_forest, "Random Forest")
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
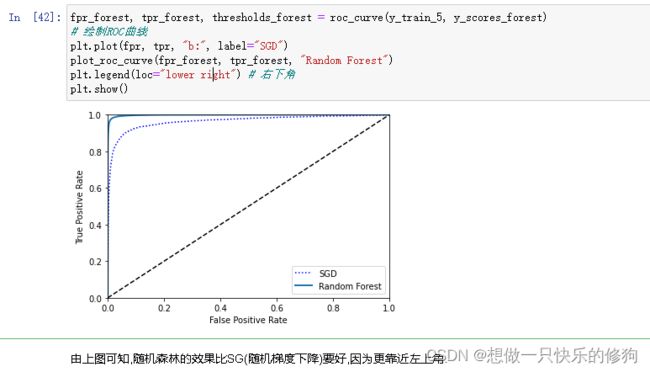
其他评估指标(AUC值、精度、召回率)如下: