3. 学习链表(LinkList)这一篇就够啦
前言
在上篇中我们学习了顺序表,通过源码我们了解到其底层就是通过数组来实现的
在ArrayList当中我们的插入和删除操作时,需要将后序的元素整体往前或者往后移动,时间复杂度为O(n),效率确实是比较低的,因此ArrayList并不适合去进行此类的操作,所以Java集合当中又引入了LinkedList,即我们口中的链表
目录
- 1. 链表
-
- 1.1 链表的概念和结构
- 2. 自己实现一个链表结构
-
- 2.1 初始化链表
- 2.2 实现链表当中的方法
-
- 2.2.1 输出链表元素
- 2.2.2查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表中
- 2.2.3 得到单链表的长度
- 2.2.4 头插法
- 2.2.5 尾插法
- 2.2.6 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
-
- 2.2.6.1 检查index下标是否正确
- 2.2.6.2 IndexNotLegalException
- 2.2.7 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
-
- 2.2.7.1 找到所需添加元素下标的前一个元素
- 2.2.8 删除第一次出现值为key的节点
-
- 2.2.8.1 找到关键字key的的前驱
- 2.2.9 删除所有值为key的节点
- 2.2.10 清空链表所有节点
- 2.3 自我实现链表所有代码
- 3. 巩固练习
1. 链表
1.1 链表的概念和结构
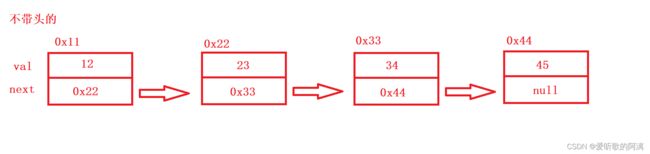
链表是一种物理上非连续,而逻辑上连续的存储结构,其间通过节点(也可以叫结点)来相互连接

val:当前节点的值
next:下一个节点的地址
head:头节点
链表也分为单向或者双向,带头或者不带头,循环或者非循环
但是我们并不需要全掌握,在这里我们重点掌握两种就OK了,剩下的就可以自己进行开发探索了
- 不带头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多
不带头需重点掌握 \color{red}{不带头需重点掌握} 不带头需重点掌握
- 无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表
2. 自己实现一个链表结构
2.1 初始化链表
首先咱们先把节点,值定义出来
public Node head;//表示存储当前链表的头结点的引用
static class Node{//定义节点
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
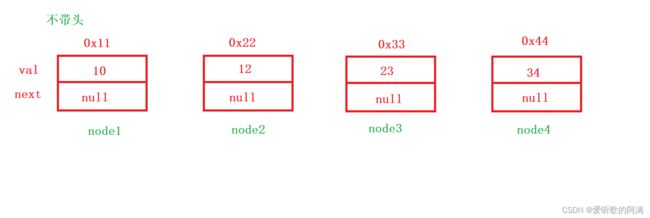
再通过穷举的方式来创建一个链表
/**
* 通过穷举的方式 创建一个链表出来
*/
public void createList() {
Node node1 = new Node(10);
Node node2 = new Node(12);
Node node3 = new Node(23);
Node node4 = new Node(34);
}
/**
* 通过穷举的方式 创建一个链表出来
*/
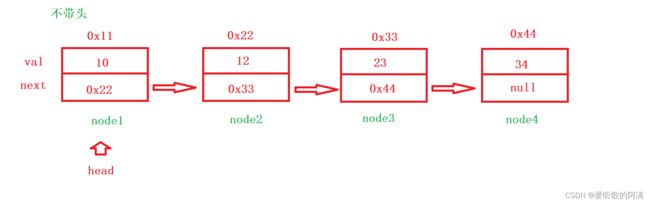
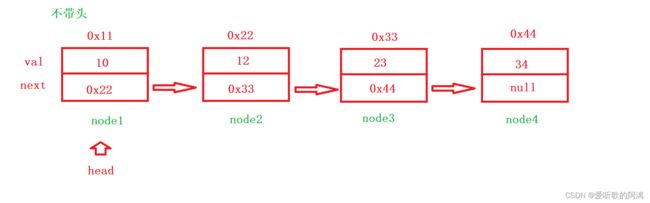
public void createList() {
Node node1 = new Node(10);
Node node2 = new Node(12);
Node node3 = new Node(23);
Node node4 = new Node(34);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
head = node1;
}
2.2 实现链表当中的方法
2.2.1 输出链表元素
思考在这里我们的display方法循环结束的条件是
head != null 还是 head.next != null 呢?
其实这里应该使用 head != null ,因为使用 head.next != null 会将最后一个元素漏掉
而 head 遍历完,想要查找其他元素就不行了,所以我们需要在定义一个 cur 变量来代替 head 节点
public void display() {
Node cur = this.head;//定义cur的目的: 让head节点保持不动
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
2.2.2查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表中
// 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表中
public boolean contains(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
2.2.3 得到单链表的长度
// 得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
2.2.4 头插法
时间复杂度:O(1)
// 头插法 O(1)
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = this.head;
这两行代码不能搞反
学习完头插法咱们给链表添加元素就不需要像之前那样去添加了,可以使用addFirst函数来进行添加
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSingleList testSingleList = new TestSingleList();
testSingleList.addFirst(10);
testSingleList.addFirst(12);
testSingleList.addFirst(23);
testSingleList.addFirst(34);
testSingleList.display();
}
2.2.5 尾插法
时间复杂度:O(n)
// 尾插法 时间复杂度:O(n)
public void addLast(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
// 注意考虑头为空的情况
if (head == null) {
}else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
由于上面头插法插入的元素为倒序
所以我们再使用尾插法创建一个链表
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSingleList testSingleList = new TestSingleList();
testSingleList.addLast(10);
testSingleList.addLast(12);
testSingleList.addLast(23);
testSingleList.addLast(34);
testSingleList.display();
}
2.2.6 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
// 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) {
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}else {
Node cur = new Node(data);
}
}
2.2.6.1 检查index下标是否正确
// 检查index下标是否正确
private void checkIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexNotLegalException("index位置不合法!");
}
}
2.2.6.2 IndexNotLegalException
public class IndexNotLegalException extends RuntimeException {
public IndexNotLegalException() {
}
public IndexNotLegalException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
2.2.7 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
// 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) {
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node node = new Node(data);;
Node cur = findIndexSubOfOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
2.2.7.1 找到所需添加元素下标的前一个元素
// 找到所需添加元素下标的前一个元素
private Node findIndexSubOfOne(int index) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (index - 1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
2.2.8 删除第一次出现值为key的节点
// 删除所有值为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
// 头结点需要单独处理
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node cur = searchPrevOfIndexKey(key);
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
Node del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
// cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
2.2.8.1 找到关键字key的的前驱
/**
* 找到关键字key的的前驱
* @param key
* @return
*/
private Node searchPrevOfIndexKey(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
2.2.9 删除所有值为key的节点
// 删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur = head.next;
Node prev = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur =cur.next;
}
}
// 如果头节点的值为key
if (this.head.val == key) {
this.head = cur;
}
}
2.2.10 清空链表所有节点
// 清空链表所有节点
public void clean() {
// this.head = null;
Node cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
Node curNext = head.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
this.head = null;
}
2.3 自我实现链表所有代码
s h i f t + F 6 可以改所有的变量名 \color{red}{shift + F6 可以改所有的变量名} shift+F6可以改所有的变量名
package demo1;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Administrator
* Date: 2022-10-21
* Time: 14:25
*/
public class TestSingleList {
public ListNode head;//表示存储当前链表的头结点的引用
static class ListNode {//定义节点
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
/**
* 通过穷举的方式 创建一个链表出来
*/
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(10);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(34);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
head = node1;
}
public void display() {
ListNode cur = this.head;//定义cur的目的: 让head节点保持不动
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
// 得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
// 头插法 O(1)
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
// 尾插法 时间复杂度:O(n)
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
// 注意考虑头为空的情况
if (head == null) {
head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
// 检查index下标是否正确
private void checkIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexNotLegalException("index位置不合法!");
}
}
// 任意位置插入, 第一个数据节点为0下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) {
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);;
ListNode cur = findIndexSubOfOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
// 找到所需添加元素下标的前一个元素
private ListNode findIndexSubOfOne(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index - 1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
public void remove(int key) {
// 头结点需要单独处理
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPrevOfIndexKey(key);
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
// cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
/**
* 找到关键字key的的前驱
* @param key
* @return
*/
private ListNode searchPrevOfIndexKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
// 删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode prev = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur =cur.next;
}
}
// 如果头节点的值为key
if (this.head.val == key) {
this.head = cur;
}
}
// 清空链表所有节点
public void clean() {
// this.head = null;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
this.head = null;
}
}
3. 巩固练习
206. 反转链表
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 当为空链表时
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
// 当只有一个元素时
if (this.head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = this.head.next;// 当前需要反转的节点
head.next = null;// head其实就是当前需要反转的节点的前驱
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}
876. 链表的中间节点
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
// 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
// 判断k的合法性
if (k <= 0 || head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == null) {
return null;// k太大了
}
}
while (fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
合并两个有序链表
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);// 傀儡节点 虚拟节点
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
tmp.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}else {
tmp.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
tmp.next = list1;
}
if (list2 != null) {
tmp.next = list2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
2022年10月22日20:17:43