基于CIFAR100的VGG网络结构详解
码字不易,点赞收藏
1 数据集概况
1.1 CIFAR100
cifar100包含20个大类,共100类,train集50000张图片,test集10000张图片。

CIFAR100下载地址:http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html
1.2 showdata.py查看数据
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pickle
import os
# 解压缩,返回解压后的字典
def unpickle(file):
fo = open(file, 'rb')
dict = pickle.load(fo, encoding='latin1')
fo.close()
return dict
def cifar100_to_images():
tar_dir = './data/cifar-100-python/' # 原始数据库目录
train_root_dir = './data/cifar100/train/' # 图片保存目录
test_root_dir = './data/cifar100/test/'
if not os.path.exists(train_root_dir):
os.makedirs(train_root_dir)
if not os.path.exists(test_root_dir):
os.makedirs(test_root_dir)
# 获取label对应的class,分为20个coarse class,共100个 fine class
meta_Name = tar_dir + "meta"
Meta_dic = unpickle(meta_Name)
coarse_label_names = Meta_dic['coarse_label_names']
fine_label_names = Meta_dic['fine_label_names']
print(fine_label_names)
# 生成训练集图片,如果需要png格式,只需要改图片后缀名即可。
dataName = tar_dir + "train"
Xtr = unpickle(dataName)
print(dataName + " is loading...")
for i in range(0, Xtr['data'].shape[0]):
image = np.reshape(Xtr['data'][i], (-1,1024)) # Xtr['data']为图片二进制数据
r = image[0, :].reshape(32, 32) # 红色分量
g = image[1, :].reshape(32, 32) # 绿色分量
b = image[2, :].reshape(32, 32) # 蓝色分量
img = np.zeros((32, 32, 3))
# RGB还原成彩色图像
img[:, :, 0] = r
img[:, :, 1] = g
img[:, :, 2] = b
###img_name:fine_label+coarse_label+fine_class+coarse_class+index
picName = train_root_dir + str(Xtr['fine_labels'][i]) + '_' + str(Xtr['coarse_labels'][i]) + '_&' + \
fine_label_names[Xtr['fine_labels'][i]] + '&_' + coarse_label_names[
Xtr['coarse_labels'][i]] + '_' + str(i) + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(picName, img)
print(dataName + " loaded.")
print("test_batch is loading...")
# 生成测试集图片
testXtr = unpickle(tar_dir + "test")
for i in range(0, testXtr['data'].shape[0]):
img = np.reshape(testXtr['data'][i], (3, 32, 32))
img = img.transpose(1, 2, 0)
picName = test_root_dir + str(testXtr['fine_labels'][i]) + '_' + str(testXtr['coarse_labels'][i]) + '_&' + \
fine_label_names[testXtr['fine_labels'][i]] + '&_' + coarse_label_names[
testXtr['coarse_labels'][i]] + '_' + str(i) + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(picName, img)
print("test_batch loaded.")
if __name__ == '__main__':
cifar100_to_images()
2 VGG网络结构
2.1 网络结构总览
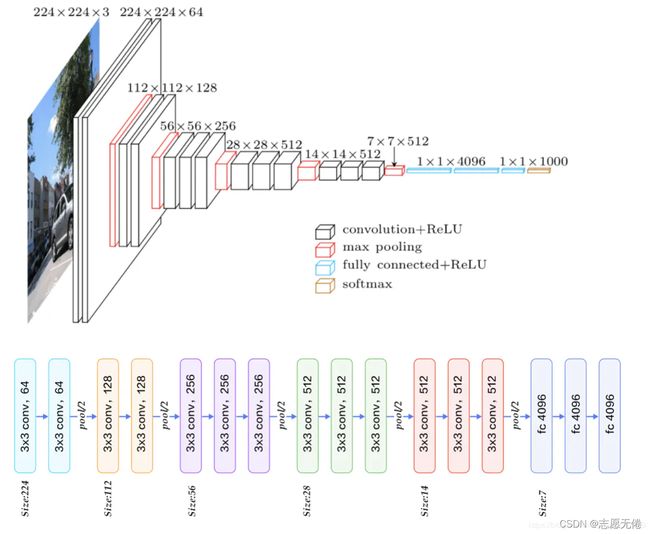
在VGG的网络中,卷积核尺寸都是3x3(padding=1),即卷积操作不会使得特征图的尺寸改变
使得特征图尺寸发生改变的只有池化操作(特征图尺寸由(H,W)变为(H/2,W/2))
搞清楚以上两点后,VGG网络就十分清晰易懂。例如下图VGG16的网络结构,输入图片的尺寸为224x224x3,VGG16中包含5个池化操作,故特征图进行扁平化之前的尺寸应该是7(224/32);
至于通道的变化就更简单了,只有卷积操作会带来通道的改变,而卷积操作中的通道改变则是通过不同的卷积核组来实现的
2.2 VGG网络结构源码
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_class=100):
super().__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, num_class)
)
def forward(self, x):
output = self.features(x)
output = output.view(output.size()[0], -1)
output = self.classifier(output)
return output
基于CIFAR100的VGG网络结构定义得很简洁,可以说是一目了然了。
对于网络结构定义,从forward函数可以看出主要包括两部分:features和classifier
features:卷积层+池化层,只涉及对网络尺寸、网络通道的改变,即VGG中全连接层之前的所有操作
classifier:全连接+分类,把从features中得到的特征图扁平化后,经过3层全连接后将类别映射到100进行分类预测
2.3 VGG中的Features构建过程
cfg = {
'A' : [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],# vgg11
'B' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],# vgg13
'D' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],# vgg16
'E' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'] # vgg19
}
def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):
layers = []
input_channel = 3
for l in cfg:
if l == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
continue
layers += [nn.Conv2d(input_channel, l, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]
if batch_norm:
layers += [nn.BatchNorm2d(l)]
layers += [nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
input_channel = l
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def vgg16_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['D'], batch_norm=True))
2.3.1 字典cfg
首先,VGG将features部分的网络结构使用字典进行了表示,其中的数字表示通道数的改变,字母M表示maxpooling操作
2.3.2 make_layers+vgg16_bn
make_layer部分就是按照cfg中给出的VGG网络结构进行网络的构建,以vgg16_bn为例:
1)确定当前层是卷积还是池化操作:如果是卷积操作,按照cfg中给出的通道数进行网络的连接;如果是池化操作,则以尺寸为2的池化核进行特征图的最大池化,当前的特征图尺寸减半。
2)对每一批batch进行标准化操作。
3)最后进行当前层的激活操作。
在CIFAR100中,输入图片尺寸为3*32*32,经过features后特征图尺寸变为512*1*1,扁平化后只剩下通道维度的尺寸512,并且512也是分类器的输入
其实这种make_layer的方式在源码中特别常见,引用量刚破30000的ResNet源码也是用这种方式进行构建的
2.4 分类器
512->4096->4096->100
三层全连接层,输出前经过softmax便构成了最后的分类器
2.5 网络完整源码
import torch.nn as nn
cfg = {
'A' : [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'B' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'D' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'E' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M']
}
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_class=100):
super().__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, num_class)
)
def forward(self, x):
output = self.features(x)
output = output.view(output.size()[0], -1)
output = self.classifier(output)
return output
def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):
layers = []
input_channel = 3
for l in cfg:
if l == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
continue
layers += [nn.Conv2d(input_channel, l, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]
if batch_norm:
layers += [nn.BatchNorm2d(l)]
layers += [nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
input_channel = l
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def vgg11_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['A'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg13_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['B'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg16_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['D'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg19_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['E'], batch_norm=True))
3 贴个最近常在脑海回响的诗
梦游天姥吟留别
李白
海客谈瀛洲,烟涛微茫信难求;
越人语天姥,云霞明灭或可睹。
天姥连天向天横,势拔五岳掩赤城。
天台四万八千丈,对此欲倒东南倾。
我欲因之梦吴越,一夜飞度镜湖月。
湖月照我影,送我至剡溪。
谢公宿处今尚在,渌水荡漾清猿啼。
脚著谢公屐,身登青云梯。
半壁见海日,空中闻天鸡。
千岩万转路不定,迷花倚石忽已暝。
熊咆龙吟殷岩泉,栗深林兮惊层巅。
云青青兮欲雨,水澹澹兮生烟。
列缺霹雳,丘峦崩摧。
洞天石扉,訇然中开。
青冥浩荡不见底,日月照耀金银台。
霓为衣兮风为马,云之君兮纷纷而来下。
虎鼓瑟兮鸾回车,仙之人兮列如麻。
忽魂悸以魄动,恍惊起而长嗟。
惟觉时之枕席,失向来之烟霞。
世间行乐亦如此,古来万事东流水。
别君去兮何时还?且放白鹿青崖间,须行即骑访名山。
安能摧眉折腰事权贵,使我不得开心颜!