西湖大学张岳老师NLP课程笔记1 Introduction
西湖大学张岳老师NLP课程笔记1 Introduction
-
参考资料
- B站链接
- 课程主页
-
《Natural Language Processing: A Machine Learning Perspective 》
-
csdn大佬笔记
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45645521/category_11685799.html
文章目录
- 西湖大学张岳老师NLP课程笔记1 Introduction
-
- 1.1 What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
-
- Main approaches
-
- Rule based(symbolic) approch (1950s-1980s)
- Statistical approach (traditional machine learning) (1980s-2000s)
- Connectionist approach (Neural networks) (2000s-now)
- 1.2 NLP Tasks
-
- 1.2.1 Fundamental NLP tasks 基础自然语言处理任务
-
- Syntactic tasks 句法分析任务
-
- Word level
- Sentence level
- Semantic tasks 语义分析任务
-
- Word level
- Sentence level
- Text entailment 自然语言推理
- Discourse tasks 篇章分析
- 1.2.2 Information Extraction tasks 信息抽取任务
-
- Information extraction (IE)
- Entities 实体
-
- Named entity recognition (NER) 命名实体识别
- Anaphora Resolution 指代消解
- Co-references 共指消解
- Relations
-
- relation extraction 关系抽取
- Knowledge graph 知识图谱
-
- Entity linking(entity disambiguation) 实体链接
- Named entity normalization 实体规范化
- Link prediction(knowledge graph completion) 链接预测/知识图谱补全
- Events
-
- Event Detection 事件检测
- News event detection (first story detection) 新事件检测
- Event factuality prediction (predict the likelihood of event) 事实性检测
- Event time extraction (e.g. temporal ordering of events 事件的时间顺序排列、timeline extration 时间线检测) 事件时间次序推断
- Causality detection 因果检测
- Event coreference resolution 事件共指消解
- Zero-pronouns 零指代消解
- Script learning 脚本学习
- Sentiment
-
- Sentiment analysis(opinion mining) 情感分析 意见挖掘
- Sentiment related tasks 情感分析相关任务
- Sarcasm detection 讽刺检测
- Sentiment lexicon acquisition 情感词典自动获取
- Emotion detection 情绪检测
- Stance detection and argumentation mining 立场检测和议论挖掘
- 1.2.3 Text generation Tasks 文本生成任务
-
- Realization 实现/ linearization/线性化
-
- Data-to-text generation 数据到文字的生成
- Summarization 文本摘要 文本总结
- Machine translation 机器翻译
- Grammar error correction 句法纠错
- Question answering (QA) 自动问答系统
-
- Knowledge-base QA 基于知识库的问答
- Reading comprehension (machine reading) 基于文本的问答/机器阅读理解
- Community QA 社区问答
- Open QA 开放问答
- Dialogue systems 对话系统
-
- Chit-chat 闲聊式的对话
- Task-oriented dialogues 基于任务的对话
- 1.2.4 Other Applications
-
- Information retrieval 信息检索
- Recommendation system
- Text mining and text analytics 文本挖掘和文本分析
- 1.3 NLP from a Machine Learning Perspective 机器学习视角下的自然语言处理
-
- 为什么要从机器学习视角出发
-
- The current dominant method
- The historical of research
- 从机器学习视角来对NLP task进行划分
-
- 可以按照输出划分 According to the output
-
- classification tasks 分类任务
- structured prediction tasks 结构预测
- regression problem 回归问题
- 可以按照训练数据划分 According to the nature of training data for machine learning
-
- unsupervised learning 无监督学习
- supervised learning 监督学习
- semi-supervised learning 半监督学习
- Resources(来自课程PPT)
1.1 What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
- In the broadest sense ,NLP refers to any program that automatically processes human languages.
- 广义上讲,NLP指的是对人类语言自动处理或合成的研究
Main approaches
Rule based(symbolic) approch (1950s-1980s)
-
The oldest approaches to NLP
-
Based on human-developed rules and lexicons (基于人类制定的语言规则)
lexicon
also the lexicon
n.[sing.] (linguistics 语言) (某语言或学科、某人或群体使用的)全部词汇
-
Challenges in resolving ambiguities
语言的歧义性,一词多义给语言学家制定的规则提出了很大的挑战
-
a well-quoted example:上世纪60年代一个著名案例的例子
在机器翻译研究的初期,人们经常举一个例子来说明机器翻译任务的艰巨性。在英语中“The spirit is willing but the flesh is weak.”,意思是“心有余而力不足”。但是当时的某个机器翻译系统将这句英文翻译到俄语,然后再翻译回英语的时候,却变成了“The Voltka is strong but the meat is rotten.”,意思是“伏特加酒是浓的,但肉却腐烂了”。从字面意义上看,“spirit”(烈性酒)与“Voltka”(伏特加)对译似无问题,而“flesh”和“meat”也都有肉的意思。
- "The spirit is strong, but the flesh is weak“ “The Vodka is good, but the meat is bad”
- 句子“精神很强大,但肉体很弱”被错误地翻译成了“伏特加很美味,但肉很难吃”。
-
Statistical approach (traditional machine learning) (1980s-2000s)
基于统计的机器学习方法,从语言学家手工标注的数据中学到重要的统计意义的特征,并把这些特征作为知识来估算一个输入对应的不同输出的概率,这样就可以把最可能的输出作为统计的结果来反映给客户,语言学家的工作从设计规则参与算法编写变成了对数据集进行标注
- Gradually adopted by both the academia(学术界) and the industry
- Using probabilistic modeling (使用概率模型)
- training data (corpus with markup)
- feature engineering
- training a model on parameters
- applying model to test data
Connectionist approach (Neural networks) (2000s-now)
计算能力提升, 大量数据训练参数很多的神经网络,输入输出的结构进行端到端关联
自然语言处理的神经网络可以在大规模的未标注的互联网语言文本进行预训练,再用少量语言学家标注的语料进行参数微调,神经网路表达能力非常强, 性能强大
-
Deep learning surpasses statistical methods( 优于,超过统计方法) as the domain approach
-
free from linguistic features (不需要语言特征)
-
very large neural models
-
pre-training over large raw text
(可以在庞大的原始文本上进行预训练)
-
1.2 NLP Tasks
We give an overview of NLP tasks in this section, which provides a background for discussing machine learning algorithms in the remaining chapters.
Note that our introduction of linguistic and task-specific concepts is brief, as this is not the main goal of the book. Interested readers can refer to dedicated materials listed in the chapter notes at the end of the chapter for further reading.
1.2.1 Fundamental NLP tasks 基础自然语言处理任务
- 起源于 计算语言学 (Computational Linguistics)这门学科,研究算法如何代替语言学家自动获得输入文本中所蕴含的语言学知识,研究 词法 句法 语义 篇章等的关系
- Phonology 音韵学
- Morphology 词法
- Syntax 句法
- Semantics 语义
- Discourse 篇章
- Pragmatics 语用学
Syntactic tasks 句法分析任务
Syntactic Tasks investigate the composition structures of languages, ranging from the word level to the sentence level
Word level
-
词的形态划分 morphological analysis
the task of morphological analysis studies automatic prediction of morphological features of input words, such as morphemes.
词根 词缀 提取出来
-
分词 word segmentation
分词任务歧义性较强
-
符号化 tokenization
-
词性标注,语法标注,词类消疑 POS Tagging (part-of-speech tagging)
-
Part-of-speech(POS)
Basic syntactic role that words play in a sentence
前面的can是情态动词 , 后面的can是名词 罐子
-
Sentence level
-
一些常用的句法范式 Grammar formalisms for syntactic parsing
- constituent grammars 成分句法
- dependency grammars 依存句法
- lexical functional grammars(LFG) 词汇功能文法
- Head-driven phrase structure grammars(HPSG) 中心词驱动短语结构语法
- [ACL2019]Head-Driven phrase structure grammar句法分析 - sonta的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94009246
- 中心词驱动短语结构语法(HPSG)——生成语法的旁门左道 - 思思的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/52973742
-
Tree adjoining grammars(TAG) 树邻接文法
- Combinatory categorical grammar(CCG) 组合范畴文法
-
constituent parsing 成分句法分析(也叫短语结构句法分析)
Constituent parsers assign phrase labels to constituent, also referred to as phrase-structure grammars.
通过层次化短语结构来表达一句话
a book 名词短语
bought a book for Mary 动词短语
Tim bought a book for Mary. 句子结构
成分句法分析就是通过算法自动找到一句话里面的层次短语结构
-
dependency parsing 依存句法分析
-
Dependency parsers analyze a sentence in head words and dependent words.
依存句法通过两个词之间的关系来组成一句话的结构
上例中有主语宾语修饰语等等关系,
- 每个词都修饰句子中唯一的词,
- 这句话中有个词不修饰任何词,它叫做这句话的根节点root节点
-
-
CCG parsing 组合范畴句法分析
-
组合范畴句法是高度词汇化的句法
- 词汇化:每个词都带有一个句法信息丰富的标签
- 例如
- 下面的bought是及物动词,标签为(S\NP)/NP,S代表一个句子,NP代表名词短语
- 它需要向右找一个名词短语作为它的宾语,消解以后得到S\NP这样一个结构,再向左边找一个名词短语,就得到一句话
- 先向右和a book(NP)组合,得到宾语,bought a book;然后又和左边的Tom结合形成S
- 如果每个词都得到了复杂的词汇化标签,那么句法分析变得简单,因为标签和标签之间的组合有较强的限制性
-
-
supertagging 浅层句法分析任务
Also called shallow parsing, a pre-processing step before parsing.
-
在组合范畴句法分析中,给每个单词打标签的这一步称为
CCG supertagging- 为啥叫super,因为每个句法标签含义很丰富,所以给每个词标记了标签,几乎就形成了句法分析
-
和成分句法相关的浅层句法分析任务叫
syntactic chunking-
identify basic syntactic phrases from a given sentence
把一句话切成比较大的短语块
-
-
Semantic tasks 语义分析任务
Word level
-
Word sense disambiguation (WSD) 词义消歧
The NLP task that disambiguates the sense of a word given a certain context, such as a sentence, is called word sense disambiguation (WSD).
-
Never trouble troubles till trouble troubles you.
-
I saw a man saw a saw with a saw.
我看见一个男人用锯子锯另一把锯子
-
-
Metaphor detection 隐喻检测
Metaphor detection is an NLP task to discover metaphoric uses of words in texts.
- Love is a battlefield.
- Bob is a couch potato. (沙发土豆,指经常泡在电视机前的人)
-
Sense relations between words
-
Synonyms :pairs of words with similar senses 同义词 /sɪnənɪmz/
- quick-fast
- bad-poor
- big-large
-
Antonyms :pairs of words with opposite relations 反义词 /ˈæntəʊnɪmz/
- big-small
- bad-good
- easy-difficult
-
Hyponyms :pairs of words in subtype–type relations 上下位词
- car-vehicle
- apple-fruit
- cat-animal
-
Meronyms : pairs of words in part–whole relations. 组成部分
- leaf-tree
- nose-face
- roof-house
-
-
Analogy 类比
判断词对和词对之间的语义关系
- king-queen / man-woman / boy-girl
- Beijing/China — London/UK
- Piano/Play – Novel/Read
Sentence level
-
Predicate-argument relations 谓词-论元结构
On the sentence level, the semantic relation between verbs and their syntactic subjects and objects belongs to predicate–argument relations, which denote meaning of events.
-
谓词:动词,事件
- 有时也可以是名词
-
论元:事件的参与者或属性
-
A typical NLP task on predicate-argument structures is semantic role labelling (SRL,语义角色标注),
-
-
form of semantic representation
-
predicate–argument
-
frame structure
-
logic 逻辑表达式
- predicate logic 谓词逻辑
- first-order logic 一阶逻辑
-
lambda calculus λ表达式
- 比一阶谓词逻辑表达能力更强
- 属于一种编程范式,表达能力可以和图灵机、任何算法表达能力相当
- 从广义上讲,所有可以表达句子含义的表达框架,包括SQL,都可以作为语义分析的输出
- 比如,一个疑问句可以转换为SQL的查询语句以便从数据库中得到答案,这也是一个语义分析任务
-
semantic graphs 语义图
-
一个表达能力丰富的语义表示框架:Semantic graphs 语义图
- Abstract Meaning Representation 抽象语义表示
- 节点表示语义单元, 边表示语义单元之间的关系
- 图中的节点和句子中的词并不是一 一对应的
- 语义图还能表达修饰关系 ,如 red apple
-
-
Text entailment 自然语言推理
-
text entailment(文本蕴含)是判断两句话之间语义关系的任务
- Textual entailment is a directional semantic relation between two texts.
- The task of textual entailment recognition is to decide whether a hypothesis text is entailed by a given premise text.
-
也叫自然语言推理 natural language inference (NLI)
- A related task, natural language inference (NLI) is the task of determining whether a hypothesis is true, false or undetermined given a premise, which reflect entailment, contradiction and neutral relations between the two input texts, respectively. Paraphrase detection is another semantic task between two sentences, which is to decide whether they are paraphrases of each other.
-
需要一个前提和一个假设
- For example, given the premise(前提) “Tim went to the Riverside for dinner”, the hypotheses(假设) “The Riverside is an eating place” and “Tim had dinner” are entailed, but the hypothesis “Tim had lunch” is not.
Discourse tasks 篇章分析
-
A discourse refers to a piece of text with multiple sub-topics and coherence relations between them.
-
Discourse parsing:Analyze the coherence relations between sub-topics in a discourse.
-
There are many different discourse structure formalisms. Rhetoric structure theory (RST) is a representative formalism which we use for discussion.
- 篇章分析有很多范式,下面主要学习 RST 修辞结构理论
-
例
四个篇章单元, 电影有趣和Tim想看是并列关系, 这两句话和他这周不能去看 组成了反义、转折关系, 前三句话和他下周期末考试组成了解释关系
-
RST篇章分析的基本步骤叫 Discourse segmentation(篇章切分)
把一段长的文本切分为基本单元
前面四句话可以用一个长句子表达
篇章切分任务可以针对一句话或多句话
and but because这种关键词(discourse markers)可以在篇章切分中有帮助
1.2.2 Information Extraction tasks 信息抽取任务
上世纪90年代末为捕获网络舆情产生的任务
/数据挖掘兴起后和语言文字相关的挖掘任务
Information extraction (IE)
- Obtain structured information from unstructured texts
Entities 实体
Named entity recognition (NER) 命名实体识别
-
To identify all named entity mentions from a given piece of text 从给定文本找出所有提到的命名实体
Anaphora Resolution 指代消解
指代消解其实属于Fundamental NLP tasks
-
resolves what a pronoun or noun phrase refers to (判断一句话中名词短语和代词指代什么)
这句话He代表Tim , it 代表book
-
Zero-pronoun resolution :detects and interprets dropped pronouns (零指代:检测和解释省略的代词)

检测省略的代词,并且判断它属于哪一个具体的对象
高中做语法单选题的回忆来了啊哈哈哈
Co-references 共指消解
-
Co-reference resolution:finds all expressions that refer to the same entities in a text
Relations
-
Relations between entities represent knowledge
-
common relations
-
hierarchical 可分层的
-
domain-specific 特定领域
-
relation extraction 关系抽取
-
identify relations between entity under a set of prespecified relation categories
- Tim和Mary的社会关系
- Tim和MSRA的隶属关系
- MSRA和Beijing的位置关系
Knowledge graph 知识图谱
- Large-scale entity and relation knowledge can be stored in a knowledge graph (KG), a type of database where entities form nodes and relations form edges.
图中的节点代表实体,节点之间的边代表实体之间的关系知识
Entity linking(entity disambiguation) 实体链接
- determines the identity of entity mentioned from text ( 把文本中的实体和知识图谱中的实体进行关联)
Named entity normalization 实体规范化
是entity linking的related task
-
finds a canonical term for named entity mentions (为提到的命名实体找到一个规范术语)
Link prediction(knowledge graph completion) 链接预测/知识图谱补全
-
Knowledge graphs allow knowledge inference
知识推理
Events
Event Detection 事件检测
Here events can be defined as open-domain semantic frames, or a set of specific frames of concern in a certain domain, such as “cooking”. Event mentions contain trigger words, which can be both verb phrases and noun phrases. The detection of event trigger words can be more challenging compared to detecting entity mentions since trigger words can take different parts of speech.
- 命名实体识别相关论文中常出现的mention该如何理解? - Sussurro的回答 - 知乎 https://www.zhihu.com/question/53590576/answer/2281734586
-
to identify mentions of events from texts
从文本中检测出触发词
Events have timing. While some events have happened, others are yet to happen or expected to happen. Several NLP tasks are related to event times.
News event detection (first story detection) 新事件检测
- to detect events that have just emerged from news or social media texts.
比如从互联网帖子里发现一些地区有人说的自然灾害等
Event factuality prediction (predict the likelihood of event) 事实性检测
- to predict the likelihood of event happenings

Event time extraction (e.g. temporal ordering of events 事件的时间顺序排列、timeline extration 时间线检测) 事件时间次序推断
- to extract the time of events from text
- to find out temporal relations of events using textual clues, which are not necessarily in their narrative order (利用文本线索找出事件的时间关系,这些线索不一定是按叙述顺序排列的(有时会有倒叙、插入))
Causality detection 因果检测
- to identify whether a given event is caused by a second event.
事件之间也存在相互指代
Event coreference resolution 事件共指消解
Zero-pronouns 零指代消解
- there is a verb phrase ellipsis(省略) in the second sentence, detection of which is useful for event extraction.
Script learning 脚本学习
Here a script refers to a set of partially ordered events in a stereotypical scenario, together with their participant roles.
-
aims to extract such commonsense knowledge automatically from narrative texts
从大量文本抽取脚本知识
订餐包含就坐、点餐、用餐、付款等小事件,这些小的事件有时候会部分出现,有时候会以不同的顺序出现
在语义学范畴,这种整体的事件框架叫script
Sentiment
Sentiment analysis(opinion mining) 情感分析 意见挖掘
-
Sentiment analysis, or opinion mining is an NLP task that extracts sentiment signals from texts.
-
There are numerous task variations.
-
sentiment classification
-
to predict the subjectivity and sentiment polarity(极性) of a given text, which can be a sentence or a full document.
-
The output can be a binary subjective/objective class, or a ternary(三元的) positive/negative/neutral class. More fine-grained(细粒度) output labels can be defined, such as a scale of [ −2, −1, 0, 1, 2], which corresponds to [very negative, negative, neutral, positive, very positive], respectively.
-
There are also tasks that offer more fine-grained details in sentiments.
- targeted sentiment
- investigates the sentiment of a text towards a certain target entity.
- aspect-oriented sentiment
- typically defined in the product review domain(源自于商品评论). The goal is to extract different aspects given a certain topic, together with the sentiment signals towards each aspect.
- More fine-grained sentiment analysis
- extracts not only the opinion target, but also the opinion holder(情感所有者) and the opinion expression.
-
![]()
Sentiment related tasks 情感分析相关任务
Sarcasm detection 讽刺检测
- to classify whether a text contains sarcasm or not
Sentiment lexicon acquisition 情感词典自动获取
- to acquire from texts a lexicon that contains sentiment-bearing words, together with their polarities and strengths from texts. The resulting lexicons are used for sentiment analysis.
Emotion detection 情绪检测
- to extract the emotion of the narrator(叙事者), such as “angry”, “disappointed” and “excited”.
Stance detection and argumentation mining 立场检测和议论挖掘
-
Sentiment analysis is also related to stance detection(立场检测), which is to detect the stance of a text towards a certain subject (i.e., “for” or “against”)
- argument mining从文字中自动搜索观点及其论据的结构的任务,有助于新闻,审稿,评论等内容的自动理解分析
1.2.3 Text generation Tasks 文本生成任务
Realization 实现/ linearization/线性化
一个基础性的文本生成任务是语义分析任务的逆运算
-
The generation of natural language text from syntactic/semantic representations
给定一个语义图,任务的输出是表达其中语义的文字
语义到文字的生成也可以看作是图到文字的生成(graph-to-text generation)
-
Semantic dependency graphs (logical forms) example:
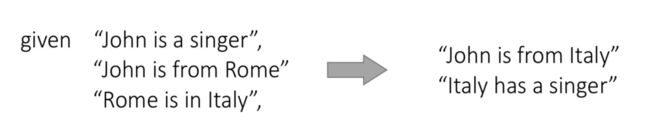
Data-to-text generation 数据到文字的生成
-
The generation of natural language text from syntactic/semantic representations
-
例
Summarization 文本摘要 文本总结
长文本→短文本 ,提取重要内容;可总结单篇文档,多篇文档(如报道同一事件的新闻)
- 抽取式文摘 extractive summarization
- 简单抽取原文片段拼凑成文本摘要
- 生成式文摘 abstractive summarization
- 用语言生成方式改写原文生成摘要
- related tasks
- 标题生成
- 关键字抽取
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rN7lOD6o-1670488706830)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xin007-kong/picture_new/img/20221208151004.png)]
Machine translation 机器翻译
从一种语言到另一种语言的生成任务
- 句子级别翻译
- 篇章级别翻译 等
- 辅助人工翻译工具
Grammar error correction 句法纠错
-
将带有语病文本自动纠正为正确文本的生成任务,可用于英语学习,文档编辑系统等
-
related tasks
Question answering (QA) 自动问答系统
Knowledge-base QA 基于知识库的问答
- 知识库可以是数据库、知识图谱等
Reading comprehension (machine reading) 基于文本的问答/机器阅读理解
- answer questions in interpretive ways
- 答案来自文章而不是结构化数据,机器先要理解文章,然后从中找出答案
Community QA 社区问答
- 如:Quora、知乎这样用户之间相互提问回答的系统
- 子任务:相关问题的搜索
- 用户提出一个问题,用算法找一找这个社区里有没有相关或相同的问题,然后直接把答案反馈给用户做参考
Open QA 开放问答
-
综合性,不限定答案来源(知识库/网上文本),经常组合知识问答、阅读理解等各种方法
-
老师提到:一个应用场景就是 用户对下一代搜索引擎提出任何问题,引擎可以直接给出答案
最近的chatGpt应该就是吧哈哈哈 ,还可以对chatGpt指定回答的简洁程度
Dialogue systems 对话系统
Chit-chat 闲聊式的对话
- 情感交流,自由聊天
- 注重理解,对话的趣味性,回答的多样性
Task-oriented dialogues 基于任务的对话
- 帮用户解决定机票、订宾馆等问题
- 包含很多子模块:用户意图理解,对话状态追踪和管理,回复生成等子任务,文本生成在其中是起关键作用的模块
![]()
1.2.4 Other Applications
Information retrieval 信息检索
其实不是NLP的子问题 ,除了文字外,视频 图像等 也是 Information retrieval关心的对象,但语言文字是信息重要载体,所以信息检索和NLP有很大的交叉
- Text classification / text clustering 文本分类
- Text topics classification
- “finance”,“sports”,“Tech”…
- Spam detection
- email spam 垃圾邮件检测
- Opinion spam detection
- whether a review contains deceptive(欺骗性的) false opinions
- Language identification
- “French”,"English“
- Rumour detection 谣言检测
- false statement
- Humor detection 幽默检测
- Text topics classification
Recommendation system
也不是NLP的子任务,但是和NLP有密切联系
-
leverage text reviews for recommending(利用文字评论来推荐)
leverage 借助,利用;杠杆
Text mining and text analytics 文本挖掘和文本分析
通过文字进行数据分析从而寻找到重要信息和决策依据
-
derive high-quality information from text
如:
- Clinical decision assistance 辅助诊疗系统
- Stock market prediction 股市预测系统
- Movie revenue prediction 电影票房预测
- Presidential election results prediction 总统选举预测
1.3 NLP from a Machine Learning Perspective 机器学习视角下的自然语言处理
为什么要从机器学习视角出发
The current dominant method
从机器学习的角度来看,NLP任务可以被分为少数类型)
-
NLP目前最主流最有效的是基于ML尤其是DL的方法,对于一个新的自然语言处理任务进行建模的时候,我们需要考虑任务的语言属性、机器学习属性、数据属性。
-
以命名实体识别为例
-
从机器学习角度来看这是一个序列标注的问题。
给定一段文本,我们需要看文本中哪些片段属于命名实体,并给这些片段打上标签。(决定作用)
-
从语言学角度来看,解决命名实体识别往往需要判断命名实体本身的拼写特点以及它上下文的特点,比如一个以大写字母为开头的英文单词,很可能是命名实体的一部分,比如United States
如果上下文是总统出访了某地,无论词的拼写是什么,它是一个地点命名实体的概率都很大,这些是语言学的特点
-
从数据角度看
如果我们有一套人工标注好的训练数据用来进行机器学习的训练,那么这套数据的标注规范(人是怎么标注命名实体的)、被标注的数据量的大小、不同类型的命名实体的分布是怎样的(统计概率是怎样的) 都会影响我们对方法的设计和选择
这三个角度里面,机器学习性质是起到最主要的决定作用的,数据特性也起到很大作用,机器学习性质相比于语言学特性在不同任务之间更通用,学习起来更方便
-
The historical of research
- NLP发展历史脉络来看,整个领域也是随着机器学习技术的进步而不断发展的
- The NLP field has been driven by the development of methods rather than tasks. In fact, a technical advance typically leads to improvements over a range of NLP tasks. Hence we center around methods for the remainder of this book, describing tasks of the same nature together.
从机器学习视角来对NLP task进行划分
Although there is a plethora of NLP tasks in the linguistic or application perspective, NLP tasks
can be categorised into much fewer types when viewed from a machine learning perspective.(尽管从语言学或应用的角度来看,NLP任务非常多,但从机器学习的角度来看,NLP任务的类型要少得多。
NLP tasks are many and dynamically evolving, but fewer according to machine learning nature (NLP任务很多,而且是动态发展的,但根据机器学习的性质来划分,可以归为少数几类)
How can we categorise NLP tasks according to their machine learning nature? There are different perspectives.
可以按照输出划分 According to the output
classification tasks 分类任务
-
Output is a distinct label from a set 输入是文本,输出是类别标签
-
e.g. 情感分类、主题分类、垃圾邮件分类、rumour detection 谣言检测等等
structured prediction tasks 结构预测
-
Outputs are structures with inter-related sub structures
- 输入是文本,输出是具有相互关联子结构的大结构(如一颗句法树)(词性标注,句法分析,关系抽取 ,语义分析, 事件抽取,命名实体识别 and so on)
- 输入是文本序列,输出也是文本序列:序列到序列 (机器翻译,文本摘要,句法纠错,对话回复生成)
-
e.g. POS-tagging and dependency parsing
-
Many NLP tasks are structured prediction tasks, As a result, how to deal with structures is a highly important problem for NLP.
regression problem 回归问题
(在NLP研究的相对较少)
In some cases, the output is neither a class label nor a structure, but a real-valued number.
- Output is a real valued number 输出是实数值而非离散类别
- e.g. predicting stock prices ,automatic essay scoring
可以按照训练数据划分 According to the nature of training data for machine learning
unsupervised learning 无监督学习
- data without human annotation
When the set of training data does not contain gold-standard outputs (i.e., manually labelled POS-tags for POS-tagging and manually labelled syntactic trees for parsing), the task setting is unsupervised learning.
supervised learning 监督学习
- data with human annotated gold-standard output labels
In contrast, when the set of training data consists of gold-standard outputs the task setting is supervised learning.
semi-supervised learning 半监督学习
- both data with labels and data without annotation
In between the two settings, semi-supervised learning uses both data with gold-standard labels and data without annotation.
- Take POS tagging for example. In the supervised learning setting, the training data consist of sentences with each word being annotated with its gold-standard POS. The unsupervised learning POS-tagging task (i.e., POS induction), on the other hand, uses only raw text as training data.
For semi-supervised learning, a relatively small set of data with human labels and a relatively large amount of raw text can be used simultaneously(同时地).
Resources(来自课程PPT)
-
NLP toolkits
- NLTK - leading platform for text processing libraries and corpora https://www.nltk.org
- AllenNLP - NLP research library built on PyTorch https://allennlp.org/
- Stanford’s Core NLP Suite http://nlp.stanford.edu/software/corenlp.shtml
- Huggingface Transformer - pretrained models ready to use https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
-
Word level syntax
- POS tagging online: https://part-of-speech.info
- The Stanford log-linear POS tagger https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/tagger.html
- NLP4j - robust POS tagging using dynamic model selection https://emorynlp.github.io/nlp4j/
- Flair - with a state-of-the-art POS tagging model https://github.com/zalandoresearch/flair/
-
Syntax
- spaCy - industrial-strength NLP in python, for parsing and more https://spacy.io/
- phpSyntaxTree - generate graphical syntax trees http://ironcreek.net/phpsyntaxtree/
- The Stanford Parser https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/lex-parser.html
- Penn Treebank https://www.sketchengine.eu/penn-treebank-tagset/
- CCGBank http://groups.inf.ed.ac.uk/ccg/ccgbank.html
-
Lexical semantics
- WordNet - the de-facto sense inventory for English https://wordnet.princeton.edu/
- Open Mind Word Expert sense-tagged data http://www.cse.unt.edu/~rada/downloads.html#omwe
- CuiTools - a complete word sense disambiguation system http://sourceforge.net/projects/cuitools/
- WDS Gate - a WSD toolkit using GATE and WEKA http://sourceforge.net/projects/wsdgate/
- SEMPRE - a toolkit for training semantic parsers https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/sempre/
-
Semantic roles
- PropBank - the proposition bank https://propbank.github.io/
- Implied Relationships - predicate argument relationships http://u.cs.biu.ac.il/~nlp/resources/
-
Logic
- GEO880 http://www.cs.utexas.edu/users/ml/nldata/geoquery.html
- DeepMind logical entailment dataset https://github.com/deepmind/logical-entailment-dataset
-
AMR
- AMR - abstract meaning representation https://amr.isi.edu/
-
Segrada - semantic graph database https://segrada.org/
-
Text entailment
- The Stanford Natural Language Inference (SNLI) Corpus https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/snli/
- MultiNLI - the multi-genre NLI corpus https://www.nyu.edu/projects/bowman/multinli/
-
Discourse segmentation
- PDTB - Penn Discourse Treebank https://www.seas.upenn.edu/~pdtb/
- Prague Discourse Treebank - annotation of discourse relations https://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/pdit2.0
-
NER
- Stanford Named Entity Recognizer (NER) https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/CRF-NER.html
- OpeNER - open Polarity Enhanced Name ENtity Recognition https://www.opener-project.eu/
- CoNLL 2003 language-indenpendent named entity recognition http://www.cnts.ua.ac.be/conll2003/ner/
- OntoNotes https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2013T19
- MUC-3 and MUC-4 datasets http://www.itl.nist.gov/iaui/894.02/related_projects/muc/
-
Co-reference
- BART coreference system http://www.bart-coref.org/
- CherryPicker - a coreference resolution tool with cluster ranker http://www.hlt.utdallas.edu/~altaf/cherrypicker/
-
Relation extraction
- The NewYorkTimes(NYT) - supervised relationship extraction https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2008T19
- ACE2004 - multilingual training corpus https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2005T09
- SemWval2010 http://semeval2.fbk.eu/
- TACRED - relation extraction dataset built on newswire, web text https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/tacred/
- RewRel - the largest supervised relation classification dataset http://www.zhuhao.me/fewrel/
-
Knowledge graph
- Microsoft Text Analytics https://labs.cognitive.microsoft.com/en-us/project-entity-linking
- Dexter - a open source framework for entity linking http://dexter.isti.cnr.it/
- neleval - for named entity liking and coreference resolution https://pypi.org/project/neleval/
-
Events
- ACE(KBP) automatic content extraction https://cs.nyu.edu/grishman/jet/guide/ACEstructures.html
- TimeBank 1.2 https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2006T08
- TAC KBP 2017 - event tracking https://tac.nist.gov/2017/KBP/data.html
- Story Cloze Test corpora http://cs.rochester.edu/nlp/rocstories/
-
Sentiment
- The Stanford Sentiment Treebank(SST) - movie reviews https://nlp.stanford.edu/sentiment/index.html
- MPQA - news articles manually annotated for opinions http://mpqa.cs.pitt.edu/corpora/
- SemEval17 - consist of 5 subtasks, both Arabic and English http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/S17-2088
- The IMDb dataset - reviews from IMDb with label https://kaggle.com/carolzhangdc/imdb-5000-movie-dataset
- MeaningCloud Https://www.meaningcloud.com
-
Machine translation
- Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation (WMT) http://www.statmt.org/wmt14/translation-task.html
- International Workshop on Spoken Language Translation (IWSLT) http://workshop2015.iwslt.org/
- OpenNMT - open source neural machine translation http://opennmt.net/
- BinQE - a machine translation dataset annotated with binary quality judgements https://ict.fbk.eu/binqe/
- T2T for neural translation https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor
-
Summarization
- The CNN / Daily Mail dataset - training machine reading systems https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.03340
-
Grammar error correction
- CoNLL-2014 Shared Task - benchmark GEC systems https://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~nlp/conll14st/
-
QA
- CoQA - a conversational question answering dataset https://stanfordnlp.github.io/coqa/
- QBLink - sequential open-domain question answering https://sites.google.com/view/qanta/projects/qblink
- DrQA: Open Domain Question Answering https://github.com/facebookresearch/DrQA
- DocQA: Multi-Paragraph Reading Comprehension by AllenAI https://github.com/allenai/document-qa
-
Dialogue system
- MultiWOZ (2018) - for goal-driven dialogue system http://dialogue.mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/index.php/corpus/
- DailyDialog Dataset (2017) http://yanran.li/dailydialog
- DeepPavlov - open-source library for dialogue systems https://deeppavlov.ai/
- KVRET - multi-turn, multi-domain, task-oriented dialogue dataset https://nlp.stanford.edu/blog/a-new-multi-turn-multi-domain-taskoriented-dialogue-dataset/
-
Recommendation system
- Amazon product review http://jmcauley.ucsd.edu/data/amazon/
- Case Recommender - recommender tool https://github.com/caserec/CaseRecommender
- MyMediaLife - recommender system library http://www.mymedialite.net/
- LIBMF - a matrix-factorization library for recommender system https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libmf/
-
Text mining and text analytics
- GATE - general architecture for text engineering https://gate.ac.uk/
- OpenNLP - Apache OpenNLP library https://opennlp.apache.org/
- LingPipe - tool kit for processing text http://alias-i.com
