GNN PyTorch functions
目录
PyTorch fundamental functions
torch.cuda()方法
torch.cuda.empty_caches()
torch file
.pt, .pth, .pkl文件
torch.save()和torch.load()函数
torch.nn
传统建模方法
torch.nn.ModuleList()
torch.nn.Sequential()
torch.nn.Linear()
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d()
torch.nn.dropout()
torch.nn.init()
torch 创建张量tensor
torch.tensor()方法
torch.Tensor()方法
torch.randn()函数
torch.randperm(n)函数
torch.ones(*sizes, out=None)函数
torch.zeros(sizes, out=None)函数
torch 操作operation
加
torch.add(input, value, other, out=None)函数
torch.sum()函数
减
乘
torch.mm()函数和torch.mul()函数
torch.matmul()函数
torch.pow()函数
除
torch.view()函数
torch 统计statistics
torch.size()函数
torch.numel()函数
torch.mean()函数
torch.utils
torch.utils.data.Dataset()函数
torch_scatter package
torch_sparse package
torch_sparse.SparseTensor
torch_geometric package
torch_geometric.nn.GATConv
torch_geometric.data.Data
torch_geometric.loader.NeighborSample
torch_geometric.loader.RandomNodeSampler包
torch_geometric报错(一): "找不到指定的模块"
PyTorch fundamental functions
- torch.cpu()方法,将变量放在cpu上,仍为tensor
- torch.detach()方法,阻断反向传播,返回值仍为tensor。
- torch.numpy()方法,将tensor转换为numpy。注意,cuda上面的变量类型只能是tensor,不能是其他。
torch.nonzero()方法
torch.nonzero()方法,返回非零元素的索引。
torch.tensor([0,1,2,0]).nonzero()
tensor([[1],
[2]])
- torch.norm(a, p=2, dim=1), 求a在dim维度上的p范数(长度)
- with torch.no_grad(),在该模块下,所有计算得出的tensor的requires_grad都自动设置为True。即使一个tensor(命令为x)的requires_grad=True,在with torch.no_grad下,由x计算得到的requires_grad也为False。
- torch.requires_grad参数
- if设置为True,则反向传播,该tensor就会自动求导,它所有依赖的节点requires_grad都为True。
- 默认为False,反向传播时就不会自动求导了,节约了显卡内存。
- torch.state_dict()方法,pytorch一种模型保存和加载的方式state_dict(),返回一个OrderDict,存储了网络结构名字和对应的参数。
torch.where()函数
返回符合条件元素的索引index,以元素tuple形式给出,参考np.where(condition)。
a = torch.tensor([2,4,6,8,10])
torch.where(a > 5) # 得到元组tuple返回的index结果
'''
(array([2, 3, 4], dtype=int64),)
'''
# 如果得到index数组,需要加索引提取
torch.where(a > 5)[0]
'''
array([2, 3, 4], dtype=int64)
'''torch.cuda()方法
pytorch深度学习框架在训练时,大多是利用GPU来提高训练速度,torch通过cuda()方法使用GPU。
cuda()方法将数据和模型送入GPU中。
model = MyNet() # 自己定义的网络类
model.cuda()
img = img.cuda()torch.cuda.empty_caches()
释放显存
torch file
.pt, .pth, .pkl文件
torch有后缀名为.pt, .pth, .pkl等后缀名的文件,但它们职级上没有什么不同,只是后缀名不同而已,根据个人喜好,用不同的后缀名。
torch.save()和torch.load()函数
torch.save()函数一般用于保存文件/模型,torch.load()函数一般用于加载文件/模型。
注意:torch.save()保存的是模型参数,而不是模型本身!
# 保存model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), mymodel.pth) # 只是保存模型权重参数,不保存模型结构
# 加载模型
model = My_model(*args, **kwargs) # 这里需要重新定义模型结构,mymodel
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(mymodel.pth)) # 这里根据模型结构,调用存储的模型参数
model.eval()
保存整个model的状态
# 保存model
torch.save(model, mymodel.pth) # 保存整个model的状态
# 加载model
model = torch.load(mymodel.pth) # 这里已经不需要重构模型结构了,直接load就可以
model.eval()torch.nn
传统建模方法
class model1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model1,self).__init__()
self.linear1=nn.Linear(1,10)
self.activation1=nn.ReLU()
self.linear2=nn.Linear(10,100)
self.activation2=nn.ReLU()
self.linear3=nn.Linear(100,10)
self.activation3=nn.ReLU()
self.linear4=nn.Linear(10,1)
def forward(self,x):
out=self.linear1(x)
out=self.activation1(out)
out=self.linear2(out)
out=self.activation2(out)
out=self.linear3(out)
out=self.activation3(out)
out=self.linear4(out)
return out
torch.nn.ModuleList()
nn.ModuleList()是一个无序性的序列,并没有实现forward()方法
nn.ModuleList()方法:
- ModuleList可以存储多个model,传统的方法一个model就要写一个forward,但如果将它们存到一个ModuleList的话,就可以使用一个forward。
- ModuleList是Module的子类,当Module使用它的时候,就能自动识别为子module,所以nn.ModuleList内部的nn.Module参数也被添加到我们网络的parameter中
- ModuleList使用网络结构具有灵活性。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class testNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(testNet, self).__init__()
self.combine = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(100,50),
nn.Linear(50,25),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.combine(x)
return x
testnet = testNet()
input_x = torch.ones(100)
output_x = testnet(input_x)
print(output_x)torch.nn.Sequential()
nn.Sequential()定义的网络中各层会按照定义的顺序进行级联,需要保证各层的输入和输出之间要衔接,并且nn.Sequential实现了forward方法。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class testNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(testNet, self).__init__()
self.combine = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(100,50),
nn.Linear(50,25),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.combine(x)
return x
testnet = testNet()
input_x = torch.ones(100)
output_x = testnet(input_x)
print(output_x)torch.nn.Linear()
nn.Linear()用于设置网络中全连接层的
相当于一个[batch_size, in_features]的输入tensor变换成了一个[batch_size, out_features]的输出tensor。
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d()
将num_features那一维进行归一化,防止梯度散射。
torch.nn.dropout()
以概率p对input tensor的值随机置0。
Hinton提出用于在training时防止过拟合的trick
torch.nn.functional.dropout(input, p=0.5, training=True, inplace=False)torch.nn.init()
权值初始化方法
- xavier_uniform()_,均匀分布
- xavier_normal_(),正态分布
torch 创建张量tensor
torch.tensor()方法
torch.tensor()创建张量。
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
t = torch.tensor(arr)
# 或直接创建一个空tensor
t = torch.tensor()torch.Tensor()方法
torch.Tensor是一种包含单一数据类型元素的多维矩阵。
定义了7种cpu tensor类型和8种GPU tensor类型:torch.Tensor默认的是(torch.FloatTensor)
- cpu tensor类型:torch.FloatTensor, torch.DoubleTensor, torch.ByteTensor, torch.CharTensor, torch.ShortTensor, torch.IntTensor, torch.LongTensor
- GPU tensor类型:torch.cuda.FloatTensor, torch.cuda.DoubleTensor, torch.cuda.ByteTensor, torch.cuda.CharTensor, torch.cuda.ShortTensor, torch.cuda.IntTensor, torch.cuda.LongTensor
import torch
x = torch.Tensor(2, 3) # 生成一个2*3的Tensor张量
# 将Tensor转换为numpy数组
y = x.numpy()
# 将numpy数组转换为Tensor
z = torch.from_numpy(y)torch.randn()函数
torch.randn()函数,产生大小为指定的,正态分布的采样点,数据类型是tensor
a=torch.randn(3) #生成一个一维的矩阵
b=torch.randn(1,3) #生成一个二维的矩阵
print(a)
print(b)
torch.mean(a)torch.randperm(n)函数
torch.randperm(n)函数返回一个随机打散的0~n-1 tensor数组
torch.randperm(4)
-----------------------------
tensor([3, 1, 2, 0])
torch.Tensortorch.ones(*sizes, out=None)函数
torch.ones()函数返回一个全为1的张量tensor,形状由可变参数sizes定义。
torch.ones(2, 3)
1 1 1
1 1 1torch.zeros(sizes, out=None)函数
torch.zeros()函数,返回一个全为标量0的张量,形状由可变参数sizes定义。
torch.zeros(2, 3)
0 0 0
0 0 0torch 操作operation
- torch.repeat(),表示沿着指定的维度重复tensor的次数
- torch.cat(), 表示按行0或按列1拼接tensor
- torch.t(),表示对二维矩阵进行转置
- torch.squeeze()方法,对数据的维度进行压缩,删掉所有为1的维度
- torch.unsqueeze()方法,对数据维度进行扩充,给指定位置加上维数为1的维度。
加
torch.add(input, value, other, out=None)函数
torch.add()函数对other张量的每一个元素乘以一个标量值value,并加到输入张量input上,并返回结果到一个新的张量out,即out = input + (other * value)。
torch.sum()函数
torch.sum()函数对输入tensor的某一维求和
a = torch.ones((2,3))
torch.sum(a, dim=0) # 对行求和
torch.sum(a, dim=1) # 对列求和减
乘
torch.mm()函数和torch.mul()函数
- torch.mul(a, b)函数,是矩阵a和b对应位相乘,比如a的维度是(1,2),b的维度是(1,2),返回的仍是(1,2)的矩阵。
- torch.mm(a, b)函数,是矩阵a和b矩阵相乘。
torch.matmul()函数
torch.matmul()函数几乎用于所有矩阵/向量相乘的情况,其乘法规则由参与乘法的两个张量的维度而定,包括: 1d * 1d, 2d * 2d, 1d * 2d, 2d * 1d, 3d and above.
- 如果两个张量都是一维的,即torch.Size([n]),此时返回两个向量的点积,作用于torch.dot()相同,同样要求两个一维向量的元素个数相同。
>>> vec1 = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> vec2 = torch.tensor([2, 3, 4])
>>> torch.matmul(vec1, vec2)
tensor(20)
>>> torch.dot(vec1, vec2)
tensor(20)
# 两个一维张量的元素个数要相同!
>>> vec1 = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> vec2 = torch.tensor([2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> torch.matmul(vec1, vec2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
RuntimeError: inconsistent tensor size, expected tensor [3] and src [4] to have the same number of elements, but got 3 and 4 elements respectively
- 如果两个参数都是二维张量,那么将返回矩阵乘积,作用与torch.mm()相同,同样要求两个张量的形状要满足矩阵乘法的条件,即(nxm) * (mxp) = (nxp)
>>> arg1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> arg1
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
>>> arg2 = torch.tensor([[-1], [2]])
>>> arg2
tensor([[-1],
[ 2]])
>>> torch.matmul(arg1, arg2)
tensor([[3],
[5]])
>>> torch.mm(arg1, arg2)
tensor([[3],
[5]])
>>> arg2 = torch.tensor([[-1], [2], [1]])
>>> torch.matmul(arg1, arg2) # 要求满足矩阵乘法的条件
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
RuntimeError: mat1 and mat2 shapes cannot be multiplied (2x2 and 3x1)
- 如果第一个参数是一维向量,第二个参数是二维张量,那么在一维向量的前面增加一个维度,然后进行矩阵乘法,矩阵乘法结束后移除添加的维度。
>>> arg1 = torch.tensor([-1, 2])
>>> arg2 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> torch.matmul(arg1, arg2)
tensor([5, 6])
>>> arg1 = torch.unsqueeze(arg1, 0) # 在一维张量前增加一个维度
>>> arg1.shape
torch.Size([1, 2])
>>> ans = torch.mm(arg1, arg2) # 进行矩阵乘法
>>> ans
tensor([[5, 6]])
>>> ans = torch.squeeze(ans, 0) # 移除增加的维度
>>> ans
tensor([5, 6])
- 如果第一个参数是二维张量,第二个参数是一维向量,那么将返回矩阵乘向量的积,作用与torch.mv()相同。
torch.pow()函数
torch.pow()函数,对输入的每个分量求幂次运算。
除
torch.view()函数
torch.view(a, b)函数的作用是重构张量的维度为a行b列,相当于numpy中的resize()功能。
- 参数为-1的意思是任意。
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.],
[5., 6.]])
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])
torch.sort()函数
torch.sort(input, dim=- 1, descending=False, stable=False, *, out=None)
- input (Tensor) – the input tensor
形式上与 numpy.narray 类似- dim (int, optional) – the dimension to sort along
维度,对于二维数据:dim=0 按列排序,dim=1 按行排序,默认 dim=1- descending (bool, optional) – controls the sorting order (ascending or descending)
降序,descending=True 从大到小排序,descending=False 从小到大排序,默认 descending=FlaseA tuple of (sorted_tensor, sorted_indices) is returned, where the sorted_indices are the indices of the elements in the original inputtensor.
import torch
x = torch.randn(3,4)
x #初始值,始终不变
tensor([[-0.9950, -0.6175, -0.1253, 1.3536],
[ 0.1208, -0.4237, -1.1313, 0.9022],
[-1.1995, -0.0699, -0.4396, 0.8043]])
sorted, indices = torch.sort(x) #按行从小到大排序
sorted
tensor([[-0.9950, -0.6175, -0.1253, 1.3536],
[-1.1313, -0.4237, 0.1208, 0.9022],
[-1.1995, -0.4396, -0.0699, 0.8043]])
indices
tensor([[0, 1, 2, 3],
[2, 1, 0, 3],
[0, 2, 1, 3]])torch 统计statistics
torch.size()函数
torch.size()函数,查看张量的维度信息
- torch.size(0)方法,表示第0维度的数据量
torch.numel()函数
torch.numel()函数,查看一个张量有多少个元素,返回int类型的元素个数。
torch.mean()函数
torch.mean()函数输入各个向量的均值。
torch.utils
torch.utils.data.Dataset()函数
代表自定义数据集方法的类。用户可以通过继承该类来自定义自己的数据集类,在继承时要求用户重载__len__()和__getitem__()这两个魔法方法。
- __len__(): 返回的是数据集大小
- __getitem__(): 实现索引数据集中的某一个数据
torch_scatter package
from torch_scatter import torch_sparse package
torch_sparse.SparseTensor
torch_geometric package
torch_geometric.nn.GATConv
PyG实现GAT,使用封装好的GATConv函数。
- model.train()和model.eval()分别定义模型的训练模型和测试模式,主要对Dropout层和BatchNorm产生影响。
- Dropout: 训练过程中,为防止模型过拟合,增加其泛化性,会随机屏蔽掉一些神经元,相当于每次经过不同的神经元,最终得到不同的模型。测试模式时,所有神经元共同作用,类似于boosting。
- BatchNorm: 训练过程中,模型每处理一次minibatch数据,BN层根据一个minibatch来计算mean和std后做归一化处理。测试时,BN层会利用训练时得到的参数来处理测试数据。如果不设置model.eval(),输入单个数据,模型会报错。
from torch_geometric.nn import GATConv # torch_geometirc继承了GAT模型。
# 导入需要的包,遇到安装问题可在官方文档或其他文章查找解决方案
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 导入GCN层、GraphSAGE层和GAT层
from torch_geometric.nn import GCNConv, SAGEConv, GATConv
from torch_geometric.datasets import Planetoid
# 加载数据,出错可自行下载,解决方案见下文
dataset = Planetoid(root='./tmp/Cora', name='Cora')
class GAT_NET(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, hidden, classes, heads=4):
super(GAT_NET, self).__init__()
self.gat1 = GATConv(features, hidden, heads=4) # 定义GAT层,使用多头注意力机制
self.gat2 = GATConv(hidden*heads, classes) # 因为多头注意力是将向量拼接,所以维度乘以头数。
def forward(self, data):
x, edge_index = data.x, data.edge_index
x = self.gat1(x, edge_index)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.gat2(x, edge_index)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = GAT_NET(dataset.num_node_features, 16, dataset.num_classes, heads=4).to(device) # 定义GAT
data = dataset[0].to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=5e-4)
model.train()
for epoch in range(200):
optimizer.zero_grad()
out = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(out[data.train_mask], data.y[data.train_mask])
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.eval()
_, pred = model(data).max(dim=1)
correct = int(pred[data.test_mask].eq(data.y[data.test_mask]).sum().item())
acc = correct / int(data.test_mask.sum())
print('GAT Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(acc))torch_geometric.data.Data
torch_geometric提供了一种使用多属性表示图的数据类型Data
- x,tensor类型,形状[num_nodes, num_node_features]
- edge_index,coo格式的图的边关系,形状为[2, num_edges]
- pos: 存储节点的坐标,形状是[num_nodes, num_dimensions]
- y: 存储样本标签。如果是每个节点都有标签,那么形状是[num_nodes, *]; 如果是整张图只有一个标签,那么形状是[1, *]。
- edge_attr: 存储边的特征。形状是[num_edges, num_edge_features]。
import torch
from torch_geometric.data import Data
# 由于是无向图,因此有 4 条边:(0 -> 1), (1 -> 0), (1 -> 2), (2 -> 1)
edge_index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2, 1]], dtype=torch.long)
# 节点的特征
x = torch.tensor([[-1], [0], [1]], dtype=torch.float)
data = Data(x=x, edge_index=edge_index)torch_geometric.loader.NeighborSampler
from torch_geometric.loader import NeighborSampler, RandomNodeSamplerA data loader that performs neighbor sampling as introduced in the "Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs" paper. 它允许对GNNs mini-batch training进行neighbor采样,并训练模型,使得大规模全连接的GNNs模型训练成为可能。
核心想法:给定mini-batch的节点和图卷积的层数L,以及每一层需要采样的邻居数目sizes,依次从每一层到第L层,对每一层进行邻居采样并返回一个bipartite(双方)子图。
- sizes是一个L长度的list,包含每一层需要采样的邻居个数。
For i in L:
- 第1层使用初始minibatch的节点进行邻居采样,返回采样结果。
- 第i (i>0)层,使用上层采样中涉及到的所有节点进行邻居采样,返回采样结果。
L层采样完成后,返回结果(batch_size, n_id, adjs),
- 其中batch_size就是mini-batch的节点数目,
- n_id是包含所有在L层卷积中遇到的节点的list,且target节点在n_id前几位。
- adjs是一个list,包含了从第L层到第1层采样的结果,所以adjs中的子图是从大到小的。每一层采样返回的结果具体形式为 (edge_index, e_id, size)。
- edge_index是采样得到的bipartite子图中source节点到target节点的边。
- e_id是edge_index的边在原始大图中的IDs,
- size就是bipartite子图的shape。
以下是一个2层采样的示意图,注意在第2层采样的时候,使用了第1层中涉及到的所有节点,包括出发点。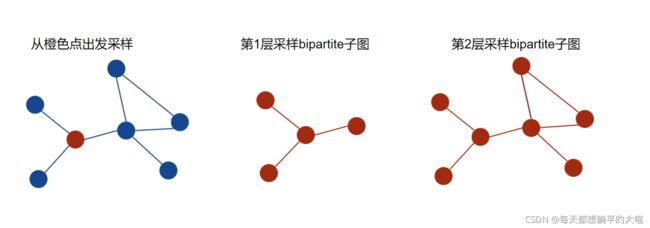
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「每天都想躺平的大喵」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39925939/article/details/121458145
torch_geometric.loader.RandomNodeSampler包
实现一个数据集的随机划分,使用num_parts确定划分数量
torch_geometric报错(一): "找不到指定的模块"
problem: 兼容性错误
solution: 重装package
pip install torch-scatter==2.0.9 -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-1.10.0+cpu.html
torch error
TypeError: cannot unpack non-iterable NoneType object(类型错误:无法解包非迭代的NoneType对象)
原因: 将单个None赋给了多个值。