【MOSMA】基于粘菌算法求解多目标优化问题附matlab代码
✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击
智能优化算法 神经网络预测 雷达通信 无线传感器
信号处理 图像处理 路径规划 元胞自动机 无人机 电力系统
⛄ 内容介绍
本文提出了一种多目标粘菌算法 (MOSMA),这是最近开发的粘菌算法 (SMA) 的多目标变体,用于处理工业中的多目标优化问题。最近,为了处理优化问题,优化社区提出了几种元启发式和进化优化技术。在评估多目标优化 (MOO) 问题时,这些方法往往会遇到低质量的解决方案,而不是解决识别帕累托最优解的准确估计和增加所有目标的分布的目标函数。SMA 方法遵循在实验室实验中从粘菌的振荡行为中获得的逻辑。与其他成熟的方法相比,SMA 算法显示出强大的性能,它是通过使用正负反馈系统结合最佳食物路径来设计的。所提出的 MOSMA 算法采用相同的底层 SMA 收敛机制,结合精英非支配排序方法来估计帕累托最优解。作为后验方法,MOSMA 中保留了多目标公式,并利用拥挤距离算子来确保增加所有目标的最佳解决方案的覆盖范围。为了验证和验证 MOSMA 的性能,考虑了 41 个不同的案例研究,包括无约束、约束和现实世界的工程设计问题。将 MOSMA 的性能与多目标共生生物搜索 (MOSOS) 进行比较,基于分解的多目标进化算法(MOEA / D)和多目标水循环算法(MOWCA)在不同性能指标方面,例如世代距离(GD),反向世代距离(IGD),最大传播(MS) 、间距和运行时间。仿真结果证明了所提出的算法在实现所有多目标问题的高质量解决方案方面的优越性,包括线性、非线性、连续和离散 Pareto 最优前沿。结果表明所提出的算法在解决复杂的多目标问题中是有效的。最大传播 (MS)、间距和运行时间。仿真结果证明了所提出的算法在实现所有多目标问题的高质量解决方案方面的优越性,包括线性、非线性、连续和离散 Pareto 最优前沿。结果表明所提出的算法在解决复杂的多目标问题中是有效的。最大传播 (MS)、间距和运行时间。仿真结果证明了所提出的算法在实现所有多目标问题的高质量解决方案方面的优越性,包括线性、非线性、连续和离散 Pareto 最优前沿。结果表明所提出的算法在解决复杂的多目标问题中是有效的。
⛄ 部分代码
%% Multiple Objective Slime Mould Algorithm (MOSMA)
% M. Premkumar, P. Jangir, R. Sowmya, H. H. Alhelou, A. A. Heidari and H. Chen,
% "MOSMA: Multi-objective Slime Mould Algorithm Based on Elitist Non-dominated Sorting,"
% in IEEE Access, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047936.
%% Objective Function
% The objective function description contains information about the
% objective function. M is the dimension of the objective space, D is the
% dimension of decision variable space, LB and UB are the
% range for the variables in the decision variable space. User has to
% define the objective functions using the decision variables. Make sure to
% edit the function 'evaluate_objective' to suit your needs.
clc
clear all
close all
D = 30; % Number of decision variables
M = 2; % Number of objective functions
K=M+D;
LB = ones(1, D).*0; % LB - A vector of decimal values which indicate the minimum value for each decision variable.
UB = ones(1, D).*1; % UB - Vector of maximum possible values for decision variables.
GEN = 200; % Set the maximum number of generation (GEN)
ecosize = 200; % Set the population size (NP)
ishow = 10;
%% Start the evolution process
Pareto = MOSMA(D,M,LB,UB,ecosize,GEN,ishow);
Obtained_Pareto= Pareto(:,D+1:D+M); % extract data to plot
Obtained_Pareto=sortrows(Obtained_Pareto,2);
True_Pareto=load('ZDT3.txt');
%% Plot data
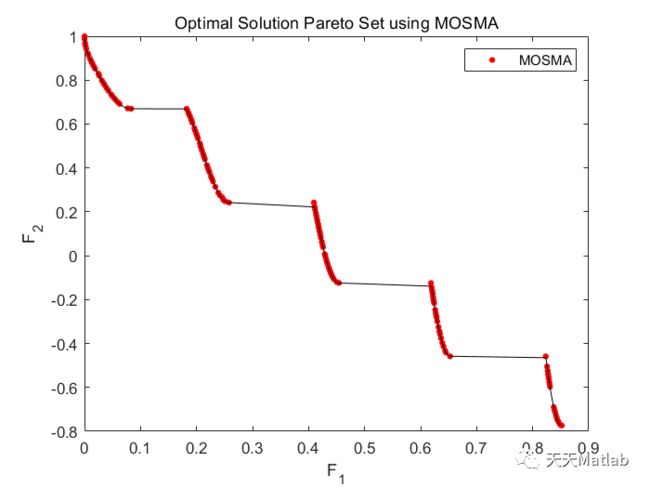
if M == 2
plot(Obtained_Pareto(:,1),Obtained_Pareto(:,2),'o','LineWidth',2,...
'MarkerEdgeColor','r','MarkerSize',2);
hold on
plot(True_Pareto(:,1),True_Pareto(:,2),'k');
title('Optimal Solution Pareto Set using MOSMA');
legend('MOSMA');
xlabel('F_1');
ylabel('F_2');
elseif M == 3
plot3(Obtained_Pareto(:,1),Obtained_Pareto(:,2),Obtained_Pareto(:,3),'o','LineWidth',2,...
'MarkerEdgeColor','r','MarkerSize',2);
hold on
plot3(Obtained_Pareto(:,1),Obtained_Pareto(:,2),Obtained_Pareto(:,3),'.','LineWidth',2,...
'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerSize',6);
title('Optimal Solution Pareto Set using MOSMA');
legend('MOSMA');
xlabel('F_1');
ylabel('F_2');
zlabel('F_3');
end
%% Metric Value
M_IGD=IGD(Obtained_Pareto,True_Pareto);
M_GD=GD(Obtained_Pareto,True_Pareto);
M_HV=HV(Obtained_Pareto,True_Pareto);
M_Spacing=Spacing(Obtained_Pareto,True_Pareto);
M_Spread=Spread(Obtained_Pareto,True_Pareto);
M_DeltaP=DeltaP(Obtained_Pareto,True_Pareto);
display(['The IGD Metric obtained by MOSMA is : ', num2str(M_IGD)]);
display(['The GD Metric obtained by MOSMA is : ', num2str(M_GD)]);
display(['The HV Metric obtained by MOSMA is : ', num2str(M_HV)]);
display(['The Spacing Metric obtained by MOSMA is : ', num2str(M_Spacing)]);
display(['The Spread Metric obtained by MOSMA is : ', num2str(M_Spread)]);
display(['The DeltaP Metric obtained by MOSMA is : ', num2str(M_DeltaP)]);
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
M. Premkumar, Pradeep Jangir, R. Sowmya, Hassan Haes Alhelou, Ali Asghar Heidari, and Huiling Chen, "MOSMA: Multi-Objective Slime Mould Algorithm Based on Elitist Non-Dominated Sorting," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 3229-3248, 2021.
⛄ Matlab代码关注
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料