Mysql基本知识、语法及操作
一、数据库的概念
1、数据库的英文单词:DataBase 简称 :DB
2、什么是数据库
----用于存储和管理数据的仓库
3、数据库的特点:
—持久化存储数据的(相当于一个文件系统)
—方便存储和管理数据
—使用了同一方式操作数据库(SQL)
二、SQL基本概念与通用语法
1、什么是SQL?
strucred Query Langage :结构化查询语言
其实就是定义了操作所有关系数据库的规则
2、SQL通用语法
—SQL语句可以单行或多行书写,以逗号结尾
—可以使用空格和缩进来增强语句的可读性
—MySql不区分大小写 建议用大写
—3种注释 – 、#、 /* */
三、SQL的CRUD操作
1、SQL分类
(1)DDL(Data Definition Language)数据库定义语言
用来定义数据库对象:数据库、表、列等。关键字:create 、drop、 alter等
(2)DML(Data Manipulation Language)数据库操作语言
用来对数据库表中的数据进行增删改。关键字:insert、delete、update等
(3)DQL(Data Query Language)数据库查询语言
用来查询数据库表中的记录(数据)。关键字:select、where等
(4)DCL(Data Control Language)数据库控制语言
用来定义数据库的访问权限和安全级别,及创建用户。关键字,grant、revoke等
DDL:操作数据库(CRUD)、表
操作数据库(CRUD)
1、C(create) :创建
创建数据库
create database 数据库名称;
创建数据库判断存不存在
create database if not exists 数据库名称;
创建数据库 并指定字符集
create database 数据库名称 character set 字符编码;
2、R(Retrieve) :查询
查询所有数据库名称
show databases;mysql自带四个数据
库information_schem、mysql、perform_schem、test
查询某个数据库的字符集:查询某个数据库的创建语句
show create database 数据库名称;
3、U(update):修改
修改数据库的字符集
alter 数据库名称 character set 字符编码;
4、D(delete):删除
删除数据库
drop database 数据库名称;
判断数据库存在 存在删除
drop database if exists 数据库名称;
5、使用数据库
查询当前正在使用的数据库名称
select database
使用数据库
use 数据库名称;
操作表
1、C(create) :创建
语法:
create table 表名(
列名1 数据类型1,
列名2 数据类型2
);
(注意最后一列不要加逗号)
数据类型:
int :整数类型
age int
double:小数类型
score double(5,2)
date: 日期,只包含年月日 yyyy-MM-dd
datetime: 日期 年月日时分秒 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
timestamp :时间戳 包含年月日 时分秒 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
如果不给这个字段儿赋值,会自动的获取系统时间添加
varchar :字符串类型
name varchar(20) :姓名最对大20个字符
blob、clob、二进制
2、R(Retrieve) :查询
查询某个数据库中所有的表名称
show tables;
查询表结构
desc 表名;
3、U(update):修改
修改表名:
alter table 表名 rename to 新的表名;
修改表的字符集:
alter table 表名 character set 字符集名称;
添加一列
alter table 表名 add 列名 数据类型;
修改列的名称、类型
alter table 表名 change 列名 新列名 新数据类型;
alter table 表名 modify sex varchar(10);
删除列
alter table 表名 drop 列名;
4、D(delete):删除
删除表:
drop table 表名;
drop table if exists 表名;
复制表:
create table 表名 like 被复制的表名;
DML:增删改表中的数据
1、添加数据:
insert into 表名(列名1,列名2,.....n) values(值1,值2,....n) ;
注意 :列名和值要一一对应
2、删除数据
delete from 表名 【where条件】;
3、修改数据:
update 表名 set 列名1 = 值1, 列名2 =值2,.... 【where条件】;
DQL:查询表中的记录
1、语法:
select
字段列表
from
表名列表
where
条件列表
group by
分组字段
having
分组之后的条件
order by
排序
limit
分页限定
2、基础查询
多个字段儿的查询
select 字段名1,字段名2,.....from 表名;
-- 查询 姓名和年龄
select name,age from student;
去除重复
distinct
select (distinct) address from student;
计算列
一般使用四则运算计算一些列的值。
ifnull(表达式1,表达式2);
表达式1 :哪个字段儿需要判断是否为null
如果该字段儿为null后替换值
起别名
as : as 也可以省略
3、条件查询
where子句后跟条件
运算符
>、< 、<= 、 >= 、<>
between .. and
in(集合)
like:(模糊查询)
占位符:
_ :单个ziuf
% :多个字符
is null
and 或 &&
or 或 ||
not 或 !|
-- 查询年龄大于20岁
select * from student where age > 20;
select * from student where age >= 20;
-- 查询年龄等于20岁
select * from student where age = 20;
-- 查询年龄不等于20岁
select * from student where age != 20;
select * from student where age <> 20;
-- 查询年龄大于等于20 小于等于30
select * from student where age >= 20 && age <= 30;
select * from student where age between 20 and age <= 30;
select * from student where age between 20 and 30;
-- 查询年龄22岁,19岁,25岁信息
select * from student where age = 22 or age = 19 or age = 25;
select * from student where age in(22,19,25);
-- 查询英语成绩为null
select * from student where english is null;
-- 查询英语成绩不为null
select * from student where english is not null;
-- 查询姓马的同学
select * from student where name like '马%';
-- 查询第二个字是化的人
select * from student where name like "_化%";
DQL查询语句
1、排序查询
语法:order by 子句,
order by 排序字段1,排序字段2,.....
排序方式:
ASC :升序,默认的
DESC:降序
注意:
如果有多个排序条件则当前值一样时才会去用第二排序字段
--按照数学成绩降序排名
select * from student order by math DESC;
--按照数学成绩排名,如果数学成绩一样,则按照英语成绩排序
select * from order by math DESC , english DESC;
2、聚合函数:将一类数据作为一个整体,进行纵向计算
count :计算个数
一般选择非空列主键
select count(name) from student;
select count(ifnull(math,0)) from student;
max :计算最大值
select max(math) from student;
min : 计算最小值
select min (math) from student;
sum : 计算和
select sum(math) from student;
avg : 计算平均值
select avg (math) from student;
注意 : 聚合函数的计算排除了null值
解决方案:
选择不包含非空的列计算
ifnull函数
3、分组查询:
语法:group by 分组字段;
注意:
分组之后查询的字段:分组字段、聚合函数
where 和 having的区别?
where在分组之前进行限定,如果不满足条件,则不参与分组。having在分组之后进行限定,如果不满足则不参与分组
where之后不可以跟聚合函数,having可以跟聚合函数
-- 按照性别分组,分别查询男、女同学的平均分
select sex,avg(math) from student group by sex;
-- 按照性别分组,分别查询男、女同学的平均分,人数
select sex,avg(math),count(id) from student group by sex;
-- 按照性别分组,分别查询男、女同学的平均分,人数要求分数低于70分的人不参与分组
select sex,avg(math),count(id) from student where math > 70 group by sex;
-- 按照性别分组,分别查询男、女同学的平均分,人数要求分数低于70分的人不参与分组,分组之后人数要大于两个
select sex,avg(math),count(id) as 人数 from student where math > 70 group by sex having 人数 > 2;
4、分页查询 :
语法:limit 开始索引,每页查询条数
公式 开始索引 = (当前的索引 -1 ) * 每页显示的条数;
-- 每页显示三条数据
select * from student limit 0,3; 第一页
select * from student limit 3,3; 第二页
四、表的约束
1、概念:
对表中的数据进行限定,保证数据的正确性、有效性和完整性
2、分类
(主键约束):primary key
主键约束:primary key
--删除主键
alter table stu modify id int ;(错误写法)
alter table stu drop primary key;
--创建完表后添加主键
alter table stu modify id int primary key;
1、注意:
含义:非空且唯一
一张表只能有一个字段为主键
主键就是表中记录的唯一标识
2、在创建表时,添加主键约束
create table stu(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20)
);
3、自动增长:
如果某一类是数值类型的,使用auto_increment 可以完成值的自动增长
(非空约束):not null 值不能为空
非空约束:not null 值不能为空
1、创建表时添加非空约束
create table stu(
id int,
name varchar(20) not null;
);
2、创建完表后,添加非空约束
alter table stu modify name varchar(20) not null;
(唯一约束):unique
唯一约束:unique值不能重复
---注意mysql中,唯一约束限定的列的值可以
有多个null
---删除唯一索引
alter table stu modify phone_number;
1、创建表时添加非空约束
create table stu(
id int,
phone_number varchar(20) unique;
);
2、创建完表后,添加非空约束
alter table stu modify phone_number varchar(20) unique;
(外键约束):foreign key
外键约束:foreign key
1、在创建表时,可以添加外键
语法:
create table 表名(
....
外键列
constraint 外键名称 foreign key 外键的列的名称 reference 主表名称(主表列mingc
);
2、删除外键
alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称;
3、创建表之后,添加外键
alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key(外键名称字段) reference 主表名称(主表列名称);
4、级联操作
添加级联操作
语法:alter table 表名 add constriant 外键名称 foreign key(外键名称) reference 主表一名称(主表名称列) on update cascade on delete cascade;
分类
级联更新: on update caseade
级联删除: on delete caseade
五 、多表操作
1、多表之间的关系
1、一对一:
如: 人和身份证
分析一个人只有一个省份证,一个身份证只能对应一个人
2、一对多(多对一):
如:部门和员工
分析:一个部门有多个员工,一个员工只能对应一个部门
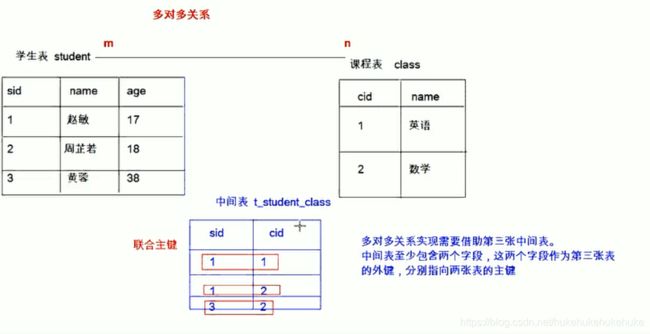
3、多对多
如:学生和课程
分析:一个学生可以选多门课程,一门课程也可以被很多学生选择
六、三大范式
1、第一范式(1NF):每一列都是不可分割的原子数据项(原子性)
2、第二范式(2NF): 在1NF的基础上,非码属性必须完全依赖候选码(在1NF基础上消除非主属性对主码的部分函数依赖)
函数依赖:A–>B,如果通过A属性的值可以唯一确定B的值,称B依赖A
完全函数依赖:A–>B,如果A是一个属性组,则B属性组的确定需要依赖于A属性组中所有的属性值
部分函数依赖:A–>B
3、第三范式(3NF):在2NF基础上消除传递依赖
七、数据库的备份和还原
1、命令行:
备份:mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 > 保存路径
还原:登录数据库、创建数据库、使用数据库、执行文件(source 文件路径)
八、多表查询和子查询
**1、笛卡尔积 **
有两个集合A,B,取这两个集合的所有组成情况。
要完成多表查询,需要消除无用的数据
2、多表查询分类
1、内连接查询:
隐式内连接:使用where条件消除无用的数据
--查询所有员工信息和对应的部门信息
select * from emp,dept where emp.id = dept.id:
--查询员工表的名称,性别,部门表的名称
select emp.name,emp.gender,dept.name from emp,dept where emp.id = dept.id;
select
t1.name,t1.gender,t2.name
from
emp t1,dept t2
where
t1.id = t2.id;
显示内连接:
语法:select 字段列表 from 表名1 inner join 表名 表名2 on 条件
内连接查询注意:
从哪些表中查询数据、条件是什么、查询哪些字段
2、外连接查询
左外连接:
语法:select 字段列表 from 表1 left outer jion 表2 on 条件;
查询的左表所有数据以及其交集部分
--查询所有员工信息,如果员工有部门,则查询部门名称,没有部门则不显示部门名称。
select
t1.*,t2.name
from
emp t1,dept t2
where
t1.id = t2.id;
select t1.*,t2.name from emp t1,innner join dept t2 on t1.id - t2.id;
右外连接:
语法:select 字段列表 from 表1 right outer jion 表2 on 条件;
查询的右表所有数据以及其交集部分
3、子查询
概念: 查询中嵌套查询,称嵌套的查询叫子查询
--查询工资最高的员工的信息
(1)查询最高工资
select max(salary) from emp;
(2)查询员工信息,并且工资等于9000的
select * from emp where slary = 9000;
一条语句完成这个操作
select * from emp where slary =(select max(salary) from emp);
4、子查询的不同情况
子查询的结果是单行单列的
子查询可以作为条件,使用运算符去判断
--查询员工工资小于平均工资的人
select - from emp where emp.salry < (select avg(salary) from emp);
子查询的结果是多行多列的
子查询可以作为条件,使用in运算符来判断
--查询财务部的所有员工信息
select id from dept where name =‘财务部’ or name ='市场部';
select * from where emp where dept_id = 3 or dept_id = 2;
select * from where emp where dept_id in(3 ,2);
合并
select * from where emp where dept_id in(select id from dept where name =‘财务部’ or name ='市场部');
子查询的结果是多行多列的
子查询可以作为一张虚拟表。
--查询员工入职日期是2011-11-09日之后的员工信息和部门信息
--子查询
select * from emp where emp.date > '2011-11-09';(做虚拟表)
select * from dept t1,(select * from emp where emp.date > '2011-11-09') t2 where t1.id = t2.id;
--普通内连接
selct * from emp t1,dept t2 where t1.id = t2.id and t1.date > '2011-11-09';
3、多表查询练习
1、查询所有员工信息,查询员工编号,姓名,工资,职务名称,职务描述
select
t1.id,t1.name,t1.salary,t2.name,t2.salary
from
emp t1,job t2
where
t1.id = t2.id;
2、查询员工编号,员工姓名,工资 职务名称 职务描述 部门名称,部门位置
select
t1.id,t1.name,t1.salary,t2.name,t2.salary,t3.name,t3.location
from
emp t1,job t2,dept t3
where
t1.id = t2.id and t1.id = t3.id;
3、查询员工姓名、工资、工资等级
select
t1.name,t1.salary,t2.*
from
emp t1,salarygrad t2
where
t1.salary between t2.minsalary and t2.maxsalary
4|查询员工名称、工资】职务名称、职务描述、部门名称、部门位置 、工资等级
select
t1.name,t1.salary,t2.name,t2.description,t3.name,t3.location,t4.grade
from
emp t1,job t2,dept t3,salraygrade t4
where
t1.id = t2.id
and t1.id = t3.id
and t1.salary between t4.minsalary and t4.maxsalary
5、查询出部门编号、部门名称、部门位置、部门人数
select
t1.id,t1.name,t1.location,t2.total
from
dept t1,(select
id,count(id)
from
emp
group by
id) t2
where t1.id = t2.id
6、查询所有员工的姓名及其直接上级的名称,没有领导的员工也需要查询
select
t1.ename,t1.mgr,t2.id,t2.ename
from
emp t1 left join on emp t2
where
t1.mgr = t2.id
九、事务
1、事务的基本介绍
概念:如果一个包含多个步骤的业务操作,被事务管理这些事务要么同时成功要么同时失败
操作:开启事务(start transaction)、回滚(rollback)、提交(commit)
MySQL数据库中事务默认自动提交
一条DML(增删改)语句会自动 提交一次失事务
事务提交有两种方式:
自动提交:
手动提交:需要先开启事务,在提交
修改事务的默认提交方式:
select &&autocommit; 1 代表自动提交0代表手动提交
2、事务的四大特征
1、原子性:是不可分割的最小操作单位,要么同时成功,要么同时失败
2、持久性:当事务提交或者回滚后,数据库会持久化的保存数据
3、隔离性;多个事务之间相互独立
4、一致性:事务操作前后,数据总量不变
3、事务的隔离级别
概念:多个事务之间隔离的,相互独立的,但是多个事务操作同一批数据,则会引发一些问题,设置不同的隔离级别可以解决这些问题
存在的问题:
1、脏读:一个事务,读取到另一个事务中没有提交的数据
2、不可重复读:在同一个事务中,两次读取到的数据不一致
3、幻读:一个事务操作(DML)数据库中所有的记录,另一个事务添加了一条数据,则第一个事务查询不到自己的修改
隔离级别
1、read uncommitted :读未提交
产生的问题: 脏读、不可重复读、幻读
2、read committed :读以提交
产生问题:不可重复读、幻读
3、repeatable read : 可重复读(MySQL默认)
产生的问题:幻读
4、serializable:串行化
可以解决所有的问题
注意:隔离级别从小到大安全性越来越高,但是效率越来越低
十、用户管理和权限管理
1、切换到mysql数据库
use mysql
2、查询user表
select * from user
3、创建用户
create user '用户名'@'主机名' indentified by '密码'
4、删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'主机名'