Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks
因为我是语义分割方向,对图像超分辨率不了解,这里简单记录一下读论文的收获。论文地址
超分辨率的输入是低分辨率,最终恢复超分辨率图片。作者发现低分辨率的图片拥有丰富的低频细节,对应图像中大块的平坦区域,然而低分辨率的每个通道在处理时候总是平等的,为了解决这个问题,作者提出了RCAN(Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks),特别的提出了一个RIR(residual in residual)结构,包含长连接,而每一个残差GROUP包含一些残差块,带有短连接。这些连接可以将低频信息传递过来,使网络更专注于高频细节。
思考:在语义分割encoder后,图片的分辨率是非常低的,此时含有大量的通道,对大量的通道我们只需要关注一些有用的,因此和超分辨率的输入是非常类似的。
超分辨率图:

语义分割图:

图像的超分辨率,我们尝试去恢复图像的高频细节,,低分辨率的图像就可以直接传进最终的高分辨率图。
RCAN框架:
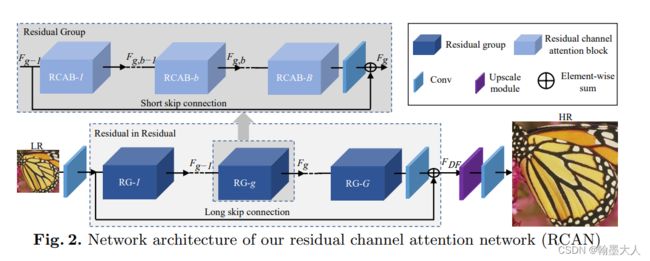
LR图片首先经过一个卷积层,提取浅层特征,然后输入进RIR模块提取深层特征,最后进行尺寸扩大,再经过重建层。
1:卷积层
使用了一个卷积层。
2:RIR层
包含G个残差组(RG),和长跳跃连接。每一个RG包含B个残差通道注意力模块,和一个短连接,这种设计可以使网络达到很深的层。

其中长连接可以用来构建更深的网络,同时也可以达到更好的性能。也可以让RIR学习到浅层的残差信息。
2.1:为了让网络关注更多有信息的特征,短连接引入进来,有了长连接和短连接,更多的低频信息就可以传递到网络训练当中。
2.2:通道注意力:就是SENet中的sequeeze and extraction模块。
实验:
在RIR中使用10个RG模块,每个RG模块,使用20个RCAB模块。在通道缩小和扩大时候使用1x1卷积,其余的卷积都使用3x3卷积。
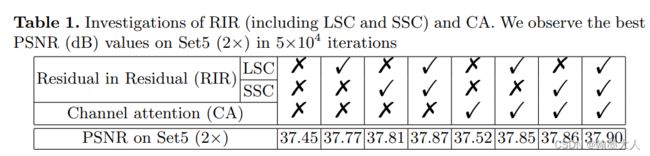
看一下各个模块的作用:
分析一下代码:
from model import common
import torch.nn as nn
def make_model(args, parent=False):
return RCAN(args)
## Channel Attention (CA) Layer
class CALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(CALayer, self).__init__()
# global average pooling: feature --> point
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
# feature channel downscale and upscale --> channel weight
self.conv_du = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.conv_du(y)
return x * y
## Residual Channel Attention Block (RCAB)
class RCAB(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, conv, n_feat, kernel_size, reduction,
bias=True, bn=False, act=nn.ReLU(True), res_scale=1):
super(RCAB, self).__init__()
modules_body = []
for i in range(2):
modules_body.append(conv(n_feat, n_feat, kernel_size, bias=bias))
if bn: modules_body.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(n_feat))
if i == 0: modules_body.append(act)
modules_body.append(CALayer(n_feat, reduction))
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
self.res_scale = res_scale
def forward(self, x):
res = self.body(x)
#res = self.body(x).mul(self.res_scale)
res += x
return res
## Residual Group (RG)
class ResidualGroup(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, conv, n_feat, kernel_size, reduction, act, res_scale, n_resblocks):
super(ResidualGroup, self).__init__()
modules_body = []
modules_body = [
RCAB(
conv, n_feat, kernel_size, reduction, bias=True, bn=False, act=nn.ReLU(True), res_scale=1) \
for _ in range(n_resblocks)]
modules_body.append(conv(n_feat, n_feat, kernel_size))
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
def forward(self, x):
res = self.body(x)
res += x
return res
## Residual Channel Attention Network (RCAN)
class RCAN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, args, conv=common.default_conv):
super(RCAN, self).__init__()
n_resgroups = args.n_resgroups #10
n_resblocks = args.n_resblocks
n_feats = args.n_feats
kernel_size = 3
reduction = args.reduction
scale = args.scale[0]
act = nn.ReLU(True)
# RGB mean for DIV2K
rgb_mean = (0.4488, 0.4371, 0.4040)
rgb_std = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
self.sub_mean = common.MeanShift(args.rgb_range, rgb_mean, rgb_std)
# define head module
modules_head = [conv(args.n_colors, n_feats, kernel_size)]
# define body module
modules_body = [
ResidualGroup(
conv, n_feats, kernel_size, reduction, act=act, res_scale=args.res_scale, n_resblocks=n_resblocks) \
for _ in range(n_resgroups)]
modules_body.append(conv(n_feats, n_feats, kernel_size))
# define tail module
modules_tail = [
common.Upsampler(conv, scale, n_feats, act=False),
conv(n_feats, args.n_colors, kernel_size)]
self.add_mean = common.MeanShift(args.rgb_range, rgb_mean, rgb_std, 1)
self.head = nn.Sequential(*modules_head)
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
self.tail = nn.Sequential(*modules_tail)
#主函数
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sub_mean(x)
x = self.head(x)
res = self.body(x)
res += x
x = self.tail(res)
x = self.add_mean(x)
return x
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict, strict=False):
own_state = self.state_dict()
for name, param in state_dict.items():
if name in own_state:
if isinstance(param, nn.Parameter):
param = param.data
try:
own_state[name].copy_(param)
except Exception:
if name.find('tail') >= 0:
print('Replace pre-trained upsampler to new one...')
else:
raise RuntimeError('While copying the parameter named {}, '
'whose dimensions in the model are {} and '
'whose dimensions in the checkpoint are {}.'
.format(name, own_state[name].size(), param.size()))
elif strict:
if name.find('tail') == -1:
raise KeyError('unexpected key "{}" in state_dict'
.format(name))
if strict:
missing = set(own_state.keys()) - set(state_dict.keys())
if len(missing) > 0:
raise KeyError('missing keys in state_dict: "{}"'.format(missing))
从主函数进入代码:
在RCAN类中,我们输入X,进过sub_mean函数,对应另一个文件下的函数:这个函数继承自卷积,你也可以把他看成一个卷积。
class MeanShift(nn.Conv2d):
def __init__(self, rgb_range, rgb_mean, rgb_std, sign=-1):
super(MeanShift, self).__init__(3, 3, kernel_size=1)
std = torch.Tensor(rgb_std)
self.weight.data = torch.eye(3).view(3, 3, 1, 1)
self.weight.data.div_(std.view(3, 1, 1, 1))
self.bias.data = sign * rgb_range * torch.Tensor(rgb_mean)
self.bias.data.div_(std)
self.requires_grad = False
接着经过head函数,multi_head函数也是一个卷积,这里对应文中的框架就是浅层的特征提取层。接着进入主体函数,即RIR函数,我们会进入到ResidualGroup函数,即RIR中的每一个block,在跳进ResidualGroup中,发现看到了RCAB函数,我们到RCAB函数中,这其实就相当于套娃。
class RCAB(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, conv, n_feat, kernel_size, reduction,
bias=True, bn=False, act=nn.ReLU(True), res_scale=1):
super(RCAB, self).__init__()
modules_body = []
for i in range(2):
modules_body.append(conv(n_feat, n_feat, kernel_size, bias=bias))
if bn: modules_body.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(n_feat))
if i == 0: modules_body.append(act)
modules_body.append(CALayer(n_feat, reduction))
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
self.res_scale = res_scale
def forward(self, x):
res = self.body(x)
#res = self.body(x).mul(self.res_scale)
res += x
return res
输入x,首先定义一个空列表,然后往列表中添加两个卷积,如果有bn再添加bn,接着再两个卷积后面添加CAlayer,即通道注意力。
class CALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(CALayer, self).__init__()
# global average pooling: feature --> point
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
# feature channel downscale and upscale --> channel weight
self.conv_du = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.conv_du(y)
return x * y
经过两个卷积的特征图,首先经过平均池化,然后经过两个卷积层,进行通道的降维和升维,最后与原始的x相乘。再回到RCAB函数中,与原始的x相加。RCAB函数结束。
class ResidualGroup(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, conv, n_feat, kernel_size, reduction, act, res_scale, n_resblocks):
super(ResidualGroup, self).__init__()
modules_body = []
modules_body = [
RCAB(
conv, n_feat, kernel_size, reduction, bias=True, bn=False, act=nn.ReLU(True), res_scale=1) \
for _ in range(n_resblocks)]
modules_body.append(conv(n_feat, n_feat, kernel_size))
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
def forward(self, x):
res = self.body(x)
res += x
return res
再返回到ResidualGroup函数中,经过n_resblocks个RCAB后,在紧接着一个卷积层,然后与原始的x相加。至此ResidualGroup函数结束。
再回到RCAN函数中,经过n_resgroups个ResidualGroup后,再紧接着一个卷积层。至此body函数就结束了,然后再与原始的x相加,RIR函数就结束了。
接着是tail函数,调用另一个文件下的upsample函数:
class Upsampler(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, conv, scale, n_feat, bn=False, act=False, bias=True):
m = []
if (scale & (scale - 1)) == 0: # Is scale = 2^n?
for _ in range(int(math.log(scale, 2))):
m.append(conv(n_feat, 4 * n_feat, 3, bias))
m.append(nn.PixelShuffle(2))
if bn: m.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(n_feat))
if act: m.append(act())
elif scale == 3:
m.append(conv(n_feat, 9 * n_feat, 3, bias))
m.append(nn.PixelShuffle(3))
if bn: m.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(n_feat))
if act: m.append(act())
else:
raise NotImplementedError
super(Upsampler, self).__init__(*m)
Upsampler返回的是一个序列,其中scale=4,那么4&3==0为true,执行第一个,接着int(math.log(scale, 2)),执行log以2为底4的对数,结果为2,则循环执行两次,往m列表里面添加两个卷积,pixelshuffle,bn,act,返回m,至此Upsampler结束。回到RCAN中,tail函数后面再加一个卷积。self.tail函数结束。
最后再经过一个self.add_mean = common.MeanShift(args.rgb_range, rgb_mean, rgb_std, 1)函数。则整个RCAN函数结束。后面是加载权重就不看了。