Opencv中关于特征点匹配定位的问题(一)
Opencv中关于特征点匹配定位的问题
- 回顾
- 定位
回顾
在我们检测到特征点之后,通常进行特征点的匹配。
首先我们先回顾一下使用Brute-Force匹配器来进行匹配。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#读取图片
img=cv2.imread('./newmm.png')
tem=cv2.imread('./templa.png')
#创建特征点检测器
orb=cv2.ORB_create()
#创建BF特征点匹配器
bf=cv2.BFMatcher_create()
#检测原图特征点
kp1,des1=orb.detectAndCompute(img,mask=None)
#检测模板图特征点
kp2,des2=orb.detectAndCompute(tem,mask=None)
#进行匹配
res=bf.match(des1,des2)
#将匹配点按照距离排序
res=sorted(res,key=lambda x:x.distance)
#将最相近的10个点绘画出来
newimg=cv2.drawMatches(img,kp1,tem,kp2,res[:10],None)
#绘制原图特征点
img=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp1,None,color=[0,0,255])
tem=cv2.drawKeypoints(tem,kp2,None,color=[0,255,0])
#显示图片
def imshow(img,axis,title=None):
axis=str(axis[0])+str(axis[1])
for i in range(len(img)):
plt.subplot(int(axis + str(i+1)))
if title:
plt.title(title[i])
i=cv2.cvtColor(img[i],cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(i)
plt.show()
all_img=[img,tem,newimg]
all_title=['img','tem','newimg']
imshow(all_img,[2,2],all_title)
定位
那么问题来了,如何对检测完成之后进行坐标定位呢。
首先我们要看bf.match生成的结果:
res=bf.match(des1,des2)
print(res)
(<DMatch 000001B9FFB81A50>, <DMatch 000001B9FFB81A70>, <DMatch 000001B9FFB81A30>, <DMatch 000001B9FFB819F0>.....)
<class 'cv2.DMatch'>
可以看见生成的是
那么我们依然可以通过dir(res[0])进行访问对象的属性。
['__class__',
'__delattr__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__le__',
'__lt__',
'__module__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__',
'distance',
'imgIdx',
'queryIdx',
'trainIdx']
然后把需要的'distance','imgIdx' 'queryIdx', 'trainIdx'打印出来:
print(res[0].distance)
print(res[0].imgIdx)
print(res[0].queryIdx)
print(res[0].trainIdx)
0.0
0
0
13
但是看着发现是一头雾水,只有res[0].distance知道说明含义。于是只能取opencv官网查阅
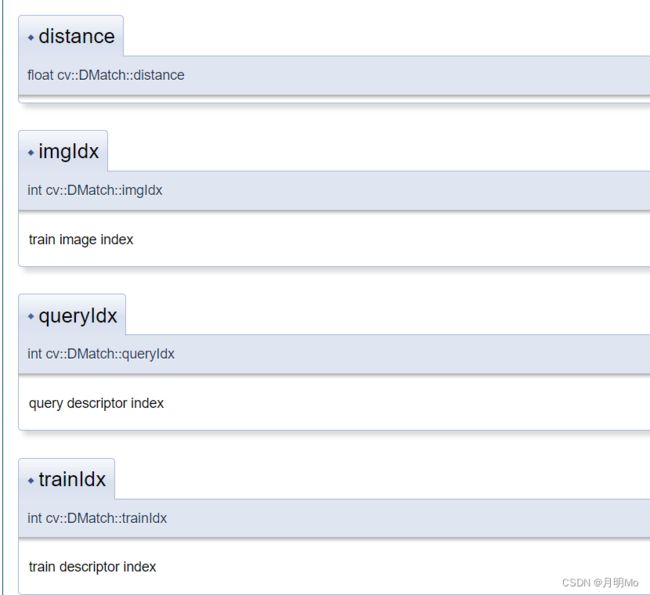
由于英语水平有限加上描述过于简单,只能凭借感觉来猜测。
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| trainIdx | 匹配原图片对应的特征点索引 |
| queryIdx | 匹配模板图片对应的特征点索引 |
| imgIdx | 图片的索引 |
有了这个之后,便自己尝试了一下,由于匹配结果是进行排序后,也就是越前面准确度越高,所以直接拿前面进行尝试。
思路是这样,将两张图片(原图和模板图)前十个res进行获得最小值坐标和最大值坐标(也就是框的左上角和右上角),然后进行描绘出来,看两遍的图片框的位置是否一样。
代码如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#读取图片
img=cv2.imread('./newmm.png')
tem=cv2.imread('./templa.png')
#创建特征点检测器
orb=cv2.ORB_create()
#创建BF特征点匹配器
bf=cv2.BFMatcher_create()
#检测原图特征点
kp1,des1=orb.detectAndCompute(img,mask=None)
#检测模板图特征点
kp2,des2=orb.detectAndCompute(tem,mask=None)
#进行匹配
res=bf.match(des1,des2)
#将匹配点按照距离排序
res=sorted(res,key=lambda x:x.distance)
def get_rect(res,kp,idx=0):
point_img=[]
#获得前十res个对应的点
for i in res[:10]:
if idx==0:
center=cv2.KeyPoint_convert(kp,keypointIndexes=[i.queryIdx])
elif idx==1:
center = cv2.KeyPoint_convert(kp, keypointIndexes=[i.trainIdx])
center=[int(np.ravel(center)[0]),int(np.ravel(center)[1])]
point_img.append(center)
#获得框的左上角点和右下角点
minres=np.argmin(point_img,axis=0)
maxres=np.argmax(point_img,axis=0)
minpoint=[point_img[minres[0]][0],point_img[minres[1]][1]]
maxpoint=[point_img[maxres[0]][0],point_img[maxres[1]][1]]
return minpoint,maxpoint
min1,max2=get_rect(res,kp1,0)
min3,max4=get_rect(res,kp2,1)
cv2.rectangle(tem,min3,max4,[255,0,0],4,16)
cv2.rectangle(img,min1,max2,[255,0,0],4,16)
#将最相近的10个点绘画出来
newimg=cv2.drawMatches(img,kp1,tem,kp2,res[:10],None)
#绘制原图特征点
img=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp1,None,color=[0,0,255])
tem=cv2.drawKeypoints(tem,kp2,None,color=[0,255,0])
#显示图片
def imshow(img,axis,title=None):
axis=str(axis[0])+str(axis[1])
for i in range(len(img)):
plt.subplot(int(axis + str(i+1)))
if title:
plt.title(title[i])
i=cv2.cvtColor(img[i],cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(i)
plt.show()
all_img=[img,tem,newimg]
all_title=['img','tem','newimg']
imshow(all_img,[2,2],all_title)



