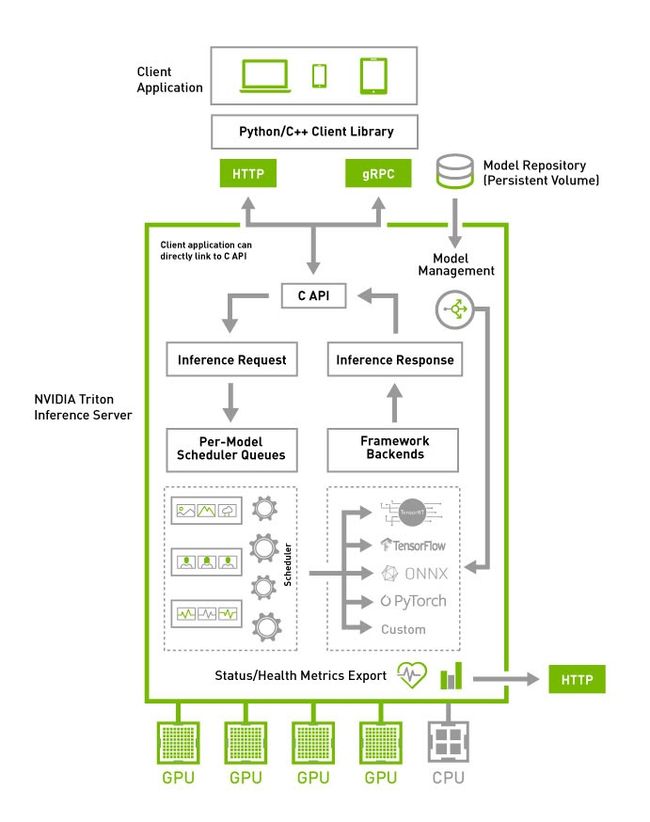
基于nvidia triton的模型工程化实践
什么是triton inference server?
它的前身是nvidia的tensorRT,triton在具备tensorRT的基础上,增加了主流的TF,pytorch,onnx等模型的推理部署支持。
是一款非常好的推理模型部署服务。
具体了解:NVIDIA Triton Inference Server | NVIDIA Developer![]() https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-triton-inference-server
https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-triton-inference-server
模型部署及优化实践
pytorch模型部署
pytorch模型需要提供jit之后的模型。
文件夹层次为:
model_name/
1/model.pt
config.pbtxt
只需要将上述文件夹拷贝到triton server里的models文件夹即可生效(可以配置triton监听文件夹变化,如果变化自动重启)。
config.pbtxt是这次讲解的重点,也是部署时最需要学习的地方。
以下是具体实例:
#this MUST be the same name with the outside folder
name: "ibuddha_chitchat"
# pytorch
platform: "pytorch_libtorch"
# you should limit this ,or else the graphic card will doom...
max_batch_size: 64
input [
{
#pytorch output this 0,1,2 silly name by default
name: "INPUT__0"
#int64 or int32, must be the same as the model define
data_type: TYPE_INT64
#dynamic sequence len, means you can input text len from 1 to 510 typically, or else you should put a fix value here
dims: [-1]
},
{
name: "INPUT__1"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [-1]
},
{
name: "INPUT__2"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [-1]
}
]
output [
{
#pytorch silly default name
name: "OUTPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [13088]
}
]
# output only one which has bigger version
version_policy: { latest {num_versions: 1}}
#version_policy: { all {}}
# enable dynamic will improve your performance greatly
dynamic_batching {
}
# enable this will make your inference faster
parameters: {
key: "INFERENCE_MODE"
value: {
string_value:"true"
}
}
# disable this. It is slower than default in my test
#parameters: {
#key: "ENABLE_NVFUSER"
# value: {
# string_value:"true"
# }
#}
#pytorch model only run in graphic card 0 by default
instance_group [
{
count: 1
kind: KIND_GPU
gpus: [ 0 ]
}
]1代表版本号(建议从1...N,0无效)
model.pt为约定名字
name为模型名字,要求与外层的文件夹名字一致,因此外面的文件夹必须改为ibuddha_chitchat。
ibuddha_chitchat/
1/model.pt
config.pbtxt
pytorch模型的platform为:pytorch_libtorch
这个实例采用的是动态batching,也是官方推荐的优化方式。
dynamic_batching {}
使能动态batch会非常有效的提高推理的系统效率。
max_batch_size 需要设置合适,太大会导致显卡显存爆(triton显存爆可能导致triton挂且无法自动重启)(注意:dynamic_batching生效时,这个选项才有效)
input代表模型的输入
pytorch的bert,典型的名字为INPUT__0..INPUT__2
数据类型到底是TYPE_INT64还是TYPE_INT32,需要根据模型训练使用的数据类型定,同样是bert,有的是INT64有的是INT32,但3个INPUT都会是相同类型(目前没有找到具体规律)
dims: [-1]
代表动态sequence,表示输入的文本长度不需要是一个固定值。
注意,由于这里是动态batching,所以第一个维度的-1可以省略不写。
(如果不是动态batching,则dims: [N, -1])
output和input的格式一样
这里实例由于是GPT模型,会返回整句话中每个位置的13088个vocab的概率(浮点型)(后处理会选择概率最高的那个token作为输出(实际会复杂些))。
version_policy用来控制版本
实例的写法是只会有一个版本,triton自动选择数字最大的那个。
(
如果需要所有版本都输出,可以写如下:
version_policy: { all {}}
)
instance_group
count为1代表只有1个实例
KIND_GPU顾名思义是运行在GPU(也可以配置运行在CPU)
gpus: [0] 代表只运行在显卡0上
注意:pytorch模型目前有一个缺陷,只能固定在某个显卡上,默认都是显卡0(有可以不限制显卡0,可运行在多个显卡的,还请告知一下作者)
onnx模型部署
整个过程和pytorch非常类似,这里只说差异点:
模型统一约定名字为model.onnx
config.pbtxt的编写中:
platform: onnxruntime_onnx
由于pytorch转onnx,可以配置input_names,所以建议给团队约定的名字,便于维护:
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids
实例的output,由于是返回句子的平均向量,因此直接是一个768长度的浮点数数组。
onnx模型也可以动态转为tensorRT,是不是能更快,需要各位自己实测。
name: "sps_sbert_onnx"
#onnx model
platform: "onnxruntime_onnx"
max_batch_size: 32
#recommend use the same name in your team, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids
input [
{
name: "input_ids"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [-1]
},
{
name: "attention_mask"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [-1]
},
{
name: "token_type_ids"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [-1]
}
]
output [
{
#recommend to use meaningful name
name: "vector"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [768]
}
]
#version_policy: { all {}}
version_policy: { latest {num_versions: 1}}
dynamic_batching { }
#you should test whether this can be faster
#change onnx
optimization { execution_accelerators {
gpu_execution_accelerator : [ { name : "tensorrt" } ]
}}tensorflow模型部署
tensorflow模型推荐采用saved_model格式
将saved_model文件夹拷贝到版本文件夹中,命名为:model.savedmodel
1/model.savedmodel
assets
saved_model.pb
variables
config.pbtxt
name: "shansou_rank"
platform: "tensorflow_savedmodel"
max_batch_size: 128
input [
{
name: "input_ids"
data_type: TYPE_INT32
#fix length of input. input should padding to max length or truncate the text over max length
dims: [128]
},
{
name: "input_mask"
data_type: TYPE_INT32
dims: [128]
},
{
name: "segment_ids"
data_type: TYPE_INT32
dims: [128]
}
]
output [
{
name: "output"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [1]
}
]
dynamic_batching { }
#this will use V100/T4 or better graphic mix precision unit
#always fasters than tensorRT
optimization { execution_accelerators {
gpu_execution_accelerator : [
{ name : "auto_mixed_precision" }
]
}}
version_policy: { latest {num_versions: 1}}nvidia和tensorflow打磨的时间最久,支持的功能也最多。
例如可以直接配置tensorRT,动态将tensorflow模型直接转为tensorRT。
将过去繁琐的转tensorRT过程,变成了极其简单的配置即可生效的过程(推荐)。
如果不加parameters一句,默认是无损的FP32精度
optimization { execution_accelerators {
gpu_execution_accelerator : [ {
name : "tensorrt"
#parameters { key: "precision_mode" value: "FP16" }}]
}}实际上,作者最终选择的是混合精度模式。
optimization { execution_accelerators {
gpu_execution_accelerator : [
{ name : "auto_mixed_precision" }
]
}}tensorflow模型选择混合精度模式后,可以发挥显卡能力7及以上的混合处理单元(V100, T4及以上均可使用)。
显卡其实有2个发动机,普通的FP32处理单元(民用发动机),混合精度处理单元(赛车发动机)。
tensorflow模型转为tensorRT,等价于民用发动机上的极致优化,属于软件优化。
tensorflow模型采用混合精度模式,等价于运行在赛车发动机上,属于硬件加强。
实测混合精度模式要明显强于tensorRT(这边的测试大约是2倍)。
目前,无法让tensorRT和混合精度模型一起生效(这是最理想的优化),期望未来可以支持。
python代码部署
可以将python代码类似模型一样部署,本质也是input->handle->output
models
└── ibuddha_chitchat_bls
├── 1
│ └── model.py
└── config.pbtxt这里讲解21.08开始才有的BLS功能(Business Logic Scripting)
常用的闲聊模型采用GPT模型,每次推理只能获取一个字,需要反复循环,且每次返回的向量非常多(网络传输时间消耗大),因此,将这部分逻辑放到triton的BLS中,在进程内完成,是非常合适的。
详看:
GitHub - triton-inference-server/python_backend: Triton backend that enables pre-process, post-processing and other logic to be implemented in Python.
name: "ibuddha_chitchat_bls"
backend: "python"
max_batch_size: 64
input [
{
name: "INPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [ -1 ]
}
]
input [
{
name: "INPUT__1"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [ -1 ]
}
]
input [
{
name: "INPUT__2"
data_type: TYPE_INT64
dims: [ -1 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUTPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_INT32
dims: [ -1 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUTPUT__1"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ -1 ]
}
]
instance_group [{ kind: KIND_CPU }]
dynamic_batching {
}由于是python代码,因此涉及第三方库的问题,需要在原triton镜像的基础上新增三方库,因此,需要额外build镜像。
这里重点讲解一点:
python backend是配置的是:instance_group [{ kind: KIND_CPU }]
具体执行的模型,运行在GPU上。
因此
infer_response = infer_request.exec()
这句完成模型推理后的结果是在GPU上的,无法直接使用
必须采用pytorch的to_dlpack将GPU的内容放到共享内存中,再用from_dlpack把共享内存的内容转为pytorch的tensor。
logits = from_dlpack(output0.to_dlpack())
triton的变量转为pytorch的tensor有2种方法:
input_ids = from_dlpack(in_0.to_dlpack())
input_ids = torch.from_numpy(in_0.as_numpy())
采用to_dlpack和from_dlpack 具有更低的消耗。
这个是没有代码优化的model.py
import triton_python_backend_utils as pb_utils
from torch.utils.dlpack import from_dlpack,to_dlpack
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
import json
import numpy as np
class TritonPythonModel:
"""Your Python model must use the same class name. Every Python model
that is created must have "TritonPythonModel" as the class name.
"""
def initialize(self, args):
"""`initialize` is called only once when the model is being loaded.
Implementing `initialize` function is optional. This function allows
the model to intialize any state associated with this model.
Parameters
----------
args : dict
Both keys and values are strings. The dictionary keys and values are:
* model_config: A JSON string containing the model configuration
* model_instance_kind: A string containing model instance kind
* model_instance_device_id: A string containing model instance device ID
* model_repository: Model repository path
* model_version: Model version
* model_name: Model name
"""
# You must parse model_config. JSON string is not parsed here
self.model_config = json.loads(args['model_config'])
input0_config = pb_utils.get_input_config_by_name(
self.model_config, "INPUT__0")
input1_config = pb_utils.get_input_config_by_name(
self.model_config, "INPUT__1")
input2_config = pb_utils.get_input_config_by_name(
self.model_config, "INPUT__2")
output0_config = pb_utils.get_output_config_by_name(
self.model_config, "OUTPUT__0")
output1_config = pb_utils.get_output_config_by_name(
self.model_config, "OUTPUT__1")
# Convert Triton types to numpy types
self.input0_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
input0_config['data_type'])
self.input1_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
input1_config['data_type'])
self.input2_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
input2_config['data_type'])
self.output0_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
output0_config['data_type'])
self.output1_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
output1_config['data_type'])
#self.cls, self.sep, self.pad, self.speaker1, self.speaker2 = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(["[CLS]", "[SEP]", "[PAD]", "[speaker1]", "[speaker2]"])
#self.special_tokens_ids = [self.cls, self.sep, self.pad, self.speaker1, self.speaker2]
self.special_tokens_ids = [0, 2, 1, 13086, 13087]
self.output_min_length = 1
self.output_max_length = 64 #TODO: change
self.temperature = 0.7
self.top_p = 0.7
self.round = 1
def execute(self, requests):
"""`execute` must be implemented in every Python model. `execute`
function receives a list of pb_utils.InferenceRequest as the only
argument. This function is called when an inference request is made
for this model. Depending on the batching configuration (e.g. Dynamic
Batching) used, `requests` may contain multiple requests. Every
Python model, must create one pb_utils.InferenceResponse for every
pb_utils.InferenceRequest in `requests`. If there is an error, you can
set the error argument when creating a pb_utils.InferenceResponse
Parameters
----------
requests : list
A list of pb_utils.InferenceRequest
Returns
-------
list
A list of pb_utils.InferenceResponse. The length of this list must
be the same as `requests`
"""
responses = []
# Every Python backend must iterate over everyone of the requests
# and create a pb_utils.InferenceResponse for each of them.
for request in requests:
# Get INPUT0
in_0 = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT__0")
in_1 = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT__1")
in_2 = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT__2")
#pytorch_tensor = from_dlpack(in_0.to_dlpack())
#print(pytorch_tensor)
# Get Model Name
#model_name = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(
# request, "MODEL_NAME")
# Model Name string
#model_name_string = model_name.as_numpy()[0]
model_name_string = "ibuddha_chitchat"
# Create inference request object
# Perform synchronous blocking inference request
# Create InferenceResponse. You can set an error here in case
# there was a problem with handling this inference request.
# Below is an example of how you can set errors in inference
# response:
#
# pb_utils.InferenceResponse(
# output_tensors=..., TritonError("An error occured"))
#
# Because the infer_response of the models contains the final
# outputs with correct output names, we can just pass the list
# of outputs to the InferenceResponse object.
#print(type(infer_response))
output_ids = []
output_confidences = []
for i in range(self.output_max_length):
infer_request = pb_utils.InferenceRequest(
model_name=model_name_string,
requested_output_names=["OUTPUT__0"],
inputs=[in_0, in_1, in_2])
infer_response = infer_request.exec()
if infer_response.has_error():
raise pb_utils.TritonModelException(
infer_response.error().message())
output0 = pb_utils.get_output_tensor_by_name(infer_response, 'OUTPUT__0')
#_logits = output0.as_numpy()
#logits = torch.from_numpy(np.array(_logits))
logits = from_dlpack(output0.to_dlpack())
#print(pytorch_tensor)
#_logits = self.triton_infer(encoded_input)[0]
#logits = torch.from_numpy(np.array(_logits))
logits = logits[0, :] / self.temperature
top_logits = self.top_filtering(logits, self.top_p)
probs = F.softmax(top_logits, dim=-1)
prev = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
if i < self.output_min_length and prev.item() in self.special_tokens_ids:
while prev.item() in self.special_tokens_ids:
prev = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
output_id = prev.item()
if output_id in self.special_tokens_ids:
break
output_ids.append(output_id)
output_confidences.append(probs[output_id].item())
input_ids = torch.from_numpy(in_0.as_numpy())
attention_mask = torch.from_numpy(in_1.as_numpy())
token_type_ids = torch.from_numpy(in_2.as_numpy())
#input_ids = from_dlpack(in_0.to_dlpack())
#attention_mask = from_dlpack(in_1.to_dlpack())
#token_type_ids = from_dlpack(in_2.to_dlpack())
input_ids = torch.cat((input_ids, torch.LongTensor([[output_id]])), 1)
attention_mask = torch.cat((attention_mask, torch.LongTensor([[1]])), 1)
token_type_ids = torch.cat((token_type_ids, torch.LongTensor([[output_id]])), 1)
in_0 = pb_utils.Tensor("INPUT__0", input_ids.numpy().astype(self.input0_dtype))
in_1 = pb_utils.Tensor("INPUT__1", attention_mask.numpy().astype(self.input1_dtype))
in_2 = pb_utils.Tensor("INPUT__2", token_type_ids.numpy().astype(self.input2_dtype))
#in_0 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("INPUT__0", to_dlpack(input_ids))
#in_1 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("INPUT__1", to_dlpack(attention_mask))
#in_2 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("INPUT__2", to_dlpack(token_type_ids))
#print(infer_response.output_tensors())
output_ids = torch.tensor(output_ids)
output_confidences = torch.tensor(output_confidences)
output_0 = pb_utils.Tensor("OUTPUT__0", output_ids.numpy().astype(self.output0_dtype))
output_1 = pb_utils.Tensor("OUTPUT__1", output_confidences.numpy().astype(self.output1_dtype))
#output_0 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("OUTPUT__0", to_dlpack(output_ids))
#output_1 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("OUTPUT__1", to_dlpack(output_confidences))
inference_response = pb_utils.InferenceResponse(
output_tensors=[output_0, output_1])
#print(type(inference_response))
responses.append(inference_response)
# You should return a list of pb_utils.InferenceResponse. Length
# of this list must match the length of `requests` list.
return responses
def top_filtering(self, logits, top_p=0.0, threshold=-float('Inf'), filter_value=-float('Inf')):
#assert logits.dim() == 1 # Only work for batch size 1 for now - could update but it would obfuscate a bit the code
if top_p > 0.0:
sorted_logits, sorted_indices = torch.sort(logits, descending=True)
cumulative_probabilities = torch.cumsum(F.softmax(sorted_logits, dim=-1), dim=-1)
sorted_indices_to_remove = cumulative_probabilities > top_p
sorted_indices_to_remove[..., 1:] = sorted_indices_to_remove[..., :-1].clone()
sorted_indices_to_remove[..., 0] = 0
indices_to_remove = sorted_indices[sorted_indices_to_remove]
logits[indices_to_remove] = filter_value
indices_to_remove = logits < threshold
logits[indices_to_remove] = filter_value
return logits
def finalize(self):
"""`finalize` is called only once when the model is being unloaded.
Implementing `finalize` function is OPTIONAL. This function allows
the model to perform any necessary clean ups before exit.
"""
print('Cleaning up...')可以参考python_backend里的examples。