OpenCV-Python官方教程-28-使用特征匹配和单应性查找对象
使用特征匹配和单应性查找对象
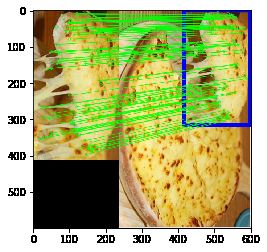
- 目标:联合使用特征提取和calib3d模块中的findHomography在杂图像中查找已知对象。
为了达到这个目的我们可以使用calib3d模块中的cv2.findHomography()函数。如果将这两幅图像中的特征点集传给这个函数,他就会找到这个对象的透视图变换。然后我们就可以使用函数cv2.perspectiveTransform()找到这个对象了。至少要 4 个正确的点才能找到这种变换。
我们已经知道在匹配过程可能会有一些错误,而这些错误会影响最终结果。为了解决这个问题,算法使用 RANSAC 和 LEAST_MEDIAN(可以通过参数来设定)。所以好的匹配提供的正确的估计被称为 inliers,剩下的被称为outliers。cv2.findHomography() 返回一个掩模,这个掩模确定了 inlier 和outlier 点。
代码演示:
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
MIN_MATCH_COUNT = 10
img1 = cv2.imread('pizza_part.jpg')
img2 = cv2.imread('pizza1.jpg')
# Initiate SIFT DETECTOR
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
# find the keypoints and descriptors with SIFT
kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img1, None)
kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(img2, None)
FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE = 0
index_params = dict(algorithm=FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE, trees=5)
search_params = dict(checks=50)
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params, search_params)
matches = flann.knnMatch(des1, des2, k=2)
# store all the good matches as per Lowe's ratio test.
good = []
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.2 * n.distance:
good.append(m)
if len(good) > MIN_MATCH_COUNT:
src_pts = np.float32([kp1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in good]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
dst_pts = np.float32([kp2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in good]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# 第三个参数 Method used to computed a homography matrix. The following methods are possible:
#0 - a regular method using all the points
#CV_RANSAC - RANSAC-based robust method
#CV_LMEDS - Least-Median robust method
# 第四个参数取值范围在 1 到 10,ᲁ绝一个点对的阈值。原图像的点经过变换后点与目标图像上对应点的误差
# 超过误差就认为是 outlier
# 返回值中 M 为变换矩阵。
M, mask = cv2.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.RANSAC, 5, 0)
matchesMask = mask.ravel().tolist()
h, w, _ = img1.shape
pts = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, h - 1], [w - 1, h - 1], [w - 1, 0]]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
dst = cv2.perspectiveTransform(pts, M)
cv2.polylines(img2, [np.int32(dst)], True, 255, 10, cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
print('Not enough matches are found - {}{}'.format(len(good), MIN_MATCH_COUNT))
matchesMask = None
draw_params = dict(matchColor=(0, 255, 0),
singlePointColor=None,
matchesMask=matchesMask,
flags=2)
img3 = cv2.drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, good, None, **draw_params)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img3, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.show()