机器学习入门项目——加州房价预测
一个项目的完整代码
获取数据
import os
import tarfile # 这个模块解压缩用的
import urllib.request
#获取数据
DOWNLOAD_ROOT = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ageron/handson-ml2/master/"
HOUSING_PATH = os.path.join("datasets", "housing")
HOUSING_URL = DOWNLOAD_ROOT + "datasets/housing/housing.tgz"
def fetch_housing_data(housing_url=HOUSING_URL, housing_path=HOUSING_PATH):
#路径不存在则创建路径
if not os.path.isdir(housing_path):
os.makedirs(housing_path)
tgz_path = os.path.join(housing_path, "housing.tgz")
#将URL表示的网络对象复制到本地文件
urllib.request.urlretrieve(housing_url, tgz_path)
#下面是和解压相关的代码
housing_tgz = tarfile.open(tgz_path)
housing_tgz.extractall(path=housing_path)
housing_tgz.close()
fetch_housing_data()
一些说明
urllib.request.urlretrieve
python tarfile模块基本使用
python路径拼接os.path.join()函数的用法
快速查看数据结构
import pandas as pd
def load_housing_data(housing_path=HOUSING_PATH):
csv_path = os.path.join(housing_path, "housing.csv")
return pd.read_csv(csv_path)
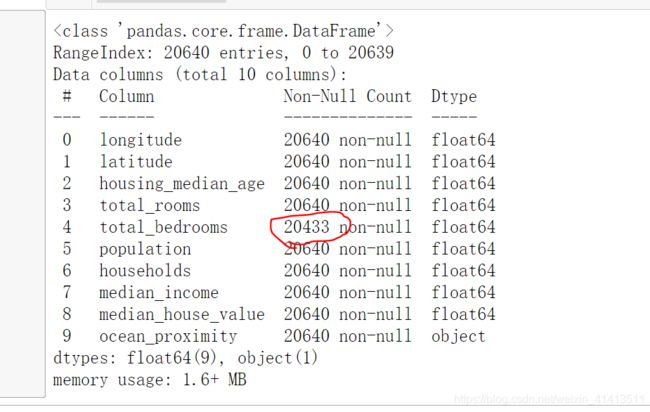
housing = load_housing_data()
housing.info()
创建测试集
#对房价中位数这个重要指标进行分层抽样
#pd.cut创建5个不同的收入类别 0-1.5为类别1 1.5-3.0为类别2
import numpy as np
housing["income_cat"] = pd.cut(housing["median_income"],
bins=[0., 1.5, 3.0, 4.5, 6., np.inf],
labels=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
split = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
#这个返回的是分组后数在原数组中的索引
#该for循环只执行一次
for train_index, test_index in split.split(housing, housing["income_cat"]):
strat_train_set = housing.loc[train_index]
strat_test_set = housing.loc[test_index]
#income_cat只是临时用于创建测试集,完了要删除,恢复原数据
for set_ in (strat_train_set, strat_test_set):
set_.drop("income_cat", axis=1, inplace=True)
数据准备
要预测的是房价中位数,所以训练的数据需要将房价中位数除去,房价中位数作为标签以验证结果
housing = strat_train_set.drop("median_house_value", axis=1) # drop labels for training set
housing_labels = strat_train_set["median_house_value"].copy()
处理缺失值
- 大部分机器学习无法在缺失的特征上工作,所以我们要处理缺失值
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy="median")
#用中位数填充的话,文本属性值要去掉
housing_num = housing.drop("ocean_proximity", axis=1)
#fit()这步就是将imputer实例适配到训练数据
#它计算了每个属性的中位值,并将结果存储在其实例变量中
imputer.fit(housing_num)
#这步才是真正将缺失值替换成中位数值
#完成训练集的转换,但X的结果是数组
X = imputer.transform(housing_num)
#重新生成dataframe格式
housing_tr = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=housing_num.columns,
index=housing_num.index)
处理文本属性
- 对于机器学习来说,数字比文本更加好处理
- ocean_proximity这个属性的文本是有限个可能的取值,而不是任意文本
采用独热编码
housing_cat = housing[["ocean_proximity"]]
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
cat_encoder = OneHotEncoder()
housing_cat_1hot = cat_encoder.fit_transform(housing_cat)
自定义转换器
- 属性组合可以达到更好的效果,将组合后的属性添加进去
- 注意这里的array知识
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
# column index
rooms_ix, bedrooms_ix, population_ix, households_ix = 3, 4, 5, 6
class CombinedAttributesAdder(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
def __init__(self, add_bedrooms_per_room=True): # no *args or **kargs
self.add_bedrooms_per_room = add_bedrooms_per_room
def fit(self, X, y=None):
return self # nothing else to do
def transform(self, X):
rooms_per_household = X[:, rooms_ix] / X[:, households_ix]
population_per_household = X[:, population_ix] / X[:, households_ix]
if self.add_bedrooms_per_room:
bedrooms_per_room = X[:, bedrooms_ix] / X[:, rooms_ix]
return np.c_[X, rooms_per_household, population_per_household,
bedrooms_per_room]
else:
return np.c_[X, rooms_per_household, population_per_household]
attr_adder = CombinedAttributesAdder(add_bedrooms_per_room=False)
housing_extra_attribs = attr_adder.transform(housing.values)
最终代码
这里使用转换流水线,将前面的转换合在一起,并多了特征缩放
list用法:pandas 几种获取dataframe列名的方式
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
#这些都必须有fit_transform()方法
num_pipeline = Pipeline([
('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy="median")),
('attribs_adder', CombinedAttributesAdder()),
('std_scaler', StandardScaler()),
])
#升级为能够处理所有列的转换器
#list说明
num_attribs = list(housing_num)
cat_attribs = ["ocean_proximity"]
full_pipeline = ColumnTransformer([
("num", num_pipeline, num_attribs),
("cat", OneHotEncoder(), cat_attribs),
])
housing_prepared = full_pipeline.fit_transform(housing)
训练模型
def display_scores(scores):
print("Scores:", scores)
print("Mean:", scores.mean())
print("Standard deviation:", scores.std())
使用线性模型模型
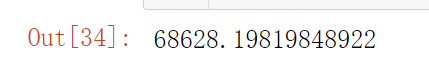
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
lin_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
housing_predictions = lin_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
lin_mse = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
lin_rmse = np.sqrt(lin_mse)
lin_rmse
使用决策树模型
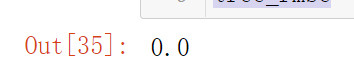
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
tree_reg = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=42)
tree_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
housing_predictions = tree_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
tree_mse = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
tree_rmse = np.sqrt(tree_mse)
tree_rmse
使用随机森林模型
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
forest_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
housing_predictions = forest_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
forest_mse = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
forest_rmse = np.sqrt(forest_mse)
forest_rmse
为了更好的进行评估,我们采用交叉验证
对线性模型进行交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
lin_scores = cross_val_score(lin_reg, housing_prepared, housing_labels,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
lin_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-lin_scores)
display_scores(lin_rmse_scores)
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
scores = cross_val_score(tree_reg, housing_prepared, housing_labels,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
tree_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-scores)
display_scores(tree_rmse_scores)
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
forest_scores = cross_val_score(forest_reg, housing_prepared, housing_labels,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
forest_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-forest_scores)
display_scores(forest_rmse_scores)
微调模型
从上面看来,使用随机森林效果比较好,接下来我们对随机森林进行微调
就是尝试大量的组合
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = [
# try 12 (3×4) combinations of hyperparameters
{'n_estimators': [3, 10, 30], 'max_features': [2, 4, 6, 8]},
# then try 6 (2×3) combinations with bootstrap set as False
{'bootstrap': [False], 'n_estimators': [3, 10], 'max_features': [2, 3, 4]},
]
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor(random_state=42)
# train across 5 folds, that's a total of (12+6)*5=90 rounds of training
grid_search = GridSearchCV(forest_reg, param_grid, cv=5,
scoring='neg_mean_squared_error',
return_train_score=True)
grid_search.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
#找出最佳的组合
grid_search.best_estimator_
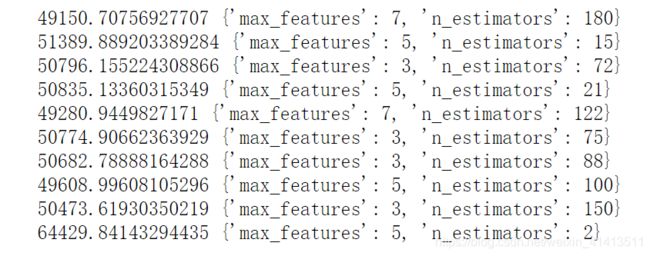
cvres = grid_search.cv_results_
for mean_score, params in zip(cvres["mean_test_score"], cvres["params"]):
print(np.sqrt(-mean_score), params)
结果为:
 最佳模型的评分为 49682 比默认参数的评分50182好
最佳模型的评分为 49682 比默认参数的评分50182好
至此找到最佳模型了
分析最佳模型及其误差
#得出一组关于每个属性相对重要程度的数值
feature_importances = grid_search.best_estimator_.feature_importances_
#之前额外加进去的属性
extra_attribs = ["rooms_per_hhold", "pop_per_hhold", "bedrooms_per_room"]
#获取独热编码转换器
cat_encoder = full_pipeline.named_transformers_["cat"]
#获取独热编码的属性,注意独热编码里面的文本值现在作为了属性名
cat_one_hot_attribs = list(cat_encoder.categories_[0])
attributes = num_attribs + extra_attribs + cat_one_hot_attribs
sorted(zip(feature_importances, attributes), reverse=True)
sort 排序
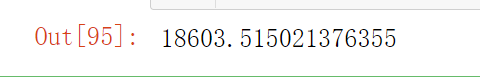
用测试集评估系统
经过前面的训练,你找到了最佳模型,现在可以用测试集评估最终模型
final_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
X_test = strat_test_set.drop("median_house_value", axis=1)
y_test = strat_test_set["median_house_value"].copy()
X_test_prepared = full_pipeline.transform(X_test)
final_predictions = final_model.predict(X_test_prepared)
final_mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, final_predictions)
final_rmse = np.sqrt(final_mse)
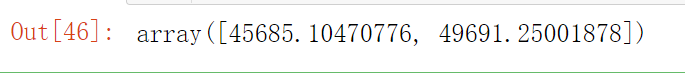
final_rmse
如果想知道计算泛化误差的95%置信区间
from scipy import stats
confidence = 0.95
squared_errors = (final_predictions - y_test) ** 2
np.sqrt(stats.t.interval(confidence, len(squared_errors) - 1,
loc=squared_errors.mean(),
scale=stats.sem(squared_errors)))
其他尝试
尝试支持向量机超参数
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = [
{'kernel': ['linear'], 'C': [10., 30., 100., 300., 1000., 3000., 10000., 30000.0]},
{'kernel': ['rbf'], 'C': [1.0, 3.0, 10., 30., 100., 300., 1000.0],
'gamma': [0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 3.0]},
]
svm_reg = SVR()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(svm_reg, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', verbose=2)
grid_search.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
grid_search.best_params_
到这里,我们已经确定了模型的参数,然后还要将全部数据放入这个参数已经确定的模型中重新进行训练
将网格搜索改为随机搜索
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from scipy.stats import randint
param_distribs = {
'n_estimators': randint(low=1, high=200),
'max_features': randint(low=1, high=8),
}
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor(random_state=42)
rnd_search = RandomizedSearchCV(forest_reg, param_distributions=param_distribs,
n_iter=10, cv=5, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', random_state=42)
rnd_search.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
查看结果
cvres = rnd_search.cv_results_
for mean_score, params in zip(cvres["mean_test_score"], cvres["params"]):
print(np.sqrt(-mean_score), params)
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from scipy.stats import expon, reciprocal
# see https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/stats.html
# for `expon()` and `reciprocal()` documentation and more probability distribution functions.
# Note: gamma is ignored when kernel is "linear"
param_distribs = {
'kernel': ['linear', 'rbf'],
'C': reciprocal(20, 200000),
'gamma': expon(scale=1.0),
}
svm_reg = SVR()
rnd_search = RandomizedSearchCV(svm_reg, param_distributions=param_distribs,
n_iter=50, cv=5, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error',
verbose=2, random_state=42)
rnd_search.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
创建一个覆盖完整的数据准备和最终预测的流水线
full_pipeline_with_predictor = Pipeline([
("preparation", full_pipeline),
("linear", LinearRegression())
])
full_pipeline_with_predictor.fit(housing, housing_labels)
full_pipeline_with_predictor.predict(some_data)
添加一个转化器,只选出最重要的属性
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
#选出最大的几个数,返回列名
def indices_of_top_k(arr, k):
return np.sort(np.argpartition(np.array(arr), -k)[-k:])
class TopFeatureSelector(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
def __init__(self, feature_importances, k):
self.feature_importances = feature_importances
self.k = k
def fit(self, X, y=None):
self.feature_indices_ = indices_of_top_k(self.feature_importances, self.k)
return self
def transform(self, X):
return X[:, self.feature_indices_]
preparation_and_feature_selection_pipeline = Pipeline([
('preparation', full_pipeline),
('feature_selection', TopFeatureSelector(feature_importances, k))
])
housing_prepared_top_k_features = preparation_and_feature_selection_pipeline.fit_transform(housing)
numpy中的argpartition