二叉树的前、中、后序遍历(递归方法 + 非递归方法)
树结构
二叉树
为什么需要树这种数据结构
数组存储方式的分析

优点: 通过下标方式访问元素,速度快。对于有序数组,还可使用二分查找提高检索速度!
缺点: 如果检索某个具体值时,或者插入值(按一定顺序)会整体移动,效率较低
链式存储方式的分析

优点: 在一定程度上对数组存储方式有优化(比如:插入一个数值节点,只需要将插入的节点链接到链表中即可,删除节点效率也很好)!
缺点: 在进行检索时,效率较低,比如(检索某个值时,需要从头节点开始遍历)!
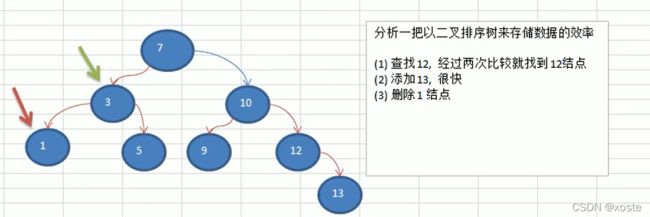
树存储方式的分析
能提高数据存储,读取的效率,比如利用 二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),既可以保证数据的检索速度,同时也可以保证数据的插入,删除,修改的速度!
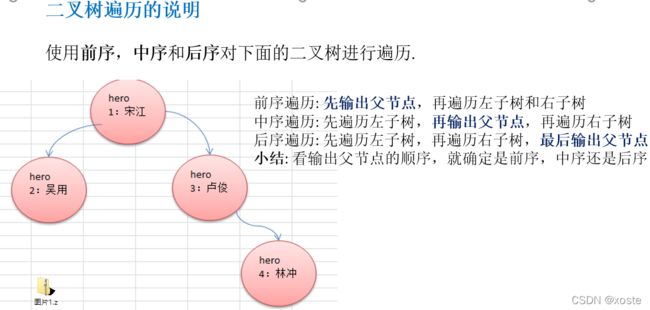
前序、中序、后序遍历
例图
代码
package com.xoste.datastructure.binarytree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @author xoste
* @date 2022/4/19 14:32
*/
public class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
public HeroNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
/**
* 递归方法
* 前序遍历
*/
public void preorder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preorder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空...");
}
}
/**
* 非递归方法
* 前序遍历
*/
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrderTraverse();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空");
}
}
/**
* 递归方法
* 中序遍历
*/
public void inorder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.inorder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空...");
}
}
/**
* 非递归方法
* 中序遍历
*/
public void inOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.inOrderTraverse();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空");
}
}
/**
* 递归方法
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postorder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postorder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空...");
}
}
/**
* 非递归方法
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrderTraverse();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空");
}
}
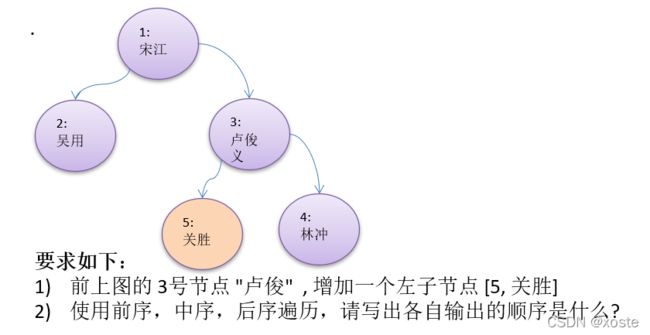
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "关胜");
// HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(6, "鲁智深");
root.setLeftNode(node2);
root.setRightNode(node3);
// node2.setRightNode(node6);
node3.setRightNode(node4);
node3.setLeftNode(node5);
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
// 递归方法
// System.out.println("前序遍历");
// binaryTree.preorder();
// System.out.println("中序遍历");
// binaryTree.inorder();
// System.out.println("后序遍历");
// binaryTree.postorder();
// 非递归方法
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.inOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
}
}
class HeroNode {
private int id;
private String name;
private HeroNode leftNode;
private HeroNode rightNode;
public HeroNode(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeftNode() {
return leftNode;
}
public void setLeftNode(HeroNode leftNode) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
}
public HeroNode getRightNode() {
return rightNode;
}
public void setRightNode(HeroNode rightNode) {
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", leftNode=" + leftNode +
", rightNode=" + rightNode +
'}';
}
/**
* 递归方法
* 前序遍历
*/
public void preorder() {
// 输出根节点,这里的 this 就是 BinaryTree类 中的成员变量 root,因为 this.root.preorder()
// this 调用谁,谁就是 this
System.out.println(this);
// 向左遍历
if (this.leftNode != null) {
this.leftNode.preorder();
}
// 向右遍历
if (this.rightNode != null) {
this.rightNode.preorder();
}
}
/**
* 非递归方法
* 前序遍历
*/
public void preOrderTraverse() {
// 定义一个辅助指针指向根节点
HeroNode temp = this;
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<HeroNode> list = new LinkedList<>();
while (temp != null) {
// 向左遍历
while (temp != null) {
// 将当前节点添加到 list 集合中
list.add(temp);
if (temp.getRightNode() != null) {
// 如果当前节点的右节点不为空,就先把右节点入栈,存起来,等所有的左节点数据遍历完后,
// 再将右节点从栈中取出,继续向左遍历,存储右节点...直到右节点为空
stack.push(temp.getRightNode());
}
// 将当前节点的指针指向当前节点的左节点
temp = temp.getLeftNode();
}
if (stack.size() > 0) {
// 将存到栈中右节点取出,即当前节点指针指向右节点,继续上面操作
temp = stack.pop();
}
}
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* 递归方法
* 中序遍历
*/
public void inorder() {
// 向左遍历
if (this.leftNode != null) {
this.leftNode.inorder();
}
// 输出根节点
System.out.println(this);
// 向右遍历
if (this.rightNode != null) {
this.rightNode.inorder();
}
}
/**
* 非递归方法
* 中序遍历
*/
public void inOrderTraverse() {
// 定义一个辅助指针 temp 指向根节点
HeroNode temp = this;
List<HeroNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (temp != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 一直向左遍历
while (temp != null) {
// 将 根节点 入栈
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.getLeftNode();
}
if (stack.size() > 0) {
// 从栈中取出栈顶的 根节点
temp = stack.pop();
// 将当前节点添加到 list 集合中
list.add(temp);
// 向右遍历
temp = temp.getRightNode();
}
}
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* 递归方法
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postorder() {
// 向左遍历
if (this.leftNode != null) {
this.leftNode.postorder();
}
// 向右遍历
if (this.rightNode != null) {
this.rightNode.postorder();
}
// 输出根节点
System.out.println(this);
}
/**
* 非递归方法
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postOrderTraverse() {
// 定义辅助指针 temp 指向根节点
HeroNode temp = this;
List<HeroNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (temp != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 一直向左遍历
while (temp != null) {
// 将根节点入栈
stack.push(temp);
if (temp.getLeftNode() != null) {
temp = temp.getLeftNode();
} else {
temp = temp.getRightNode();
}
}
if (stack.size() > 0) {
// 从栈中取出栈顶元素
temp = stack.pop();
// 将当前元素添加到 list 集合中
list.add(temp);
}
// 当栈不为空,且栈顶元素的右节点 = 当前节点,取栈顶元素
while (stack.size() > 0 && stack.peek().getRightNode() == temp) {
// 取栈顶元素
temp = stack.pop();
// 将当前节点添加到 list 集合中
list.add(temp);
}
// 当栈不为空时,temp 就只指向栈顶元素的右节点
if (stack.size() > 0) {
temp = stack.peek().getRightNode();
} else {
temp = null;
}
}
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
该文章来源于 B站,韩顺平老师的数据结构与算法教程!