Python构建简单线性回归模型教程
本文介绍如何构建简单线性回归模型及计算其准确率,最后介绍如何持久化模型。
线性回归模型
线性回归表示发现函数使用线性组合表示输入变量。简单线性回归很容易理解,使用了基本的回归技术,一旦理解了这些基本概念,可以更好地学习其他类型的回归模型。
回归用于发现输入变量和输出变量之间的关系,一般变量为实数。我们的目标是估计映射从输入到输出的映射核函数。下面从一个简单示例开始:
1 --> 2
3 --> 6
4.3 --> 8.6
1.1 --> 14.2
看到上面数据,估计你已经看出它们之间的关系:f(x) = 2x
但是现实数据不会这么直接。下面示例数据来自Vehicles.txt文件。每行数据使用逗号分割,第一个数据为输入数据,第二个为输出数据,我们的目标是发现线性回归关系:基于汽车登记量估计省份人口数量。示例数据如下:
145263, 127329
204477, 312027
361034, 573694
616716, 891181
885665, 1059114
773600, 1221218
850513, 1326513
996733, 1543752
827967, 1571053
1011436,1658138
1222738,1970521
2404651,3744398
2259795,4077166
2844588,4404246
2774071,4448146
3011089,4915123
3169307,5074261
3346791,5850850
3702114,5888472
5923476,10008349
- 加载数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn import linear_model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.metrics as sm
import pickle
filename = "data/vehicles.txt"
x = []
y = []
with open(filename, 'r') as lines:
for line in lines:
xt, yt = [float(i) for i in line.split(',')]
x.append(xt)
y.append(yt)
上面代码加载文件至x,y变量中,x是自变量,y是响应变量。在循环内读取每一行,然后基于逗号分裂为两个变量并转为浮点型。
- 划分训练集和测试集
构建机器学习模型,需要划分训练集和测试集,训练集用于构建模型,测试集用于验证模型并检查模型是否满足要求。
num_training = int(0.8 * len(x))
num_test = len(x) - num_training
# 训练数据占80%
x_train = np.array(x[: num_training]).reshape((num_training, 1))
y_train = np.array(y[: num_training])
# 测试数据占20%
x_test = np.array(x[num_training:]).reshape((num_test, 1))
y_test = np.array(y[num_training:])
首先取80%数据作为训练集,剩余的作为测试集。这时我们构造了四个数组:x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test。
- 训练模型
现在准备训练模型,需要使用regressor对象。
# Create linear regression object
linear_regressor = linear_model.LinearRegression()
# Train the model using the training sets
linear_regressor.fit(x_train, y_train)
首先从sklearn库中导入linear_model方法,用于实现线性回归,里面包括目标值:输入变量的线性组合。然后使用LinearRegression() 函数执行最小二乘法执行线性回归。最后fit函数用于拟合线性模型,需要传入两个参数:x_train,y_train。
- 预测数据
上面基于训练集拟合线性模型,使用fit方法接收训练数据训练模型。为了查看拟合程度,我们可以使用训练数据进行预测:
y_train_pred = linear_regressor.predict(X_train)
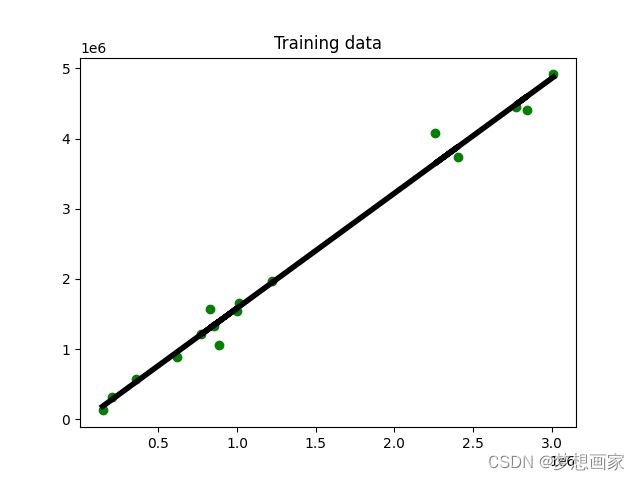
- 画图展示线性拟合情况
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(x_train, y_train, color='green')
plt.plot(x_train, y_train_pred, color='black', linewidth=4)
plt.title('Training data')
plt.show()
前面使用训练模型预测训练数据。对于未知数据不能确定模型性能,我们需要基于测试数据进行测试。
- 预测数据测试
下面基于测试数据进行预测并画图展示:
y_test_pred = linear_regressor.predict(x_test)
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(x_test, y_test, color='green')
plt.plot(x_test, y_test_pred, color='black', linewidth=4)
plt.title('Test data')
plt.show()
与我们预想的一致,省人口与汽车注册量成正相关。
评估模型精度
上面构建了回归模型,但我们需要评估模型的质量。这里我们定义错误为实际值与预测值之间的差异,下面我们看如何计算回归模型的精度。
- 计算回归模型精度
print("MAE =", round(sm.mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_test_pred), 2))
print("MSE =", round(sm.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred), 2))
print("Median absolute error =",
round(sm.median_absolute_error(y_test, y_test_pred), 2))
print("Explain variance score =",
round(sm.explained_variance_score(y_test, y_test_pred), 2))
print("R2 score =", round(sm.r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred), 2))
输出结果:
MAE = 241907.27
MSE = 81974851872.13
Median absolute error = 240861.94
Explain variance score = 0.98
R2 score = 0.98
R2得分接近1表示模型预测效果非常好。计算每个指标会很麻烦,一般选择一两个指标来评估模型。一个好的做法是MSE较低,解释方差得分较高。
-
Mean absolute error: 所有数据集的平均绝对值误差
-
Mean squared error: 所有数据集的平均误差平方,是最常用的指标之一。
-
Median absolute error: 所有数据集的误差中位数,该指标主要用于消除异常值影响
-
Explained variance score: 模型在多大程度上能够解释数据集中的变化。1.0的分数表明我们的模型是完美的。
-
R2 score: 这被读作r²,是决定系数。表示模型对未知样本的预测程度。最好的分数是1.0,但也可以是负值。
模型持久化
训练完模型,可以保存至文件中,下次需要模型预测可直接从文件加载。
下面看如何持久化模型。需要使用pickle模块,实现存储Python对象,它是Python标准库的一部分。
# 写入文件
output_model_file = "3_model_linear_regr.pkl"
with open(output_model_file, ' wb') as f:
pickle.dump(linear_regressor, f)
# 加载使用
with open(output_model_file, ' rb') as f:
model_linregr = pickle.load(f)
y_test_pred_new = model_linregr.predict(x_test)
print("New mean absolute error =",
round(sm.mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_test_pred_new), 2))
输出结果:
New mean absolute error = 241907.27
这里从文件加载数据至model_linregr变量,预测结果与上面一致。