AI学习(五):用tensorflow object detection 训练自己的数据集
0.前言
检测效果还是不错的,这里我使用了100张train图片和50张test图片进行标注(标注图片的时候尽量找清楚的,不要找一些犄角旮旯的,我吃过亏的,训练效果很不好),训练步数40000+,batch size=24。接下来我们开始吧。
1.labellmg的下载和使用
对下载好的jpg格式的图片进行标注,期间,需要下载labellmg。下载地址:https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg/releases

下载下来后是一个压缩文件,这是一款绿色软件,解压缩后,打开就能用。根据视频做好标注。
我是在object_detection文件夹下建了一个叫images的文件夹,在文件夹里,我分别建了一个叫train和test的文件,把train和test的图片分别放在了里面。然后进行的标注。

电脑切换到英文输入法,按下“w”,就会出现十字框。然后对你想标注的对象进行标注。

这就是标注的结果。生成了XML文件。
2.生成CSV文件
打开spyder,新建文件,将下面这段代码输入进去,重命名为xml_to_csv
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jan 16 00:52:02 2018
@author: Xiang Guo
"""
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
os.chdir('F:\\ML\\models-master\\research\\object_detection\\images\\train')
path = 'F:\\ML\\models-master\\research\\object_detection\\images\\train'
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
def main():
image_path = path
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('zjl_train.csv', index=None)
print('Successfully converted xml to csv.')
main()

绿色的路径是要对应到你的train文件和test文件的,生成train的csv时候是…\train,生成test的csv文件的时候是…\test.
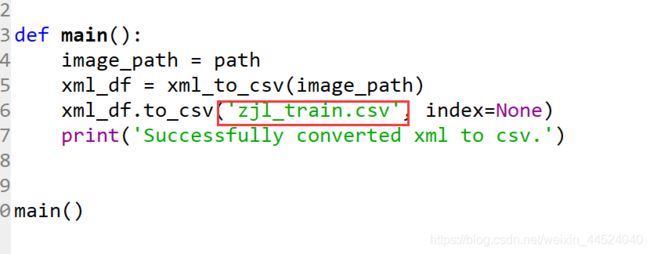
这里选择你想生成的文件的名字。点击下图标红的按钮。

最终我在train文件夹中生成了 zjl_train.csv,在test文件夹中生成了zjl_test.csv。
3.生成record文件。
把刚刚生成的train.csv和test.csv文件复制到object_detection文件下的data文件中
打开spyder,复制下面代码,保存命名为generate_tfr.py。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jan 16 01:04:55 2018
@author: Xiang Guo
"""
"""
Usage:
# From tensorflow/models/
# Create train data:
python generate_tfr.py --csv_input=data/zjl_train.csv --output_path=data/train.record
# Create test data:
python generate_tfr.py --csv_input=data/zjl_test.csv --output_path=data/test.record
"""
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
os.chdir('F:\\ML\\models-master\\research\\object_detection\\')
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('csv_input', '', 'Path to the CSV input')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', '', 'Path to output TFRecord')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# TO-DO replace this with label map
def class_text_to_int(row_label):
if row_label == 'zjl':
return 1
else:
None
def split(df, group):
data = namedtuple('data', ['filename', 'object'])
gb = df.groupby(group)
return [data(filename, gb.get_group(x)) for filename, x in zip(gb.groups.keys(), gb.groups)]
def create_tf_example(group, path):
with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)), 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
encoded_jpg_io = io.BytesIO(encoded_jpg)
image = Image.open(encoded_jpg_io)
width, height = image.size
filename = group.filename.encode('utf8')
image_format = b'jpg'
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
classes_text = []
classes = []
for index, row in group.object.iterrows():
xmins.append(row['xmin'] / width)
xmaxs.append(row['xmax'] / width)
ymins.append(row['ymin'] / height)
ymaxs.append(row['ymax'] / height)
classes_text.append(row['class'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_text_to_int(row['class']))
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classes_text),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classes),
}))
return tf_example
def main(_):
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.output_path)
path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'images/train')
examples = pd.read_csv(FLAGS.csv_input)
grouped = split(examples, 'filename')
for group in grouped:
tf_example = create_tf_example(group, path)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
output_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), FLAGS.output_path)
print('Successfully created the TFRecords: {}'.format(output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
注意第99行,这里时提取test和train的csv的路径,
1.生成test.Record,如图红框位置,你要改成’images/test’,保存,然后在anaconda prompt中在object_detection文件夹下运行 :
python generate_tfr.py --csv_input=images/train/chair_train.csv --output_path=data/train.record
这说明是从data文件下提取test.csv文件,同时在data文件下输出test.record
2.生成test.Record,如图红框位置,你要改成’images/train’,保存,然后在anaconda prompt中在object_detection文件夹下运行:
python generate_tfr.py --csv_input=images/test/chair_test.csv --output_path=data/test.record
这说明是从data文件下提取train.csv文件,同时在data文件下输出train.record

这时候你就看到了在data文件下分别生成了test.record和train.record。如下图所示。

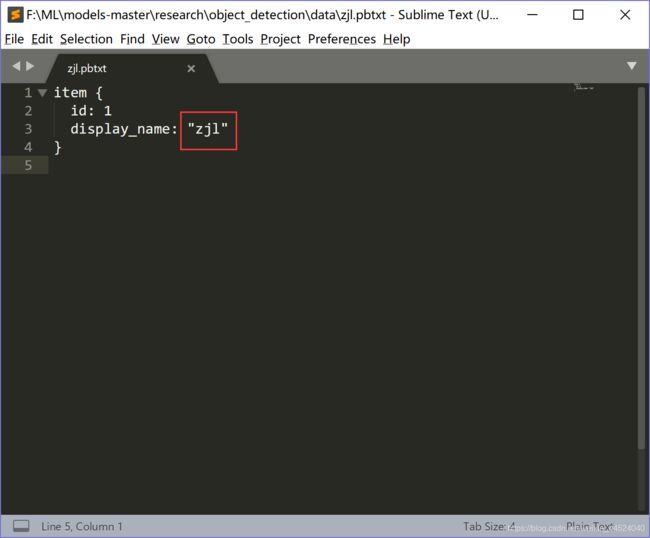
这里有好多label map,随便找一个在这个文件夹下复制粘贴,重命名为“zjl”,打开zjl,将下面的全部删除(你想想出现几个种类就留下几个item),更改红框位置的名称。
4.配置训练文件
我下载了一个app,sublime text,百度直接下载就行,就是一个记事本打开用的。下载完后打开,将下面的代码复制进去,重命名为ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco,在object_detection文件夹下新建一个文件夹,重命名为training,将ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco保存到training中。

修改你希望的种类数量,这里修改为1.
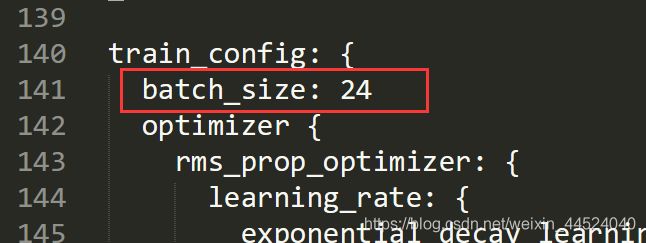
batch_size我是修改为24,数字越大越容易收敛,训练速度越慢。网上有说为了先尝试一下修改为1的,但是我就出问题了,所以我修改为24,问题解决。

注意修改上图中标注的位置的路径
# SSD with Mobilenet v1 configuration for MSCOCO Dataset.
# Users should configure the fine_tune_checkpoint field in the train config as
# well as the label_map_path and input_path fields in the train_input_reader and
# eval_input_reader. Search for "PATH_TO_BE_CONFIGURED" to find the fields that
# should be configured.
model {
ssd {
num_classes: 1
box_coder {
faster_rcnn_box_coder {
y_scale: 10.0
x_scale: 10.0
height_scale: 5.0
width_scale: 5.0
}
}
matcher {
argmax_matcher {
matched_threshold: 0.5
unmatched_threshold: 0.5
ignore_thresholds: false
negatives_lower_than_unmatched: true
force_match_for_each_row: true
}
}
similarity_calculator {
iou_similarity {
}
}
anchor_generator {
ssd_anchor_generator {
num_layers: 6
min_scale: 0.2
max_scale: 0.95
aspect_ratios: 1.0
aspect_ratios: 2.0
aspect_ratios: 0.5
aspect_ratios: 3.0
aspect_ratios: 0.3333
}
}
image_resizer {
fixed_shape_resizer {
height: 300
width: 300
}
}
box_predictor {
convolutional_box_predictor {
min_depth: 0
max_depth: 0
num_layers_before_predictor: 0
use_dropout: false
dropout_keep_probability: 0.8
kernel_size: 1
box_code_size: 4
apply_sigmoid_to_scores: false
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
}
feature_extractor {
type: 'ssd_mobilenet_v1'
min_depth: 16
depth_multiplier: 1.0
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
loss {
classification_loss {
weighted_sigmoid {
}
}
localization_loss {
weighted_smooth_l1 {
}
}
hard_example_miner {
num_hard_examples: 3000
iou_threshold: 0.99
loss_type: CLASSIFICATION
max_negatives_per_positive: 3
min_negatives_per_image: 0
}
classification_weight: 1.0
localization_weight: 1.0
}
normalize_loss_by_num_matches: true
post_processing {
batch_non_max_suppression {
score_threshold: 1e-8
iou_threshold: 0.6
max_detections_per_class: 100
max_total_detections: 100
}
score_converter: SIGMOID
}
}
}
train_config: {
batch_size: 24
optimizer {
rms_prop_optimizer: {
learning_rate: {
exponential_decay_learning_rate {
initial_learning_rate: 0.0004
decay_steps: 800720
decay_factor: 0.95
}
}
momentum_optimizer_value: 0.9
decay: 0.9
epsilon: 1.0
}
}
# Note: The below line limits the training process to 200K steps, which we
# empirically found to be sufficient enough to train the pets dataset. This
# effectively bypasses the learning rate schedule (the learning rate will
# never decay). Remove the below line to train indefinitely.
num_steps: 200000
data_augmentation_options {
random_horizontal_flip {
}
}
data_augmentation_options {
ssd_random_crop {
}
}
}
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "data/train.record"
}
label_map_path: "data/zjl.pbtxt"
}
eval_config: {
num_examples: 8000
# Note: The below line limits the evaluation process to 10 evaluations.
# Remove the below line to evaluate indefinitely.
max_evals: 10
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "data/test.record"
}
label_map_path: "data/zjl.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
5.准备训练
然后在object_detection文件夹下运行:
python train.py --logtostderr --train_dir=training/ --pipeline_config_path=training/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config
从现在开始,开始训练。
这里我使用了100+train和50+test张照片,训练步数40000+

再在object_detection打开,输入tensorboard --logdir=training

我是训练到40000步+然后就停止了,直接点击"×"号,就能停止训练。
6.测试结果

在object_detection中新建一个文件夹,将名字命名为“zjl_detection”
打开training文件夹,我们会看到有新生成的文件。Anaconda Prompt 定位到 models\research\object_detection 文件夹下,运行
python export_inference_graph.py \ --input_type image_tensor \ --pipeline_config_path training\ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config \ --trained_checkpoint_prefix training/model.ckpt-40414 \ --output_directory zjl_detection

40414这个数字要修改成training文件夹中对应的最大数字,zjl_detection要对应到刚刚新建好的文件夹的名称。
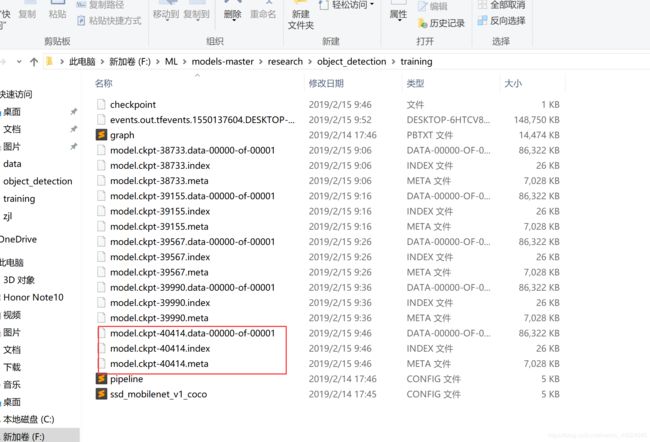
回车后,命令开始运行,运行结束后zjl_detection生成新的文件。

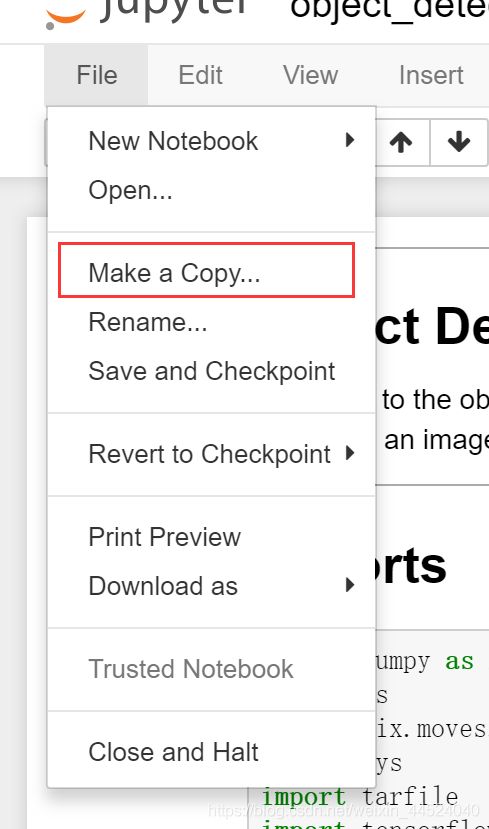
Anaconda Prompt 定位到 models\research\object_detection 文件夹下,运行jupyter notebook。打开自带的object_detection_tutorial.ipynb,打开后复制一下这个文件,重命名为zjl(最好不要出现中文哦)。
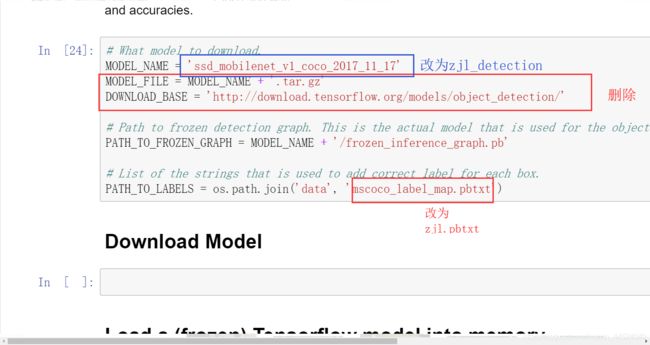
从网上下载几张周杰伦的图片,放入object_detection/test_images中,重命名为image1 ,image2。。。。。。


点击run all,开始运行。会等待一段时间。
运行结束。
补充
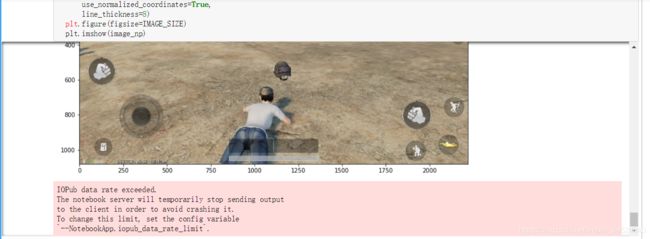
运行程序最后,可能会出现这种问题。在anaconda prompt中输入:jupyter notebook --generate-config,可以看到生成一个路径

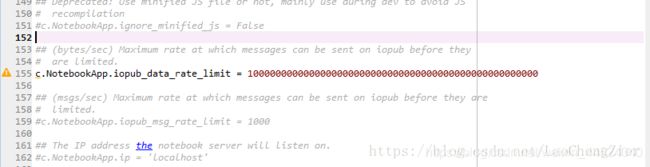
找到对应路径下的文件,从中找到iopub_data_rate_limit,在去掉注释后多加好多0得意
重新启动jupyter notebook,即可看到原先报错的内容可以显示啦

