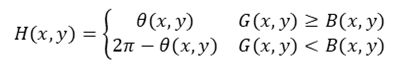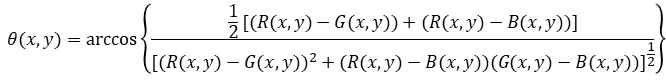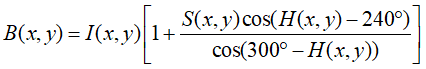色彩空间转换
彩色图像的颜色空间
三原色原理
为了标准化起见,国际照明委员会(CIE)规定用波长为700nm、546.1nm、435.8nm的单色光分别作为红(R)、绿(G)、蓝(B)三原色。红绿蓝三原色按照比例混合可以得到各种颜色,其配色方程为︰C=aR+bG+cB
彩色模型(也称彩色空间或彩色系统)︰简化彩色规范
- 坐标系-子空间:每种颜色用坐标系的单个点表示
- 彩色模型有很多︰在实际项目开发应用较多的有RGB、CMY ( CMYK)、HSI、YUv、YCbCr、Lab等。
RGB模型与颜色空间坐标系
- 常用的一种彩色信息表达方式
- 用红、绿、蓝三原色的亮度来定量表示颜色
- 该模型也称为加色混色模型
- 以RGB三色光相互叠加来实现混色的方法
- 适合于显示器等发光体的显示
图1 RGB颜色空间坐标系
- 如图1所示,RGB颜色空间基于三维直角坐标系,包括R、G、B三个原始光谱分量。
- RGB颜色空间中的R、G、B三个分量的值分别描述了红色、绿色、蓝色的亮度值。
- 为了方便描述,将三个分量都进行归一化,使得三元组中的每个数值表示红色、绿色、蓝色三者的比例。在图1中,原点(0, 0, 0)代表黑色,点(1, 1, 1)代表白色,点(1, 0, 0)代表红色,点(0, 1, 0)代表绿色,点(0, 0, 1)代表蓝色。
RGB图像的大小
- 每一幅红、蓝、绿图像都是一幅8bit图像
- RGB图像的每一个像素包含24bit位深
- 24bit位深的彩色图像称为全(真)彩色图像
- 全彩色图像的颜色种类总数为2的24次方,16777216
HSI颜色模型与颜色空间
HSI(Hue-Saturation-Intensity , HSI)模型用H、S、I三参数描述颜色特性。
- H(色调)由角度来表示,彩色的色调反映了该彩色最接近什么样的光谱波长;
- S(饱和度)表示颜色的深浅程度,饱和度越高,颜色越深;
- I(亮度)由物体反射系数来决定。反射系数越大,物体的亮度越大,反之越小。
- I分量为强度或亮度与图像的彩色信息无关;
- H和S分量为彩色信息与人感受颜色的方式紧密相连。
图2 HSI颜色空间
- 如图2所示,HSI颜色空间圆锥体的中间横截面称为色环,色环更加清晰地展示了色调和饱和度两个参数。
- 如果把亮度作为色环的垂线,那么H、S、I构成一个柱形彩色空间。HSI模型的三个属性定义了一个三维颜色空间。
- 色调H由角度表示,其反映了该颜色最接近哪个光谱波长。在色环中,0°表示红色光谱,120°表示绿色光谱,240°表示蓝色光谱。饱和度S由色环的圆心到颜色点的半径表示,距离越长表示饱和度越高,则颜色越鲜明。
RGB与HSI的转换
给定一幅RGB颜色空间格式的图像,将图像的R分量、G分量、B分量分别归一化。在RGB颜色空间中,位于(x,y)空间位置的像素点的颜色用该像素点的R分量R(x,y)、G分量G(x,y)和B分量B(x,y)三个数值表示。在HSI颜色空间中,位于空间位置的像素点的H分量H(x,y)、S分量S(x,y)、I分量I(x,y)可分别由以下公式计算得到:
(1)当H(x,y)∈ [00,1200)时转换公式为:
(2)当H(x,y)∈ [1200,2400)时转换公式为:
(3)当H(x,y)∈ [2400,3600)时转换公式为:
编写RGB与HSI彩色空间转换实验
对于彩色图像的直方图均衡化,首先需利用HSI函数将图像转换至HSI颜色空间,再利用设计的RGB函数将图像从HSI颜色空间转换至RGB颜色空间进行显示。最终,对彩色图像进行图像切割、检测操作,比如切割苹果、检测火焰等,根据测试效果。
代码
RGB转HIS函数;
1 #RGB转HSI颜色空间
2 def HSI(self,img):
3 r = img[:,:,0].astype(np.float32)
4 g = img[:,:,1].astype(np.float32)
5 b = img[:,:,2].astype(np.float32)
6
7 I = (r+g+b)/3
8 I = I/255
9 img_min = np.min(img,axis=-1)
10 S = 1 - (3/(r+g+b)*img_min)
11 a = 0.5*((r-g)+(r-b))
12 botton = ((r-g)**2+((r-b)*(g-b))+ sys.float_info.min)**0.5
13 den =a /botton
14 den[den>1]=1
15 den[den<-1]=-1
16 H = np.arccos(den)
17 index = np.where(g<b)
18 H[index]= 2*m.pi-H[index]
19 H /= 2 * m.pi
20 H[S == 0] = 0
21
22 hsi = np.zeros([img.shape[0],img.shape[1],img.shape[2]],dtype=np.float32)
23 hsi[:,:,0] = H
24 hsi[:,:,1] = S
25 hsi[:,:,2] = I
26 return hsi
HIS转RGB函数;
1 #HSI转RGB颜色空间
2 def RGB(self,hsi):
3 #rgb
4 H = hsi[:,:,0]
5 S = hsi[:,:,1]
6 I = hsi[:,:,2]
7 H *=2*m.pi
8
9 rgb = np.zeros(hsi.shape,np.uint8)
10 R = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32)
11 G = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32)
12 B = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32)
13
14 index = np.where((H>=0)&(H<2*m.pi/3))
15 R[index] = I[index] * (1+(S[index]*np.cos(H[index]))/(np.cos(m.pi/3-H[index])))
16 B[index] = I[index]*(1-S[index])
17 G[index] = 3*I[index]-(B[index]+R[index])
18
19 index = np.where((H>=2*m.pi/3)&(H<4*m.pi/3))
20 R[index] = I[index]*(1-S[index])
21 G[index] = I[index] * (1+(S[index]*np.cos(H[index]-2*m.pi/3))/(np.cos(m.pi-H[index])))
22 B[index] = 3*I[index]-(R[index]+G[index])
23
24 index = np.where((H>=4*m.pi/3)&(H<2*m.pi))
25 B[index] = I[index] * (1+(S[index]*np.cos(H[index]-4*m.pi/3))/(np.cos(5*m.pi/3-H[index])))
26 G[index] = I[index]*(1-S[index])
27 R[index] = 3*I[index]-(G[index]+B[index])
28
29 rgb[:,:,0] = (255*R).astype(np.uint8)
30 rgb[:,:,1] = (255*G).astype(np.uint8)
31 rgb[:,:,2] = (255*B).astype(np.uint8)
32 return rgb
对苹果进行切割;
1 #苹果检测
2 def appleDetect(self,img):
3 # img = img.astype(np.float32)
4 r = img[:,:,0]
5 g = img[:,:,1]
6 b = img[:,:,2]
7 hsi = self.HSI(img)
8 H = hsi[:,:,0]
9 H *=2*m.pi
10 print(img.shape)
11 apple = np.zeros(img.shape,dtype=np.uint32)
12 detect_ground = np.where(((H>=0)&(H<=m.pi/3.6))|((H>m.pi*1.3)&(H<=2*m.pi)))
13 apple[:,:,0][detect_ground] = r[detect_ground]
14 apple[:,:,1][detect_ground] = g[detect_ground]
15 apple[:,:,2][detect_ground] = b[detect_ground]
16 apple = apple.astype(np.uint8)
17 cv.imshow("apple_img",apple)
对火焰进行检测;
1 #火焰检测
2 def fireDetect(self,img):
3
4 r = img[:,:,0]
5 g = img[:,:,1]
6 b = img[:,:,2]
7 hsi = self.HSI(img)
8 H = hsi[:,:,0]
9 S = hsi[:,:,1]
10 I = hsi[:,:,2]
11 S *= 100
12 I *= 255
13 H *=2*m.pi
14 # rgb = self.RGB(hsi)
15 detect_ground = np.where((H >= 2*m.pi/3) & (H< 2 * m.pi) & (S >= 20 )& (I >=100))
16 fire = np.zeros(img.shape,dtype=np.uint32)
17 # print(detect_ground)
18 fire[:,:,0][detect_ground] = r[detect_ground]
19 fire[:,:,1][detect_ground] = g[detect_ground]
20 fire[:,:,2][detect_ground] = b[detect_ground]
21 # print(fire)
22 fire = fire.astype(np.uint8)
23 cv.imshow("fire",fire)
图像显示;
1 #图像显示
2 def main(self):
3 img_apple = cv.imread("./data/images/apple.jpg")
4 img_fire = cv.imread("./data/images/fire.jpg")
5 hsi = self.HSI(img_apple)
6 rgb = self.RGB(hsi)
7 self.appleDetect(img_apple)
8 self.fireDetect(img_fire)
9 cv.imshow("orgin_apple",img_apple)
10 # cv.imshow("I",I)
11 # cv.imshow("S",S)
12 # cv.imshow("H",H)
13 cv.imshow("hsi",hsi)
14 cv.imshow("hsi_to_rgb_img",rgb)
程序执行;
1 if __name__=="__main__":
2 PicDetect().main()
3 k = cv.waitKey(0)&0xFF
4 if k == 27:
5 cv.destroyAllWindows()
6