激光SLAM源码解析S-LOAM(一)点云特征提取
点云帧数据
激光雷达点云数据会以一定频率从激光雷达传输到接收器,比如10Hz,就是每间隔0.1秒发送一帧点云数据。
激光SLAM接收到每帧点云数据后,需要提取特征点,然后进行点云配准得到帧间位姿变换,累计变换得到里程计。
点云特征数据
点云特征点的提取,主要目的是为了配准,然而过滤掉大量非特征点数据,起到了减少数据量的作用。
因为点云本身是稀疏的,所以点云的主要是特征是面特征,其次是线特征,很难利用点特征。
平面的特征是曲率小,因此点云中曲率小的点可以标记为平面点,曲率可以用来提取点云平面特征。
空间面曲率的计算可以用点周围小片区域来估计。有一种简单计算曲率(空间面曲率)的方法,就是用线曲率近似面曲率。
点云曲率的挑选需要用到点云索引。虽然激光雷达产生的点云帧是二维的,但是pcl中存储的点云是一维的(不方便操作)。根据激光雷达点云帧的产生机制,我们可以对一维pcl点云重建索引,将点信息存储在二维数组中。
点云数据的输出
最终需要的点云数据是平面特征点云,我们可以把平面特征点云发布出去供后面配准程序使用,同时也可以把原始点云帧发布出去方便在rviz中查看。
S-LOAM代码结构
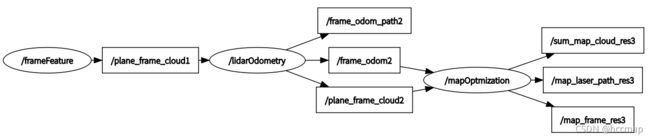
S-LOAM的ros节点图
header.h
代码注释较详细,如下所示。
#ifndef SLOAM_HEADER_H
#define SLOAM_HEADER_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h"
#include "nav_msgs/Odometry.h"
#include "nav_msgs/Path.h"
#include "pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h"
#include "pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h"
#include "ceres/ceres.h"
#include "ceres/rotation.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//int N_SCAN_ROW=16; // 激光雷达线数,16线
int N_SCAN_ROW=64; // 激光雷达线数,64线
/**
* 点信息结构
* value,indexInRow
*/
typedef struct {
float value; // 属性值,比如曲率
int indexInRow; // 行内点索引
} PointInfo;
/**
* 点结构
* x,y,z,intensity,ring,time
* 按照pcl规定,自定义点云结构,主要用于点云数据的接收与解析
* 自定义点云结构的缺点是,在有些pcl函数中无法识别,比如kdtree中
*/
struct VelodynePointXYZIRT {
PCL_ADD_POINT4D // 位置
PCL_ADD_INTENSITY; // 激光点反射强度,也可以存点的索引
//uint16_t ring; // 各点所在扫描线号,可选
//float time; // 各点时间戳,相对于帧第一个点时间差,可选
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
} EIGEN_ALIGN16; // 内存16字节对齐,EIGEN SSE优化要求
// 注册为PCL点云格式
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT (VelodynePointXYZIRT,
(float, x, x)(float, y, y)(float, z, z)(float, intensity, intensity)
//(uint16_t, ring, ring)(float, time, time)
)
/**
* 6D位姿点结构定义(x,y,z,roll,pitch,yaw)
* x,y,z,intensity,roll,pitch,yaw,time
*/
struct PointXYZIRPYT
{
PCL_ADD_POINT4D
PCL_ADD_INTENSITY;
float roll;
float pitch;
float yaw;
double time;
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
} EIGEN_ALIGN16;
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT (PointXYZIRPYT,
(float, x, x)(float, y, y)(float, z, z)(float, intensity, intensity)
(float, roll, roll)(float, pitch, pitch)(float, yaw, yaw)
(double, time, time)
)
#endif //SLOAM_HEADER_H frameFeature.cpp
代码注释较详细,如下所示。
/**
* Created by haocaichao on 2021/8/29
*
* 点云特征提取
* (1)接收原始点云
* (2)重建点云索引
* (3)计算点云曲率
* (4)提取平面特征点,点云抽稀
* (5)发布点云
*/
#include "header.h"
typedef VelodynePointXYZIRT PointType; //点类型名称重定义,用于接收点云中各点
typedef pcl::PointXYZI PointTypeOut; //pcl点类型名称重定义,简化
ros::Subscriber sub_lidar_frame_cloud; //定义ros订阅者,接收激光雷达
ros::Publisher pub_plane_frame_cloud; //定义ros发布者,发布平面特征点云
ros::Publisher pub_org_frame_cloud; //定义ros发布者,发布原始点云
//定义pcl点云对象,存储原始点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr framePtr(new pcl::PointCloud());
//定义pcl点云对象,存储平面特征点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr framePlanePtr(new pcl::PointCloud());
//定义容器,存储每线点云
std::vector> v_scan_row = std::vector>(N_SCAN_ROW);
//定义容器,存储每线点云中各点信息
std::vector> v_scan_row_info = std::vector>(N_SCAN_ROW);
float planeMin=0.5; //定义平面曲率最小门槛值
int planeSpan=2; //定义点间隔,用于抽稀
int rowIndexStart=0; //定义点云线内点起点索引
int rowIndexEnd=0; //定义点云线内点终点索引
pcl::VoxelGrid downSizeFilterPlane; //定义点云下采样对象,用于点云抽稀
//接收原始点云,处理,发布
void cloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &cldMsg) {
framePtr->clear(); //存储点云之前需要先清空
framePlanePtr->clear();
v_scan_row = std::vector>(N_SCAN_ROW);
v_scan_row_info = std::vector>(N_SCAN_ROW);
//将ros点云消息类型转换为pcl点云对象
pcl::fromROSMsg(*cldMsg, *framePtr);
//遍历点云各点,重建点云索引
for (size_t i = 0; i < framePtr->points.size(); ++i) {
PointType point;
point.x = framePtr->points[i].x;
point.y = framePtr->points[i].y;
point.z = framePtr->points[i].z;
point.intensity = framePtr->points[i].intensity;
int scanID = -1;
int flag = 2; //1-使用原始点云线号ring信息 2-根据垂向角度计算点云线号
if (flag == 1) {
// scanID = framePtr->points[i].ring;
} else {
//计算垂向角度
float angle = atan(point.z / sqrt(point.x * point.x + point.y * point.y)) * 180 / M_PI;
if (N_SCAN_ROW == 16) { //16线点云线号计算
if (angle >= -15 || angle <= 15) {
scanID = int((angle + 15) / 2 + 0.5);
}
}
if (N_SCAN_ROW == 64) { //64线点云线号计算
if (angle >= -24.33 || angle <= 2) {
if (angle >= -8.83){
scanID = int((2 - angle) * 3.0 + 0.5);
}else{
scanID = N_SCAN_ROW / 2 + int((-8.83 - angle) * 2.0 + 0.5);
}
}
}
}
if (scanID > -1 && scanID < N_SCAN_ROW) { //每条扫描线是一个点云对象
PointInfo p_info;
p_info.value = 0;
p_info.indexInRow = v_scan_row[scanID].size();
point.intensity=p_info.indexInRow+scanID/100.0;
v_scan_row[scanID].push_back(point); //用数组存储各线点云数据
v_scan_row_info[scanID].push_back(p_info); //用另一个数组同步存储各点信息
}
}
//计算点云曲率
for (int i = 0+rowIndexStart; i < N_SCAN_ROW-rowIndexEnd; i++) {
for (int j = 5; j < int(v_scan_row[i].size()) - 5; j++) {
float diffX =
v_scan_row[i].points[j - 5].x + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 4].x + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 3].x +
v_scan_row[i].points[j - 2].x + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 1].x
- 10 * v_scan_row[i].points[j].x
+ v_scan_row[i].points[j + 1].x + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 2].x + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 3].x +
v_scan_row[i].points[j + 4].x + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 5].x;
float diffY =
v_scan_row[i].points[j - 5].y + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 4].y + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 3].y +
v_scan_row[i].points[j - 2].y + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 1].y
- 10 * v_scan_row[i].points[j].y
+ v_scan_row[i].points[j + 1].y + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 2].y + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 3].y +
v_scan_row[i].points[j + 4].y + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 5].y;
float diffZ =
v_scan_row[i].points[j - 5].z + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 4].z + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 3].z +
v_scan_row[i].points[j - 2].z + v_scan_row[i].points[j - 1].z
- 10 * v_scan_row[i].points[j].z
+ v_scan_row[i].points[j + 1].z + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 2].z + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 3].z +
v_scan_row[i].points[j + 4].z + v_scan_row[i].points[j + 5].z;
//存储各线各点曲率值
v_scan_row_info[i][j].value = (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ);
}
}
//遍历各线,再遍历各点,根据曲率门槛值筛选出平面特征点云
for (int i = 0+rowIndexStart; i < N_SCAN_ROW-rowIndexEnd; i++) {
size_t jstart = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < v_scan_row_info[i].size(); j++) {
if (j >= jstart && v_scan_row_info[i][j].value < planeMin) {
PointTypeOut pt;
pt.x = v_scan_row[i][v_scan_row_info[i][j].indexInRow].x;
pt.y = v_scan_row[i][v_scan_row_info[i][j].indexInRow].y;
pt.z = v_scan_row[i][v_scan_row_info[i][j].indexInRow].z;
pt.intensity = v_scan_row[i][v_scan_row_info[i][j].indexInRow].intensity;
framePlanePtr->push_back(pt);
jstart = j + planeSpan; //按指定间隔提取点云,相当于抽稀
}
}
}
//点云下采样,抽稀
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_temp(new pcl::PointCloud());
downSizeFilterPlane.setInputCloud(framePlanePtr);
downSizeFilterPlane.filter(*cloud_temp);
//发布平面特征点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 planeCloudMsg;
pcl::toROSMsg(*framePlanePtr, planeCloudMsg); //将pcl点云对象转换为ros点云消息类型
planeCloudMsg.header.stamp = cldMsg->header.stamp;
planeCloudMsg.header.frame_id = "map";
pub_plane_frame_cloud.publish(planeCloudMsg);
//发布原始点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 orgCloudMsg;
orgCloudMsg=*cldMsg;
orgCloudMsg.header.frame_id="map";
pub_org_frame_cloud.publish(orgCloudMsg);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
//针对不同线数激光雷达数据,设置不同参数
if(N_SCAN_ROW==16){
planeMin=0.05;
planeSpan=3;
}
if(N_SCAN_ROW==64){
planeMin=0.005;
planeSpan=25;
rowIndexStart=5;
rowIndexEnd=5;
}
downSizeFilterPlane.setLeafSize(0.2,0.2,0.2); //设置抽稀参数
ros::init(argc, argv, "FrameFeature");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
//订阅原始激光雷达数据
sub_lidar_frame_cloud = nh.subscribe("/velodyne_points", 10, cloudHandler);
//发布平面特征点云
pub_plane_frame_cloud = nh.advertise("/plane_frame_cloud1", 100);
//发布原始点云
pub_org_frame_cloud = nh.advertise("/org_frame_cloud1", 100);
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m----> FrameFeature Started.\033[0m");
ros::spin();
return 0;
} 代码地址为(GitHub - haocaichao/S-LOAM: S-LOAM(Simple LOAM) 是一种简单易学的激光SLAM算法,整个程序只有几百行代码,十分方便学习与试验分析。)。