【图像轮廓与图像分割修复】
文章目录
- 前言
-
- 1、查找并绘制轮廓
-
- C++代码示例一
- 结果
- C++代码示例二
- 结果
- 2、寻找物体的凸包
-
- C++代码示例一
- 结果
- C++代码示例二
- 结果
- 3、使用多边形将轮廓包围
-
- 结果
- C++代码示例一
- 结果
- C++代码示例二
前言
虽然Canny之类的边缘检测算法可以根据像素之间的差异,检测出轮廓边界的像素,但是它并没有将轮廓作为一个整体。
- 如何查找并绘制轮廓
- 如何寻找物体的凸包
- 如何使用多边形逼近物体
- 认识图像的矩
- 如何利用OpenCV进行图像修补
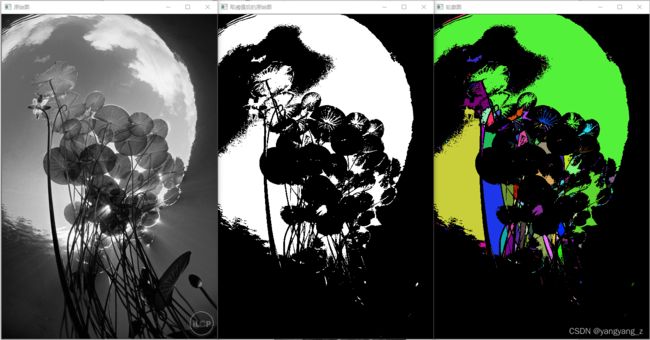
1、查找并绘制轮廓
一个轮廓一般对应一系列的点,也就是图像中的一条曲线,其表示方法可能根据不同的情况而有所不同。在OpenCV中可以用findContours()函数从二值图像中查找轮廓。
C++代码示例一
#include结果
C++代码示例二
#include结果
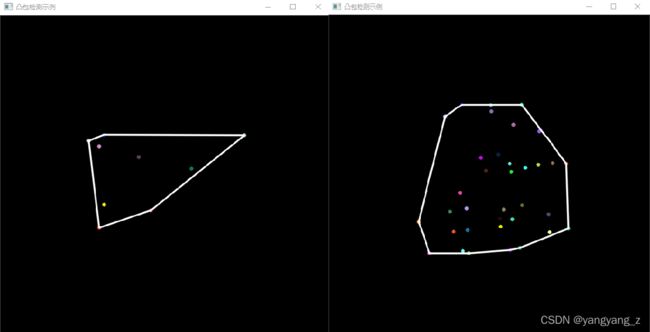
2、寻找物体的凸包
凸包(Convex Hull)是一个计算机中常见的概念。简单来说,给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构造成的凸多边形,它是能包含点集中所有点的。
C++代码示例一
#include结果
C++代码示例二
#include结果
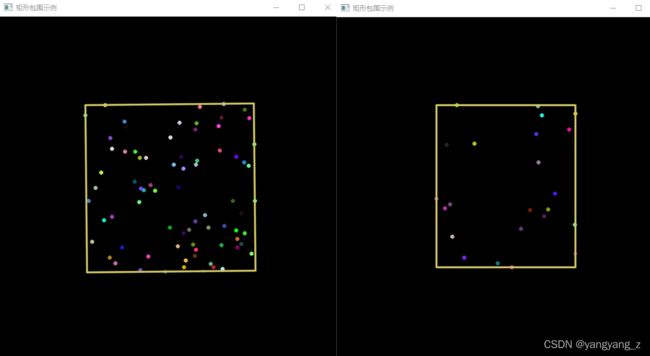
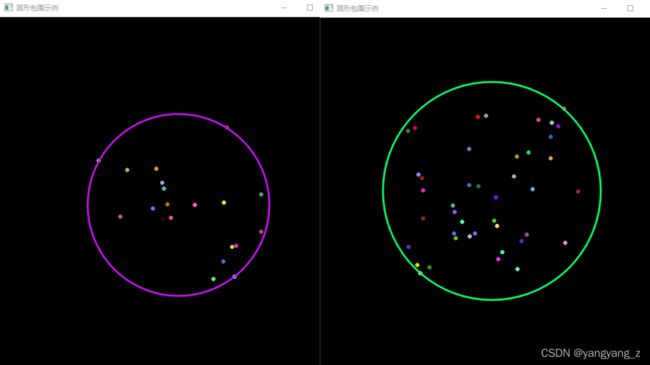
3、使用多边形将轮廓包围
在实际应用中,常常会有将检测到的轮廓用多边形表示出来的需求。
- 返回外部矩形边界:boundingRect()函数
- 寻找最小包围矩形:minAreaRect()函数
- 寻找最小包围圆形:minEnclosingCircle()函数
- 用椭圆拟合二维点集:fitEllipse()函数
- 逼近多边形曲线:approxPolyDP()函数
结果
C++代码示例一
#include结果
C++代码示例二
#include