各种注意力机制PyTorch实现
给出了整个系列的PyTorch的代码实现,以及使用方法。
各种注意力机制
Pytorch implementation of “Beyond Self-attention: External Attention using Two Linear Layers for Visual Tasks—arXiv 2020.05.05”
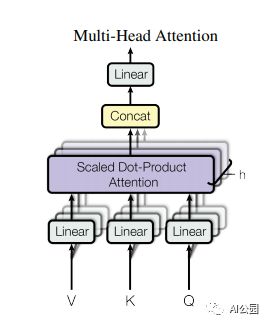
Pytorch implementation of “Attention Is All You Need—NIPS2017”
Pytorch implementation of “Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks—CVPR2018”
Pytorch implementation of “Selective Kernel Networks—CVPR2019”
Pytorch implementation of “CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module—ECCV2018”
Pytorch implementation of “BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module—BMCV2018”
Pytorch implementation of “ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks—CVPR2020”
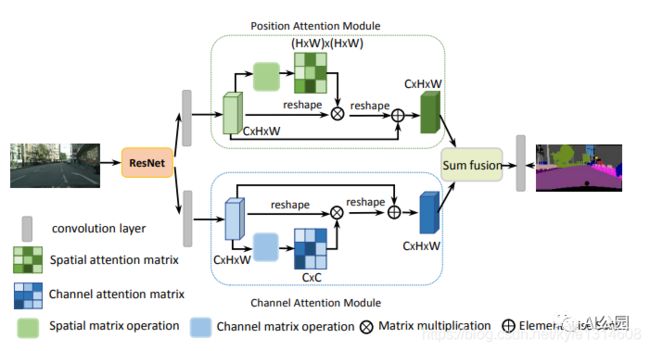
Pytorch implementation of “Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation—CVPR2019”
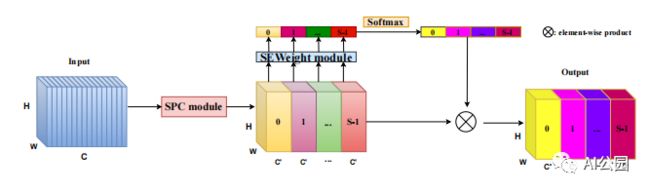
Pytorch implementation of “EPSANet: An Efficient Pyramid Split Attention Block on Convolutional Neural Network—arXiv 2020.05.30”
Pytorch implementation of “ResT: An Efficient Transformer for Visual Recognition—arXiv 2020.05.28”
- 外部注意力
1.1. 论文
“Beyond Self-attention: External Attention using Two Linear Layers for Visual Tasks”
1.2. 概要
from attention.ExternalAttention import ExternalAttention
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,49,512)
ea = ExternalAttention(d_model=512,S=8)
output=ea(input)
print(output.shape)
- 自注意力
2.1. 论文
“Attention Is All You Need”
1.2. 概要
from attention.SelfAttention import ScaledDotProductAttention
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,49,512)
sa = ScaledDotProductAttention(d_model=512, d_k=512, d_v=512, h=8)
output=sa(input,input,input)
print(output.shape)
- 简化的自注意力
3.1. 论文
None
3.2. 概要
from attention.SimplifiedSelfAttention import SimplifiedScaledDotProductAttention
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,49,512)
ssa = SimplifiedScaledDotProductAttention(d_model=512, h=8)
output=ssa(input,input,input)
print(output.shape)
- Squeeze-and-Excitation 注意力
4.1. 论文
“Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks”
4.2. 概要
from attention.SEAttention import SEAttention
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
se = SEAttention(channel=512,reduction=8)
output=se(input)
print(output.shape)
- SK 注意力
5.1. 论文
“Selective Kernel Networks”
5.2. 概要
from attention.SKAttention import SKAttention
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
se = SKAttention(channel=512,reduction=8)
output=se(input)
print(output.shape)
- CBAM 注意力
6.1. 论文
“CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module”
6.2. 概要
from attention.CBAM import CBAMBlock
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
kernel_size=input.shape[2]
cbam = CBAMBlock(channel=512,reduction=16,kernel_size=kernel_size)
output=cbam(input)
print(output.shape)
- BAM 注意力
7.1. 论文
“BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module”
7.2. 概要
from attention.BAM import BAMBlock
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
bam = BAMBlock(channel=512,reduction=16,dia_val=2)
output=bam(input)
print(output.shape)
- ECA 注意力
8.1. 论文
“ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks”
8.2. 概要
from attention.ECAAttention import ECAAttention
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
eca = ECAAttention(kernel_size=3)
output=eca(input)
print(output.shape)
- DANet 注意力
9.1. 论文
“Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation”
9.2. 概要
from attention.DANet import DAModule
import torch
if __name__ == '__main__':
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
danet=DAModule(d_model=512,kernel_size=3,H=7,W=7)
print(danet(input).shape)
- 金字塔拆分注意力
10.1. 论文
“EPSANet: An Efficient Pyramid Split Attention Block on Convolutional Neural Network”
10.2. 概要
from attention.PSA import PSA
import torch
if __name__ == '__main__':
input=torch.randn(50,512,7,7)
psa = PSA(channel=512,reduction=8)
output=psa(input)
print(output.shape)
- 高效多头自注意力
11.1. 论文
“ResT: An Efficient Transformer for Visual Recognition”
11.2. 概要
from attention.EMSA import EMSA
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
if __name__ == '__main__':
input=torch.randn(50,64,512)
emsa = EMSA(d_model=512, d_k=512, d_v=512, h=8,H=8,W=8,ratio=2,apply_transform=True)
output=emsa(input,input,input)
print(output.shape)
MLP 系列
Pytorch implementation of “RepMLP: Re-parameterizing Convolutions into Fully-connected Layers for Image Recognition—arXiv 2020.05.05”
Pytorch implementation of “MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision—arXiv 2020.05.17”
Pytorch implementation of “ResMLP: Feedforward networks for image classification with data-efficient training—arXiv 2020.05.07”
Pytorch implementation of “Pay Attention to MLPs—arXiv 2020.05.17”
- RepMLP
1.1. 论文
“RepMLP: Re-parameterizing Convolutions into Fully-connected Layers for Image Recognition”
1.2. 概要
from mlp.repmlp import RepMLP
import torch
from torch import nn
N=4 #batch size
C=512 #input dim
O=1024 #output dim
H=14 #image height
W=14 #image width
h=7 #patch height
w=7 #patch width
fc1_fc2_reduction=1 #reduction ratio
fc3_groups=8 # groups
repconv_kernels=[1,3,5,7] #kernel list
repmlp=RepMLP(C,O,H,W,h,w,fc1_fc2_reduction,fc3_groups,repconv_kernels=repconv_kernels)
x=torch.randn(N,C,H,W)
repmlp.eval()
for module in repmlp.modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d) or isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm1d):
nn.init.uniform_(module.running_mean, 0, 0.1)
nn.init.uniform_(module.running_var, 0, 0.1)
nn.init.uniform_(module.weight, 0, 0.1)
nn.init.uniform_(module.bias, 0, 0.1)
#training result
out=repmlp(x)
#inference result
repmlp.switch_to_deploy()
deployout = repmlp(x)
print(((deployout-out)**2).sum())
- MLP-Mixer
2.1. 论文
“MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision”
2.2. 概要
from mlp.mlp_mixer import MlpMixer
import torch
mlp_mixer=MlpMixer(num_classes=1000,num_blocks=10,patch_size=10,tokens_hidden_dim=32,channels_hidden_dim=1024,tokens_mlp_dim=16,channels_mlp_dim=1024)
input=torch.randn(50,3,40,40)
output=mlp_mixer(input)
print(output.shape)
- ResMLP
3.1. 论文
“ResMLP: Feedforward networks for image classification with data-efficient training”
3.2. 概要
from mlp.resmlp import ResMLP
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,3,14,14)
resmlp=ResMLP(dim=128,image_size=14,patch_size=7,class_num=1000)
out=resmlp(input)
print(out.shape) #the last dimention is class_num
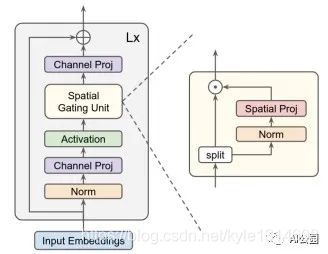
- gMLP
4.1. 论文
“Pay Attention to MLPs”
from mlp.g_mlp import gMLP
import torch
num_tokens=10000
bs=50
len_sen=49
num_layers=6
input=torch.randint(num_tokens,(bs,len_sen)) #bs,len_sen
gmlp = gMLP(num_tokens=num_tokens,len_sen=len_sen,dim=512,d_ff=1024)
output=gmlp(input)
print(output.shape)
Re-Parameter 系列
Pytorch implementation of “RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again—CVPR2021”
Pytorch implementation of “ACNet: Strengthening the Kernel Skeletons for Powerful CNN via Asymmetric Convolution Blocks—ICCV2019”
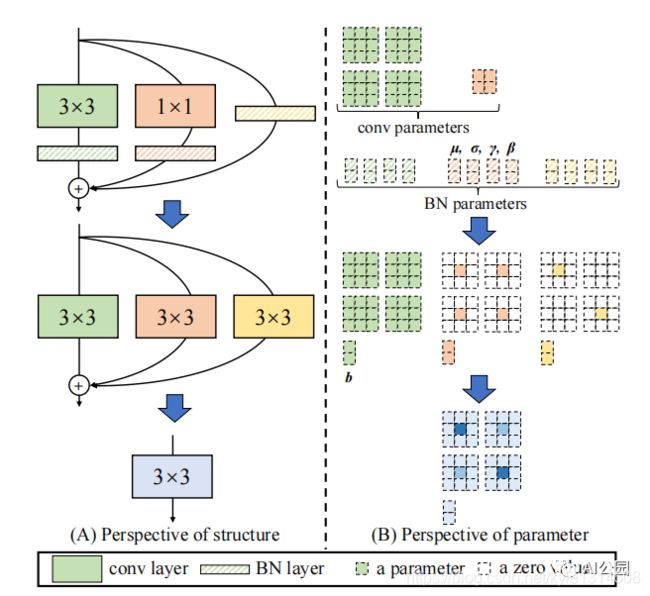
- RepVGG
1.1. 论文
“RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again”
1.2. 概要
from rep.repvgg import RepBlock
import torch
input=torch.randn(50,512,49,49)
repblock=RepBlock(512,512)
repblock.eval()
out=repblock(input)
repblock._switch_to_deploy()
out2=repblock(input)
print('difference between vgg and repvgg')
print(((out2-out)**2).sum())
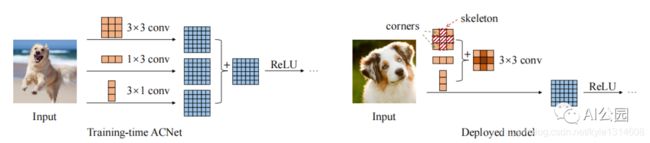
- ACNet
2.1. 论文
“ACNet: Strengthening the Kernel Skeletons for Powerful CNN via Asymmetric Convolution Blocks”
2.2. 概要
from rep.acnet import ACNet
import torch
from torch import nn
input=torch.randn(50,512,49,49)
acnet=ACNet(512,512)
acnet.eval()
out=acnet(input)
acnet._switch_to_deploy()
out2=acnet(input)
print('difference:')
print(((out2-out)**2).sum())