【Python机器学习】层次聚类AGNES、二分K-Means算法的讲解及实战演示(图文解释 附源码)
需要源码和数据集请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言私信~~~
层次聚类
在聚类算法中,有一类研究执行过程的算法,它们以其他聚类算法为基础,通过不同的运用方式试图达到提高效率,避免局部最优等目的,这类算法主要有网格聚类和层次聚类算法
网格聚类算法强调的是分批统一处理以提高效率,具体的做法是将特征空间划分为若干个网格,网格内的所有样本看成一个单元进行处理,网格聚类算法要与划分聚类或密度聚类算法结合使用,网格聚类算法处理的单元只与网格数量有关,与样本数量无关,因此在数据量大时,网格聚类算法可以极大地提高效率
层次(Hierarchical)聚类算法强调的是聚类执行的过程,分为自底向上的凝聚方法和自顶向下的分裂方法两种。
凝聚方法是先将每一个样本点当成一个簇,然后根据距离和密度等度量准则进行逐步合并。
分裂方法是先将所有样本点放在一个簇内,然后再逐步分解。
前者的典型算法有AGNES算法,后者的典型算法有二分k-means算法。
1:二分 k-means算法
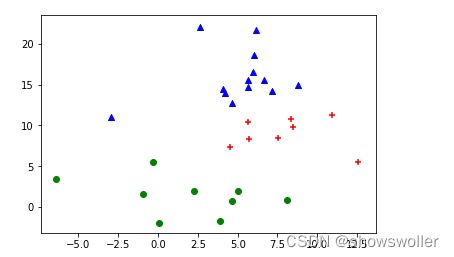
二分k-means算法先将所有点看成一个簇,然后将该簇一分为二,之后选择其中一个簇继续分裂。选择哪一个簇进行分裂,取决于对其进行的分裂是否可以最大程度降低SSE值。如此分裂下去,直到达到指定的簇数目k为止
效果展示如下
部分代码如下 下面是分裂主循环代码
while len(SSE) < n_clusters:
max_changed_SSE = 0
tag = -1
for i in range(len(SSE)): # 对每个簇进行试分簇,计算SSE的减少量
estimator = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=2, n_init=n_init).fit(samples[i]) # 二分簇
changed_SSE = SSE[i] - estimator.inertia_
print(estimator.inertia_, ' - ', changed_SSE)
if changed_SSE > max_changed_SSE: # 比较SSE值是不是减少了
max_changed_SSE = changed_SSE
tag = i
# 正式分簇
estimator = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=2, n_init=n_init).fit(samples[tag])
indexs0 = np.where(estimator.labels_ == 0) # 标签为0的样本在数组中的下标
cluster0 = samples[tag][indexs0] # 从簇中分出标签为0的新簇
indexs1 = np.where(estimator.labels_ == 1)
cluster1 = samples[tag][indexs1] # 从簇中分出标签为1的新簇
del samples[tag]
samples.append(cluster0)
samples.append(cluster1)
del SSE[tag]
estimator = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=1, n_init=n_init).fit(cluster0)
SSE.append(estimator.inertia_) # 新簇的SSE值
estimator = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=1, n_init=n_init).fit(cluster1)
SSE.append(estimator.inertia_)2:AGNES算法
AGNES(AGglomerative NESting)算法先将每个样本点看成一个簇,然后根据簇与簇之间的距离度量将最近的两个簇合并,一直重复合并到指定的簇数目k为止。
代码参数如下所示
class sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2, affinity=’euclidean’, memory=None, connectivity=None, compute_full_tree=’auto’, linkage=’ward’, pooling_func=’deprecated’, distance_threshold=None)
n_clusters是指定的分簇数
linkage是簇距离度量方法,支持ward、complete、average和single四种方法。complete、average和single分别对应簇最大距离、簇平均距离和簇最小距离。
Ward方法与其它方法不一样,它不是按距离合并簇,而是合并使得偏差(样本点与簇中心的差值)平方和增加最小的两个簇。它先要对所有簇进行两两试合并,并计算偏差平方和的增加值,然后取增加最小的两个簇进行合并。
效果展示如下
部分代码如下
# Set up cluster parameters
plt.figure(figsize=(9 * 1.3 + 2, 14.5))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=.02, right=.98, bottom=.001, top=.96, wspace=.05,
hspace=.01)
plot_num = 1
default_base = {'n_neighbors': 10,
'n_clusters': 3}
datasets = [
(noisy_circles, {'n_clusters': 2}),
(noisy_moons, {'n_clusters': 2}),
(varied, {'n_neighbors': 2}),
(aniso, {'n_neighbors': 2}),
(blobs, {}),
(no_structure, {})]
for i_dataset, (dataset, algo_params) in enumerate(datasets):
# update parameters with dataset-specific values
params = default_base.copy()
params.update(algo_params)
X, y = dataset
# normalize dataset for easier parameter selection
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
# ============
# Create cluster objects
# ============
ward = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(
n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='ward')
complete = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(
n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='complete')
average = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(
n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='average')
single = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(
n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='single')
clustering_algorithms = (
('Single Linkage', single),
('Average Linkage', average),
('Complete Linkage', complete),
('Ward Linkage', ward),
)
for name, algorithm in clustering_algorithms:
t0 = time.time()
# catch warnings related to kneighbors_graph
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.filterwarnings(
"ignore",
message="the number of connected components of the " +
"connectivity matrix is [0-9]{1,2}" +
" > 1. Completing it to avoid stopping the tree early.",
category=UserWarning)
algorithm.fit(X)
t1 = time.time()
if hasattr(algorithm, 'labels_'):
y_pred = algorithm.labels_.astype(int)
else:
y_pred = algorithm.predict(X)
plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(clustering_algorithms), plot_num)
if i_dataset == 0:
plt.title(name, size=18)
colors = np.array(list(islice(cycle(['#377eb8', '#ff7f00', '#4daf4a',
'#f781bf', '#a65628', '#984ea3',
'#999999', '#e41a1c', '#dede00']),
int(max(y_pred) + 1))))
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=10, color=colors[y_pred])
plt.xlim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.ylim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.text(.99, .01, ('%.2fs' % (t1 - t0)).lstrip('0'),
transform=plt.gca().transAxes, size=15,
horizontalalignment='right')
plot_num += 1
plt.show()创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~