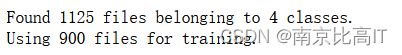深度学习实战第三周--天气识别
本周使用卷积神经网络进行天气识别
该数据集中包含四种天气,含有1125张图片,数据集较少,如果直接训练后用来应用肯定不行
1.显卡设置
设置使用GPU训练,我本机带有GPU,如果你不想设置,那就直接忽略本步,默认使用CPU
import tensorflow as tf
gpus=tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
gpus0=gpus[0]
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpus0,True)
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpus0],"GPU")2.相关依赖&数据集导入
import os,PIL,pathlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers,models
data_dir="D:/天气识别数据集/天气识别数据集/weather_photos"
data_dir=pathlib.Path(data_dir)3.图片统计
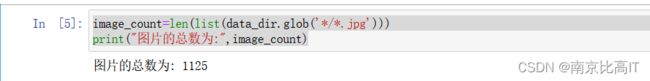
image_count=len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.jpg')))
print("图片的总数为:",image_count)结果如下:
查看图片是否可以加载
roses=list(data_dir.glob('sunrise/*.jpg'))
PIL.Image.open(str(roses[0]))结果如下:
4.训练集和相关的网络设置
batch_size=32
img_height=180
img_width=180
train_ds=tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(data_dir,
validation_split=0.2,
subset="training",
seed=123,
image_size(img_height,img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)
val_ds=tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(data_dir,
validation_split=0.2,
subset="validation",
seed=123,
image_size=(img_height,img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)
class_names=train_ds.class_names
print(class_names)训练集划分结果如下:
验证集划分结果:
四种天气类型:
![]()
可视化部分图片:
代码:
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
for images,labels in train_ds.take(1):
for i in range(20):
ax=plt.subplot(5,10,i+1)
plt.imshow(images[i].numpy().astype('uint8'))
plt.title(class_names[labels[i]])
plt.axis("off")结果:
查了输入的图片的张量和标签的张量大小:
for image_batch,labels_batch in train_ds:
print(image_batch.shape)
print(labels_batch.shape)
break5.数据集配置
shuffle():作用为打乱数据。
prefetch():预取数据,加速运行
prefetch()功能详细介绍:CPU正在准备数据时,加速器处于空闲状态。相反,当加速器控制模型时,CPU处于闲置状态。因此,训练所用的时间时CPU预处理时间和加速器训练时间的总和。Prefetch()将训练步骤的预处理和模型执行过程重叠到一块。当加速器正在执行第N个训练步时,CPU准备第N+1的数据。这样做可以缩短训练的单步用时,而且可以缩短提取和转化数据所需要的时间。如果不使用perfetch(),CPU和GPU/TPU在大部分时间处于空闲状态
而使用perfetch()可以显著减少空闲时间
cache():将数据集缓存到内存中,加速运行
代码设置:
AUTOTUNE=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
train_ds=train_ds.cache().shuffle(1000).prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
val_ds=val_ds.cache().shuffle(1000).prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)6.网络搭建
num_classes=4
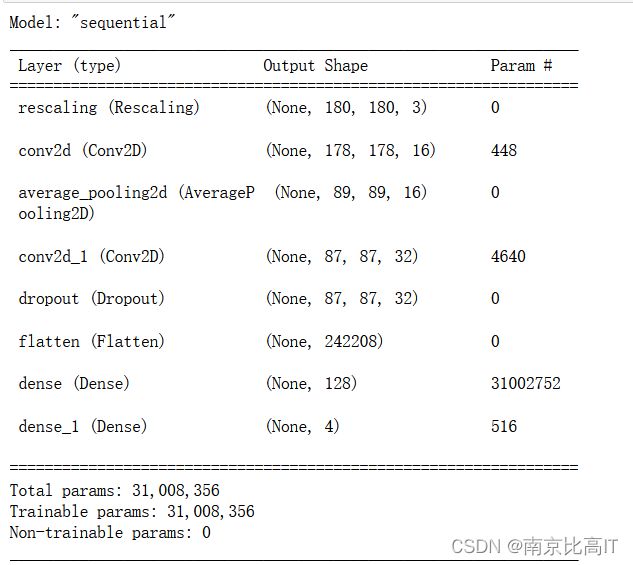
model=models.Sequential([
layers.experimental.preprocessing.Rescaling(1./255,input_shape=(img_height,img_width,3)),
layers.Conv2D(16,(3,3),activation='relu',input_shape=(img_height,img_width,3)),
layers.AveragePooling2D((2,2)),
layers.Conv2D(32,(3,3),activation='relu'),
layers.Dropout(0.3),
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(128,activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(num_classes)
])
model.summary()这是一个kreas的网络,其中使用了平均池化,降低了损失,使用了正则化层,提高模型的拟合能力,既降低模型的方差。
设置优化器(使用Adam,学习率设置为0.001),并进行模型编译:
opt=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001)
model.compile(optimizer=opt,loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),metrics=['accuracy'])
设置训练批次,并开始训练:
epochs=10
history=model.fit(
train_ds,
validation_data=val_ds,
epochs=epochs
)7.训练结果可视化
acc=history.history['accuracy'] val_acc=history.history['val_accuracy'] loss=history.history['loss'] val_loss=history.history['val_loss'] epochs_range=range(epochs) plt.figure(figsize=(12,4)) plt.subplot(1,2,1) plt.plot(epochs_range,acc,label="Training Accuracy") plt.plot(epochs_range,val_acc,label="Vaildation Accuracy") plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.title('Training and Vaildation Accuracy') plt.subplot(1,2,2) plt.plot(epochs_range,loss,label="Training Loss") plt.plot(epochs_range,val_loss,label="Vaildation Loss") plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.title('Training and Vaildation Accuracy')绘制了模型的训练集准确度和测试集准确度,以及模型的训练集损失和测试集损失
观察左图,随着训练批次的增多,模型的验证机精确度明显低于训练集精确度,这是说明模型的方差较大,即模型过拟合,解决方案:增加正则化层或者增加数据进行训练等
观察右图,训练集损失明显低于验证集损失,基于此,更加说明模型过拟合,模型的方差比较大。
8.总结
基于本次的实操,CNN卷积神经网络的效果十分明显,计算机视觉是有趣的,本文中出现的模型过拟合问题源于搭建的算法模型过于简单,建议增多,一部分原因也是数据集较少的缘故造成的,基于此,计算机视觉需要大量的数据作为支撑来进行探索,个人建议如果你选择计算机视觉的话,要做好算力和数据集的准备。
小可爱可以点赞加关注吗?写作不易,还望理解!