Tensorflow 01: mnist-softmax
最近想把 tensorflow 好好看一遍,打好基础。俗话说,基础不牢,地动山摇。所以从基础开始,一遍遍的看 tensorflow 官网教程。每学习官网的一个案例,就写一篇博客,使自已能够坚持下去。主要是想从code的角度来了解学习tensorflow。今天介绍的是用tensorflow 中的softmax实现mnist手写体数字的分类识别。
mnist数据加载
# coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
"""
mnist 数据集了解
每个图片大小:28 x 28
"""
# 训练集
train_img = mnist.train.images
print('train_img.shape: '),
print train_img.shape
train_label = mnist.train.labels
print('train_label.shape: '),
print train_label.shape
# 测试集
test_img = mnist.test.images
test_label = mnist.test.labels
# 验证集
validate_img = mnist.validation.images
validate_label = mnist.validation.labelstensorflow中已经把mnist的训练集/验证集/测试集做好了。其中:
train_img.shape: (55000, 784)
train_label.shape: (55000, 10)
test_img.shape: (10000, 784)
test_label.shape: (10000, 10)
validate_img.shape: (5000, 784)
validate_label.shape: (5000, 10)
同时,tensorflow中还提供了一个API用于按batch_size来获取训练集中的batch:
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)其中batch_xs.shape: (100, 784), 对应获取到的100张图片,batch_ys: (100, 10)对应获取到的100张图片的one_hot vector。
计算图构建与训练
# 构造计算图
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
# loss function 代价函数
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
# 用于评估准确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 训练
# 用于记录每次训练后loss的值
loss_val = []
# 用于记录每次训练后模型在测试集上的准确率的值
acc = []
for idx in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
loss_tmp = sess.run(cross_entropy, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
loss_val.append(loss_tmp)
acc_tmp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels})
acc.append(acc_tmp)
# 绘图
plt.figure()
plt.plot(loss_val)
plt.xlabel('number of iteration')
plt.ylabel('loss value')
plt.figure()
plt.plot(acc)
plt.xlabel('number of iteration')
plt.ylabel('accuracy value')
plt.show()训练结果
每次训练迭代后的loss变化曲线:
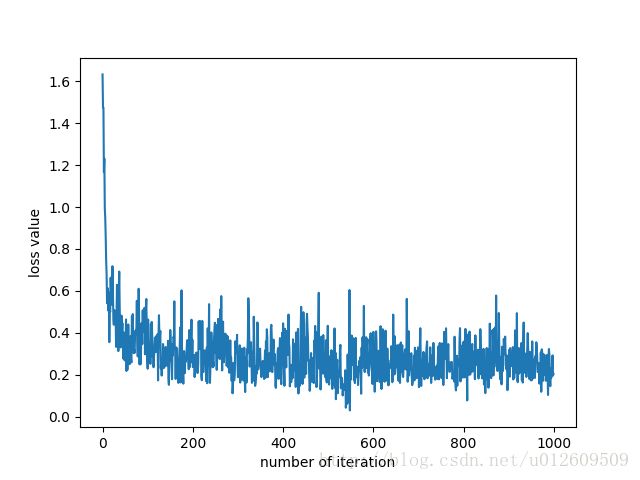
注意:这里计算的loss对针对训练集中的参与训练的一个batch而言的。可以看到,采用随机梯度下降法,虽然计算速度加快了,但loss的抖动也比较大。
每次迭代后在测试集上的准确率变化曲线:

可以看到,最终的准确率在92%左右。
用到的tensorflow API介绍
- tf.matmul(A, B)
用于矩阵A与矩阵B相乘。注意不是element-wise乘法,而是真正意义上的矩阵相乘。
2.tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1])
沿着指定的轴(在Python中,对于二维ndarray,1代表行,0代表列),计算ndarray中的元素的和。
3.tf.argmax(y, 1)
沿着指定的轴,计算ndarray y 中最大值出现的索引位置
4.tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
判断2个ndarray对应位置的元素是否相等,如果相等,结果为True,否则为False。
