使用Spring Security做方法层的权限拦截
Spring Security中可以通过Authentication(认证)和Authorization(授权)的功能,识别用户身份并完成用户授权。
通常的做法是在用户访问某些资源时,通过拦截器方法确认用户身份,如果当前用户身份不明(未登录或者是匿名用户)且被访问资源是非公开资源时,系统会强制跳转至登录页面,在用户登录完成后再跳转回原地址,继续访问资源。
这些拦截功能基本都是使用Filter在请求未到达DispatcherServlet前就完成处理了。但如果我们需要在细粒度上进行访问权限控制的话,那该怎么办呢?
比如我们想要在某个@Service类的某些方法上增加权限校验,只有具有特定角色的用户才能访问这些资源,这种场景该如何实现呢?
Spring Security通过使用MethodSecurityInterceptor实现了上述场景下的权限管理,本文将介绍具体该如何实现。
内部机制和原理参看Spring Security Reference中的Method Security章节
搭建应用
首先我们引入相关依赖,主要是spring-boot-starter-web和spring-boot-starter-security。
4.0.0
org.example
SpringSecurity
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.3.3.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
在工程中创建org.example.security包,在这个包下面新建一个Application类,作为应用的启动类。
增加Spring Boot应用标准启动代码:
package org.example.security;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}
增加Spring Security相关配置
首先我们定义一个UserDetailsService类型的Bean对象。Spring Security在用户登录时,使用该对象校验用户身份是否正确。在这个对象中,我们创建了两个用户:user用户具有USER角色,admin用户具有USER和ADMIN角色,密码都是password。
@Bean
public UserDetailsService users() {
User.UserBuilder users = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder();
UserDetails user = users
.username("user")
.password("password")
.roles("USER")
.build();
UserDetails admin = users
.username("admin")
.password("password")
.roles("USER", "ADMIN")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user, admin);
}
现在需要调整下Spring Security的默认配置。Spring Security的默认配置,会对所有url请求进行强制认证,也就是所有url请求都需要首先触发登录过程。
Spring Security默认配置是通过在
SecurityAutoConfiguration上使用@Import注解,引入了SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration,引入的SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration里面配置了默认的Spring Security配置类。
我们希望将认证和授权的操作下移到Service层,在@Service的具体方法上进行拦截。因此需要修改Spring Security配置,将所有url的请求全部放行,不做拦截。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class DefaultConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().permitAll());
http.formLogin(withDefaults());
}
}
authorize.anyRequest().permitAll()的意思是所有的请求都放行。
虽然请求到@Controller层不会被拦截了,但是在@Service层如果请求未做过认证授权,仍然需要通过login的方式进行认证授权。因此需要使用http.formLogin(withDefaults())启用form登录特性。
Service层的设计
我们定义一个MyService类,提供三个方法:
-
doServiceAsUser:这个方法需要访问者具有USER角色 -
doServiceAsAdmin:这个方法需要访问者具有ADMIN角色 -
doServiceAsAnyone:这个方法不需要认证授权即可访问
通过使用SpEL语法和相关注解可以实现我们想要的效果,代码如下:
@Service
static class MyService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')")
String doServiceAsUser() {
return "This is the response to ROLE_USER";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
String doServiceAsAdmin() {
return "This is the response to ROLE_ADMIN";
}
String doServiceAsAnyone() {
return "This is the response to ANYONE";
}
}
@PreAuthorize注解会在调用方法前拦截,判定当前访问者是否满足条件,不满足则抛出AccessDenyException,该异常会在外层被一个名为ExceptionTranslationFilter的Filter捕获到。ExceptionTranslationFilter会调用其内部的一个AuthenticationEntryPoint属性的方法将请求重定向到登录页面。
关于SpEL在Spring Security的使用,参看Spring Security Reference中的Expression-Based Access Control章节。
Controller层设计
简便起见,直接使用Application作为@Controller类。使用api/dispatcher/{type}地址进行分发,实现:
-
api/dispatcher/user:调用doServiceAsUser -
api/dispatcher/admin:调用doServiceAsAdmin -
api/dispatcher/else:调用doServiceAsAnyone
另外,我们需要将MyService对象注入到@Controller中,代码如下:
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class Application {
@Autowired MyService myService = null;
@RequestMapping("api/dispatcher/{type}")
String doService(@PathVariable String type) {
switch (type) {
case "user":
return myService.doServiceAsUser();
case "admin":
return myService.doServiceAsAdmin();
default :
return myService.doServiceAsAnyone();
}
}
}
启用Method Security特性
在Application类上增加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解,启用功能。prePostEnabled = true表示我们将使用@PreAuthorize注解对相关方法进行拦截。同@PreAuthorize相似的,还有@PreFilter,@PostFilter,@PostAuthorize三个注解。
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class Application {
}
汇总
完整的Application代码如下(为了方便展示,我们将所有代码写在了一个类中,真正做工程的时候,还是需要根据功能的不同拆分出不同的层次的):
package org.example.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import static org.springframework.security.config.Customizer.withDefaults;
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class Application {
@Autowired MyService myService = null;
@RequestMapping("api/dispatcher/{type}")
String doService(@PathVariable String type) {
switch (type) {
case "user":
return myService.doServiceAsUser();
case "admin":
return myService.doServiceAsAdmin();
default :
return myService.doServiceAsAnyone();
}
}
@Service
static class MyService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')")
String doServiceAsUser() {
return "This is the response to ROLE_USER";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
String doServiceAsAdmin() {
return "This is the response to ROLE_ADMIN";
}
String doServiceAsAnyone() {
return "This is the response to ANYONE";
}
}
@Bean
public UserDetailsService users() {
User.UserBuilder users = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder();
UserDetails user = users
.username("user")
.password("password")
.roles("USER")
.build();
UserDetails admin = users
.username("admin")
.password("password")
.roles("USER", "ADMIN")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user, admin);
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class DefaultConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().permitAll());
http.formLogin(withDefaults());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}
测试
1. 匿名访问
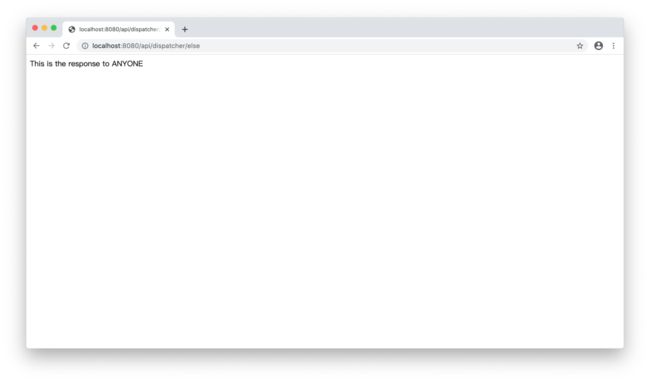
输入http://localhost:8080/api/dispatcher/else,浏览器返回结果如下:
2. USER角色访问
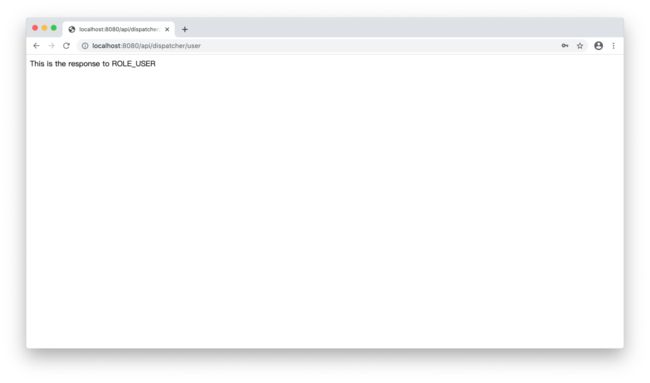
输入http://localhost:8080/api/dispatcher/user,浏览器首先返回登录页面:
使用user/password登录,浏览器正常返回结果:
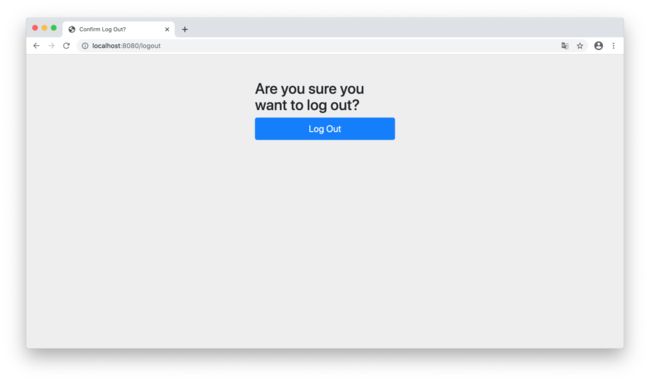
然后输入http://localhost:8080/logout,将user用户登出
再次输入http://localhost:8080/api/dispatcher/user,使用admin/password登录,浏览器正常返回结果(admin也具有USER角色):
输入http://localhost:8080/logout,将admin用户登出
3. ADMIN角色访问
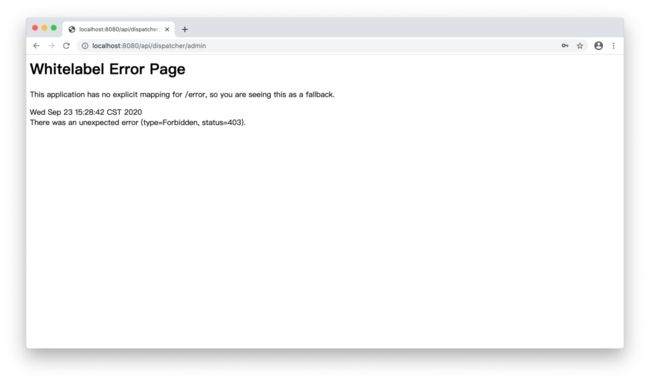
在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/api/dispatcher/admin,首先使用user/password登录,系统返回403错误(user用户不具有ADMIN角色):
输入http://localhost:8080/logout,将user用户登出后再次输入http://localhost:8080/api/dispatcher/admin。
现在使用admin/password用户登录,系统正常返回: