目标检测代码解读三(YOLOv3SPP)
![]() 自2014年
自2014年RCNN论文发表之后,机器学习在目标检测领域得到了飞速发展,本系列文章将介绍一些目标检测发展的里程碑著作的代码实现。
YOLOv3SPP
1.解析网络结构的参数文件
yolov3-spp.cfg记录了网络结构,其内容格式如下






parse_model_cfg函数用于读取该配置文件内的参数,其步骤为:
- 读取(除了空格和注释外的)每一行正文
- 用字典
mdefs记录每个层的参数 - 将anchors的形状和大小用矩阵存储
def parse_model_cfg(path: str):
# 读取文件信息
with open(path, "r") as f:
lines = f.read().split("\n")
# 去除空行和注释行
lines = [x for x in lines if x and not x.startswith("#")]
# 去除每行开头和结尾的空格符
lines = [x.strip() for x in lines]
mdefs = [] # module definitions
for line in lines:
if line.startswith("["): # this marks the start of a new block
mdefs.append({})
mdefs[-1]["type"] = line[1:-1].strip() # 记录module类型
# 如果是卷积模块,设置默认不使用BN
if mdefs[-1]["type"] == "convolutional":
mdefs[-1]["batch_normalize"] = 0
else:
key, val = line.split("=")
key = key.strip()
val = val.strip()
if key == "anchors":
# anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326
val = val.replace(" ", "") # 将空格去除
mdefs[-1][key] = np.array([float(x) for x in val.split(",")]).reshape((-1, 2)) # np anchors
elif (key in ["from", "layers", "mask"]) or (key == "size" and "," in val):
mdefs[-1][key] = [int(x) for x in val.split(",")]
else:
# TODO: .isnumeric() actually fails to get the float case
if val.isnumeric(): # return int or float 如果是数值的情况
mdefs[-1][key] = int(val) if (int(val) - float(val)) == 0 else float(val)
else:
mdefs[-1][key] = val # return string 是字符的情况
return mdefs
2. 搭建网络结构
根据解析得到的网络结构参数,create_modules进行网络结构的搭建
def create_modules(modules_defs: list, img_size):
"""
Constructs module list of layer blocks from module configuration in module_defs
:param modules_defs: 通过.cfg文件解析得到的每个层结构的列表
:param img_size:
:return:
"""
img_size = [img_size] * 2 if isinstance(img_size, int) else img_size
# 删除解析cfg列表中的第一个配置(对应[net]的配置)
modules_defs.pop(0) # cfg training hyperparams (unused)
output_filters = [3] # input channels
module_list = nn.ModuleList()
# 统计哪些特征层的输出会被后续的层使用到(可能是特征融合,也可能是拼接)
routs = [] # list of layers which rout to deeper layers
yolo_index = -1
# 遍历搭建每个层结构
for i, mdef in enumerate(modules_defs):
modules = nn.Sequential()
if mdef["type"] == "convolutional":
bn = mdef["batch_normalize"] # 1 or 0 / use or not
filters = mdef["filters"]
k = mdef["size"] # kernel size
stride = mdef["stride"] if "stride" in mdef else (mdef['stride_y'], mdef["stride_x"])
if isinstance(k, int):
modules.add_module("Conv2d", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=output_filters[-1],
out_channels=filters,
kernel_size=k,
stride=stride,
padding=k // 2 if mdef["pad"] else 0,
bias=not bn))
else:
raise TypeError("conv2d filter size must be int type.")
if bn:
modules.add_module("BatchNorm2d", nn.BatchNorm2d(filters))
else:
# 如果该卷积操作没有bn层,意味着该层为yolo的predictor
routs.append(i) # detection output (goes into yolo layer)
if mdef["activation"] == "leaky":
modules.add_module("activation", nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True))
else:
pass
elif mdef["type"] == "BatchNorm2d":
pass
elif mdef["type"] == "maxpool":
k = mdef["size"] # kernel size
stride = mdef["stride"]
modules = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=stride, padding=(k - 1) // 2)
elif mdef["type"] == "upsample":
if ONNX_EXPORT: # explicitly state size, avoid scale_factor
g = (yolo_index + 1) * 2 / 32 # gain
modules = nn.Upsample(size=tuple(int(x * g) for x in img_size))
else:
modules = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=mdef["stride"])
elif mdef["type"] == "route": # [-2], [-1,-3,-5,-6], [-1, 61]
layers = mdef["layers"]
filters = sum([output_filters[l + 1 if l > 0 else l] for l in layers])
routs.extend([i + l if l < 0 else l for l in layers])
# 将多个特征矩阵在深度维度上进行拼接
modules = FeatureConcat(layers=layers)
elif mdef["type"] == "shortcut":
layers = mdef["from"]
filters = output_filters[-1]
# routs.extend([i + l if l < 0 else l for l in layers])
routs.append(i + layers[0])
# 将多个特征矩阵的值进行相加操作
modules = WeightedFeatureFusion(layers=layers, weight="weights_type" in mdef)
elif mdef["type"] == "yolo":
yolo_index += 1 # 记录是第几个yolo_layer [0, 1, 2]
stride = [32, 16, 8] # 预测特征层对应原图的缩放比例
# 对yolo的输出进行处理
modules = YOLOLayer(anchors=mdef["anchors"][mdef["mask"]], # anchor list
nc=mdef["classes"], # number of classes
img_size=img_size,
stride=stride[yolo_index])
# Initialize preceding Conv2d() bias (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02002.pdf section 3.3)
try:
j = -1
# bias: shape(255,) 索引0对应Sequential中的Conv2d
# view: shape(3, 85)
b = module_list[j][0].bias.view(modules.na, -1)
b.data[:, 4] += -4.5 # obj
b.data[:, 5:] += math.log(0.6 / (modules.nc - 0.99)) # cls (sigmoid(p) = 1/nc)
module_list[j][0].bias = torch.nn.Parameter(b.view(-1), requires_grad=True)
except Exception as e:
print('WARNING: smart bias initialization failure.', e)
else:
print("Warning: Unrecognized Layer Type: " + mdef["type"])
# Register module list and number of output filters
module_list.append(modules)
output_filters.append(filters)
# 记录是否需要输出
routs_binary = [False] * len(modules_defs)
for i in routs:
routs_binary[i] = True
return module_list, routs_binary
3. YOLO输出处理
YOLOLayer函数对YOLO输出进行处理,步骤为:
- 更新
grids信息并生成新的grids参数
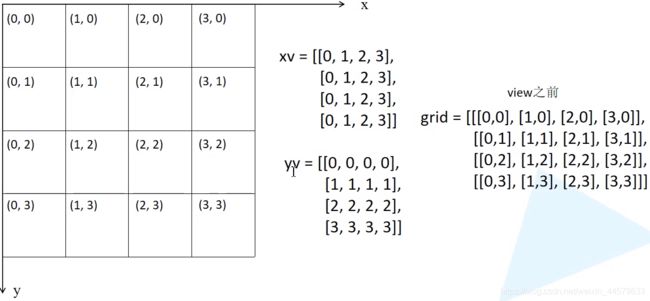
def create_grids(self, ng=(13, 13), device="cpu"):
"""
更新grids信息并生成新的grids参数
:param ng: 特征图大小
:param device:
:return:
"""
self.nx, self.ny = ng
self.ng = torch.tensor(ng, dtype=torch.float)
# build xy offsets 构建每个cell处的anchor的xy偏移量(在feature map上的)
if not self.training: # 训练模式不需要回归到最终预测boxes
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(self.ny, device=device),
torch.arange(self.nx, device=device)])
# batch_size, na, grid_h, grid_w, wh
self.grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).view((1, 1, self.ny, self.nx, 2)).float()
if self.anchor_vec.device != device:
self.anchor_vec = self.anchor_vec.to(device)
self.anchor_wh = self.anchor_wh.to(device)
- 在训练过程中,输出得到的预测信息
(bs, self.na, self.no, self.ny, self.nx) - 在推理过程中,用得到的预测信息
p计算在feature map上的坐标和长宽,计算公式如下,然后换算映射回原图尺度
- 对
bias初始化
class YOLOLayer(nn.Module):
"""
对YOLO的输出进行处理
"""
def __init__(self, anchors, nc, img_size, stride):
super(YOLOLayer, self).__init__()
self.anchors = torch.Tensor(anchors)
self.stride = stride # layer stride 特征图上一步对应原图上的步距 [32, 16, 8]
self.na = len(anchors) # number of anchors (3)
self.nc = nc # number of classes (80)
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs (85: x, y, w, h, obj, cls1, ...)
self.nx, self.ny, self.ng = 0, 0, (0, 0) # initialize number of x, y gridpoints
# 将anchors大小缩放到grid尺度
self.anchor_vec = self.anchors / self.stride
# batch_size, na, grid_h, grid_w, wh,
# 值为1的维度对应的值不是固定值,后续操作可根据broadcast广播机制自动扩充
self.anchor_wh = self.anchor_vec.view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2)
self.grid = None
if ONNX_EXPORT:
self.training = False
self.create_grids((img_size[1] // stride, img_size[0] // stride)) # number x, y grid points
def forward(self, p):
if ONNX_EXPORT:
bs = 1 # batch size
else:
bs, _, ny, nx = p.shape # batch_size, predict_param(255), grid(13), grid(13)
if (self.nx, self.ny) != (nx, ny) or self.grid is None: # fix no grid bug
self.create_grids((nx, ny), p.device)
# view: (batch_size, 255, 13, 13) -> (batch_size, 3, 85, 13, 13)
# permute: (batch_size, 3, 85, 13, 13) -> (batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 85)
# [bs, anchor, grid, grid, xywh + obj + classes]
p = p.view(bs, self.na, self.no, self.ny, self.nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() # prediction
if self.training:
return p
elif ONNX_EXPORT:
# Avoid broadcasting for ANE operations
m = self.na * self.nx * self.ny # 3*
ng = 1. / self.ng.repeat(m, 1)
grid = self.grid.repeat(1, self.na, 1, 1, 1).view(m, 2)
anchor_wh = self.anchor_wh.repeat(1, 1, self.nx, self.ny, 1).view(m, 2) * ng
p = p.view(m, self.no)
# xy = torch.sigmoid(p[:, 0:2]) + grid # x, y
# wh = torch.exp(p[:, 2:4]) * anchor_wh # width, height
# p_cls = torch.sigmoid(p[:, 4:5]) if self.nc == 1 else \
# torch.sigmoid(p[:, 5:self.no]) * torch.sigmoid(p[:, 4:5]) # conf
p[:, :2] = (torch.sigmoid(p[:, 0:2]) + grid) * ng # x, y
p[:, 2:4] = torch.exp(p[:, 2:4]) * anchor_wh # width, height
p[:, 4:] = torch.sigmoid(p[:, 4:])
p[:, 5:] = p[:, 5:self.no] * p[:, 4:5]
return p
else: # inference
# [bs, anchor, grid, grid, xywh + obj + classes]
io = p.clone() # inference output
io[..., :2] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., :2]) + self.grid # xy 计算在feature map上的xy坐标
io[..., 2:4] = torch.exp(io[..., 2:4]) * self.anchor_wh # wh yolo method 计算在feature map上的wh
io[..., :4] *= self.stride # 换算映射回原图尺度
torch.sigmoid_(io[..., 4:])
return io.view(bs, -1, self.no), p # view [1, 3, 13, 13, 85] as [1, 507, 85]
4. 网络前向传递
class Darknet(nn.Module):
"""
YOLOv3 spp object detection model
"""
def __init__(self, cfg, img_size=(416, 416), verbose=False):
super(Darknet, self).__init__()
# 这里传入的img_size只在导出ONNX模型时起作用
self.input_size = [img_size] * 2 if isinstance(img_size, int) else img_size
# 解析网络对应的.cfg文件
self.module_defs = parse_model_cfg(cfg)
# 根据解析的网络结构一层一层去搭建
self.module_list, self.routs = create_modules(self.module_defs, img_size)
# 获取所有YOLOLayer层的索引
self.yolo_layers = get_yolo_layers(self)
# 打印下模型的信息,如果verbose为True则打印详细信息
self.info(verbose) if not ONNX_EXPORT else None # print model description
def forward(self, x, verbose=False):
# yolo_out收集每个yolo_layer层的输出
# out收集每个模块的输出
yolo_out, out = [], []
if verbose:
print('0', x.shape)
str = ""
for i, module in enumerate(self.module_list):
name = module.__class__.__name__
if name in ["WeightedFeatureFusion", "FeatureConcat"]: # sum, concat
if verbose:
l = [i - 1] + module.layers # layers
sh = [list(x.shape)] + [list(out[i].shape) for i in module.layers] # shapes
str = ' >> ' + ' + '.join(['layer %g %s' % x for x in zip(l, sh)])
x = module(x, out) # WeightedFeatureFusion(), FeatureConcat()
elif name == "YOLOLayer":
yolo_out.append(module(x))
else: # run module directly, i.e. mtype = 'convolutional', 'upsample', 'maxpool', 'batchnorm2d' etc.
x = module(x)
out.append(x if self.routs[i] else [])
if verbose:
print('%g/%g %s -' % (i, len(self.module_list), name), list(x.shape), str)
str = ''
if self.training: # train
return yolo_out
elif ONNX_EXPORT: # export
# x = [torch.cat(x, 0) for x in zip(*yolo_out)]
# return x[0], torch.cat(x[1:3], 1) # scores, boxes: 3780x80, 3780x4
p = torch.cat(yolo_out, dim=0)
return p
else: # inference or test
x, p = zip(*yolo_out) # inference output, training output
x = torch.cat(x, 1) # cat yolo outputs
return x, p
5.数据读取
数据读取的步骤:
-
读取图片
-
读取图片对应的标签信息
-
读取图片对应的形状信息
-
计算每个图片的高/宽比,将图像和对应的标签、形状按照高宽比重新排序,以便于使每个
batch中的图像拥有类似的高宽比 -
根据每个
batch中的图像大小,计算该batch采用的统一尺度
① 如果最大的高宽比maxi<1,也就是w>h。相框的长根据最大高宽比的图片,将较长边w设为img_size,h则采用相对指定尺度的比例,向上取32的整数倍。
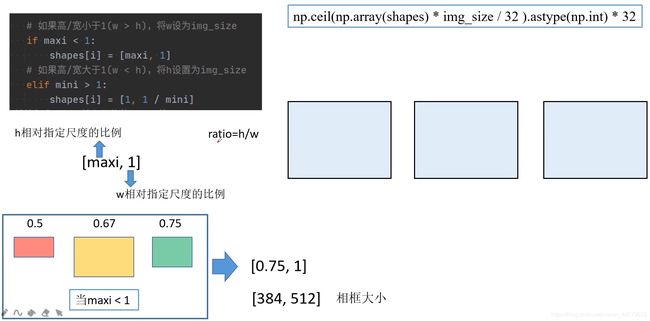
将三张图片,宽与相框对齐,长按照自己的长宽比等比例缩放,填充在相框中如下图所示:

② 如果最大的高宽比mini>1,也就是h>w。相框的长根据最大高宽比的图片,将较长边h设为img_size,w则采用相对指定尺度的比例,向上取32的整数倍。

将三张图片,长与相框对齐,宽按照自己的长宽比等比例缩放,填充在相框中如下图所示:
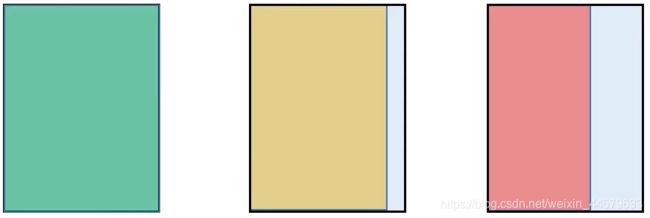
-
检查标注信息的格式,对标签的坐标进行处理
class LoadImagesAndLabels(Dataset): # for training/testing
def __init__(self,
path, # 指向data/my_train_data.txt路径或data/my_val_data.txt路径
# 这里设置的是预处理后输出的图片尺寸
# 当为训练集时,设置的是训练过程中(开启多尺度)的最大尺寸
# 当为验证集时,设置的是最终使用的网络大小
img_size=416,
batch_size=16,
augment=False, # 训练集设置为True(augment_hsv),验证集设置为False
hyp=None, # 超参数字典,其中包含图像增强会使用到的超参数
rect=False, # 是否使用rectangular training
cache_images=False, # 是否缓存图片到内存中
single_cls=False, pad=0.0, rank=-1):
try:
path = str(Path(path))
# parent = str(Path(path).parent) + os.sep
if os.path.isfile(path): # file
# 读取对应my_train/val_data.txt文件,读取每一行的图片路劲信息
with open(path, "r") as f:
f = f.read().splitlines()
else:
raise Exception("%s does not exist" % path)
# 检查每张图片后缀格式是否在支持的列表中,保存支持的图像路径
# img_formats = ['.bmp', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tif', '.dng']
self.img_files = [x for x in f if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in img_formats]
except Exception as e:
raise FileNotFoundError("Error loading data from {}. {}".format(path, e))
# 如果图片列表中没有图片,则报错
n = len(self.img_files)
assert n > 0, "No images found in %s. See %s" % (path, help_url)
# batch index
# 将数据划分到一个个batch中
bi = np.floor(np.arange(n) / batch_size).astype(np.int)
# 记录数据集划分后的总batch数
nb = bi[-1] + 1 # number of batches
self.n = n # number of images 图像总数目
self.batch = bi # batch index of image 记录哪些图片属于哪个batch
self.img_size = img_size # 这里设置的是预处理后输出的图片尺寸
self.augment = augment # 是否启用augment_hsv
self.hyp = hyp # 超参数字典,其中包含图像增强会使用到的超参数
self.rect = rect # 是否使用rectangular training
# 注意: 开启rect后,mosaic就默认关闭
self.mosaic = self.augment and not self.rect # load 4 images at a time into a mosaic (only during training)
# Define labels
# 遍历设置图像对应的label路径
# (./my_yolo_dataset/train/images/2009_004012.jpg) -> (./my_yolo_dataset/train/labels/2009_004012.txt)
self.label_files = [x.replace("images", "labels").replace(os.path.splitext(x)[-1], ".txt")
for x in self.img_files]
# Read image shapes (wh)
# 查看data文件下是否缓存有对应数据集的.shapes文件,里面存储了每张图像的width, height
sp = path.replace(".txt", ".shapes") # shapefile path
try:
with open(sp, "r") as f: # read existing shapefile
s = [x.split() for x in f.read().splitlines()]
# 判断现有的shape文件中的行数(图像个数)是否与当前数据集中图像个数相等
# 如果不相等则认为是不同的数据集,故重新生成shape文件
assert len(s) == n, "shapefile out of aync"
except Exception as e:
# print("read {} failed [{}], rebuild {}.".format(sp, e, sp))
# tqdm库会显示处理的进度
# 读取每张图片的size信息
if rank in [-1, 0]:
image_files = tqdm(self.img_files, desc="Reading image shapes")
else:
image_files = self.img_files
s = [exif_size(Image.open(f)) for f in image_files]
# 将所有图片的shape信息保存在.shape文件中
np.savetxt(sp, s, fmt="%g") # overwrite existing (if any)
# 记录每张图像的原始尺寸
self.shapes = np.array(s, dtype=np.float64)
# Rectangular Training https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
# 如果为ture,训练网络时,会使用类似原图像比例的矩形(让最长边为img_size),而不是img_size x img_size
# 注意: 开启rect后,mosaic就默认关闭
if self.rect:
# Sort by aspect ratio
s = self.shapes # wh
# 计算每个图片的高/宽比
ar = s[:, 1] / s[:, 0] # aspect ratio
# argsort函数返回的是数组值从小到大的索引值
# 按照高宽比例进行排序,这样后面划分的每个batch中的图像就拥有类似的高宽比
irect = ar.argsort()
# 根据排序后的顺序重新设置图像顺序、标签顺序以及shape顺序
self.img_files = [self.img_files[i] for i in irect]
self.label_files = [self.label_files[i] for i in irect]
self.shapes = s[irect] # wh
ar = ar[irect]
# set training image shapes
# 计算每个batch采用的统一尺度
shapes = [[1, 1]] * nb # nb: number of batches
for i in range(nb):
ari = ar[bi == i] # bi: batch index
# 获取第i个batch中,最小和最大高宽比
mini, maxi = ari.min(), ari.max()
# 如果高/宽小于1(w > h),将w设为img_size
if maxi < 1:
shapes[i] = [maxi, 1]
# 如果高/宽大于1(w < h),将h设置为img_size
elif mini > 1:
shapes[i] = [1, 1 / mini]
# 计算每个batch输入网络的shape值(向上设置为32的整数倍)
self.batch_shapes = np.ceil(np.array(shapes) * img_size / 32. + pad).astype(np.int) * 32
# cache labels
self.imgs = [None] * n # n为图像总数
# label: [class, x, y, w, h] 其中的xywh都为相对值
self.labels = [np.zeros((0, 5), dtype=np.float32)] * n
extract_bounding_boxes, labels_loaded = False, False
nm, nf, ne, nd = 0, 0, 0, 0 # number mission, found, empty, duplicate
# 这里分别命名是为了防止出现rect为False/True时混用导致计算的mAP错误
# 当rect为True时会对self.images和self.labels进行从新排序
if rect is True:
np_labels_path = str(Path(self.label_files[0]).parent) + ".rect.npy" # saved labels in *.npy file
else:
np_labels_path = str(Path(self.label_files[0]).parent) + ".norect.npy"
if os.path.isfile(np_labels_path):
x = np.load(np_labels_path, allow_pickle=True)
if len(x) == n:
# 如果载入的缓存标签个数与当前计算的图像数目相同则认为是同一数据集,直接读缓存
self.labels = x
labels_loaded = True
# 处理进度条只在第一个进程中显示
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar = tqdm(self.label_files)
else:
pbar = self.label_files
# 遍历载入标签文件
for i, file in enumerate(pbar):
if labels_loaded is True:
# 如果存在缓存直接从缓存读取
l = self.labels[i]
else:
# 从文件读取标签信息
try:
with open(file, "r") as f:
# 读取每一行label,并按空格划分数据
l = np.array([x.split() for x in f.read().splitlines()], dtype=np.float32)
except Exception as e:
print("An error occurred while loading the file {}: {}".format(file, e))
nm += 1 # file missing
continue
# 如果标注信息不为空的话
if l.shape[0]:
# 标签信息每行必须是五个值[class, x, y, w, h]
assert l.shape[1] == 5, "> 5 label columns: %s" % file
assert (l >= 0).all(), "negative labels: %s" % file
assert (l[:, 1:] <= 1).all(), "non-normalized or out of bounds coordinate labels: %s" % file
# 检查每一行,看是否有重复信息
if np.unique(l, axis=0).shape[0] < l.shape[0]: # duplicate rows
nd += 1
if single_cls:
l[:, 0] = 0 # force dataset into single-class mode
self.labels[i] = l
nf += 1 # file found
# Extract object detection boxes for a second stage classifier
if extract_bounding_boxes:
p = Path(self.img_files[i])
img = cv2.imread(str(p))
h, w = img.shape[:2]
for j, x in enumerate(l):
f = "%s%sclassifier%s%g_%g_%s" % (p.parent.parent, os.sep, os.sep, x[0], j, p.name)
if not os.path.exists(Path(f).parent):
os.makedirs(Path(f).parent) # make new output folder
# 将相对坐标转为绝对坐标
# b: x, y, w, h
b = x[1:] * [w, h, w, h] # box
# 将宽和高设置为宽和高中的最大值
b[2:] = b[2:].max() # rectangle to square
# 放大裁剪目标的宽高
b[2:] = b[2:] * 1.3 + 30 # pad
# 将坐标格式从 x,y,w,h -> xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax
b = xywh2xyxy(b.reshape(-1, 4)).revel().astype(np.int)
# 裁剪bbox坐标到图片内
b[[0, 2]] = np.clip[b[[0, 2]], 0, w]
b[[1, 3]] = np.clip[b[[1, 3]], 0, h]
assert cv2.imwrite(f, img[b[1]:b[3], b[0]:b[2]]), "Failure extracting classifier boxes"
else:
ne += 1 # file empty
# 处理进度条只在第一个进程中显示
if rank in [-1, 0]:
# 更新进度条描述信息
pbar.desc = "Caching labels (%g found, %g missing, %g empty, %g duplicate, for %g images)" % (
nf, nm, ne, nd, n)
assert nf > 0, "No labels found in %s." % os.path.dirname(self.label_files[0]) + os.sep
# 如果标签信息没有被保存成numpy的格式,且训练样本数大于1000则将标签信息保存成numpy的格式
if not labels_loaded and n > 1000:
print("Saving labels to %s for faster future loading" % np_labels_path)
np.save(np_labels_path, self.labels) # save for next time
# Cache images into memory for faster training (Warning: large datasets may exceed system RAM)
if cache_images: # if training
gb = 0 # Gigabytes of cached images 用于记录缓存图像占用RAM大小
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar = tqdm(range(len(self.img_files)), desc="Caching images")
else:
pbar = range(len(self.img_files))
self.img_hw0, self.img_hw = [None] * n, [None] * n
for i in pbar: # max 10k images
self.imgs[i], self.img_hw0[i], self.img_hw[i] = load_image(self, i) # img, hw_original, hw_resized
gb += self.imgs[i].nbytes # 用于记录缓存图像占用RAM大小
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar.desc = "Caching images (%.1fGB)" % (gb / 1E9)
# Detect corrupted images https://medium.com/joelthchao/programmatically-detect-corrupted-image-8c1b2006c3d3
detect_corrupted_images = False
if detect_corrupted_images:
from skimage import io # conda install -c conda-forge scikit-image
for file in tqdm(self.img_files, desc="Detecting corrupted images"):
try:
_ = io.imread(file)
except Exception as e:
print("Corrupted image detected: {}, {}".format(file, e))